Deposition Of Cohesive Sediments
The cohesion of sediment occurs with the small grain sizes associated with silts and clays, or particles smaller than 4Ï on the phi scale. If these fine particles remain dispersed in the water column, Stokes law applies to the settling velocity of the individual grains, although due to seawater being a strong electrolyte bonding agent, flocculation occurs where individual particles create an electrical bond adhering each other together to form flocs. “The face of a clay platelet has a slight negative charge where the edge has a slight positive charge when two platelets come into close proximity with each other the face of one particle and the edge of the other are electrostatically attracted.” Flocs then have a higher combined mass which leads to quicker deposition through a higher fall velocity, and deposition in a more shoreward direction than they would have as the individual fine grains of clay or silt.
What Is Coastal Deposition
Deposition is when material that is being transported is dropped by constructive waves. It happens because waves have less energy.
Deposition happens when the swash is stronger than the backwash and is associated with constructive waves.
So, where does deposition happen? Deposition is likely to occur when:
- waves enter an area of shallow water
- waves enter a sheltered area, eg a cove or bay
- there is little wind
- a river or estuary flows into the sea reducing wave energy
- there is a good supply of material and the amount of material being transported is greater than the wave energy can transport.
Deposition creates a range of landforms. You can find out more on the depositional landforms page.
Lower Course/ Stage Of Old :
- The river starts to flow through a broad, level plain with heavy debris brought down from upper and middle courses.
- Vertical erosion has almost stopped and lateral erosion still goes on.
- The work of the river is mainly deposition, building up its bed and forming an extensive flood plain.
- Landforms like braided channels, floodplains, levees, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas etc. can be seen at this stage.
You May Like: Define Y Intercept In Math
How Are Beaches Formed By Deposition
The ocean floor is constantly being pushed and pulled by the Earths tectonic plates. This creates a series of trenches, valleys, and ridges. As the ocean floor is pushed down, it eventually collects sediments and materials from the Earths surface. These materials are then pushed and shoved along the floor by the Earths movement. Eventually, the sediments reach the oceans surface and are deposited.
What Is The Meaning Of Sedimentation
Sedimentation can be described as the tendency for the particles which are in suspension to settle out of the fluid content. Here they are entrained and then they come to rest against a specific barrier. This happens due to their own motion through the fluid which is in the response to all the forces that are acting on them. The forces can be because of the gravitational pull, due to the centrifugal caused by acceleration or electromagnetism.
In terms of geology, sedimentation is generally described as the opposite process of erosion that is the terminal end where the sediment transport. In this sense, it also includes the termination of the transport by the process of saltation or the true bedload transport.
You May Like: How To Find Half Life Chemistry
Factors That Influence Sediment Transport
Sediment transport is not constant. In fact, it is constantly subject to change. In addition to the changes in sediment load due to geology, geomorphology and organic elements, sediment transport can be altered by other external factors. The alteration to sediment transport can come from changes in water flow, water level, weather events and human influence.
