List Of The Advantages Of A Correlational Research Study
1. Neither variable goes through a manipulative process. When you choose a correlational research study to review variables, then neither one goes through a manipulative process. It is the distinctive feature of this method. Researchers could observe participants in a public setting or a closed environment because it doesnt matter where or how the variables get measured.
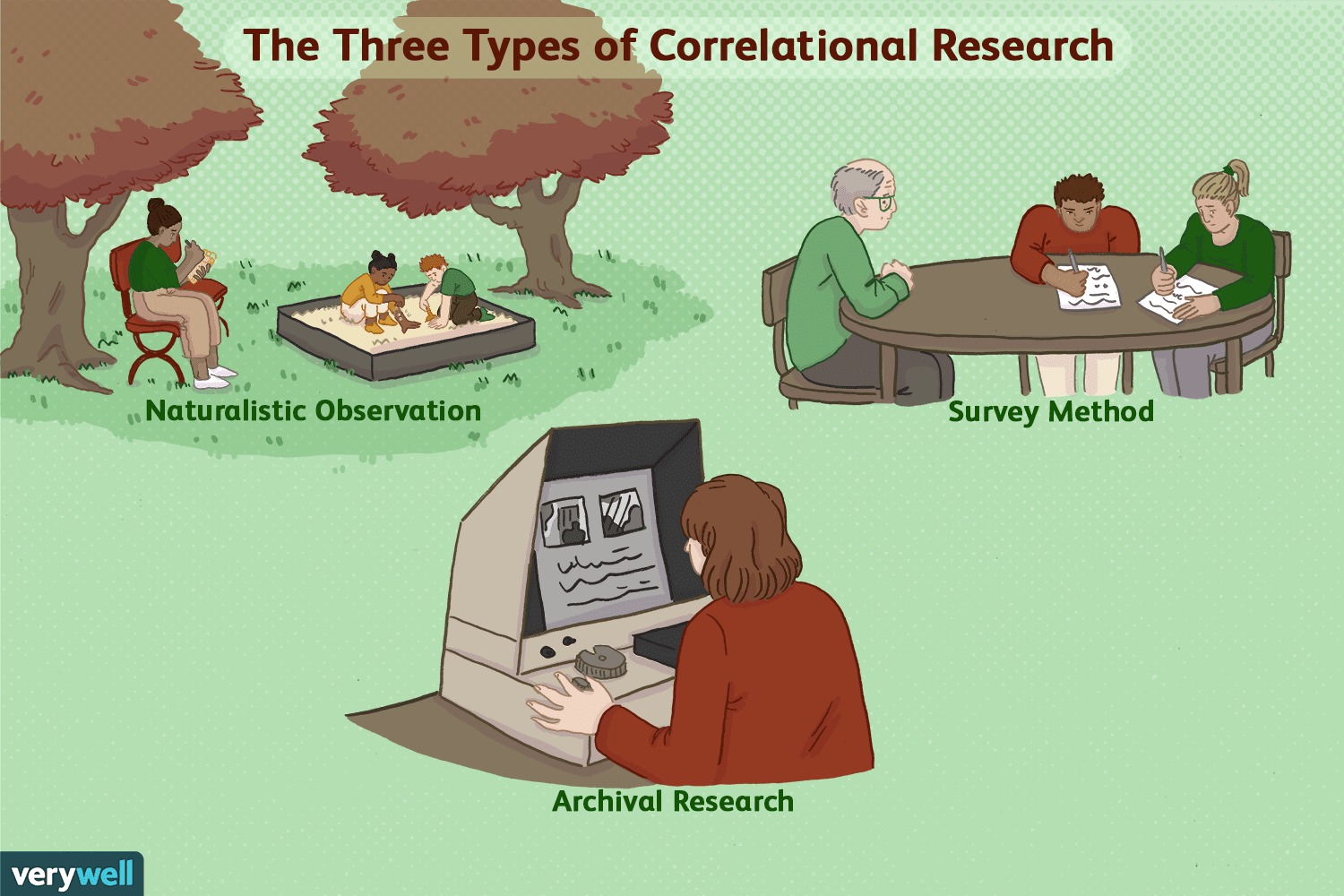
2. Two different data collection methods are available with correlational research. The data gathered from a correlational research study can come from either naturalistic observation or archival data. The first option is a type of field research where those responsible for the work might observe situations in real-life scenarios as unobtrusively as possible. When people know that they are under observation, then there is a significant risk that their behaviors will change. If the participants remain anonymous with the work conducted in a public setting, then it is an ethical approach.
