What Continent Is Saudi Arabia In
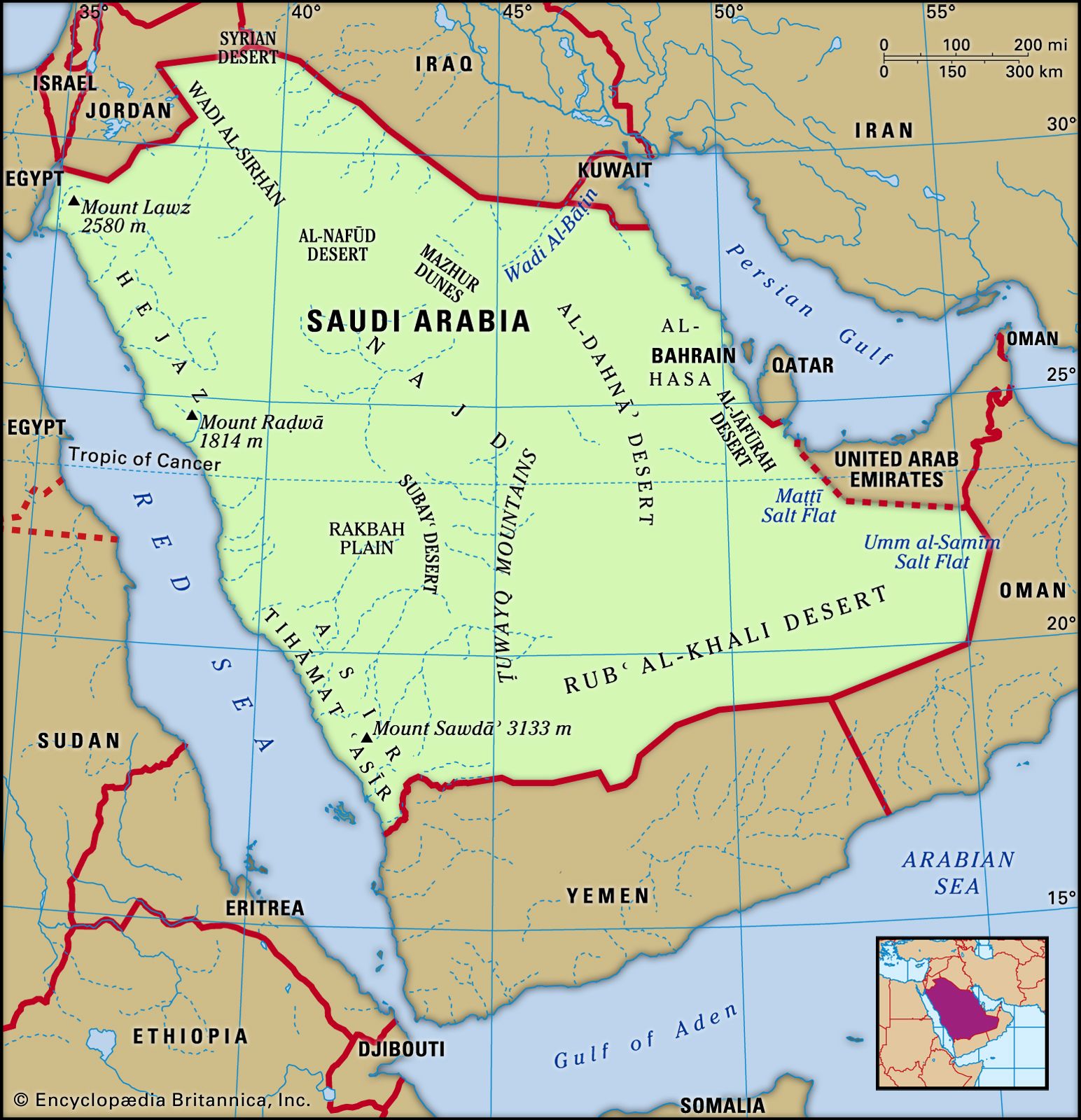
Saudi Arabia is located in the Middle Eastern region of Asia. It was colonized by Turkey until 1926 when it became a sovereign state. The capital city of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh. As of 2012, Saudi Arabia has a population of approximately 26.5 million people. The population density is 12 people per square kilometer. Saudi Arabia is the only country that borders both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf.
