What Are The Uses Of Tetrahydrofuran
- What Are The Uses Of Tetrahydrofuran ?
Weve taken a look in a recent blog post at what tetrahydrofuran is. Here, well look in a little more depth at the uses and applications of tetrahydrofuran.
As a brief reminder before we dive in, THF is a colourless, miscible and polar organic compound with a strong smell. Made up of four carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom, it is a heterocyclic ether. Other names for tetrahydrofuran are oxolone and butylene oxide.
Lesson Summary Inorganic Describes Matter That Is Not And Never Was Living Inorganic Compounds Are Generally Described As Those Compounds That Do Not Contain Carbon
What does inorganic mean in chemistry?
Inorganic is a word used to describe matter that is not and never was living. Inorganic compounds are generally described as those compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds .
What is an example of something inorganic?
Examples of inorganic substances include: magnesium sulfate , potassium chloride , potassium sulfate , calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, calcium phosphate, and calcium carbonate.
What is the difference between organic and inorganic chemistry?
Inorganic is a word used to describe matter that is not and never was living. This can be contrasted with the word organic which means carbon containing. Inorganic chemistry is the field of science that deals with the property and behavior of inorganic compounds. Organic chemistry deals with the property and behavior of organic compounds.
Active Oxygen In Peroxides
Each peroxy group is considered to contain one active oxygen atom. The concept of active oxygen content is useful for comparing the relative concentration of peroxy groups in formulations, which is related to the energy content. In general, energy content increases with active oxygen content, and thus the higher the molecular weight of the organic groups, the lower the energy content and, usually, the lower the hazard.
The term active oxygen is used to specify the amount of peroxide present in any organic peroxide formulation. One of the oxygen atoms in each peroxide group is considered “active”. The theoretical amount of active oxygen can be described by the following equation:
- Atheoretical = 16p/m × 100,
where p is the number of peroxide groups in the molecule, and m is the molecular mass of the pure peroxide.
Organic peroxides are often sold as formulations that include one or more phlegmatizing agents. That is, for safety sake or performance benefits the properties of an organic peroxide formulation are commonly modified by the use of additives to phlegmatize , stabilize, or otherwise enhance the organic peroxide for commercial use. Commercial formulations occasionally consist of mixtures of organic peroxides, which may or may not be phlegmatized.
Read Also: Is Ap Human Geography Hard
Organic Reaction Workup Formulas For Specific Reagents Reactions With Triphenylphosphine Oxide:
Diethyl ether tetrahydrofuran alcoholic solvents and water are incompatible with grignard reagents and organolithium reagents. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. Hydroboration the mechanism is said to be highly streospecific since addition of both atom happens simultaneously on the same face . Organic reaction workup formulas for specific reagents reactions with triphenylphosphine oxide: The water solubility of thf is complex. Bh 3 as a reagent for hydroboration of alkenes . Thf is the solvent that is used to stabilize the dimer of bh 3 which is a flammable, toxic, and explosive gas: Its used in boration of alkene. T = 20 °c unless specified otherwise. In general the alkyl halide is added to an excess of magnesium suspended in the solvent. . The values were obtained from the crc , or vogel’s practical organic chemistry . The general form of the reaction is as follows:
In reductions in organic chemistry 2nd ed., american chemical society monograph 188: Here is an excellent organic extraction solvent: 8.4 solvents in organic chemistry 343 .
What Is Thf Used For In Organic Chemistry
Explain Below What Do You Want to report!
From: Bhopal/India
Tetrahydrofuran is a versatile solvent used in laboratory organic synthesis and in industrial products such as varnishes. Tetrahydrofuran , or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula 4O. THF stand for Tetrahydrofuran a cyclic ether. A solvent is used to create solutions, and in this case THF serves to dissolve or form solutions with other organic compounds. THF stands for Tetrahydrofuran, and is a common ether-type solvent. THF is used as a solvent in organic synthesis and chromatographic analysis, and is an intermediate of nylon-6,6.
Explain Below What Do You Want to report!
Explain Below What Do You Want to comment!
Rishit Sodhi answered
The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group . Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. tert-Butyloxycarbonyl is a protecting group often used in the synthesis of organic compounds. Chemical shifts are reported as -values in ppm. Amine is one of the commonly used functionalities in synthetic organic chemistry, and its protection in the form of an N-tert-butoxycarbonyl derivative has.