The second option relies on the use of collected data from previous research efforts. The information is straightforward, giving researchers access to specific points that can lead to a greater understanding of the potential variables involved in each situation.
Even if the researchers dont know the individuals or situations being studied with correlational research, their findings are still applicable to the scenarios under review.
How To Use Online Forms For Correlational Research
One of the most popular methods of conducting correlational research is by carrying out a survey which can be made easier with the use of an online form. Surveys for correlational research involve generating different questions that revolve around the variables under observation and, allowing respondents to provide answers to these questions.
Using an online form for your correlational research survey would help the researcher to gather more data in minimum time. In addition, the researcher would be able to reach out to more survey respondents than is plausible with printed correlational research survey forms.
In addition, the researcher would be able to swiftly process and analyze all responses in order to objectively establish the statistical pattern that links the variables in the research. Using an online form for correlational research also helps the researcher to minimize the cost incurred during the research period.
To use an online form for a correlational research survey, you would need to sign up on a data-gathering platform like Formplus. Formplus allows you to create custom forms for correlational research surveys using the Formplus builder.
You can customize your correlational research survey form by adding background images, new color themes or your company logo to make it appear even more professional. In addition, Formplus also has a survey form template that you can edit for a correlational research study.
Correlational Research Designs: Types Examples & Methods
A human mind is a powerful tool that allows you to sift through seemingly unrelated variables and establish a connection with regards to a specific subject at hand. This skill is what comes to play when we talk about correlational research.
Correlational research is something that we do every day think about how you establish a connection between the doorbell ringing at a particular time and the milkman’s arrival. As such, it is expedient to understand the different types of correlational research that are available and more importantly, how to go about it.
Read Also: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Causality: Conducting Experiments And Using The Data
As youve learned, the only way to establish that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables is to conduct a scientific experiment. Experiment has a different meaning in the scientific context than in everyday life. In everyday conversation, we often use it to describe trying something for the first time, such as experimenting with a new hair style or a new food. However, in the scientific context, an experiment has precise requirements for design and implementation.
The Experimental Hypothesis
In order to conduct an experiment, a researcher must have a specific hypothesis to be tested. As youve learned, hypotheses can be formulated either through direct observation of the real world or after careful review of previous research. For example, if you think that the use of technology in the classroom has negative impacts on learning, then you have basically formulated a hypothesisnamely, that the use of technology in the classroom should be limited because it decreases learning. How might you have arrived at this particular hypothesis? You may have noticed that your classmates who take notes on their laptops perform at lower levels on class exams than those who take notes by hand, or those who receive a lesson via a computer program versus via an in-person teacher have different levels of performance when tested .
Designing an Experiment
Adherence To Good Practices In Prospective Observational Studies
The Good Research Practices Task Force published a set of recommendations in designing, conducting and reporting prospective observational studies for comparative effectiveness research that are relevant to eHealth evaluation. Their key recommendations are listed below.
- Key policy questions should be defined to allow inferences to be drawn.
- Hypothesis testing protocol design to include the hypothesis/questions, treatment groups and outcomes, measured and unmeasured confounders, primary analyses, and required sample size.
- Rationale for prospective observational study design over others is based on question, feasibility, intervention characteristics and ability to answer the question versus cost and timeliness.
- Study design choice is able to address potential biases and confounders through the use of inception cohorts, multiple comparator groups, matching designs and unaffected outcomes.
- Explanation of study design and analytic choices is transparent.
- Study execution is carried out in ways that ensure relevance and reasonable follow-up is not different from the usual practice.
- Study registration takes place on publicly available sites prior to its initiation.
Recommended Reading: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
How Correlational Studies Work
Correlational studies are a type of research often used in psychology, as well as other fields like medicine. Correlational research is a preliminary way to gather information about a topic. The method is also useful if researchers are unable to perform an experiment.