Saudi Arabia Satellite Map
Saudi Arabia occupies an area of 2,149,690 square kilometers and is the 13th-largest state in the world. In comparison, its smaller than Algeria but larger than Iran. The landscape is one of the driest in the world. For example, this includes Rub al Khali in the southeastern part of the country, which is the worlds largest contiguous sand desert. But its a mix of salt flats, gravel plains with a few lakes, wadis, and permanent streams. Less than 7% of Saudi Arabia is suitable for arable land. It lies between 16°N and 33°N latitudes so the climate is mostly arid and semi-arid along its southwest coast. Overall, the temperature is hot during the day and low at night.
PHYSICAL
Brief History Of Saudi Arabia
The history of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia dates back to about 1747 when the ruler of the central Arabian Peninsula, Muhammad Bin Saud, formed an alliance with the Muslim scholar and reformer Muhammad Bin Abdul Wahab, a partnership that led to the founding of the modern state.
The Al-Saud family ruled much of the Arabian Peninsula throughout the 19th century. In 1902, Abdul Aziz Bin Abdul Rahman Al-Saud succeeded in recapturing Riyadh from the Al-Rashid and in the following thirty years united the numerous and disparate tribes into one nation.
The foundation of the modern Kingdom of Saudi Arabia took place on September 23, 1932, a day that is commemorated as National Day.
Also Check: What Does Converse Mean In Geometry
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
Saudi Arabia, arid, sparsely populated kingdom of the Middle East.
Extending across most of the northern and central Arabian Peninsula, Saudi Arabia is a young country that is heir to a rich history. In its western highlands, along the Red Sea, lies the Hejaz, which is the cradle of Islam and the site of that religions holiest cities, Mecca and Medina. In the countrys geographic heartland is a region known as Najd , a vast arid zone that until recent times was populated by nomadic tribes. To the east, along the Persian Gulf, are the countrys abundant oil fields that, since the 1960s, have made Saudi Arabia synonymous with petroleum wealth. Those three elementsreligion, tribalism, and untold wealthhave fueled the countrys subsequent history.
Saudi Arabia, once a country of small cities and towns, has become increasingly urban traditional centres such as Jeddah, Mecca, and Medina have grown into large cities, and the capital, Riyadh, a former oasis town, has grown into a modern metropolis. Most of the regions traditional nomads, the Bedouin, have been settled in cities or agrarian communities.
Presentation Of Saudi Arabia : Geography
- Country’s official name :
- Riyadh
- Population of main cities:
- Riyadh Jeddah Mecca Medina Ad-Dammam Hofuf Taif Tabuk
- Area:
- 2,149,690 km²
- Type of Climate :
-
Saudi Arabia has a desert climate. Topography plays an important role in making the climate of Saudi Arabia so varied. In Jeddah it is warm for most of the year. Riyadh, which is inland, is hotter in summer and colder in winter, when occasional heavy rainstorms occur.
Though average rainfall is less than 5 inches, in the Asir highlands it may exceed 10 inches. The temperature in the country varies greatly, from as low as freezing in the winter to 50 degrees Celsius in the summer.
Frequent sand-laden winds blow from the northern deserts for days at 25-30 miles per hour.
- Local Time:
- It is %T:%M %A In Riyadh
- Summer Time Period :
Don’t Miss: Is Physics Hard In High School
Monarchy And Royal Family
House of SaudFahdRonald ReaganDonald Trumpsupplied money and armsmujahideen
The king combines legislative, executive, and judicial functions and royal decrees form the basis of the country’s legislation. The king is also the prime minister, and presides over the Council of Ministers of Saudi Arabia and Consultative Assembly of Saudi Arabia. The royal family dominates the political system. The family’s vast numbers allow it to control most of the kingdom’s important posts and to have an involvement and presence at all levels of government. The number of princes is estimated to be at least 7,000, with most power and influence being wielded by the 200 or so male descendants of Ibn Saud. The key ministries are generally reserved for the royal family, as are the 13 regional governorships.