Compatible With The Following Exam Boards
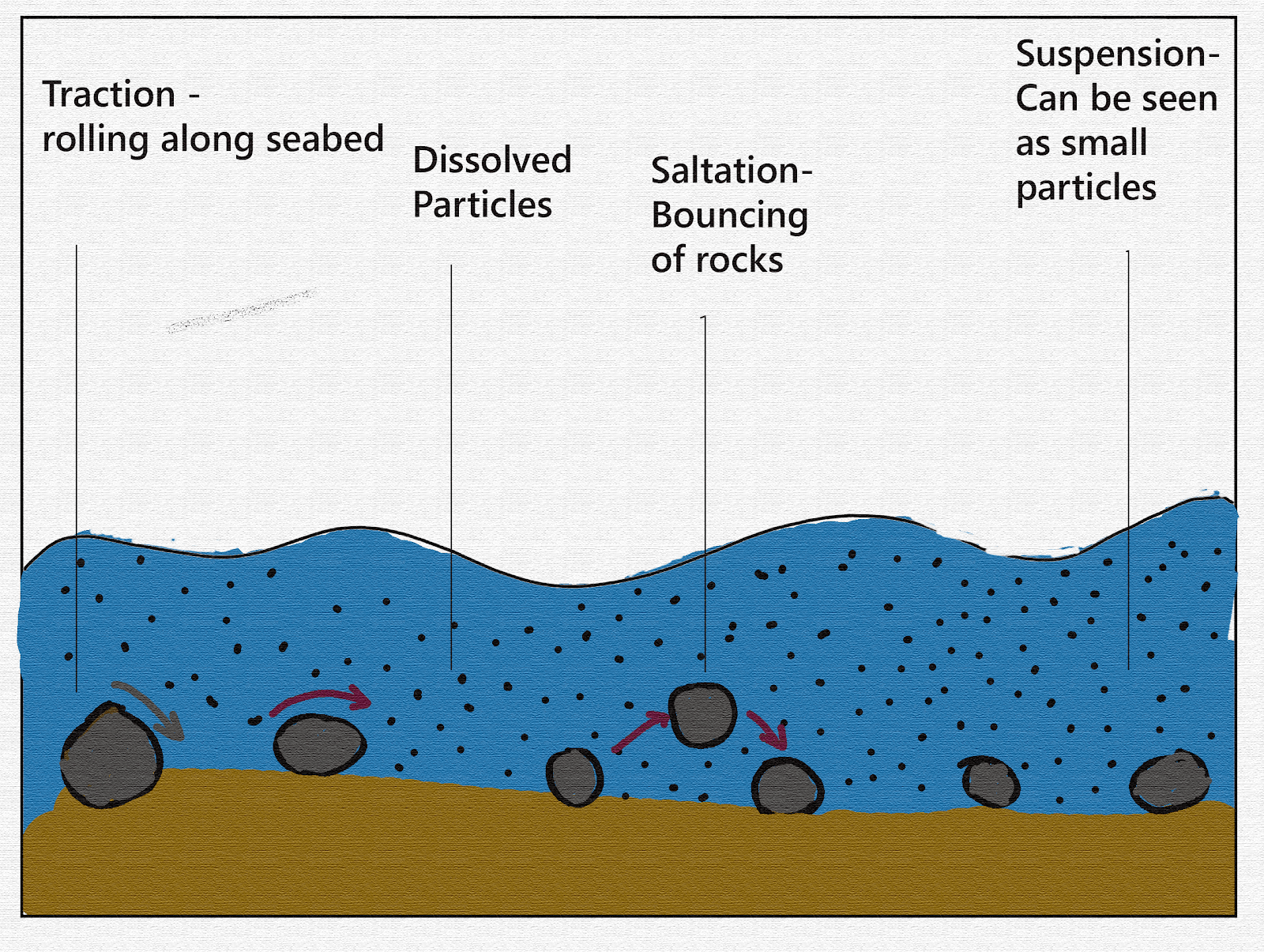
Coastal deposition is a coastal process that involves the action of waves, and how they can often deposit sediments such as sand, rock, and pebbles. Gravity and friction play a key role in the transport and deposition of these materials as these are the driving forces that the waves experience. These sediments and materials are transported by waves through different methods, such as suspension, saltation, solution, and traction.