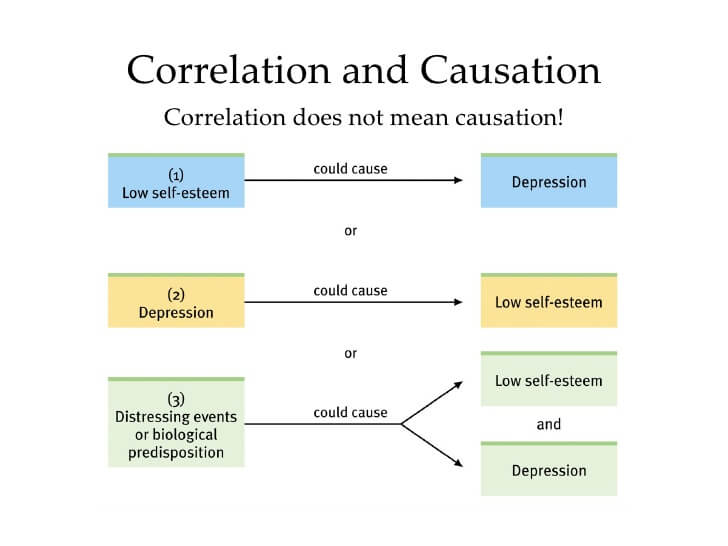
Researchers use correlations to see if a relationship between two or more variables exists, but the variables themselves are not under the control of the researchers.
While correlational research can demonstrate a relationship between variables, it cannot prove that changing one variable will change another. In other words, correlational studies cannot prove cause-and-effect relationships.
Data Collection In Correlational Research
Again, the defining feature of correlational research is that neither variable is manipulated. It does not matter how or where the variables are measured. A researcher could have participants come to a laboratory to complete a computerized backward digit span task and a computerized risky decision-making task and then assess the relationship between participants scores on the two tasks. Or a researcher could go to a shopping mall to ask people about their attitudes toward the environment and their shopping habits and then assess the relationship between these two variables. Both of these studies would be correlational because no independent variable is manipulated. However, because some approaches to data collection are strongly associated with correlational research, it makes sense to discuss them here. The two we will focus on are naturalistic observation and archival data. A third, survey research, is discussed in its own chapter, Chapter 9.
You May Like: Theory Of Everything 2 Music
Review: What Is A Correlational Study And Why Is It Important
Psychology is a science, and like any other, its knowledge must be scientifically obtained, verified and validated. For this, psychologists conduct three types of research:
Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
You might be wondering: if correlational studies only show this correlations why are they important in the first place if you could just conduct an experiment manipulating the relevant variables and getting to more solid conclusions?
Other advantages are that correlational studies are usually less expensive and easier to conduct than experiments and they allow for general predictions. They can also represent the first steps in a new field of research, leading to further studies and advances.
Assessing Relationships Among Multiple Variables
Most complex correlationalresearch involves measuring several variablesoften both categorical andquantitativeand then assessing the statistical relationships among them. Forexample, researchers Nathan Radcliffe and William Klein studied a sample ofmiddle-aged adults to see how their level of optimism relates to several othervariables related to having a heart attack . Theseincluded their health, their knowledge of heart attack risk factors, and theirbeliefs about their own risk of having a heart attack. They found that moreoptimistic participants were healthier , knew about heart attack risk factors, and correctly believedtheir own risk to be lower than that of their peers.
Table 8.2 Correlation MatrixShowing Correlations Among the Need for Cognition and Three Other VariablesBased on Research by Cacioppo and Petty
|
+.03 |
Don’t Miss: Paris Jackson’s Parents
Correlational Research: Seeking Relationships Among Variables
In contrast to descriptive research, which is designed primarily to provide static pictures, correlational researchinvolves the measurement of two or more relevant variables and an assessment of the relationship between or among those variables. For instance, the variables of height and weight are systematically related because taller people generally weigh more than shorter people. In the same way, study time and memory errors are also related, because the more time a person is given to study a list of words, the fewer errors he or she will make. When there are two variables in the research design, one of them is called the predictor variable and the other the outcome variable. The research design can be visualized as shown in Figure 3.9, where the curved arrow represents the expected correlation between these two variables.
One way of organizing the data from a correlational study with two variables is to graph the values of each of the measured variables using a scatter plot. As you can see in Figure 3.10 a scatter plot is a visual image of the relationship between two variables. A point is plotted for each individual at the intersection of his or her scores for the two variables. When the association between the variables on the scatter plot can be easily approximated with a straight line, as in parts and of Figure 3.10 the variables are said to have a linear relationship.
Correlation Coefficients: Determining Correlation Strength
Correlation Coefficients: Determining Correlation Strength
Instead of drawing a scattergram a correlation can be expressed numerically as a coefficient, ranging from -1 to +1. When working with continuous variables, the correlation coefficient to use is Pearsonâs r.
The correlation coefficient indicates the extent to which the pairs of numbers for these two variables lie on a straight line. Values over zero indicate a positive correlation, while values under zero indicate a negative correlation.
A correlation of â1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, meaning that as one variable goes up, the other goes down. A correlation of +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning that as one variable goes up, the other goes up.