In its Corruption Perceptions Index for 2010, Transparency International gave Saudi Arabia a score of 4.7 . Saudi Arabia has undergone a process of political and social reform, such as to increase public transparency and good governance, but nepotism and patronage are widespread when doing business in the country the enforcement of the anti-corruption laws is selective and public officials engage in corruption with impunity. A number of prominent Saudi Arabian princes, government ministers, and businesspeople, including Prince Al-Waleed bin Talal, were arrested in Saudi Arabia in November 2017.
History And Ethnic Relations
Emergence of the Nation. Saudi Arabia’s cultural roots lie deep in antiquity. Although remote from centers of ancient civilizations, Arabia’s people had a multiplicity of contacts with Egypt, Syria, and Iraq and with the Roman and Byzantine empires. Ancient Arabia was home to states, cities, and other manifestations of complex cultures and societies. Of particular significance to ancient Arabia was the domestication of the dromedary in the southern part of the peninsula between 3000 and 2500 B.C.E.
, which marks the first year of the Islamic era . By the time of Muhammad’s death in 632, almost all the tribal and local communities in Arabia had declared their loyalty to him as a political leader and most had accepted Islam. The process of conversion was completed under the leadership of Islam’s first caliph, Abu Bakr. The religion was then carried by Arabian converts throughout the Middle East and north Africa.
Islam brought not only a new religion but a new way of life that included innovations in legal and political concepts and practices and a new identity that was universalistic and cosmopolitan. The new Muslim identity, politics, and laws transcended the social and cultural borders of existing communities that had been organized as localities or kinbased tribes.
In 1744, the sheikh swore an oath with Muhammad Al Saud, the emir of ad-Diriyah, that they would collaborate to establish a state
umara ulama
Recommended Reading: What Is E In Chemistry
Topography And Natural Regions
The Arabian Peninsula is an ancient massif composed of stable crystalline rock whose geologic structure developed concurrently with the Alps. Geologic movements caused the entire mass to tilt eastward and the western and southern edges to tilt upward. In the valley created by the fault, called the Great Rift, the Red Sea was formed. The Great Rift runs from the Mediterranean along both sides of the Red Sea south through Ethiopia and the lake country of East Africa, gradually disappearing in the area of Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Scientists analyzing photographs taken by United States astronauts on the joint United States-Soviet space mission in July 1975 detected a vast fan-shaped complex of cracks and fault lines extending north and east from the Golan Heights. These fault lines are believed to be the northern and final portion of the Great Rift and are presumed to be the result of the slow rotation of the Arabian Peninsula counterclockwise in a way that will, in approximately ten million years, close off the Persian Gulf and make it a lake.
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 706km² of tidal flats in Saudi Arabia, making it the 37th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.
Return To Ottoman Domination
The Al Saud returned to power in 1824, but their area of control was mainly restricted to the Saudi heartland of the Najd region, known as the Second Saudi State. However, their rule in Najd was soon contested by new rivals, the Rashidis of Ha’il. Throughout the rest of the 19th century, the Al Saud and the Al Rashid fought for control of the interior of what was to become Saudi Arabia. By 1891, the Al Saud were conclusively defeated by the Al Rashid, who drove the Saudis into exile in Kuwait.
Meanwhile, in the Hejaz, following the defeat of the First Saudi State, the Egyptians continued to occupy the area until 1840. After they left, the Sharifs of Mecca reasserted their authority, albeit with the presence of an Ottoman governor and garrison.
By the early 20th century, the Ottoman Empire continued to control or have suzerainty over most of the peninsula. Subject to this suzerainty, Arabia was ruled by a patchwork of tribal rulers with the Sharif of Mecca having preeminence and ruling the Hejaz.
In 1916, with the encouragement and support of Britain and France , the sharif of Mecca, Hussein bin Ali, led a pan-Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire, with the aim of securing Arab independence and creating a single unified Arab state spanning the Arab territories from Aleppo in Syria to Aden in Yemen.
