How Do Living Things Obtain Their Food
When you think of food, do you usually come up with images of your favorite food? This is a natural process, since food is important for every living thing. To fulfill this basic need, all living things either make their own food or get it from some other source. Humans can eat both plants and animals. Some animals consume other animals, while some animals eat plants as their food. Ultimately, we see that everybody on this planet is dependent on plants for their food. But then, what do plants eat? Actually, plants eat sunlight and a gas called carbon dioxide, both of which are easily available right here on earth. The process by which land plants produce their own food using sunlight and carbon dioxide is known as . While carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaves, the sunlight is captured by a chemical molecule in the plant, called chlorophyll . All photosynthetic organisms contain Chl.
- Figure 1 – A simplified view of how plants produce food for us.
- The leaves of green plants contain chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight for producing food. This food is then used by the plant itself as well as other animals, including humans.
Why Are Ecosystems Important
Weve been able to control fire, practice agronomy, and build transport automobiles. Weve constructed factories, dams, solar panels and were always discovering new ways of exploring space.
Still, the human races desire to acquire, alter and convert natural ecosystems for economic benefit appears never-ending.
For example, when we convert a plain to produce cereal fields, were considerably transforming that local ecosystem. At times, we completely alter it from its original foundations.
Human activities have had such a major influence on ecosystems that we are now discussing the;Anthropocene timeline.
This is a timeline that outlines the substantial effect of human activities on the Earths atmospheric, biospheric, geologic and hydrologic structures.
This period in time also studies fluctuations happening due to;climate change;events, which is largely triggered by human activity. We can observe these changes all over the world.
When;trees are cut down;in the Amazonian forest, the ecosystem alters as species struggle to survive and the local moisture and climate both change adversely. In addition, constructing a dam similarly modifies the supply of water and affects the species existing along the rivers course.
The issue was that the lessening of the wolf population impacted the whole ecosystem in the long run, even shifting the course of the local river. This phenomenon is known as a trophic cascade.
Structure Of The Ecosystem
The structure of an ecosystem is characterised by the organisation of both biotic and abiotic components. This includes the distribution of energy in our environment. It also includes the climatic conditions prevailing in that particular environment.;
The structure of an ecosystem can be split into two main components, namely:;
- Biotic Components
- Abiotic Components
The biotic and abiotic components are interrelated in an ecosystem. It is an open system where the energy and components can flow throughout the boundaries.
Structure of Ecosystem highlighting the biotic and abiotic factors
Recommended Reading: How To Get Answers On Delta Math
Ecosystem Degradation And Decline
As human population and per capita consumption grow, so do the resource demands imposed on ecosystems and the effects of the human ecological footprint. Natural resources are vulnerable and limited. The environmental impacts of anthropogenic actions are becoming more apparent. Problems for all ecosystems include: environmental pollution, climate change and biodiversity loss. For terrestrial ecosystems further threats include air pollution, soil degradation, and deforestation. For aquatic ecosystems threats also include unsustainable exploitation of marine resources , , microplastics pollution, the effects of climate change on oceans , and building on coastal areas.
Many ecosystems become degraded through human impacts, such as soil loss, air and water pollution, habitat fragmentation, water diversion, fire suppression, and introduced species and invasive species.:437
These threats can lead to abrupt transformation of the ecosystem or to gradual disruption of biotic processes and degradation of abiotic conditions of the ecosystem. Once the original ecosystem has lost its defining features, it is considered collapsed . Ecosystem collapse could be reversible and in this way differs from species extinction. Quantitative assessments of the risk of collapse are used as measures of conservation status and trends.
The Importance Of Biological Diversity
Biological resources provided by the Earth play essential role in economic and social development of the humans. Therefore, it is of great importance to acknowledge an enormous value of biological diversity both to present and future generations. However, ecosystems and species have never been under such threat as they are nowadays. Loss of species caused by human activities continues at an alarming rate .As a reaction to the seriousness of the problem, in November 1988 the United Nations
You May Like: Honors Algebra 2 Linear Function Word Problems Answers
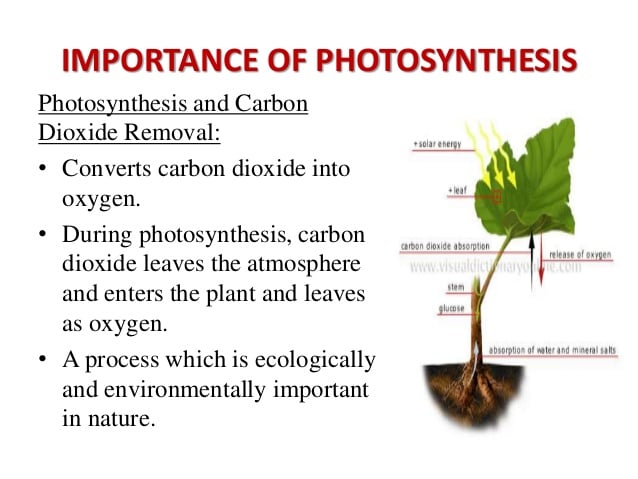
The Importance Of Photosynthesis
The processes of all organismsfrom bacteria to humansrequire energy. To get this energy, many organisms access stored energy by eating food. Carnivores eat other animals and herbivores eat plants. But where does the stored energy in food originate? All of this energy can be traced back to the process of photosynthesis and light energy from the sun.
