Nobel Prize In Economic Sciences
John Hicks shared the 1972 Prize in Economic Sciences with Kenneth J Arrow for general equilibrium theory and welfare economics. Hicks created widely used conceptual tools for the analysis of price mechanisms, technical change, and demand for money. He was suspicious of theory for theorys sake, the American idealisation of free markets and reliance on econometrics for contact with reality.
Hicks taught at the London School of Economics from 1926 after trying journalism at the Manchester Guardian. His pioneering work on general equilibrium theory was published while he was Professor of Political Economy at Manchester , after which he worked at Oxford. A close friend of the Manchester economic historian TS Ashton, he published A Theory of Economic History in 1969.
When Will The Other Nobel Prizes Be Announced
-
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry will be awarded on Wednesday by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in Stockholm. Last year, Benjamin List and David W.C. MacMillan won for their development of a new tool that spurred research into new drugs and reduced the chemistrys effect on the environment.
-
The Nobel Prize in Literature will be awarded on Thursday by the Swedish Academy in Stockholm. Last year, Abdulrazak Gurnah won for his uncompromising and compassionate penetration of the effects of colonialism and the fate of the refugee in the gulf between cultures and continents.
-
The Nobel Peace Prize will be awarded on Friday by the Norwegian Nobel Institute in Oslo. Last year, , both journalists, won for their efforts in the struggle to protect press freedoms.
-
Next week, the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences will be awarded on Monday by the Swedish Academy in Stockholm. Last year, the prize went to David Card, Joshua D. Angrist and Guido W. Imbens.
All of the prize announcements will also be streamed live by the Nobel Prize organization. Prize winners will receive their awards at a ceremony in Stockholm in December.
Winners Of The Nobel Prize For Physics
verified
Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
verified
The Nobel Prize for Physics is awarded, according to the will of Swedish inventor and industrialist Alfred Bernhard Nobel, to those who, during the preceding year, shall have conferred the greatest benefit on mankind in the field of physics. It is conferred by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in Stockholm.
The table provides a list of winners of the Nobel Prize for Physics.
| year |
|---|
Don’t Miss: What Is Vapor Pressure Lowering In Chemistry
Watch: 3 Physicists Share Nobel Prize For Quantum Science Discoveries
STOCKHOLM Three scientists jointly won this years Nobel Prize in physics on Tuesday for their work on quantum information science that has significant applications, for example in the field of encryption.
Watch the event in the player above.
Frenchman Alain Aspect, American John F. Clauser and Austrian Anton Zeilinger were cited by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for discovering the way that unseen particles, such as photons or tiny bits of matter, can be linked, or entangled, with each other even when they are separated by large distances.
Being a little bit entangled is sort of like being a little bit pregnant. The effect grows on you, Clauser said in a Tuesday morning phone interview with The Associated Press.
It all goes back to a feature of the universe that even baffled Albert Einstein and connects matter and light in a tangled, chaotic way.
Clauser, 79, was awarded his prize for a 1972 experiment that helped settle a famous debate about quantum mechanics between Einstein and famed physicist Niels Bohr. Einstein described a spooky action at a distance that he thought would eventually be disproved.
I was betting on Einstein, Clauser said. But unfortunately I was wrong and Einstein was wrong and Bohr was right.
List Of All Nobel Prize Winners In Physics
: 6 December 2022
Before we get into the list of Nobel Prizes in Physics, lets have a quick intro about the Prize.
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded every year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of physics.
Nobel Prize in Physics is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel who died in 1896, awarded for outstanding contributions to Physics. As dictated by Nobels will, the award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobels death. Each recipient receives a Medal, a Diploma, and a Monetary Award Prize that has varied throughout the years.
Page Contents
Also Check: What Does Relationship Mean In Math Terms
List Of Nobel Laureates In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel , awarded for outstanding contributions in physics. As dictated by Nobel’s will, the award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel’s death. Each recipient receives a medal, a diploma and a monetary award prize that has varied throughout the years.
