Secure Attachment Frees The Mind To Learn
Children who are brought up with enormous stress, due to lack of comfort, among other necessities, are so busy preparing for danger that they cant concentrate. Conversely, when children feel safe and supported, learning takes care of itself.
A secure attachment is the first social connection that helps your baby start learning: The parent serves as a secure base from which the child can explore trust in the parent makes it easier for secure children to seek assistance with learning from parents fruitful, pleasant interactions between parent and child obviously facilitate exchange of information and through attachment, children develop a coherent sense of self and others that enable them to think clearly and regulate their thought process efficiently.
Between 18 And 20 Months Your Baby Should
- Know and understand at least 10 words.
- Use at least four consonants in words or babbling, like b, d, m, n, p, t.
- Use words, gestures and signals to communicate needs, like pointing at something.
- Enjoy simple pretend play, like hugging or feeding a doll or stuffed animal.
- Demonstrate familiarity with people or body parts by pointing or looking at them when named.
Responding With The Abcs Of Attachment
My child comes home from school, upset that someone made fun of her favorite new dinosaur shirt. She is crying and very sad. I acknowledge her sadness, mirroring her mental state . I may say wow, that sounds like your feelings were really hurt. That would make me feel sad, too. Can you tell me more about it? With this, I am not only reminding my child that I am here to support her, but Im instilling a self-acceptance in her. When she knows her emotions are acknowledged, she knows she can feel her feelings, without judgment or negative repercussions . Finally, when my daughter regularly experiences attunement and balance, this leads to a sense of consistency between her internal emotions and her external experience with her caregiver .
A secure attachment style can be developed and strengthened when the ABCs of attachment are regularly demonstrated.
With stress levels at an all-time high, there may be times that we respond in ways that are abrupt and unkind. This doesnt have to be a new pattern. This is where implementing a repair is important.
Recommended Reading: Segment Addition Postulate Color By Number Worksheet Answer Key
How Attachment Styles Are Formed
Attachment styles are typically developed in infancy based on our relationships with our earliest caregivers. Researchers believe attachment style is formed within our first year of living, between 7 to 11 months of age, according to mental health counselor Grace Suh, LMHC, LPC. According to Mancao, it’s “determined by how the primary caregiver responds to the child’s cues when they are experiencing emotional stress.”
“Human beings are born helpless, so we are hardwired at birth to search for and attach to a reliable caregiver for protection,” Peter Lovenheim, author of The Attachment Effect, writes at mbg. “The quality of that first bondloving and stable or inconsistent or even absentactually shapes the developing brain, influencing us throughout life in how we deal with loss and how we behave in relationships.”
Here’s a quick primer on what circumstances lead to each of the four attachment types:
Caregivers are not the only ones who shape your attachment style, however. People’s attachment styles may also be influenced by other significant relationships throughout their lives. “A person can have had a secure attachment during childhood, however, betrayals and infidelity in adulthood can lead to an insecure attachment,” says Mancao.
Attachment Theory In Babies Infants And Early Childhood Development
According to Bowlby and Ainsworth, attachments with the primary caregiver develop during the first 18 months or so of the childs life, starting with instinctual behaviors like crying and clinging . These behaviors are quickly directed at one or a few caregivers in particular, and by 7 or 8 months old, children usually start protesting against the caregiver leaving and grieve for their absence.
Once children reach the toddler stage, they begin forming an internal working model of their attachment relationships. This internal working model provides the framework for the childs beliefs about their own self-worth and how much they can depend on others to meet their needs.
In Bowlby and Ainsworths view, the attachment styles that children form based on their early interactions with caregivers form a continuum of emotion regulation, with anxious-avoidant attachment at one end and anxious-resistant at the other.
Secure attachment falls at the midpoint of this spectrum, between overly organized strategies for controlling and minimizing emotions and the uncontrolled, disorganized, and ineffectively managed emotions.
The most recently added classification, disorganized-disoriented, may display strategies and behaviors from all across the spectrum, but generally, they are not effective in controlling their emotions and may have outbursts of anger or aggression .
You May Like: What Is Relationship In Math
How Does Insecure Attachment Develop
Insecure attachment develops in the situations when the childs needs are not fulfilled, typically in two ways, the child either does not receive what s/he needs, but has parents who are expressly anxious and chaotic in his/her attempts to calm the child, or has parents who ignore the childs needs and who do not react
Get In Touch With Your Real Needs
At the end of the day, all insecure attachment styles are people who tend to form insecure relationships because of deeply held fears that their relationships will not work out. So it’s important to figure out how to make yourself feel more secure in your relationships. Part of that involves being aware of what your needs and desires are in relationships.
