Animal Form And Function
The cells in each animal body are bathed in interstitial fluid, which make up the cell’s environment. This fluid and all its characteristics can be described as the animal’s internal environment, which is in contrast to the external environment that encompasses the animal’s outside world. Animals can be classified as either regulators or conformers. Animals such as mammals and birds are regulators as they are able to maintain a constant internal environment such as body temperature despite their environments changing. These animals are also described as homeotherms as they exhibit thermoregulation by keeping their internal body temperature constant. In contrast, animals such as fishes and frogs are conformers as they adapt their internal environment to match their external environments. These animals are also described as poikilotherms or ectotherms as they allow their body temperatures to match their external environments. In terms of energy, regulation is more costly than conformity as an animal expands more energy to maintain a constant internal environment such as increasing its basal metabolic rate, which is the rate of energy consumption. Similarly, homeothermy is more costly than poikilothermy. Homeostasis is the stability of an animal’s internal environment, which is maintained by negative feedback loops.
The Basic Principles Of Modern Biology
Four principles unify modern biology, according to the book “Managing Science” :
Plant Form And Function
The plant body is made up of organs that can be organized into two major organ systems: a root system and a shoot system. The root system anchors the plants into place. The roots themselves absorb water and minerals and store photosynthetic products. The shoot system is composed of stem, leaves, and flowers. The stems hold and orient the leaves to the sun, which allow the leaves to conduct photosynthesis. The flowers are shoots that have been modified for reproduction. Shoots are composed of phytomers, which are functional units that consist of a node carrying one or more leaves, internode, and one or more buds.
Read Also: Differential Geometry Problems And Solutions
Schools Of Thought In Epistemology
Rationalism is the epistemological view that reason is the chief source of knowledge and the main determinant of what constitutes knowledge. More broadly, it can also refer to any view which appeals to reason as a source of knowledge or justification. Rationalism is one of the two classical views in epistemology, the other being empiricism. Rationalists claim that the mind, through the use of reason, can directly grasp certain truths in various domains, including logic, mathematics, ethics, and metaphysics. Rationalist views can range from modest views in mathematics and logic to ambitious metaphysical systems .
Skepticism is a position that questions the possibility of human knowledge, either in particular domains or on a general level. Skepticism does not refer to any one specific school of philosophy, but is rather a thread that runs through many epistemological debates. Ancient Greek skepticism began during the Hellenistic period in philosophy, which featured both Pyrrhonism and Academic skepticism . Among ancient Indian philosophers, skepticism was notably defended by the Ajñana school and in the Buddhist Madhyamika tradition. In modern philosophy, René Descartes‘ famous inquiry into mind and body began as an exercise in skepticism, in which he started by trying to doubt all purported cases of knowledge in order to search for something that was known with absolute certainty.