About: Nobel Prize In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony.
You May Like: What Is Sensory Awareness In Psychology
Nobel Prize In Physics Is Awarded To 3 Scientists For Work Exploring Quantum Weirdness
Alain Aspect, John F. Clauser and Anton Zeilinger were recognized for their experiments in an area that has broad implications for secure information transfer and quantum computing.
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this articleGive this articleGive this article
By Isabella Kwai, Cora Engelbrecht and Dennis Overbye
Three physicists whose works each showed that nature is even weirder than Einstein had dared to imagine have been named winners of the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics.
John Clauser, of J.F. Clauser and Associates in Walnut Creek, Calif. Alain Aspect of the Institut dOptique in Palaiseau, France and Anton Zeilinger of the University of Vienna in Austria, will split a prize of 10 million Swedish kronor.
Quantum information science is a vibrant and rapidly developing field, she said. Its predictions have opened doors to another world, and it has also shaken the very foundation of how we interpret measurements.
As Daniel Kabat, a physics professor at Lehman College in New York, explained recently, Were used to thinking that information about an object say that a glass is half full is somehow contained within the object. Instead, he says, entanglement means objects only exist in relation to other objects, and moreover these relationships are encoded in a wave function that stands outside the tangible physical universe.
First Nobel Prizes Awarded
The first Nobel Prizes are awarded in Stockholm, Sweden, in the fields of physics, chemistry, medicine, literature and peace on December 10, 1901. The ceremony came on the fifth anniversary of the death of Alfred Nobel, the Swedish inventor of dynamite and other high explosives. In his will, Nobel directed that the bulk of his vast fortune be placed in a fund in which the interest would be annually distributed in the form of prizes to those who, during the preceding year, shall have conferred the greatest benefit on mankind. Although Nobel offered no public reason for his creation of the prizes, it is widely believed that he did so out of moral regret over the increasingly lethal uses of his inventions in war.
Nitroglycerin remained dangerous, however, and in 1864 Nobels nitroglycerin factory blew up, killing his younger brother and several other people. Searching for a safer explosive, Nobel discovered in 1867 that the combination of nitroglycerin and a porous substance called kieselguhr produced a highly explosive mixture that was much safer to handle and use. Nobel christened his invention dynamite, for the Greek word dynamis, meaning power. Securing patents on dynamite, Nobel acquired a fortune as humanity put his invention to use in construction and warfare.
READ MORE: Did a Premature Obituary Inspire the Nobel Prize?
You May Like: What Is Frame Of Reference In Physics
Previous Winners Of The Nobel Prize In Physics
2013 – Francois Englert and Peter Higgs shared the prize for formulating the theory of the Higgs boson particle.
2012 – Serge Haroche and David J Wineland were awarded the prize for their work with light and matter.
2011 – The discovery that the expansion of the Universe was accelerating earned Saul Perlmutter, Brian P Schmidt and Adam Riess the physics prize.
2010 – Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov were awarded the prize for their discovery of the “wonder material” graphene.
2009 – Charles Kuen Kao won the physics Nobel for helping to develop fibre optic cables.
In its award citation, the Nobel committee declared: “Incandescent light bulbs lit the 20th Century the 21st Century will be lit by LED lamps.”
“With 20% of the world’s electricity used for lighting, it’s been calculated that optimal use of LED lighting could reduce this to 4%,” she said.
“Akasaki, Amano and Nakamura’s research has made this possible. This is physics research that is having a direct impact on the grandest of scales, helping protect our environment, as well as turning up in our everyday electronic gadgets.”
LED lamps have the potential to help more than 1.5 billion people around the world who do not have access to electricity grids – because they are efficient enough to run on cheap, local solar power.
Professor Ian Walmsley, a physicist at Oxford University, said the jury had made a “fantastic choice”.
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
Ernest Rutherford came from New Zealand to study with JJ Thomson in Cambridge. He then worked with the chemist Frederick Soddy at McGill University, showing that radioactive substances decay at constant rates, emitting characteristic radiations: alpha and beta particles and gamma rays. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908 while he was Langworthy Professor of Physics at Manchester.