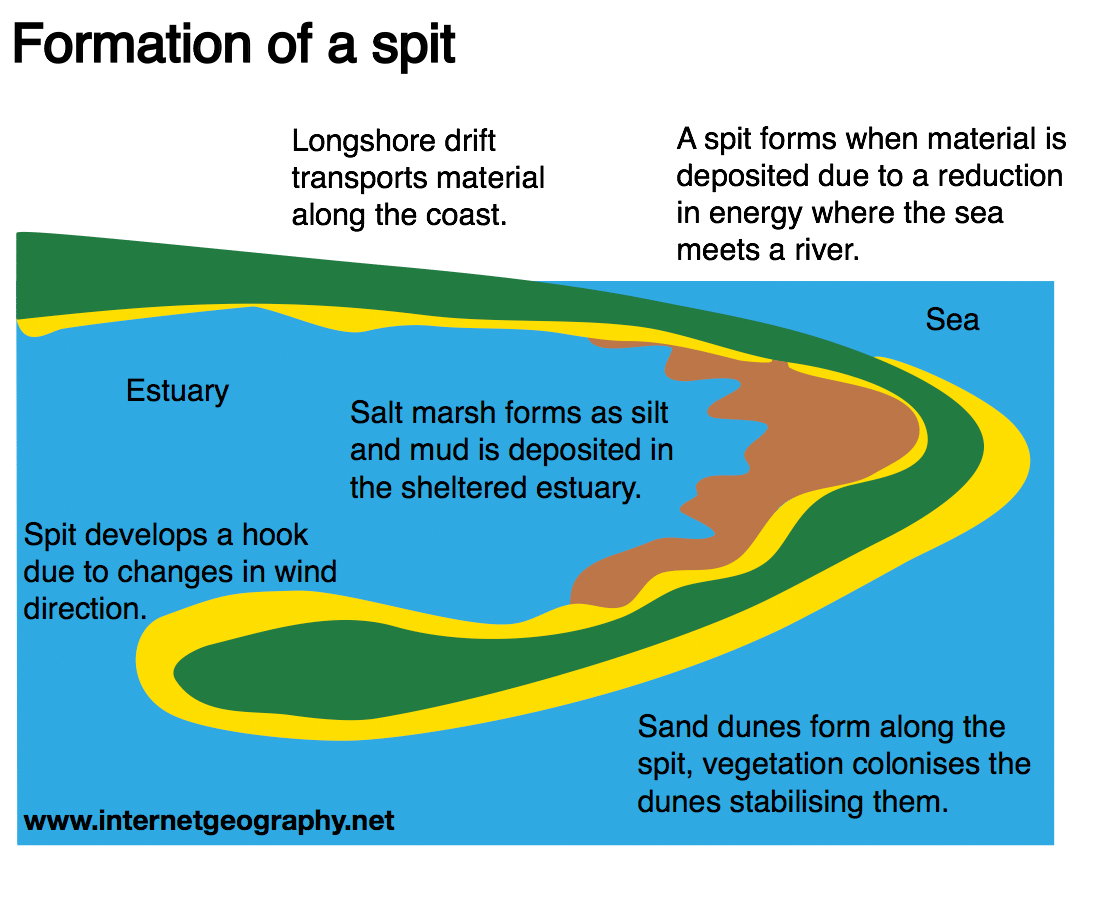
This coastal process is important as it allows for the displacement of different materials, and this displacement is usually the main cause for the development and formation of different depositional landforms such as beaches, lagoons, spits, and tombolos. Coastal deposition is the main reason behind as to why people notice materials that are particularly different from the surrounding environment around shorelines and beach areas. Most of the time these sediments and materials come from different parts of the ocean floor, and were carried away by the action of waves.
Before we discuss the different landforms formed by this coastal process, we must first gain an understanding of coastal deposition. The following are the different physical processes that influence the occurrence of coastal deposition.
Also Check: Is Paris Jackson Really Michaels Daughter
Landforms Of Coastal Deposition
Some coastal areas are dominated by erosion, an example being the Pacific coast of Canada and the United States, while others are dominated by deposition, examples being the Atlantic and Caribbean coasts of the United States. But on almost all coasts, both deposition and erosion are happening to varying degrees most of the time, although in different places. This is clearly evident in the Tofino area of Vancouver Island , where erosion is the predominant process on the rocky headlands, while depositional processes predominate within the bays. On deposition-dominant coasts, the coastal sediments are still being eroded from some areas and deposited in others.
The main factor in determining if a coast is dominated by erosion or deposition is its history of tectonic activity. A coast like that of British Columbia is tectonically active, and compression and uplift have been going on for tens of millions of years. This coast has also been uplifted during the past 15,000 years by isostatic rebound due to deglaciation. The coasts of the United States along the Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico have not seen significant tectonic activity in a few hundred million years, and except in the northeast, have not experienced post-glacial uplift. These areas have relatively little topographic relief, and there is now minimal erosion of coastal bedrock.