Cartesian skepticism
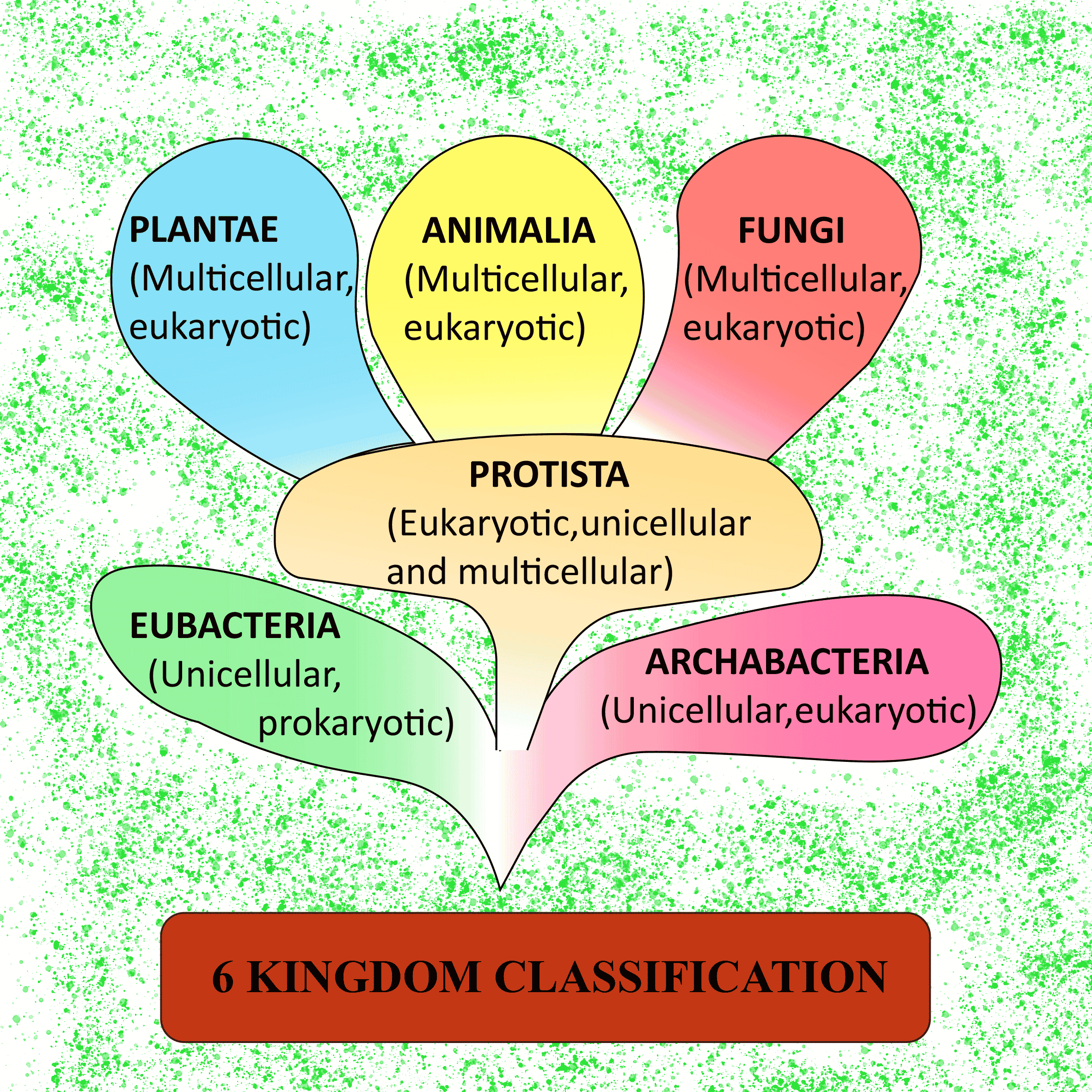
The Many Branches Of Biology

Although there are only four unifying principles, biology covers a broad range of topics that are broken into many disciplines and subdisciplines.
On a high level, the different fields of biology can each be thought of as the study of one type of organism, according to “Blackie’s Dictionary of Biology ” . For example, zoology is the study of animals, botany is the study of plants and microbiology is the study of microorganisms.
Within those broader fields, many biologists specialize in researching a specific topic or problem. For example, a scientist may study behavior of a certain fish species, while another scientist may research the neurological and chemical mechanisms behind the behavior.
What is a scientific hypothesis?
There are numerous branches and subdisciplines of biology, but here is a short list of some of the more broad fields that fall under the umbrella of biology:
Biochemistry: The study of the chemical processes that take place in or are related to living things, according to the Biochemical Society . For example, pharmacology is a type of biochemistry research that focuses on studying how drugs interact with chemicals in the body, as described in a 2010 review in the journal Biochemistry.
Ecology: The study of how organisms interact with their environment. For example, an ecologist may study how honeybee behavior is affected by humans living nearby.
Read Also: How Has Japan’s Geography Affected Its History
A Biologist Explains: What Is Life
Is Mimivirus alive?
CC BY 4.0
Although biology is the study of life, even biologists don’t agree on what ‘life’ actually is. While scientists have proposed hundreds of ways to define it, none have been widely accepted. And for the general public, a dictionary won’t help because definitions will use terms like organisms or animals and plants — synonyms or examples of life — which sends you round in circles.
Instead of defining the word, textbooks will describe life with a list of half a dozen features based on what it has or what it does. For what life has, one feature is the cell, a compartment to contain biochemical processes. Cells are often listed because of the influential cell theory developed in 1837-1838, which states that all living things are composed of cells, and the cell is the basic unit of life. From single-celled bacteria to the trillions of cells that make up a human body, it does seem as though all life has compartments.
A list of features will also mention what life does — processes like growth, reproduction, ability to adapt and metabolism . Such views are echoed by experts such as biochemist Daniel Koshland, who listed his seven pillars of life as program, improvization, compartmentalization, energy, regeneration, adaptability and seclusion.
Is a Mule alive?
Capri23auto on Pixabay
It’s life, but not as we know it
Is Data from ‘Star Trek: The Next Generation’ alive?