What Organisms Benefit From Interactions
Symbiosis is any relationship between two or more biological species. Mutualism: In mutualistic interactions, both species benefit from the interaction. A classic example of mutualism is the relationship between insects that pollinate plants and the plants that provide those insects with nectar or pollen.
Don’t Miss: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
Origin And Development Of The Term
The term “ecosystem” was first used in 1935 in a publication by British ecologist Arthur Tansley. The term was coined by Arthur Roy Clapham, who came up with the word at Tansley’s request. Tansley devised the concept to draw attention to the importance of transfers of materials between organisms and their environment.:9 He later refined the term, describing it as “The whole system, … including not only the organism-complex, but also the whole complex of physical factors forming what we call the environment”. Tansley regarded ecosystems not simply as natural units, but as “mental isolates”. Tansley later defined the spatial extent of ecosystems using the term “ecotope“.
G. Evelyn Hutchinson, a limnologist who was a contemporary of Tansley’s, combined Charles Elton‘s ideas about trophic ecology with those of Russian geochemist Vladimir Vernadsky. As a result, he suggested that mineral nutrient availability in a lake limited algal production. This would, in turn, limit the abundance of animals that feed on algae. Raymond Lindeman took these ideas further to suggest that the flow of energy through a lake was the primary driver of the ecosystem. Hutchinson’s students, brothers Howard T. Odum and Eugene P. Odum, further developed a “systems approach” to the study of ecosystems. This allowed them to study the flow of energy and material through ecological systems.:9
Aquatic Ecosystems Freshwater Locations: Lakes Rivers And Ponds
Freshwater ecosystems make up roughly 3% of the Earths surface.
Aquatic ecosystem further comprises of estuaries before freshwater encounters salt, marshlands, pond ecosystem , lakes and rivers.
Since fresh water is crucial for all life, aquatic biomes are really important. Still they are very minor in contrast to other habitats, and have been used as dumping grounds for a long time.;
National Geographic;states that;freshwater species are 4-6x more in jeopardy of vanishing than terrestrial or marine species. Freshwater ecosystem and coastal marine systems are also at high risk of eutrophication, a natural occurrence which pushes plants to grow.
Eutrophication is begun by amplified amounts of sediments which in turn surge levels of nutrients and boost excessive plant growth. As vegetation dies after exhausting nutrients ; their decay results in hypoxic or dead zones.
Recommended Reading: When Was Geometry Dash Made
How Do Habitats Help Form Ecosystems
As mentioned earlier, inside every ecosystem there are habitats of numerous sizes.
A habitat is a dwelling with a population . All the populations living in the same place at the same time interact, forming a community. Such community also intermingles with the non-living world around it, therefore establishing an ecosystem.
The habitat essentially makes available for the organisms: nourishment, water, temperature, oxygen and other properties they need to live and thrive.
Biomass Energy: A Carbon Neutral Resource
The extensive global use of fossil fuels greatly increased the release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere leading to important climate changes. There is a dire need for alternative energy sources and hence biofuels produced from photosynthetic organisms or organic wastes offer the great opportunity to address the world’s dependence on oil and to reduce CO2 emissions.
While the burning of fossil fuels increases the CO2 levels in the atmosphere by releasing carbon sequestered millions of years ago, the use of biomass maintains a closed carbon cycle returning carbon previously incorporated by growing plants to the atmosphere . Different biomass sources show large variations in terms of yield, quality, and cost. In the past, biomass from food crops, hydrocarbon-rich plants, waste reuse, or weed and wild plants were investigated for energy production and it was shown that the efficiency of mass-to-energy conversion is related to their biomass composition, i.e., the quantitative proportion between the three main organic constituents cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin .
Recently a new energy production line from biomass derived from photosynthetic microorganisms has been added to the already known carbon neutral methodologies. While there are still challenges, the results obtained so far show the potential of this innovative approach .
You May Like: What Is Psychometrics In Psychology
Dark Reaction Of Photosynthesis Light
- Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
- It is a light-independent process in which sugar molecules are formed from the water and carbon dioxide molecules.
- The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and ATP products of the light reaction.
- Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule or glucose.