In the laboratory built at the University by Arthur Schuster, Rutherford created a world centre for experiments in atomic physics. Highlights included an experiment in 1909 by Ernest Marsden and Hans Geiger, which suggested that atoms have dense nuclei the nuclear model of atomic structure and the first artificial transmutation of an atomic nucleus .
Read Also: Is Love An Emotion Psychology
Nobel Prize In Physics
| Outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of Physics | |
| Date | 10 December 1901 121 years ago |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| 9 million Swedish kronor | |
| First awarded | |
|
|
The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony.
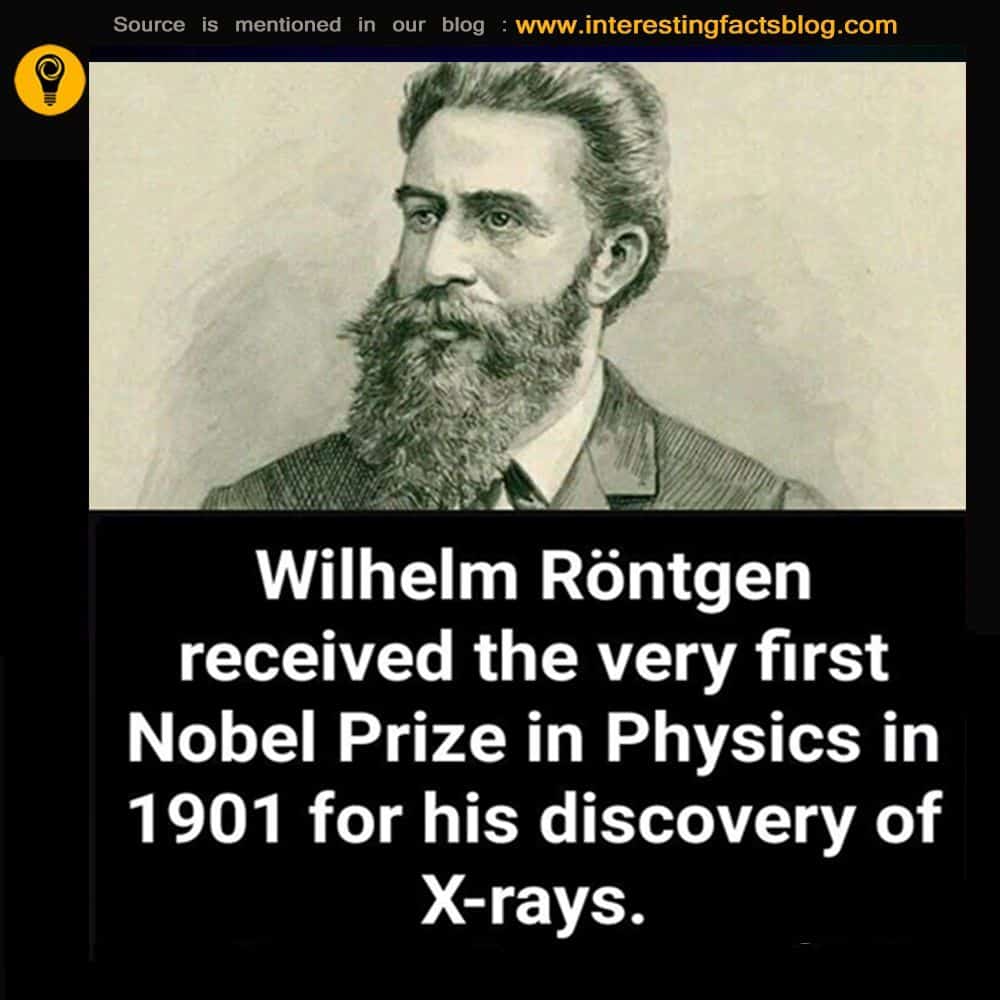
The first Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen in recognition of the extraordinary services he rendered by the discovery of X-rays. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and is widely regarded as the most prestigious award that a scientist can receive in physics. It is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel’s death. As of 2022 a total of 221 individuals have been awarded the prize.
