What Is The Density
Density is a measure of how compact the mass in a substance or object is. The density of an object or substance can be calculated from this equation: density in kilograms per meter cubed is equal to the mass in kilograms, divided by volume in meters cubed. Density is a measure of mass per unit of volume. In general, gases have the lowest densities, but these densities are highly dependent on the pressure and temperature which must always be specified. The density range of solids is quite wide. Metals, whose atoms pack together quite compactly, have the highest densities, although that of lithium, the highest metallic element, is quite low.
Was this answer helpful?
Relationship Between Chemistry And Other Branches Of Science
Science can be defined as the systematic study of the natural universe, its structure, and everything it encompasses. Due to the immensity of the natural universe, science has been divided into several disciplines that deal with certain aspects of the universe. The three primary subcategories of science under which these disciplines can be grouped are:
- The Formal Sciences: Involves the study of the language disciplines that concern formal systems. Examples of scientific disciplines that fall under this category include logic and mathematics. Can be thought of as the language of science.
- The Natural Sciences: Involves the study of natural phenomena through experiments and observations. Chemistry, physics, and biology fall under this category of science.
- The Social Sciences: Involves the study of human societies and the relationships between the humans that dwell in these societies. Examples of scientific disciplines that fall under this category include psychology, sociology, and economics.
When the relationships between the major branches of science are considered, chemistry is found to lie close to the centre .
Thus, chemistry can be viewed as a central science whose roots bore into several other subdisciplines of science.
What Makes Organic Chemistry
Organic compounds are molecules that contain carbon atoms covalently bonded to hydrogen atoms . This means that all organic compounds have in common the presence of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms. In addition, different organic compounds may contain oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and other elements.
Don’t Miss: Beth Thomas Married
What Is Example Of Specific Words
Specific Words are words that, through the use of modifiers, name a specific idea, thing, person and the likes. These kinds of words are used when you want to limit your discussion to a particular idea. Examples of these words would include rocking chair, dollar, gym equipment, pepper and high-heeled shoes.
Do Doctors Use Organic Chemistry
Most doctors dont use organic chemistry. A high percentage of medical students started their careers majoring in subjects such as chemistry, physics, engineering, and so on, and they retain that perspective on science. Most doctors dont use organic chemistry. Most doctors dont use general chemistry either.
You May Like: Four Main Areas Of Biological Contamination
Examples Of Chemistry In A Sentence
chemistrychemistrychemistrychemistry The Hollywood ReporterchemistryWashington PostchemistryThe AtlanticchemistryThe New YorkerchemistryNew York TimeschemistryCar and DriverchemistryFortunechemistryVulture
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘chemistry.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Define Chemistry Physics And Biology
Who are the experts?Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
These are the three main disciplines of science.
PHYSICS : this is derived from the Greek word ‘physis’, which means ‘nature’. It is basically, in simple words, the study of the abiotic, i.e. non-living components of nature and its varied processes, which is divided into basic sub-divisions and their specific…
Recommended Reading: Holt Geometry Chapter 7 Test Form C Answers
Webster Dictionaryrate This Definition:
Chemistrynoun
that branch of science which treats of the composition of substances, and of the changes which they undergo in consequence of alterations in the constitution of the molecules, which depend upon variations of the number, kind, or mode of arrangement, of the constituent atoms. These atoms are not assumed to be indivisible, but merely the finest grade of subdivision hitherto attained. Chemistry deals with the changes in the composition and constitution of molecules. See Atom, Molecule
Etymology:
Chemistrynoun
an application of chemical theory and method to the consideration of some particular subject as, the chemistry of iron the chemistry of indigo
Etymology:
Chemistrynoun
Etymology:
How Is Chemistry Used In Everyday Life
Digestion relies on chemical reactions between food and acids and enzymes to break down molecules into nutrients the body can absorb and use. Soaps and detergents act as emulsifiers to surround dirt and grime so it can be washed away from clothing, dishes, and our bodies. Drugs work because of chemistry.
Recommended Reading: How To Solve Half Life Equations In Chemistry
What Is Chemistry In Your Life
Chemistry is a big part of our everyday life. We start the day with Chemistry. One can find chemistry in daily life in the foods we eat, the air we breathe, cleaning chemicals, our emotions and literally every object we can see or touch. … Our body is made up of chemical compounds, which are combinations of elements.
What Is A Good Example Of Analytical Skills
You use them to solve problems that may not have obvious solutions or have several variables. There are many types of analytical skills, including communication, creativity, critical thinking, data analysis, and research. Highlight and provide examples of your skills in your resume, cover letter, and interviews.