“Learn to be assertive and set boundaries. Honor what you feel, and express your needs in words without manipulation and hidden meanings,” Suh says. “Securely attached people are often direct and appropriately confrontational to create a healthy and meaningful relationship.”
Read Also: Define Relation In Math Terms
An Apology Is Necessary
A repair consists of an apology, acknowledging the misstep, and hopes for the future. For example, Im sorry that I raised my voice at you when I tripped over the toy. I was frustrated. Im sorry that it scared you. Next time, I will try not to yell when I have big feelings. Can we work together to clean up your toys so that no one hurts themselves?
This not only restores the disconnect that occurred when you yelled or became angry, but models to your child that its completely okay to make mistakes.
Our children learn a lot about themselves and their place in the world through the ways that their caregivers interact with them. Being mindful during parent-child interaction is a great way to demonstrate to the child their importance. Through emotional connection, our children begin to develop their sense of self.
How We Really Pick Our Romantic Partners
Because as children, they are confident in caregiver availability, secure children are free to focus their energies on play and exploring their interpersonal and natural environments. Having secure bases to return to when they meet with inevitable goal blockages or become frightened, these children will explore in ever-widening circles. By extension, they should become increasingly successful in achieving their goals and develop hopeful ways of thinking. In this latter respect, when children seek comfort after failures, parents go beyond soothing distress and also provide the children with new strategies to use in successive goal pursuits.
As this process is continually repeated and children begin to internalizing the parents secure base functions they develop the confidence to act independently. Accordingly, as they mature through adolescence into adulthood, secure children become increasingly efficacious individuals who believe that they are lovable and worthy of support, others as available and responsive, and the world is a safe and predictable place. By extension, they have strong frustration tolerance, can tolerate ambiguity in relationships and at work, can deal effectively with others , and can overcome the challenges that life throws in the way.
Read Also: Prentice Hall Gold Geometry Answer Key
Learn The Processes Needed To Build A Secure Non
If only everyone could read social situations accurately, not get flooded or hijacked by strong emotions, and respond in a kind, empathetic, non-defensive and constructive manner, the world would be a more accepting and predictable place.
Of course, we all have times when situations trigger strong emotions and behaviors that dont yield the best results. That having been said, certain personality traits enable some people to cope with stressors more adaptively than others. The one I’m focusing on in this post is known as a secure attachment style.
About 55 percent of people emerge from childhood with secure attachment styles. Attachment styles are the building blocks of our personalities. They are like mental roadmaps that help us understand and predict how the environment and other people are likely to react to us in different situations.
Through helping predict how people and the environment are likely to react, they also help us prepare mentally and emotionally to cope with whatever comes our way. Because these patterns of perceiving, understanding, and coping with the environment are practiced so many times across our early childhood years and into adulthood, they become automatic processes that are ingrained, not only in our thoughts and behaviors but in the very structures of our brains and emotional systems.
Secure Attachment Is A Foundation Of True Self
Self-esteem has become a controversial concept. Not long ago, many parents and other adults dealing with children believed that self-esteem came from ensuring that children didnt feel inferior to others: a gold star for everyone! Just for showing up!
But conventional wisdom has held that its competence, actually, that feeds self-esteem. At this point it probably wont surprise you to read that secure attachment is the foundation for confidence and other attributes needed to develop competence.
When a parent is there for us a lot of the time, we get the message that we must be pretty deserving. If when a baby cries his mother consistently shows up to soothe him, mom is essentially sending the message that I am here, and you are worth it, from which the baby can conclude, You are here, and I must be worth it.
Secure babies start life with the big advantage of already knowing that when nothing makes sense in the world, there is someone who thinks theyre worth being with, no matter what.
Lastly, the idea that low self-esteem increases stress seems self-evident. We want our children to feel good about who they are and what they can do and not be wracked with envy or relentless competitiveness to prove their self-worth.
Read Also: F=ma Past Exams
Goodness Of Fit: The Interaction Of Child And Parent Characteristics
Finally, infants characteristics such as temperament not only affect parents sensitivity and responsiveness, they also affect infants outcomes. Based on previous research, Yair Ziv and Jude Cassidy have hypothesized that parents are more susceptible to poor parenting when they rear more-irritable infants than less-irritable infants. It is speculated that irritable infants may have more trouble with emotional and behavioral regulation, and thus are more dependent on adults for assistance in self-regulation. As such, the best approach to understanding infants independence is to consider relevant child and parent characteristics as well as contextual factors.