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
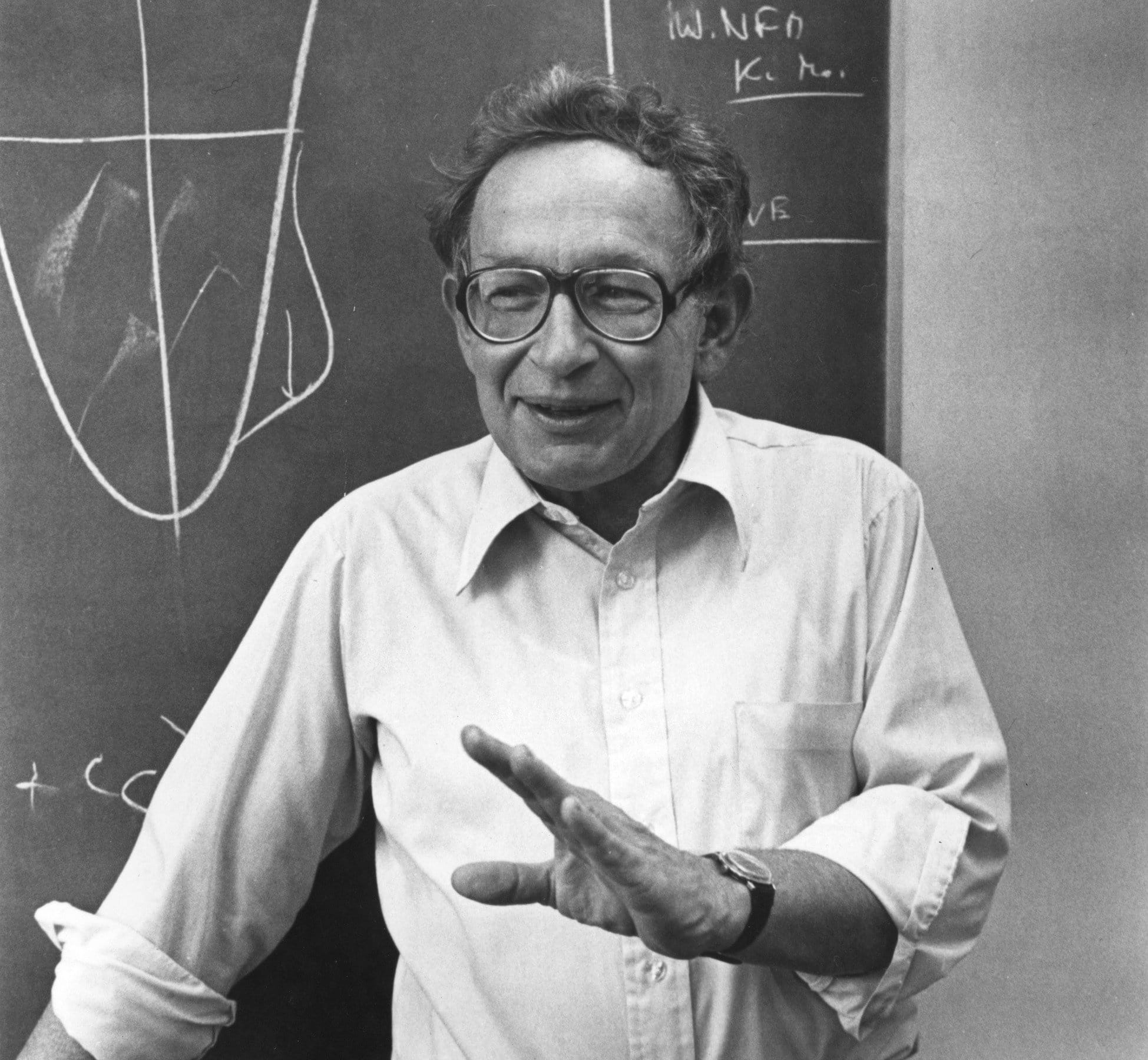

AV Hill shared the 1922 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Otto Myerhof. Hills physical studies of heat production and muscle mechanics had correlated revealingly with Myerhofs biochemical research. From 1923 Hill worked at University College London, leading the development of biophysics. He was active in the politics of science, and especially important in resettling Jewish scientists from Nazi Germany.