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Psychology
Medicine And Health Care
A rich body of traditional medicine previously existed in Saudi Arabia. Physical ailments were treated with the use of herbs and other plants and also by cauterization or burning a specific part of the body with a hot iron. Severe mental health problems were often addressed through special readings of the Koran. Modern Western medicine is now wide-spread and is used by all segments of the society. Public and private hospitals and clinics are established throughout the country, and several specialist hospitals with state-of-the-art medical technologies and practice exist in the major cities. Still, travel abroad to other Arab countries and to Europe and the United States for medical treatment remains common and is supported by the state.
The Kingdom Of Saudi Arabia
The history of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia begins properly on September 23, 1932, when by royal the dual kingdom of the Hejaz and Najd with its dependencies, administered since 1927 as two separate units, was unified under the name of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The chief immediate effect was to increase the unity of the kingdom and to decrease the possibility of Hejazi separatism, while the name underscored the central role of the royal family in the kingdoms creation. No attempt was made to change the supreme authority of the king as the absolute monarch of the new regime. Indeed, his power was emphasized in 1933 by his choice of his son Saud as heir apparent.
Read Also: How To Use Manipulatives In Math
Middle Ages And Rise Of Islam
Shortly before the advent of Islam, apart from urban trading settlements , much of what was to become Saudi Arabia was populated by nomadic pastoral tribal societies. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born in Mecca in about 571 CE. In the early 7th century, Muhammad united the various tribes of the peninsula and created a single Islamic religious polity. Following his death in 632, his followers rapidly expanded the territory under Muslim rule beyond Arabia, conquering huge and unprecedented swathes of territory in a matter of decades. Arabia soon became a more politically peripheral region of the Muslim world as the focus shifted to the vast and newly conquered lands.
Arabs originating from modern-day Saudi Arabia, the Hejaz in particular, founded the Rashidun , Umayyad , Abbasid , and the Fatimid caliphates. From the 10th century to the early 20th century, Mecca and Medina were under the control of a local Arab ruler known as the Sharif of Mecca, but at most times the Sharif owed allegiance to the ruler of one of the major Islamic empires based in Baghdad, Cairo or Istanbul. Most of the remainder of what became Saudi Arabia reverted to traditional tribal rule.
Nongovernmental Organizations And Other Associations
The giving of alms or a tithe is one of the five pillars of Islam. This religious obligation sometimes is paid as a tax to Islamic states. Considerable private donations are made to philanthropic societies that address the changing needs of the poor and the handicapped. Other private voluntary organizations deal with community needs, establish sports and cultural clubs, and contribute to development programs that complement state activities. These associations normally are registered with the ministry of social affairs and often receive financial support from the state in addition to contributions from citizens.
You May Like: Who Is The Father Of Chemistry Biology And Physics
Where Is Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is a sovereign Western Asian Nation, occupying the central region of the Arabian Peninsula in Southwest Asia. It is located in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth. Saudi Arabia is bordered by 8 nations: Jordan in the Northwest, Iraq in the North and Northeast, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and United Arab Emirates in the east, Oman in the Southeast and Yemen in the South. The Persian Gulf is in the northeast and Red Sea to the West of Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia is often referred to as The Land of the Two Holy Mosques for Mecca and Medina the two holy pilgrimages of the religion of Islam.
In This Country Profile
other: 98.24%
Natural hazards: frequent sand and dust stormsEnvironment current issues: desertification depletion of underground water resources the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies has prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities coastal pollution from oil spills.
Environment international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution- Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements.
:: People of Saudi Arabia ::
Population: 28,146,656 note: includes 5,576,076 non-nationals
Age structure:0-14 years: 38% 15-64 years: 59.5% 65 years and over: 2.4%
Median age:female: 19.8 years
Population growth rate: 1.954% Birth rate: 28.85 births/1,000 population Death rate: 2.49 deaths/1,000 population Net migration rate: -6.82 migrant/1,000 population
Sex ratio:under 15 years: 1.04 male/female15-64 years: 1.3 male/female65 years and over: 1.08 male/femaletotal population: 1.19 male/female
Infant mortality rate:total: 11.94 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 13.58 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 10.23 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth: 3.89 children born/woman total population: 76.09 yearsfemale: 78.25 years
Total fertility rate: 3.89 children born/woman HIV/AIDS adult prévalence rate: 0.01% HIV/AIDS people living with HIV/AIDS: NAHIV/AIDS deaths: NA
You May Like: What Is Classical Physics And Modern Physics
The Arts And Humanities
Literature. The main art form in Saudi Arabia is in the realm of literature. Classical Arabic poetry is highly valued, while a wide range of colloquial poetic forms is popular and are widely used in different social settings. Recitations of poetry are common at weddings and to mark other important public events. The novel has also become popular among both men and women authors. Local publishing houses exist, while authors also have access to publishers in other Arab countries. The state censor of publications, however, plays a powerful role in deciding what can be published.