CBS Studios
Life is an entity with the ability to adapt to its environment.
What Does Qualitative And Quantitative Mean
Quantitative data are used when a researcher is trying to quantify a problem or address the what or how many aspects of a research question. Qualitative data describes qualities or characteristics. It is collected using questionnaires interviews or observation and frequently appears in narrative form.
You May Like: Transition To Algebra Unit 1 Answers
What Is The Definition Of Living In Biology
Something that can grow move reproduce consciousness respire and carry out various cellular activities are said to be living. Living things can grow move reproduce respires i.e. possess various life processes. Living things have structures known as cells they grow and exhibit movement or locomotion.
What Do Biologists Do
Biologists can work in many different fields, including research, healthcare, environmental conservation and art, according to the American Institute of Biological Sciences . Here are a few examples:
Research: Biologists can perform research in many types of settings. Microbiologists, for instance, may study bacterial cultures in a laboratory setting. Other biologists may perform field research, where they observe animals or plants in their native habitat. Many biologists may work in the lab and in the field for example, scientists may collect soil or water samples from the field and analyze them further in the lab, like at North Carolina University’s Soil and Water Lab .
Conservation: Biologists can help with efforts in environmental conservation by studying and determining how to protect and conserve the natural world for the future. For example, biologists may help educate the public on the importance of preserving an animal’s natural habitat and participate in endangered species recovery programs to stop the decline of an endangered species, according to the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service .
Healthcare: People who study biology can go on to work in healthcare, whether they work as doctors or nurses, join a pharmaceutical company to develop new drugs and vaccines, research the efficacy of medical treatments or become veterinarians to help treat sick animals, according to the American Institute of Biological Sciences .
Recommended Reading: Gradpoint Geometry B Posttest Answers
How Do You Find Standard Deviation Biology
How to Calculate the Standard Deviation:
What does standard deviation mean a level biology?
Standard deviation measures the spread of data around the mean value. It is very useful when comparing consistency between different data sets.
How do you find the standard deviation of an experiment?
Calculate the Sample Standard Deviation
Is Obesity A Disease
Obesity is a complex disease that occurs when an individuals weight is higher than what is considered healthy for his or her height. Obesity affects children as well as adults. Many factors can contribute to excess weight gain including eating patterns, physical activity levels, and sleep routines.
You May Like: Parcc Released Items Algebra 2
Central Concepts In Epistemology
Nearly all debates in epistemology are in some way related to knowledge. Most generally, “knowledge” is a familiarity, awareness, or understanding of someone or something, which might include facts , skills , or objects . Philosophers tend to draw an important distinction between three different senses of “knowing” something: “knowing that” , “knowing how” , and “knowing by acquaintance” . Epistemology is primarily concerned with the first of these forms of knowledge, propositional knowledge. All three senses of “knowing” can be seen in our ordinary use of the word. In mathematics, you can know that 2 + 2 = 4, but there is also knowing how to add two numbers, and knowing a person , place , thing , or activity . While these distinctions are not explicit in English, they are explicitly made in other languages, including French, Portuguese, Spanish, Romanian, German and Dutch . The theoretical interpretation and significance of these linguistic issues remains controversial.
A priori and a posteriori knowledge
One of the most important distinctions in epistemology is between what can be known a priori and what can be known a posteriori . The terms originate from the Analytic methods of Aristotle’s Organon, and may be roughly defined as follows:
Views that emphasize the importance of a priori knowledge are generally classified as rationalist. Views that emphasize the importance of a posteriori knowledge are generally classified as empiricist.
Constructing A Model Of Function For De Novo Gene Birth Research
We sought to construct an understanding of function specifically tailored to de novo gene birth. We reasoned that this aim would be best achieved by studying how the term is used in the scientific practice of this particular field of research. Indeed, the objects of study and the technical methodologies in this field may lend themselves to different interpretations of function than in other fields such as regulatory genomics, physiology or ecology. In order to derive an initial model of function adapted to de novo gene birth research, we first rhetorically analyzed the scientific literature in the field together with philosophical publications about genomic function. We then applied the constant comparative method of the grounded theory of social sciences to samples of 20 published abstracts in the field . Through an organized, iterative process of defining and discussing usages of the term, we inductively converged on the interpretation that, in this set of abstracts, authors writing about the function of a molecular object were almost always describing one or more of the following properties of the object: Expression, Capacities, Interactions, Physiological Implications and Evolutionary Implications. These properties represent five meanings of function that are defined in Table 1.