Exercises
On the map, sketch where you would expect the following to form:
- A spit
- A tombolo
The Occurrence Of Null Point Theory
Akaroa Harbour is located on Banks Peninsula, Canterbury, New Zealand, 43°48â²S172°56â²E / 43.800°S 172.933°E / -43.800 172.933. The formation of this harbour has occurred due to active erosional processes on an extinct shield volcano, whereby the sea has flooded the caldera, creating an inlet 16 km in length, with an average width of 2 km and a depth of â13 m relative to mean sea level at the 9 km point down the transect of the central axis. The predominant storm wave energy has unlimited fetch for the outer harbour from a southerly direction, with a calmer environment within the inner harbour, though localised harbour breezes create surface currents and chop influencing the marine sedimentation processes. Deposits of loess from subsequent glacial periods have in filled volcanic fissures over millennia, resulting in volcanic basalt and loess as the main sediment types available for deposition in Akaroa Harbour
Kirby R. takes this concept further explaining that the fines are suspended and reworked aerially offshore leaving behind lag deposits of the main bivalve and gastropod shells separated out from the finer substrate beneath, waves and currents then heap these deposits to form chenier ridges throughout the tidal zone, which tend to be forced up the foreshore profile but also along the foreshore. Cheniers can be found at any level on the foreshore and predominantly characterise an erosion-dominated regime.
You May Like: Glencoe Geometry: Chapter 7 Test Answer Key
Where Does Sediment Come From
Sediment comes from geologic, geomorphic, and organic factors 10. The amount, material and size of the transported sediment is a sum of these influences in any particular waterway. Sediment transported in rivers with headwaters from a mountain range often include glacial silt, while a body of water surrounded by swampland will be inundated with decomposing organic material 23.
What Is Deposition In Geography
Deposition occurs when the sea loses energy and drops any matter that it may be carrying. Deposition is a coastal process.
In geography, deposition refers to the way that constructive waves are developed. When certain conditions arise, the sea cannot maintain its energy and thus drops any materials it was carrying, such as sand, pebbles and other rock particles.
This may occur in several different locations, including areas such as a sheltered cove or a bay. Lack of wind may also cause a deposition. It can also be caused when waves enter a shallow area, or if there is too much material for the water to carry.
You May Like: Importance Of Standardization In Chemistry
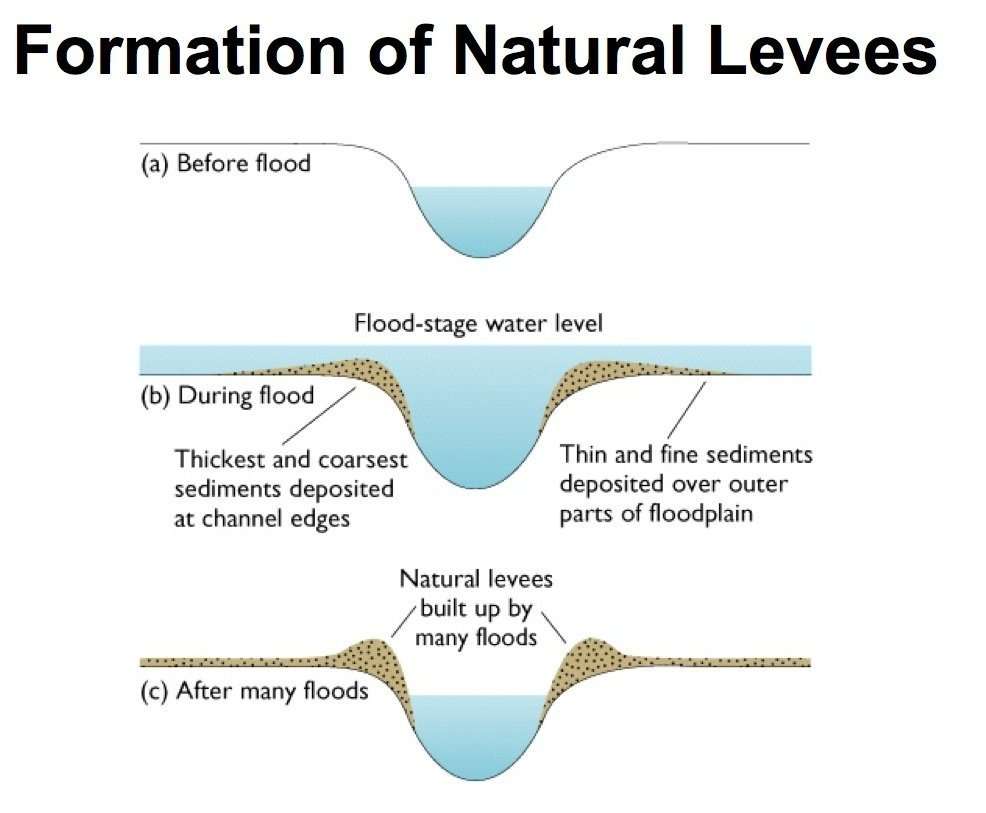
Flood Plains Natural Levees
- Deposition develops a flood plain just as erosion makes valleys.
