Is There A Scientific Dictionary
This dictionary provides scientists, science writers, and all who work in scientific publishing with a clear style guide for the presentation of scientific information. In over 9,700 entries, it reflects widely accepted usage and follows the recommendations of international scientific bodies such as IUPAC and IUPAP.
What Happens When We Degrade
To degrade is defined as to treat someone with disrespect, to lower someones rank, to make something not as good, or to break down or deteriorate. When you talk down to someone and insult him, this is an example of a time when you degrade the person. To lower in quality or value make inferior or less valuable.
Where Do Biology Graduates Work
Biology graduates can hold a wide range of jobs, some of which may require additional education. A person with a degree in biology could work in agriculture, health care, biotechnology, education, environmental conservation, research, forensic science, policy, science communication, and many other areas.
biology, study of living things and their vital processes. The field deals with all the physicochemical aspects of life. The modern tendency toward cross-disciplinary research and the unification of scientific knowledge and investigation from different fields has resulted in significant overlap of the field of biology with other scientific disciplines. Modern principles of other fieldschemistry, medicine, and physics, for exampleare integrated with those of biology in areas such as biochemistry, biomedicine, and biophysics.
Biology is subdivided into separate branches for convenience of study, though all the subdivisions are interrelated by basic principles. Thus, while it is custom to separate the study of plants from that of animals , and the study of the structure of organisms from that of function , all living things share in common certain biological phenomenafor example, various means of reproduction, cell division, and the transmission of genetic material.
Don’t Miss: Why Are There Different Branches Of Chemistry
What Are New Entries In Dictionary Of Biology
This new eighth edition has been fully revised and updated to reflect recent progress in the fields of biology, biophysics, and biochemistry, with particular expansion to the areas of ecology, cell biology, and plant and animal development. Over 150 new entries include de-extinction, ecological footprint, rewilding, and Zika virus.
Animal Form And Function

The cells in each animal body are bathed in interstitial fluid, which make up the cell’s environment. This fluid and all its characteristics can be described as the animal’s internal environment, which is in contrast to the external environment that encompasses the animal’s outside world. Animals can be classified as either regulators or conformers. Animals such as mammals and birds are regulators as they are able to maintain a constant internal environment such as body temperature despite their environments changing. These animals are also described as homeotherms as they exhibit thermoregulation by keeping their internal body temperature constant. In contrast, animals such as fishes and frogs are conformers as they adapt their internal environment to match their external environments. These animals are also described as poikilotherms or ectotherms as they allow their body temperatures to match their external environments. In terms of energy, regulation is more costly than conformity as an animal expands more energy to maintain a constant internal environment such as increasing its basal metabolic rate, which is the rate of energy consumption. Similarly, homeothermy is more costly than poikilothermy. Homeostasis is the stability of an animal’s internal environment, which is maintained by negative feedback loops.
Water and salt balance
Nutrition and digestion
Breathing
Circulation
Also Check: Chapter 10 Test Form 2c
What Are The Major Topics In The Dictionary Of Biology
It includes biographies of key scientists, and feature articles on important topics, such as bioinformatics, genetically modified organisms, microarray technology, and RNA interference. The dictionarys chronologies chart developments in major fields including cell biology, genetics, microscopy, and vitamins.
The Basic Principles Of Modern Biology
Four principles unify modern biology, according to the book “Managing Science” :
Recommended Reading: Edgenuity Function Operations Answers
Basic Principles Of Biology
The foundation of biology as it exists today is based on five basic principles. They are the cell theory, gene theory, evolution, homeostasis, and laws of thermodynamics.