Shrishti Maharaj answered
Navya Naik answered
Atiksh Pradhan answered
Rishit Sodhi answered
Kaia Singh answered
Adah Hora answered
Mehar Dugal answered
Yug Jhaveri answered
Luv Raj answered
Rudra De answered
Yug Jhaveri answered
Rachit Sachar answered
Rushil Kapoor answered
Laksh Shroff answered
Pranay Prasad answered
Also Check: Algebra 1 Eoc Fsa Practice Test
Thermal Decomposition Of Organic Peroxides
Organic peroxides are useful in chemical synthesis due to their propensity to . In doing so they generate useful radicals that can initiate polymerization to create polymers, modify polymers by grafting or visbreaking, or cross-link polymers to create a thermoset. When used for these purposes, the peroxide is highly diluted, so the heat generated by the exothermic decomposition is safely absorbed by the surrounding medium . But when a peroxide is in a more pure form, the heat evolved by its decomposition may not dissipate as quickly as it is generated, which can result in increasing temperature, which further intensifies the rate of exothermic decomposition. This can create a dangerous situation known as a self-accelerating decomposition.
A self-accelerating decomposition occurs when the rate of peroxide decomposition is sufficient to generate heat at a faster rate than it can be dissipated to the environment. Temperature is the main factor in the rate of decomposition. The lowest temperature at which a packaged organic peroxide will undergo a self-accelerating decomposition within a week is defined as the self-accelerating decomposition temperature .
Polar Protic And Aprotic Solvents
Solvents used in organic chemistry are characterized by their physical characteristics. Among the most important are whether the solvents are polar or non-polar, and whether they are protic or aprotic. Because non-polar solvents tend to be aprotic,the focus is upon polar solvents and their structures.
Don’t Miss: Geometry Dash Demon Key Hack
What Is Thf Organic Chemistry
Explain Below What Do You Want to report!
From: Varanasi/India
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry – Tetrahydrofuran Tetrahydrofuran : A five-membered heterocyclic ring consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, or a molecule containing this ring. Tetrahydrofuran , or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula 4O. THF refers to Tetra Hydro Furan. A solvent is used to create solutions, and in this case THF serves to dissolve or form solutions with other organic compounds. Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry – Tetrahydrofuran Tetrahydrofuran : A five-membered heterocyclic ring consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, or a molecule containing this ring. Tetrahydrofuran is merely a solvent.
Explain Below What Do You Want to report!
Explain Below What Do You Want to comment!
Rishit Sodhi answered
The tert-butyloxycarbonyl protecting group or tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group . Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. tert-Butyloxycarbonyl is a protecting group often used in the synthesis of organic compounds. Chemical shifts are reported as -values in ppm. Amine is one of the commonly used functionalities in synthetic organic chemistry, and its protection in the form of an N-tert-butoxycarbonyl derivative has.
Shrishti Maharaj answered
Navya Naik answered
Atiksh Pradhan answered
Rishit Sodhi answered
Kaia Singh answered
Adah Hora answered
Mehar Dugal answered
Yug Jhaveri answered
Luv Raj answered
Classification Of Inorganic Compounds
The Inorganic compounds that are classified as:
- Acids Acids are those compounds that dissolve in water and generate hydrogen ions or H+ Ions. The examples of acids include Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, sulphuric acid, vinegar, etc. One example of the acidic reaction is shown below-Hydrochloric acid + water H+ + Cl
- Bases A base is a type of substance or a compound that produces hydroxyl ions when kept in water. The bases like potassium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium hydroxide produce OH- ions when dissolved in water. Potassium Hydroxide + H2O K+ + OH
- Salts As you might be familiar with the word Salt. The substances obtained as a result of the reaction between an acid and a base are called Salts. The table salt of sodium hydroxide is one of the typical examples of salts.
- Oxides The compounds which consist of one oxygen atom called Oxides.
You May Like: Segment And Angle Addition Worksheet Answers
Characterization Of Inorganic Compounds
Because of the diverse range of elements and the correspondingly diverse properties of the resulting derivatives, inorganic chemistry is closely associated with many methods of analysis. Older methods tended to examine bulk properties such as the electrical conductivity of solutions, melting points, solubility, and acidity. With the advent of quantum theory and the corresponding expansion of electronic apparatus, new tools have been introduced to probe the electronic properties of inorganic molecules and solids. Often these measurements provide insights relevant to theoretical models. Commonly encountered techniques are:
- Electron-spin resonance: ESR allows for the measurement of the environment of paramagnetic metal centres.
Furans And Related Compounds
Tetrahydrofurans are an important class of five-membered oxygen heterocycles, often present in a great variety of natural products and synthetic compounds of biological interests . This type of heterocyclic compound is widely used in cosmetic formulations, perfumes, and flavors . Fig. 4.2 enlists mucoxin, a natural product with high potential as specific antitumor agent against breast carcinoma furans 9a-c are also known for flavoring agents with insecticidal activity .