You May Like: Paris Jackson Mom And Dad
Melting And Boiling Properties
Organic compounds typically melt and many boil. In contrast, while inorganic materials generally can be melted, many do not boil, and instead tend to degrade. In earlier times, the melting point and boiling point provided crucial information on the purity and identity of organic compounds. The melting and boiling points correlate with the polarity of the molecules and their molecular weight. Some organic compounds, especially symmetrical ones, sublime. A well-known example of a sublimable organic compound is para-dichlorobenzene, the odiferous constituent of modern mothballs. Organic compounds are usually not very stable at temperatures above 300 °C, although some exceptions exist.
The Five Main Branches Of Chemistry
Traditionally, chemistry is broken into five main branches, according to the online chemistry textbook published by LibreText. There are also more specialized fields, such as food chemistry, environmental chemistry and nuclear chemistry, but this section focuses on chemistry’s five major subdisciplines.
Analytical chemistry involves the analysis of chemicals, and includes qualitative methods like looking at color changes, as well as quantitative methods like examining the exact wavelength of light that a chemical absorbed to result in that color change.
These methods enable scientists to characterize many different properties of chemicals, and can benefit society in a number of ways. For example, analytical chemistry helps food companies make tastier frozen dinners by detecting how chemicals in food change when they are frozen over time. Analytical chemistry is also used to monitor the health of the environment by measuring chemicals in water or soil, for example.
Biochemistry, as mentioned above, uses chemistry techniques to understand how biological systems work at a chemical level. Thanks to biochemistry, researchers have been able to map out the human genome, understand what different proteins do in the body and develop cures for many diseases.
Related: Autoimmune disease: definition and examples
Inorganic chemistry is used to create a variety of products, including paints, fertilizers and sunscreens.
Recommended Reading: John Thomas Brother Of Beth Thomas
The Scope Of Chemistry
The days are long past when one person could hope to have a detailed knowledge of all areas of chemistry. Those pursuing their interests into specific areas of chemistry communicate with others who share the same interests. Over time a group of chemists with specialized research interests become the founding members of an area of specialization. The areas of specialization that emerged early in the history of chemistry, such as organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and industrial chemistry, along with biochemistry, remain of greatest general interest. There has been, however, much growth in the areas of polymer, environmental, and medicinal chemistry during the 20th century. Moreover, new specialities continue to appear, as, for example, pesticide, forensic, and computer chemistry.
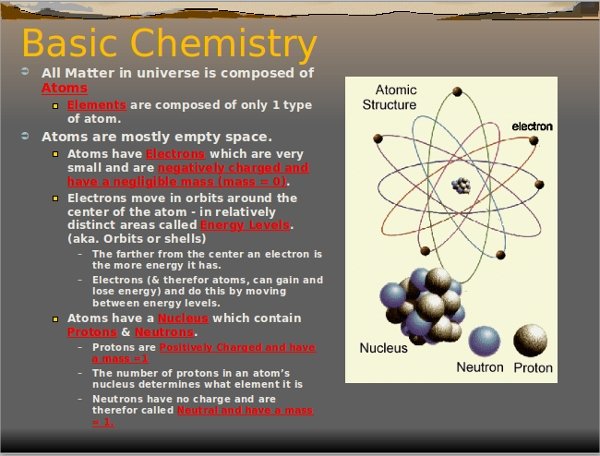
Elements And Atoms: What’s The Difference
The atom, by contrast, is a microscopic concept which in modern chemistry relates the unique character of every chemical element to an actual physical particle.
The idea of the atom as the smallest particle of matter had its origins in Greek philosophy around 400 BCE but was controversial from the start It was not until 1803 that John Dalton proposed a rational atomic theory to explain the facts of chemical combination as they were then known, thus being the first to employ macroscopic evidence to illuminate the microscopic world.
It took almost until 1900 for the atomic theory to became universally accepted. In the 1920’s it became possible to measure the sizes and masses of atoms, and in the 1970’s techniques were developed that produced images of individual atoms.
Read Also: Beth Thomas Rad
Examples Of Chemistry In Our Daily Lives
Chemical reactions are constantly taking place around us. The human body facilitates thousands of chemical reactions every day. From the digestion of food to the movement of muscles all bodily actions involve chemical reactions. A few other examples of chemistry in the day-to-day lives of humans are listed below.
- The process of photosynthesis that enables plants to convert water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen is a chemical reaction. This process is the foundation upon which the entire food chain is built.
- Soaps and detergents that are used for hygiene work using a chemical process known as emulsification. Furthermore, they are produced using a chemical process known as saponification.