- A riverbed made of river deposits is the active flood plain and the flood plain above the bank of the river is the inactive flood plain.
- Natural levees are found along the banks of large rivers. They are low, linear and parallel ridges of coarse deposits along the banks of a river.
- The levee deposits are coarser than the deposits spread by flood water away from the river.
Meanders And Oxbow Lakes
- Meanders are loop-like channel patterns develop over the flood and delta plains.
- They are actually not a landform but only a type of channel pattern formed as a result of deposition.
- They are formed basically because of three reasons: propensity of water flowing over very gentle gradient to work laterally on the banks unconsolidated nature of alluvial deposits making up the bank with many irregularities Coriolis force acting on fluid water deflecting it like deflecting the wind.
- The concave bank of a meander is known as cut-off bank and the convex bank is known as a slip-off
- As meanders grow into deep loops, the same may get cut-off due to erosion at the inflection point and are left as oxbow lakes.
- For large rivers, the sediments deposited in a linear fashion at the depositional side of a meander are called as Point Bars or Meander Bars.
Also Check: Algebra With Pizzazz Books Never Written Answer Key
Agents Participating In Deposition
There are four agents that participate in the process of deposition. They are as below:
Frozen rivers/glaciers: They get the eroded material into them and transfer to some other location as they slide from an actual place.
Gravity: It interfere with the erosion when the rocks fall due to the earthquake.
Wind: It plays its part to carry the lighter material with it such as sand or dust particles and drops them away where it ends blowing.
Water: It works with all powers in different forms. The water in rivers and streams take up the sediment particles with it. In the form of floods, it carries heavier sediments with it to different locations. In the form of rainwater, it carries the sediments to various locations and deposits them.
Deposition Facts For Kids
Deposition is the geological process where material is added to a land . This can happen in many places, such as a beach or river. Some parts of a shoreline build up and grow out, whereas other parts of the shoreline erode and fall into the sea.
In deposition, wind and water lay down grains of material that have been eroded and transported from another place. Deposition happens when the forces which transport sediments are weaker than the forces of particle weight and friction. This causes a resistance to movement, and the particles drop down.
Deposition can also refer to the buildup of sediment from organically derived matter or chemical process.
Don’t Miss: Who Is Paris Jackson’s Mother
Examples Of Deposition In A Sentence
depositiondepositionsdepositiondeposition PEOPLE.comdeposition VarietydepositionUSA TODAYdepositionThe Arizona RepublicdepositionThe WeekdepositionNew York TimesdepositionCNNdepositionSan Antonio Express-News
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘deposition.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Sediment And Organic Factors
In addition to the mineral-based aspect, sediment can be organic in source. Organic sediment comes from decaying algae, plants, and other organic material that falls in the water 4. Bacteria attached to this detritus or other inorganic matter are also categorized as organic 18. Organic sediment transport is will vary by location and season. In one estuarine study, the organic portion of the suspended load fell from 85% to 18% from February to November due to seasonal effects on sediment transport 18.
Some phytoplankton can play a unique role in their contribution to sediment loads. In addition to the organic factor they provide, specific phytoplankton can contribute an inorganic component as well 1. This inorganic material comes from diatom frustules and calcium carbonate detritus. While this material is not specifically organic, it is organic in origin 1.