Figure 4.2. Bioactive tetrahydrofurans.
Zeolites and clays have been used as effective acid microporous catalysts in certain organic rearrangements useful for the synthesis of fine chemicals. For instance, the Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether, followed by intramolecular hydroxyalkylation of the resulting olefin 10 afforded 2-methyldihydrobenzofuran .
Scheme 4.7. Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether and subsequent intramolecular hydroalkylation giving 2-methyldihydrobenzofuran .
Nevin Mathew et al. also reported the Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether catalyzed by mesoporous MCM-41 . In this case, conversion to products was higher when increasing the Al content in the mesoporous silica suggesting, therefore, that the reaction occurs inside the pores. The Si/Al ratio in the catalysts has an effect in the reaction selectivity MCM-41 with lower Si/Al ratios led preferentially to compound 10 at lower temperatures.
Scheme 4.8. Intramolecular cyclization of cis-4-decenol .
You May Like: What Happened To Beth Thomas Biological Father
Types Of Reactions And Examples Of Inorganic Compounds
There are about four types of chemical reactions of Inorganic chemistry namely combination, decomposition, single displacement and double displacement reactions.
Thermodynamics And Inorganic Chemistry

An alternative quantitative approach to inorganic chemistry focuses on energies of reactions. This approach is highly traditional and empirical, but it is also useful. Broad concepts that are couched in thermodynamic terms include redox potential, acidity, phase changes. A classic concept in inorganic thermodynamics is the Born-Haber cycle, which is used for assessing the energies of elementary processes such as electron affinity, some of which cannot be observed directly.
Recommended Reading: Hbo Documentary Child Of Rage
Types Of Organic Peroxides
Major classes of organic peroxides include:
- hydroperoxides, compounds with the functionality ROOH .
- peroxy acids and esters, compounds with the functionality RCOOH and RCOOR’ .
- diacyl peroxides, compounds with the functionality RCOOCR .
- dialkylperoxides, compounds with the functionality ROOR .
These compounds occur in nature or are useful in commercial settings. Still other more specialized peroxy compounds are known.
Would You Like To Join Ask Sawal
Ask Sawal is a fast growing question and answer discussion forum.
15 lakh+ questions were answered by our Ask Sawal Members.
Each day 1000s of questions asked& 1000s of questions answered.
Ask any question and get answer from 2.5 Lakh+ Ask Sawal Members.
Constant moderation and reporting option makes questions and answers spam free.
And also, we have free blogging platform. Write an article on any topic.
We have 10000+ visitors each day. So a beneficial platform for link building.
We are allowing link sharing. Create backlinks to your blog site or any site.
Gain extra passive income by sharing your affiliate links in articles and answers.
Also Check: K+ Chemistry
Protic Vs Aprotic Solvents
The table above distinguishes between protic and aprotic solvents. For the solvents included in the table, the distinguishing feature is the presence of an -OH group, and that is the most common characteristic of a protic solvent. However, there are exceptions, such as nitromethane, CH3NO2, which is also considered a protic solvent. That might suggest that Bronsted acidity is the most important feature, because nitromethane is very acidic, with a pKa of about 10. However, acetone is still considered a polar aprotic solvent, despite the fact that it is relatively acidic, and not significantly less acidic than alcohols. Then again, acetone are, indeed, poor solvents when using strong bases due to their relatively high acidity.
Use Of Cpme In Oxidation Processes
The chemical stability of CPME to oxidation can be exploited in the epoxidation of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by polyoxometalate nanoparticles. Indeed, within a set of 18 ecofriendly solvents plus MeCN and CHCl3, tris-dodecyltrimethylammonium in CPME and 2-MeTHF give the best results in terms of turnover frequency .
Figure 2
Initial turnover frequency observed for the epoxidation of cyclooctene in various solvents.
Moreover, CPME is the best choice to ensure that the catalyst nanoparticles remain in suspension. The described procedure has successfully been extended to various olefins with competitive rates, good yields, and high selectivities, and the nanoparticles can be easily separated from the reaction product and recycled over five consecutive steps.
The oxidation of ynamides to α-keto imides has been realized by a combination of N-iodosuccinimide , DMSO, and air, and the best results are afforded in CPME, possibly also because of its inherent stability to the acidity developed during the reaction .
|
Entry |
|
|---|---|
|
toluene |
- âTs=tosyl. âReaction run under an argon atmosphere. âReaction run under an O2 atmosphere.