- Even the sunscreen used by humans to protect themselves from the harmful UV-A and UV-B radiation of the sun is based on chemistry. These lotions and creams consist of a combination of inorganic and organic compounds that either filter or block the incoming ultraviolet radiation.
Follow the link to learn more about the importance of chemistry in everyday life.
What Is Chemistry In Daily Life
Chemistry is a big part of our everyday life. One can easily observe this branch of science in different spheres of human life such as in the food we eat, the air we breathe, the various cleansing agents we use, so much so that even human emotions are sometimes a result of chemical reactions within our body!
Read Also: Core Connections Algebra Chapter 1 Answers
What Is Chemistry One Sentence
The definition of chemistry is a branch of science that deals with the form and properties of matter and substances or the interaction between individuals. An example of chemistry is the study of protons and neutrons. An example of chemistry is the feeling of affection and attraction between a couple. noun.
What Do Chemists Do
Chemists work in a variety of fields, including research and development, quality control, manufacturing, environmental protection, consulting and law. They can work at universities, for the government or in private industry, according to the ACS.
Here are some examples of what chemists do:
Research and development
In academia, chemists performing research aim to further knowledge about a particular topic, and may not necessarily have a specific application in mind. Their results, however, can still be applied to relevant products and applications.
In industry, chemists in research and development use scientific knowledge to develop or improve a specific product or process. For example, food chemists improve the quality, safety, storage and taste of food pharmaceutical chemists develop and analyze the quality of drugs and other medical formulations and agricultural chemists develop fertilizers, insecticides and herbicides necessary for large-scale crop production.
Sometimes, research and development may not involve bettering the product itself, but rather the manufacturing process involved in making that product. Chemical engineers and process engineers devise new ways to make the manufacturing of their products easier and more cost effective, such as increasing the speed and/or yield of a product for a given budget.
Environmental protection
Also Check: Elton John Wife And Kids
What Chemistry Is And Why You Should Study It
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
If you look ‘chemistry’ up in Webster’s Dictionary, you’ll see the following definition:
“chem·is·try n., pl. -tries. 1. the science that systematically studies the composition, properties, and activity of organic and inorganic substances and various elementary forms of matter. 2. chemical properties, reactions, phenomena, etc.: the chemistry of carbon. 3. a. sympathetic understanding rapport. b. sexual attraction. 4. the constituent elements of something the chemistry of love. .”
A common glossary definition is short and sweet: Chemistry is the “scientific study of matter, its properties, and interactions with other matter and with energy”.
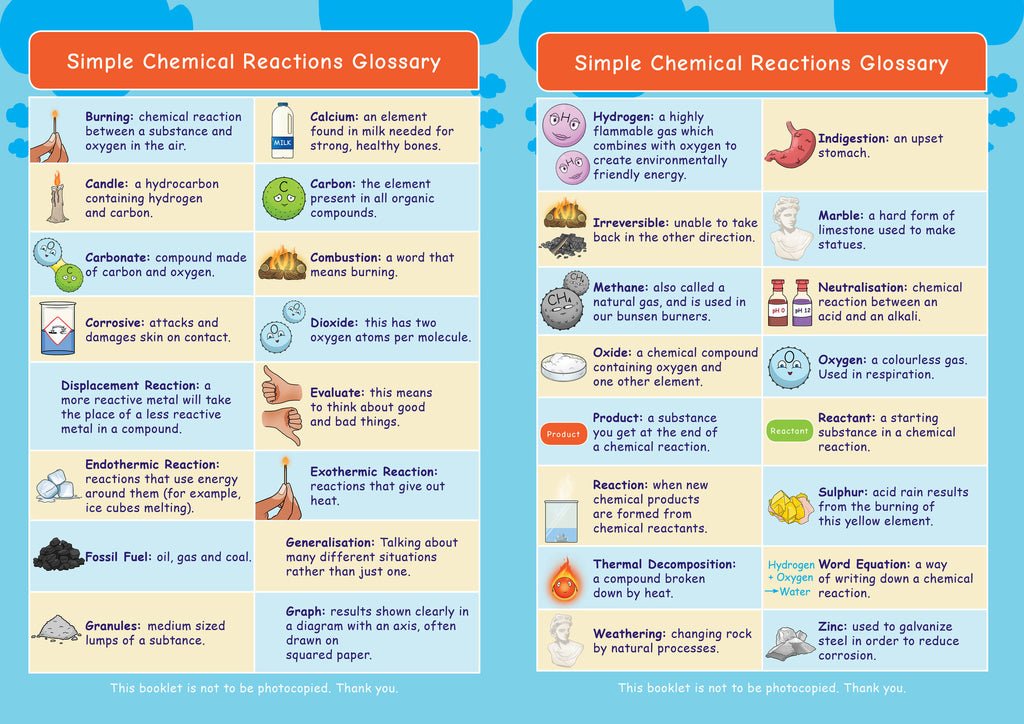
How Do I Type A Simple Chemical Equation In Microsoft Word

How do I type a simple chemical equation in Microsoft Word? I can do subscripts, but long arrows are more difficult. I can’t get them to align with the text.