The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to:
3CO2 + 6 NADPH + 5H2O + 9ATP G3P + 2H+ + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
* G3P glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Also Read:;Cyclic And Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Processes In The Biological Pump

Processes in the biological pumpCarbon fluxes in white boxes are in GtCyr1 and carbon masses in dark boxes are in Gt C
In the diagram on the right, phytoplankton convert CO2, which has dissolved from the atmosphere into the surface oceans , into particulate organic carbon during primary production . Phytoplankton are then consumed by copepods, krill and other small zooplankton grazers, which in turn are preyed upon by higher trophic levels. Any unconsumed phytoplankton form aggregates, and along with zooplankton faecal pellets, sink rapidly and are exported out of the mixed layer . Krill, copepods, zooplankton and microbes intercept phytoplankton in the surface ocean and sinking detrital particles at depth, consuming and respiring this POC to CO2 , such that only a small proportion of surface-produced carbon sinks to the deep ocean . As krill and smaller zooplankton feed, they also physically fragment particles into small, slower- or non-sinking pieces , retarding POC export. This releases dissolved organic carbon either directly from cells or indirectly via bacterial solubilisation . Bacteria can then remineralise the DOC to DIC .
Don’t Miss: What Is Energy In Quantum Physics
What Is Light Energy
The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation . Humans can see only a fraction of this energy, which portion is therefore referred to as visible light. The manner in which solar energy travels is described as waves. Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength, the distance between consecutive points of a wave. A single wave is measured from two consecutive points, such as from crest to crest or from trough to trough .
Figure 8. The wavelength of a single wave is the distance between two consecutive points of similar position along the wave.
Visible light constitutes only one of many types of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the sun and other stars. Scientists differentiate the various types of radiant energy from the sun within the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of radiation . The difference between wavelengths relates to the amount of energy carried by them.
Figure 9. The sun emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. This radiation exists at different wavelengths, each of which has its own characteristic energy. All electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, is characterized by its wavelength.
External And Internal Factors
Ecosystems are controlled by both external and internal factors. External factors, also called state factors, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. On broad geographic scales, climate is the factor that “most strongly determines ecosystem processes and structure”.:14 Climate determines the biome in which the ecosystem is embedded. Rainfall patterns and seasonal temperatures influence photosynthesis and thereby determine the amount of energy available to the ecosystem.:145
Parent material determines the nature of the soil in an ecosystem, and influences the supply of mineral nutrients. Topography also controls ecosystem processes by affecting things like microclimate, soil development and the movement of water through a system. For example, ecosystems can be quite different if situated in a small depression on the landscape, versus one present on an adjacent steep hillside.:39:66
Other external factors that play an important role in ecosystem functioning include time and potential biota, the organisms that are present in a region and could potentially occupy a particular site. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can end up doing things very differently simply because they have different pools of species present.:321 The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function.
Recommended Reading: What Is Biomass In Biology
Megae Bay Research Paper
Pollutants from factories, cars, boats, and litter are all the things humans use to pollute the bay. The bay contains a high amount of phosphorus and nitrogen. Phosphorus and nitrogen are needed for organisms and plants to be able to survive. However, an excess amount of phosphorus and nitrogen degrade the quality of Chesapeake bays water. Phosphorus and nitrogen feed algae blooms that block sunlight to the underwater bay grass and leaving a low supply of oxygen in the water.
Why Is Photosynthesis So Important To Ecosystems
importantecosystemecosystemecosystem
People Also Asked, What is the importance of photosynthesis to the ecosystem?
Green plants and trees use to make food from sunlight, carbon dioxide and water in the atmosphere: It is their primary source of energy. The importance of photosynthesis in our life is the oxygen it produces. Without there would be little to no oxygen on the planet.
Also know, why is photosynthesis important to humans? is important, in fact essential, to all life for a number of reasons. Because of , plants essentially function as filters that take carbon dioxide, which is poisonous to humans and many other life forms, from the atmosphere and replace it with oxygen, which makes life possible.
Contents
Read Also: How To Find Ksp Chemistry
The Global Significance Of Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis is crucially important to the biosphere for the following reasons:
Attribution
The Cambrian Period: The First Premophic Period Of The Paleozoic Period
The Cambrian period is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era which was about 56 million years from the end of the prior Precambrian to the beginning of the Ordovician Period. The Cambrian period is the beginning of a large difference in life on Earth. Before the Cambrian most of the life was very simple and unicellular. For the first time we began to see more multicellular forms of life. “The oceans became oxygenated. Although there was a lot of atmospheric oxygen by the beginning of
You May Like: What Does Scale Drawing Mean In Math
Ecosystem Goods And Services
Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend. Ecosystem goods include the “tangible, material products” of ecosystem processes such as water, food, fuel, construction material, and medicinal plants. They also include less tangible items like tourism and recreation, and genes from wild plants and animals that can be used to improve domestic species.
Ecosystem services, on the other hand, are generally “improvements in the condition or location of things of value”. These include things like the maintenance of hydrological cycles, cleaning air and water, the maintenance of oxygen in the atmosphere, crop pollination and even things like beauty, inspiration and opportunities for research. The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment , a major UN-sponsored effort to analyze the impact of human actions on ecosystems and human well-being, identified four major categories of ecosystem services: provisioning, regulating, cultural and supporting services. While material from the ecosystem had traditionally been recognized as being the basis for things of economic value, ecosystem services tend to be taken for granted.