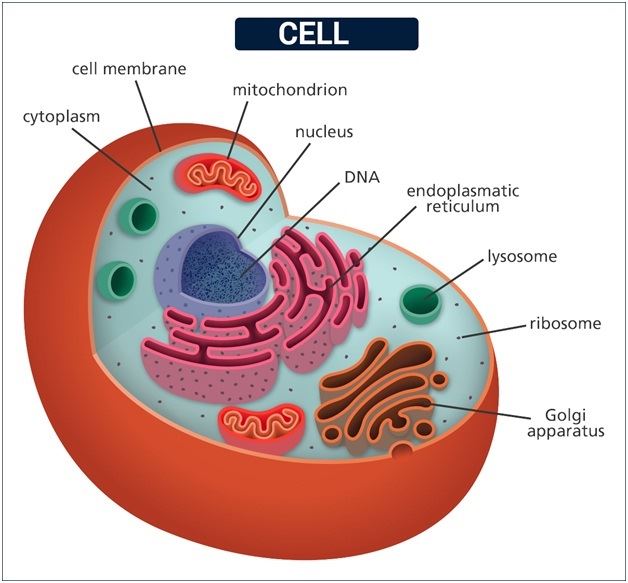
- Cell Theory: all living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life.
- Gene Theory: traits are inherited through gene transmission. Genes are located on chromosomes and consist of DNA.
- Evolution: any genetic change in a population that is inherited over several generations. These changes may be small or large, noticeable or not so noticeable.
- Homeostasis: ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes.
- Thermodynamics: energy is constant and energy transformation is not completely efficient.
Subdiciplines of BiologyThe field of biology is very broad in scope and can be divided into several disciplines. In the most general sense, these disciplines are categorized based on the type of organism studied. For example, zoology deals with animal studies, botany deals with plant studies, and microbiology is the study of microorganisms. These fields of study can be broken down further into several specialized sub-disciplines. Some of which include anatomy, cell biology, genetics, and physiology.
What Is Biology At Ntnu
The word biology is derived from the greek words /bios/ meaning /life/ and /logos/ meaning /study/ and is defined as the science of life and living organisms. An organism is a living entity consisting of one cell e.g. bacteria, or several cells e.g. animals, plants and fungi.
Aspects of biological science range from the study of molecular mechanisms in cells, to the classification and behaviour of organisms, how species evolve and interaction between ecosystems.
Biology often overlaps with other sciences for example, biochemistry and toxicology with biology, chemistry, and medicine biophysics with biology and physics stratigraphy with biology and geography astrobiology with biology and astronomy. Social sciences such as geography, philosophy, psychology and sociology can also interact with biology, for example, in administration of biological resources, developmental biology, biogeography, evolutionary psychology and ethics.
Recommended Reading: Michael Jackson Kids Biological Father
What Does Identical Mean In Biology
identical – Medical Definition
Biology
Thereof, what does the word identical?
Also called: quantitatively identical exactly alike, equal, or agreeing. designating either or both of a pair of twins of the same sex who developed from a single fertilized ovum that split into twoCompare fraternal (def.
Likewise, what is the root word of identical? Great mind may think alike, but they’ll never be identical. Twins, on the other hand, very well may be if they’ve come from the same split embryo that is. It makes sense then, that the word identical has linguistic roots in the Latin word idem, meaning “the same.”
Similarly one may ask, does identical mean exactly the same?
Similar and identicalWe use similar if two or more things are not entirely the same, or identical if two or more things are exactly the same. We use the patterns similar to and identical to, a similar + noun or a similar + one and an identical + noun or an identical + one.
How do you define identical twins?
identical twinone of a pair of twins who develop from a single fertilized ovum and therefore have the same genotype, are of the same sex, and usually resemble each other closely.
You May Like Also
Origin Of The Term Biology
Before the term biology was adapted, other terms existed which described the study of plants and animals. For instance, the term Natural History was used to explain animals, plants, fungi and other lifeforms in their natural environment.
Furthermore, it was observational rather than an experimental field of study. Hence, a person who would study natural history is termed as a natural historian or a naturalist. Other terms that came before biology included Natural Theology and Natural philosophy.
The term Biology, in the modern sense, was introduced through the works of Michael Christoph Hanow in 1766. However, it was introduced independently four more times through the works of Thomas Beddoes , Karl Friedrich Burdach , Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck .
Read Also: 5 Areas Of Chemistry
What Is The Meaning Of Biological Of System
- Réponse publiée par: sicienth
answer:
the state or quality that distinguishes living beings or organisms from dead ones and from inorganic matter, characterized chiefly by metabolism, growth, and the ability to reproduce and respond to stimuli.
Explanation:
- Réponse publiée par: Laurenjayshree
answer:
the biological perspective states that all thoughts, feeling & behavior ultimately have a biological cause. it is one of the major perspectives in psychology and involves such things as studying the brain, genetics, hormones, and the immune and nervous systems. Last Update: 2020-11-03 Usage Frequency
Explanation:
What Is Biotechnology
At its simplest, biotechnology is technology based on biology – biotechnology harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products that help improve our lives and the health of our planet. We have used the biological processes of microorganisms for more than 6,000 years to make useful food products, such as bread and cheese, and to preserve dairy products.
Modern biotechnology provides breakthrough products and technologies to combat debilitating and rare diseases, reduce our environmental footprint, feed the hungry, use less and cleaner energy, and have safer, cleaner and more efficient industrial manufacturing processes.
Biotech is helping to heal the world by harnessing nature’s own toolbox and using our own genetic makeup to heal and guide lines of research by:
- Reducing rates of infectious disease
- Saving millions of children’s lives
- Changing the odds of serious, life-threatening conditions affecting millions around the world
- Tailoring treatments to individuals to minimize health risks and side effects
- Creating more precise tools for disease detection and
- Combating serious illnesses and everyday threats confronting the developing world.
Biotech uses biological processes such as fermentation and harnesses biocatalysts such as enzymes, yeast, and other microbes to become microscopic manufacturing plants. Biotech is helping to fuel the world by:
Read Also: Geometry Unit 1 Test Answer Key
How Are Cyst Removed
Procedure: Cyst removal may be performed under general anesthesia or sedation depending on the size and location. The surgeon will make an incision on the skin above or near the cyst to either drain or remove it. The skin may be sutured closed and covered with steri-strips and a gauze dressing or surgical glue.
Make Transformation A East With The Right Tools For Your Lab
Whether its a media dispenser for a microbiology lab, colony picking tools to precisely select your desired strains, automated transformation systems, or the like, Hudson Robotics has your back. Look through the Hudson Robotics range of synthetic biology offerings, and contact us for a quote or consult today!
Contact Us
You May Like: Chapter 4 Test Form 1 Algebra 2 Answers
Bacterial Transformation In Biology: What Is The Process
In the lab, bacterial transformation is a four-step process. The first step begins with preparing competent cells that need to be transformed. This usually involves injecting a desired bacterial strain in a liquid medium as a starter culture and then creating a larger amount of culture. The strain is then made competent through the process of heat shock or electroporation.
Once cells are competent, they are put through another round of heat shock or electroporation in the presence of plasmid DNA. This results in the uptake of the plasmid DNA by the competent cells. The transformed cells are then cultured again to increase cell viability and efficiency of the molecular cloning process.
Lastly, when answering what is transformation in biology transformed cells are plated with the required resources to identify and recover the desired transformants. Then these transformants are used for other processes such as protein expression, subcloning, and plasmid isolation.
What Is Inhibition In Biology
4.8/5biologyinhibitbiological inhibitorinhibitorbiologicalanswer here
Inhibit comes from the Latin inhibitus, meaning “to hold in”, “to restrain”, or “to keep”. In biology, there are various molecules whose function is to inhibit. In biology, an inhibiting molecule controls, prevents, restrains, arrests, or regulates, as in “to inhibit an action”.
One may also ask, what are the three types of enzyme inhibition? We will discuss four types of enzyme inhibition competitive, non- competitive, uncompetitive, and suicide. Of these, the first three types are reversible.
Also to know is, what does an inhibitor do?