The substrate scope can be extended to nine additional examples, and the products are obtained in moderate to acceptable yields furthermore the oxidation of diarylalkynes to the corresponding 1,2-diketones is also possible .
Scheme 66
Aerobic cross-dehydrogenative coupling of terminal alkynes with tertiary amines.
Scheme 67
Read Also: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Lah Lithium Aluminum Hydride Lithium Tetrahydridoaluminate
LiAlH4 is a very common, strong reducing agent, which reduces a vast number of different functional groups.
Recent Literature
The preparation of alkenyl halides of any length from inexpensive starting reagents is reported. Standard organic transformations were used to prepare straight-chain -olefin halides in excellent overall yields with no detectable olefin isomerization and full recovery of any unreacted starting material.T. W. Baughman, J. C. Sworen, K. B. Wagener, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 10943-10948.
A tethered alkene functionality can be used as a traceless directing group for a zirconium catalyzed reductive cleavage of Csp3 and Csp2carbon-heteroatom bonds, including C-O, C-N, and C-S bonds. The reaction is especially useful for cleavage of homoallylic ethers and the removal of terminal allyl and propargyl groups.C. Matt, F. Kölblin, J. Streuff, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 6909-6913.
Secondary -chloroketimines react with lithium aluminium hydride in ether to afford mixtures of cis– and trans-1,2,3-trisubstituted aziridines by nucleophilic addition of hydride across the imino bond and subsequent intramolecular nucleophilic substitution. Tertiary -chloroketimines react similarly to yield 1,2,2,3-tetrasubstituted aziridines. ,-Dichloroketimines react in a stereospecific way to afford cis-aziridines, exclusively.N. De Kimpe, L. Moens, Tetrahedron, 1990,46, 2965-2974.
What Is The Ph Of A Solution Obtained By Dissolving Two Extra
What is the pH of a solution obtained by dissolving two extra-strength aspirin tablets, containing 400 mg of acetylsalicylicacid each, in 340 mL of water?Express your answer to two decimal places.O AE?pH =
Answer
Couldyouplease tell me the value of Ka to solve furtherDatePagePlease Rake-33MAnys Acetyl salioylic acid Weight of HChalu in 1 tabletayou my2 tablet = 400 x 2800 mg800 x 10 3sgMolecular mass of HG HO4 = 180= 180g/mol.. moles of HGHz Oy = mass800 x 103 g -4.44X103molar massmoles186 g/molMolarity of Helg Hz Oy – molu 4.44810 3 = 13.06810Volume 0.34 mlICE table for acetyl salicylic acid isHC GHz Oy Cq HO4.- Cq HOy- + H+Initial13.066103ChangeEquilibrium 13:06x103_xKa = acid dissociation constant.Ka= HCqHz Oyx. n13.064163 -+O0of aRtxa
Take a picture of your question and get a handwritten, expert solution in 15 mins on average.
You May Like: Definition Of Reduction In Math
Solubilities Are In Water And Are Reported As Grams Solvent/100 Grams Water
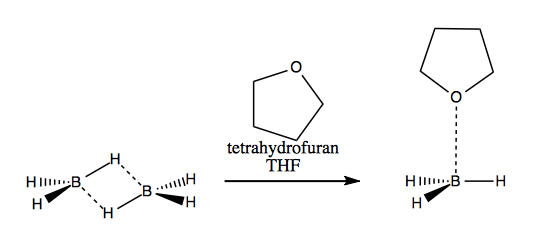
Because its dipole moment can interact favorably with other dipoles, it also dissolves polar compounds . The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. While diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran are commonly used as solvents, other polar nonprotic solvents are suitable, including: Solubilities are in water and are reported as grams solvent/100 grams water. Also the nonpolar aprotic solvent of molecular formula c 4 h 8 o containing this ring. Brown in the late 1950s and it was recognized in his receiving the nobel prize in chemistry in 1979. The tetrahydropyranyl ether is a useful protecting group for the protection of alcohols and phenols, offering stability towards strongly basic reaction conditions, organometallics, hydrides, acylating reagents and alkylation reagents. Here is an excellent organic extraction solvent: It is colorless and miscible in water, with a boiling point of 66 ºc. Its a polar a protic solvent used for various organic reaction. Bh 3 as a reagent for hydroboration of alkenes . So that’s why we also need the bh3. Triethylamine , dimethylsulphide , dimethylselenide , and dimethyltelluride .
Thf stand for tetrahydrofuran a cyclic ether. Also, the thf here supports boron to be present as bh3. Reactivity of the alkyl halide: In normal situations, boron would dimerize to form b2h6. Because thf can accept hydrogen bonds, it dissolves water and many alcohols.