After training and research in physiology at Cambridge, Hill worked on ballistics during World War I. In 1920 he was appointed at Manchester as Brackenbury Professor of Physiology. He rapidly renovated the department and developed his sophisticated measurements of heat production during and after muscle contraction. One of the Universitys life sciences buildings was named for him in 2008.
Recommended Reading: Common Core Regents Algebra 2
First Step To Nobel Prize In Physics
| The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia’s general notability guideline. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted.Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Find sources: “First Step to Nobel Prize in Physics” news ·newspapers ·books ·scholar ·JSTOR |
The First Step to Nobel Prize in Physics is an annual international competition in research projects in physics. It originated and is based in Poland.
Speed Read: An Illuminating Accident
On a dark November evening in 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen was perplexed by a fluorescent screen in his laboratory that was glowing for no apparent reason. Röntgens experiment on how cathode-ray tubes emit light appeared to be affecting something that was not part of the study. It took weeks spent eating and sleeping in his lab to identify the cause of this mysterious glow a discovery with which Röntgens name is linked for all time, and which earned him the very first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.
Röntgens discovery of a new form of energy would be subsequently named after him, but he always preferred the term X-rays from the mathematical designation for something unknown as no one understood what these remarkable rays actually were. In a series of experiments Röntgen discovered X-rays could travel distances of metres, and could pass through materials such as cardboard, wood and aluminum unimpeded, but not denser materials such as lead and, perhaps more notably, bone.
For a man known to be quiet and reserved, the instant global attention Röntgen and his discoveries received seems ironic, but this was thanks to another of his traits. Researchers worldwide could experiment on X-rays as Röntgen refused to patent his findings, convinced that his inventions and discoveries belong to the world at large.
Don’t Miss: Does The Biological Father Have To Sign Adoption Papers
The International Peace Movement In Focus
Henry Dunant, founder of the International Committee of the Red Cross, shared the first Nobel Peace Prize with Frédéric Passy, a leading international pacifist of the time. Since then, the Red Cross has been awarded the Peace Prize three times.
First published 6 July 2016
To cite this section MLA style: The very first Nobel Prizes. NobelPrize.org. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2023. Fri. 6 Jan 2023. < https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/themes/the-very-first-nobel-prizes>
Meet Marie Curie The First Woman To Win A Nobel Prize
FACT: Not only is Marie Curie the first woman to ever be awarded the Nobel Prize, she is also the only woman to have won it twice, and in two separate sciences .
While searching for a Parisian laboratory to continue her experimentation, she was introduced to Pierre Curie, a highly regarded professor at the School of Physics. At 35 years old, Pierre was already an internationally recognised physicist and though his papers had been well received by distinguished colleagues, he was still an outsider in the French academic community. Like Marie he did not care for outward distinctions or a career. The two married in July 1895.
During her studies Marie had heard about Henri Becquerels discovery of a sort of radiation emitting from uranium salts and decided to study these uranium rays for her doctoral thesis. She soon discovered that the intensity of the rays was in direct proportion to the amount of uranium in her sample. Nothing she did to the uranium affected the rays. This, she said, shows that radioactivity is an atomic property. She also found that two minerals, pitchblende and chalcite, were much more radioactive than uranium itself, and realised that they must contain a new radioactive element.
After the exciting results of Maries early experiments Pierre abandoned his study of crystals to join her in her search for new substances.
The original version of this piece is from the Science Museum.
Do you like this post?
Also Check: What Is Circadian Rhythm Psychology