Recommended Reading: What Is Ug In Physics
What Is Biology At Ntnu
The word biology is derived from the greek words /bios/ meaning /life/ and /logos/ meaning /study/ and is defined as the science of life and living organisms. An organism is a living entity consisting of one cell e.g. bacteria, or several cells e.g. animals, plants and fungi.
Aspects of biological science range from the study of molecular mechanisms in cells, to the classification and behaviour of organisms, how species evolve and interaction between ecosystems.
Biology often overlaps with other sciences for example, biochemistry and toxicology with biology, chemistry, and medicine biophysics with biology and physics stratigraphy with biology and geography astrobiology with biology and astronomy. Social sciences such as geography, philosophy, psychology and sociology can also interact with biology, for example, in administration of biological resources, developmental biology, biogeography, evolutionary psychology and ethics.
What Is The Function Of Axil
An axil is the angle between the upper side of a leaf and the stem from which it grows. Knowing the location of the axil helps you to locate the bud, because in flowering plants buds develop in the axils of leaves. These types of buds are known as axillary buds.
What is an Axil Class 6?
An axil is the angle between the leaf and the stem from which it grows. Herbs They are usually short and have green and tender stems, which may or may not have branches.
What is difference between apical and axillary bud?
Apical buds occur at the end, or apex, of stems. Because of this location, they are also known as terminal buds. Axillary buds occur at a leaf node, which is where a leaf emerges from the stem of a stem.
You May Like: What Jobs Do You Need Geography For
What Is Difference Between Transcribe And Translation
Transcription, simply put, is documenting something into written form. For example, the process of listening to a recording of, say, an interview or a lecture and then transcribing into a readable document is transcription. Whereas translation would be converting text into another language.
What are the steps of translation and transcription?
Transcription takes place in the nucleus. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA molecule. RNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Translation reads the genetic code in mRNA and makes a protein.
Plant Nutrition And Transport
Like all other organisms, plants are primarily made up of water and other molecules containing elements that are essential to life. The absence of specific nutrients ” rel=”nofollow”> essential elements), many of which have been identified in hydroponic experiments, can disrupt plant growth and reproduction. The majority of plants are able to obtain these nutrients from solutions that surrounds their roots in the soil. Continuous leaching and harvesting of crops can deplete the soil of its nutrients, which can be restored with the use of fertilizers. Carnivorous plants such as Venus flytraps are able to obtain nutrients by digesting other arthropods whereas parasitic plants such as mistletoes can parasitize other plants for water and nutrients.
You May Like: What Is Secure Attachment In Psychology
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
biology, study of living things and their vital processes. The field deals with all the physicochemical aspects of life. The modern tendency toward cross-disciplinary research and the unification of scientific knowledge and investigation from different fields has resulted in significant overlap of the field of biology with other scientific disciplines. Modern principles of other fieldschemistry, medicine, and physics, for exampleare integrated with those of biology in areas such as biochemistry, biomedicine, and biophysics.
Biology is subdivided into separate branches for convenience of study, though all the subdivisions are interrelated by basic principles. Thus, while it is custom to separate the study of plants from that of animals , and the study of the structure of organisms from that of function , all living things share in common certain biological phenomenafor example, various means of reproduction, cell division, and the transmission of genetic material.
How Multiple Meanings Of Function Are Used In The Field Of De Novo Gene Birth
With this model in hand, we analyzed whether the multiple meanings of function impact understanding of the literature in the field of de novo gene birth. Each member of our team independently assigned one or more meanings to each instance of the word function found in our database of abstracts, gathering contextual evidence primarily from the sentence in which the term was used . The abstracts generally provided enough context for each independent reader to confidently assign meanings to most instances, with only rare assignments of the label vague . Hence, the Pittsburgh model gave readers a key to decipher more specifically what authors meant by the word function. However, and importantly, a quantitative analysis revealed only that 12% of assignments were unanimous, where the same single meaning was chosen by all readers . In other words, the same instance of the word in the same sentence was most of the times interpreted differently by our team members. The most confusing instances, with 4 or 6 distinct assignments, were all assigned vague by at least one reader. This analysis indicates that when the meaning of function is unspecified, the literature in this field of research can become confusing.
Interpreting the word function in scientific abstracts related to de novo gene birth.
Figure 1source data 1.
Independent and consensus assignments.
Don’t Miss: What Grades Do You Need To Study Psychology