Also, I can’t figure out how to put a delta above the arrow for heat. I have tried the Chemistry add-on from Microsoft, but that does not seem to help with equations.
If you are using MS Word 2007 or newer, use the equation feature. It is designed for math but works okay for chemistry.
Go to the insert tab.
Type in your equation. Use the buttons in the ribbon to do superscripts and subscripts. Alternatively you can use _ for subscript and ^ for superscript. The default is to have letters italicized , so you will want to fix that.
There are also shortcut commands to render most the common things you want. For example, underscore _ creates a subscript and a caret ^ creates a superscript Shortcut for typing subscript and superscript in MS Word 2007|2010|2013|2016 and office 365 . You have access to a wide range of arrows from a pull-down menu, but -> will give you a simple right arrow . This feature on Word will also accept some tex commands for formatting equations.
To get a long arrow, click on the operator but and choose the arrow with the word “yields” written over it under common operator structures. For up arrow and down arrow showing gas liberation and precipitation use \uparrow or \downarrow followed by space Shortcut for typing arrows of chemical equation in Word 2007 and above.
Finally, finish your equation.
You May Like: Compass Rose For Kids
What Are The Branches Of Chemistry And Their Definition
Ernest Z. Jackie Shlecter Priya mrpauller.weebly.com
The five major branches of chemistry are organic, inorganic, analytical, physical, and biochemistry. These divide into many sub-branches.
Explanation:
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Organic chemistry involves the study of the structure, properties, and preparation of chemical compounds that consist primarily of carbon and hydrogen.
Organic chemistry overlaps with many areas including
- Medicinal chemistry the design, development, and synthesis of medicinal drugs. It overlaps with pharmacology .
- Organometallic chemistry the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal.
- Polymer chemistry the study of the chemistry of polymers.
- Physical organic chemistry the study of the interrelationships between structure and reactivity in organic molecules.
- Stereochemistry the study of the spatial arrangements of atoms in molecules and their effects on the chemical and physical properties of substances.
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Inorganic chemistry is the study of the properties and behaviour of inorganic compounds.
It covers all chemical compounds except organic compounds.
Inorganic chemists study things such as crystal structures, minerals, metals, catalysts, and most elements in the Periodic Table.
Branches of inorganic chemistry include:
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
Analytical chemistry involves the qualitative and quantitative determination of the chemical components of substances.
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
BIOCHEMISTRY
Princeton’s Wordnetrate This Definition:
chemistry, chemical sciencenoun
the science of matter the branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions
chemistrynoun
the chemical composition and properties of a substance or object
“the chemistry of soil”
chemistry, interpersonal chemistry, alchemynoun
the way two individuals relate to each other
“their chemistry was wrong from the beginning — they hated each other” “a mysterious alchemy brought them together”
Also Check: Ccl4 Electron Pair Geometry
What To Study To Be A Chemist
The basic requirement for becoming a chemist is a Bachelor’s Degree in Chemistry or a related field. Computer science, physics, mathematics, and biology classes along with coursework in organic, inorganic, and physical chemistry equip future chemists with the knowledge needed for a successful career.
How Are Chemistry And Biology Related
Chemistry is the study of substancesthat is, elements and compoundswhile biology is the study of living things. However, these two branches of science meet in the discipline of biochemistry, which studies the substances in living things and how they change within an organism.
chemistry, the science that deals with the properties, composition, and structure of substances , the transformations they undergo, and the energy that is released or absorbed during these processes. Every substance, whether naturally occurring or artificially produced, consists of one or more of the hundred-odd species of atoms that have been identified as elements. Although these atoms, in turn, are composed of more elementary particles, they are the basic building blocks of chemical substances there is no quantity of oxygen, mercury, or gold, for example, smaller than an atom of that substance. Chemistry, therefore, is concerned not with the subatomic domain but with the properties of atoms and the laws governing their combinations and how the knowledge of these properties can be used to achieve specific purposes.
Read Also: Elastic Force Definition