There is no rule for determining what size of correlation is considered strong, moderate or weak. The interpretation of the coefficient depends on the topic of study.
When studying things that are difficult to measure, we should expect the correlation coefficients to be lower . When we are studying things that are more easier to measure, such as socioeconomic status, we expect higher correlations .)
In these kinds of studies, we rarely see correlations above 0.6. For this kind of data, we generally consider correlations above 0.4 to be relatively strong correlations between 0.2 and 0.4 are moderate, and those below 0.2 are considered weak.
Don’t Miss: People Who Are Always Late Psychology
Final Words On Correlational Research
Just like every other research method, correlational research has its pros and cons. There is plenty of hypotheses that this type is useful for and there is a time and a place to apply it. Understanding what this type is all about can help you to understand its application in everyday life, as well.
Does Correlational Research Always Involve Quantitative Variables
A common misconception among beginning researchers is that correlational research must involve two quantitative variables, such as scores on two extraversion tests or the number of daily hassles and number of symptoms people have experienced. However, the defining feature of correlational research is that the two variables are measuredneither one is manipulatedand this is true regardless of whether the variables are quantitative or categorical. Imagine, for example, that a researcher administers the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale to 50 American college students and 50 Japanese college students. Although this feels like a between-subjects experiment, it is a correlational study because the researcher did not manipulate the students nationalities. The same is true of the study by Cacioppo and Petty comparing college faculty and factory workers in terms of their need for cognition. It is a correlational study because the researchers did not manipulate the participants occupations.
Figure 6.2 Results of a Hypothetical Study on Whether People Who Make Daily To-Do Lists Experience Less Stress Than People Who Do Not Make Such Lists
You May Like: Ccl4 Electron Geometry
Correlation Definitions Examples & Interpretation
By Dr. Saul McLeod, updated 2020
Correlation means association – more precisely it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. There are three possible results of a correlational study: a positive correlation, a negative correlation, and no correlation.
A positive correlation is a relationship between two variables in which both variables move in the same direction. Therefore,when one variable increases as the other variable increases, or one variable decreases while the other decreases. An example of positive correlation would be height and weight. Taller people tend to be heavier. A negative correlation is a relationship between two variables in which an increase in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other. An example of negative correlation would be height above sea level and temperature. As you climb the mountain it gets colder . A zero correlation exists when there is no relationship between two variables. For example there is no relationship between the amount of tea drunk and level of intelligence.
Scattergrams
A correlation can be expressed visually. This is done by drawing a scattergram .
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to aweb browser thatsupports HTML5 video
A scattergram is a graphical display that shows the relationships or associations between two numerical variables , which are represented as points for each pair of score.
Research Focus: Video Games And Aggression
Consider an experiment conducted by Anderson and Dill . The study was designed to test the hypothesis that viewing violent video games would increase aggressive behaviour. In this research, male and female undergraduates from Iowa State University were given a chance to play with either a violent video game or a nonviolent video game . During the experimental session, the participants played their assigned video games for 15 minutes. Then, after the play, each participant played a competitive game with an opponent in which the participant could deliver blasts of white noise through the earphones of the opponent. The operational definition of the dependent variable was the level and duration of noise delivered to the opponent. The design of the experiment is shown in Figure 3.17
Two advantages of the experimental research design are the assurance that the independent variable occurs prior to the measured dependent variable, and the creation of initial equivalence between the conditions of the experiment .
Experimental designs have two very nice features. For one, they guarantee that the independent variable occurs prior to the measurement of the dependent variable. This eliminates the possibility of reverse causation. Second, the influence of common-causal variables is controlled, and thus eliminated, by creating initial equivalence among the participants in each of the experimental conditions before the manipulation occurs.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Characteristics Of Correlational Research
Correlational research has three main characteristics. They are:
- Non-experimental: Correlational study is non-experimental. It means that researchers need not manipulate variables with a scientific methodology to either agree or disagree with a hypothesis. The researcher only measures and observes the relationship between the variables, without altering them or subjecting them to external conditioning.
- Backward-looking: Correlational research only looks back at historical data and observes events in the past. Researchers use it to measure and spot historical patterns between two variables. A correlational study may show a positive relationship between two variables, but this can change in the future.
- Dynamic: The patterns between two variables from correlational research are never constant and are always changing. Two variables having a negative correlation in the past can have a positive correlation relationship in the future due to various factors.
What Are Different Types Of Correlational Research Outputs
Don’t Miss: Is Michael Jackson The Biological Father Of Paris