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules or compounds that bind to enzymes and result in a decrease in their activity. An inhibitor can bind to an enzyme and stop a substrate from entering the enzyme’s active site and/or prevent the enzyme from catalyzing a chemical reaction. There are two categories of inhibitors.
What is a non competitive inhibitor in biology?
Non–competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme and binds equally well to the enzyme whether or not it has already bound the substrate.
Read Also: Who Is Paris Jacksons Father
What Is Transformation In Biology
Transformation is the specific process where exogenous genetic material is directly taken up and incorporated by a cell through its cell membrane. This usually occurs when the cell is in a state of competence, which is a state where the cell can uptake exogenous material. A state of competence is typically a time-limited one caused by environmental conditions around the cell.
It can occur naturally in the environment or laboratory conditions referred to as natural competence. It can also be artificially induced by treating laboratory cultures to make cell membranes permeable to the exogenous genetic material around them.
Combining the knowledge of colony microbiology and transformation is a crucial part of molecular cloning and synthetic biology.
What Is Cyst In Female Body
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets in an ovary or on its surface. Women have two ovaries each about the size and shape of an almond on each side of the uterus. Eggs , which develop and mature in the ovaries, are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years.
You May Like: Test Form 2b Answers Chapter 7
Are There Appendices To The Dictionary Of Biology
Numerous appendices include classifications of the animal and plant kingdoms, SI units, Nobel prizewinners, and a new appendix on anatomical terms. With new diagrams and updated web links, this remains the market-leading dictionary for students of biology, both at sixth form college and university level.
Why Is Biology Important
As a field of science, biology helps us understand the living world and the ways its many species function, evolve, and interact. Advances in medicine, agriculture, biotechnology, and many other areas of biology have brought improvements in the quality of life. Fields such as genetics and evolution give insight into the past and can help shape the future, and research in ecology and conservation inform how we can protect this planets precious biodiversity.
Also Check: Unit 1 Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate Answer Key
Examples Of Biology In A Sentence
biologybiologybiologybiology WSJbiologySTATScientific AmericanbiologySmithsonian Magazinebiology Forbesbiology Washington Postbiology Wiredbiology Detroit Free Press
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘biology.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
The Many Branches Of Biology
Although there are only four unifying principles, biology covers a broad range of topics that are broken into many disciplines and subdisciplines.
On a high level, the different fields of biology can each be thought of as the study of one type of organism, according to “Blackie’s Dictionary of Biology” . For example, zoology is the study of animals, botany is the study of plants and microbiology is the study of microorganisms.
Related: Plant photos: Amazing botanical shots by Karl Blossfeldt
Within those broader fields, many biologists specialize in researching a specific topic or problem. For example, a scientist may study behavior of a certain fish species, while another scientist may research the neurological and chemical mechanisms behind the behavior.
There are numerous branches and subdisciplines of biology, but here is a short list of some of the more broad fields that fall under the umbrella of biology:
Recommended Reading: Holt Geometry Worksheets
Uses Of Transformation In The Lab
If you know why colonies are important in the study of microbiology and molecular biology and the different types of colonies, you must also understand what the transformation process is used for.
For example, molecular cloning, in which transformation plays a major part, is necessary for genome organization, recombinant protein production, creation of transgenic organisms, gene therapy, and more.
Definition Of Transformation In Biology
Transformation is an important component of molecular genetics studies into the process began in the 1920s when a physician named F.Griffith realized that Streptococcus pneumoniae could convert between being harmless and disease-causing.What is transformation in biology? The theory he had back then was that a transforming principle released by dead S.pneumoniae cells caused living cells around them to form a capsule membrane that turns the pathogen into its disease-causing form. This theory has since been expanded upon with the discovery of DNA.
So, what is the meaning of transformation in biology? Transformation is one of the three processes where genetic material is transferred from one microbial cell to another, the other two being conjugation and archaeal DNA transfer.
You May Like: Michael Jackson Kids Real Father