Also Check: Algebra Nation Section 4 Test Yourself Answers
What Is Sediment Transport
Sediment transport is the movement of organic and inorganic particles by water 10. In general, the greater the flow, the more sediment that will be conveyed. Water flow can be strong enough to suspend particles in the water column as they move downstream, or simply push them along the bottom of a waterway 11. Transported sediment may include mineral matter, chemicals and pollutants, and organic material.
Another name for sediment transport is sediment load. The total load includes all particles moving as bedload, suspended load, and wash load 11.
What Are The Different Types Of Deposition
glaciers are formed by the breaking down of rock.
- A beach is where sand is deposited by waves.
- It is also where wind carries sand.
- The Beach is eroded by waves , which carries the sand back into the ocean.
. Consequently, what are the types of deposition?
Depositional landforms are the visible evidence of processes that have deposited sediments or rocks after they were transported by flowing ice or water, wind or gravity. Examples include beaches, deltas, glacial moraines, sand dunes and salt domes.
Additionally, what are the three main types of depositional environments? The many depositional environments which can be grouped into three major categories – , transitional, and continental. See the Basics Table of depositional environments for a more detailed breakdown of each of the categories and the sedimentary rocks, structures and fossils that are common to each environment.
People also ask, what are the five types of deposition?
Stream Deposition
- Alluvial fans.
- Deltas.
- Topset beds are nearly horizontal layers of sediment deposited by the distributaries as they flow away from the mouth and toward the delta front.
- Braided streams.
Recommended Reading: Prince Jackson Real Father
Erosion And Deposition By Streams
Streams, any running water from a rivulet to a raging river, complete the hydrologic cycle by returning precipitation that falls on land to the oceans. Some of this water moves over the surface and some moves through the ground as groundwater. Flowing water does the work of both erosion and deposition.
Deposition Effects On Geographical Environment
Deposition affects the geographical environment in many ways. Following are them:
Gravity: It creates rock-sliding on the sides of the mountains and the rocks are deposited at the bottom.
Weight: The weight of the eroded material also creates rockslides.
Wind: Wind creates different sand dune patterns in deserts while taking the sand with it.
Rivers: When the rivers deposit sand and other eroded material with them, they create deltas. So, the water speed slows while reaching to deltas to be a part of the ocean.
Ocean Waves: The ocean waves with a forceful power create beaches and sand bars by continuously depositing sand to a particular location.
Also Check: How To Study For A Geography Bee
Formation Of Depositional Landforms
When rocks and cliffs are being continuously weathered, eroded, and moved, these generate a huge material that needs to be deposited or laid down somewhere else. There are processes in which sediments or rocks get transported by flowing ice or water, wind or gravity, and they are deposited on the landforms such as glacial moraines, deltas, beaches, dunes, and salt domes.
If the process causing the deposit is recent and continuing, the shapes of such landforms change over a relatively short period. On the other hand, the processes that were completed millions of years ago tend to leave some depositional landforms as their remnants.
What Does Running Water Do
- Running water, which doesnt need any further explanation, has two components: one is overland flow on the general land surface as a sheet and the other is linear flow as streams and rivers in valleys.
- The overland flow causes sheet erosion and depending upon the irregularities of the land surface, the overland flow may concentrate into narrow to wide paths.
- During the sheet erosion, minor or major quantities of materials from the surface of the land are removed in the direction of flow and gradual small and narrow rills will form.
- These rills will gradually develop into long and wide gullies, the gullies will further deepen, widen and lengthen and unite to give rise to a network of valleys. .
- Once a valley is formed, it later develops into a stream or river.
You May Like: Molecular Shape Of Ccl4
Erosion And Deposition: Action Of Running Water And Groundwater
Last updated on by ClearIAS Team
In the previous articles, we were discussing various types of endogenic and exogenic processes. We have also seen that erosion and deposition are some of the exogenic processes. In this post, we are dealing with the geomorphic agents running water and groundwater, which causes erosion and deposition. They form various erosional and depositional landforms.
Even though we are considering the erosional and depositional activities and their landform creation, it should be kept in mind that they are always aided by weathering and mass movements. There are some other independent controls like stability of sea level tectonic stability of landmass climate etc. which influence the evolution of these landforms.