Graphic Arts. Painting and sculpture are practiced, but a rich variety of folk art in weaving, decorative arts, furniture making, and similar work is of a high quality. The making of jewelry in both traditional and modern styles is also common.
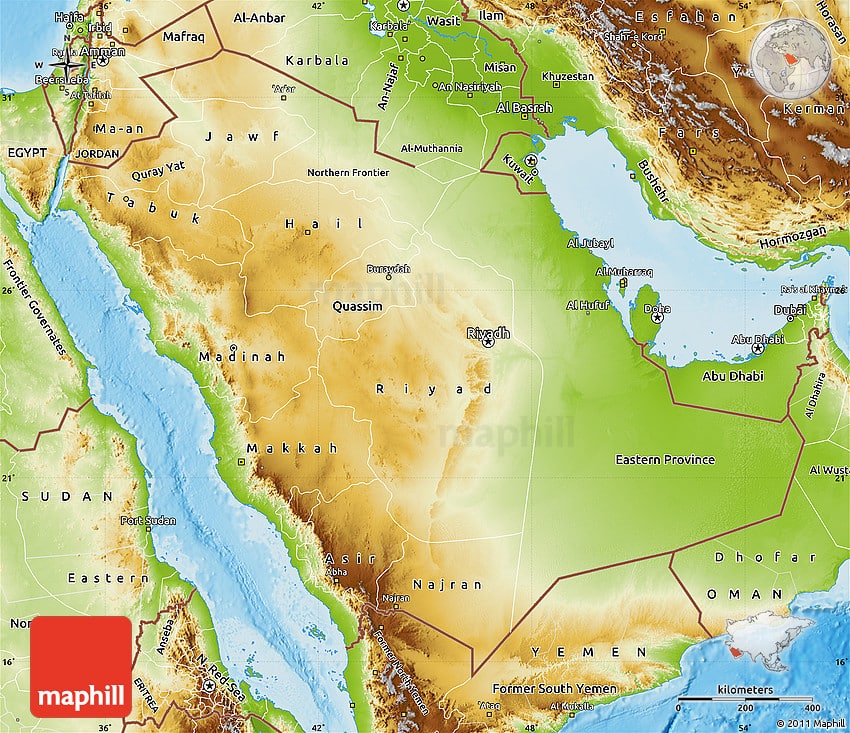
Saudi Arabia Physical Map
Saudi Arabia has a diverse terrain but its most recognized feature is the Arabian Desert. Additionally, it has several mountainous areas such as the Sarawat Mountains in the south. At 3,015 meters , Jabal Sawda is the highest point in Saudi Arabia. Whereas the Persian Gulf, Red Sea is the lowest point at 0 meters sea level. The Great Rift runs from the Mediterranean to the Afar Triple Junction and through Ethiopia. Its the spreading between the African Plate and the Arabian Plate that formed the Red Sea on the west side of Saudi Arabia.
ADMINISTRATION
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Of2
Second And Third Saudi States
The House of Saud returned to power in the second Saudi state in 1824. The state lasted until 1891 when it succumbed to the Al Rashid dynasty of Ha’il. In 1902, Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud captured Riyadh, the Al-Saud dynasty’s ancestral capital, from the rival Al-Rashid family. Continuing his conquests, Abdul Aziz subdued Al-Hasa, the rest of Nejd, and the Hejaz between 1913 and 1926. On January 8, 1926, Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud became the King of Hejaz. On January 29, 1927, he took the title King of Nejd . By the Treaty of Jeddah, signed on May 20, 1927, the United Kingdom recognized the independence of Abdul Aziz’s realm . In 1932, these regions were unified as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.