Matthew J. Dykas, … Jude Cassidy, in, 2011
Examples: The Types Styles And Stages

The adult attachment styles follow the same general pattern described above:
Each of these styles should be thought of as a continuum of attachment behaviors, rather than a specific type of person. Someone with a generally secure attachment style may on occasion display behaviors more suited to the other types, or someone with a dismissive-avoidant style may form a secure bond with a particular person.
Therefore, these types should be considered a way to describe and understand an individuals behavior rather than an exact description of someones personality.
Based on a persons attachment style, the way he or she approaches intimate relationships, marriage, and parenting can vary widely.
The number of ways in which this theory can be applied or used to explain behavior is compounded and expanded by the fact that relationships require two people any attachment behaviors that an individual displays will impact and be influenced by the attachment behaviors of other people.
Given the huge variety of individuals, behaviors, and relationships, it is not surprising that there is so much conflict and confusion.
It is also not surprising, although no less unfortunate, that many relationships end up in divorce or dissolution, an event that may continue an unhealthy cycle of attachment in the children of these unions.
Recommended Reading: Half Life Equation Chem
The Confusion About Bonding And The Secure Attachment Bond
The words bond or bonding are commonly used to describe both caretaking and the emotional exchange that forms the attachment process, even though they are very different ways of connecting with your child.
- One is a connection based on the care a parent provides for their infant child, while the other is based on the quality of nonverbal emotional communication that occurs between parent and child.
- Both types of parent-child interaction can occur simultaneously. While feeding, bathing, or otherwise caring for your child, you can also build the emotional connection by recognizing and responding to your childs nonverbal cues.
- Before experts understood the radical changes going on in the infant brain during the first months and years of life, both the caretaking process and the attachment process looked very similar. Now, though, they are able to recognize and painstakingly record an infants nonverbal responses to highlight the process of attachment in infants.
How A Caretakers Well
The feelings you experience as a primary caretaker can shape the developmental process occurring in your childs brain. If you are overly stressed, depressed, traumatized, or unavailable for whatever reason, you may not have the awareness or sensitivity to provide the positive emotional mirroring your child needs for secure attachment.
Sometimes even a healthy, caring, and responsible caretaker may have trouble understanding and initiating a secure attachment bond with their child. If, as a child, you didnt experience a secure attachment bond with your own primary caregiver, you may be unaware of what secure attachment looks or feels like. But adults can change for the better, too. Just as you can strengthen yourself with exercise and a healthy diet, you can also learn to manage overwhelming stress and deal with emotions that may interfere with your ability to create a secure attachment bond.
Affordable Online Therapy for Parenting Issues
Get professional help from BetterHelps network of licensed therapists.
Need urgent help? .
Recommended Reading: Geometry Segment And Angle Addition Worksheet Answers
What Is Your Attachment Style
Here’s a simple attachment style quiz to identify your own attachment style. You can also try this attachment test based on the parameters studied in the scientific research, created by R. Chris Fraley, Ph.D., a psychologist at the University of Illinois who has researched attachment theory in depth.
In general, though, many people can read the descriptions of the four attachment styles and intuitively recognize themselves in one of them. Here’s a quick gut-check for you: Below are the descriptions of the main attachment types used in Hazan and Shaver’s foundational research on attachment theory. Read the statements and pick the one that most resonates with you:
Importantly, it’s also possible to have a different attachment style in different situations, according to Mancao.
Prosocial Behavior And Interpersonal Relationships
Longitudinal studies have found that a history of responsive care resulting in secure attachment is associated with a number of positive social developmental outcomes. Yet it is difficult to draw certain conclusions as to the role of early attachment security in later social competence because the parentchild relationship involves many aspects in addition to attachment. In general, findings suggest that children who were classified as securely attached during the first year of their lives were judged during the preschool years to be more socially competent and empathic toward their peers, as well as to have higher self-esteem, than children with a history of insecure attachment. During middle childhood, children who where classified as secure in their early attachment relationships were also found to be more socially accepted by their peers and more adept at forming close friendships than children who were classified as insecure. Moreover, secure infants grow to be adolescents who are more capable of creating intimacy than do insecure infants. However, the correlational nature of this evidence precludes any firm conclusions regarding the causal role played by attachment security. The early attachment relationship is only one component within a larger developmental context predicting later competence in interpersonal domains.
Kevin John OConnor, Sue Ammen, in, 2013
Read Also: Chapter 3 Test Form 2c Answers
What Is A Secure Attachment
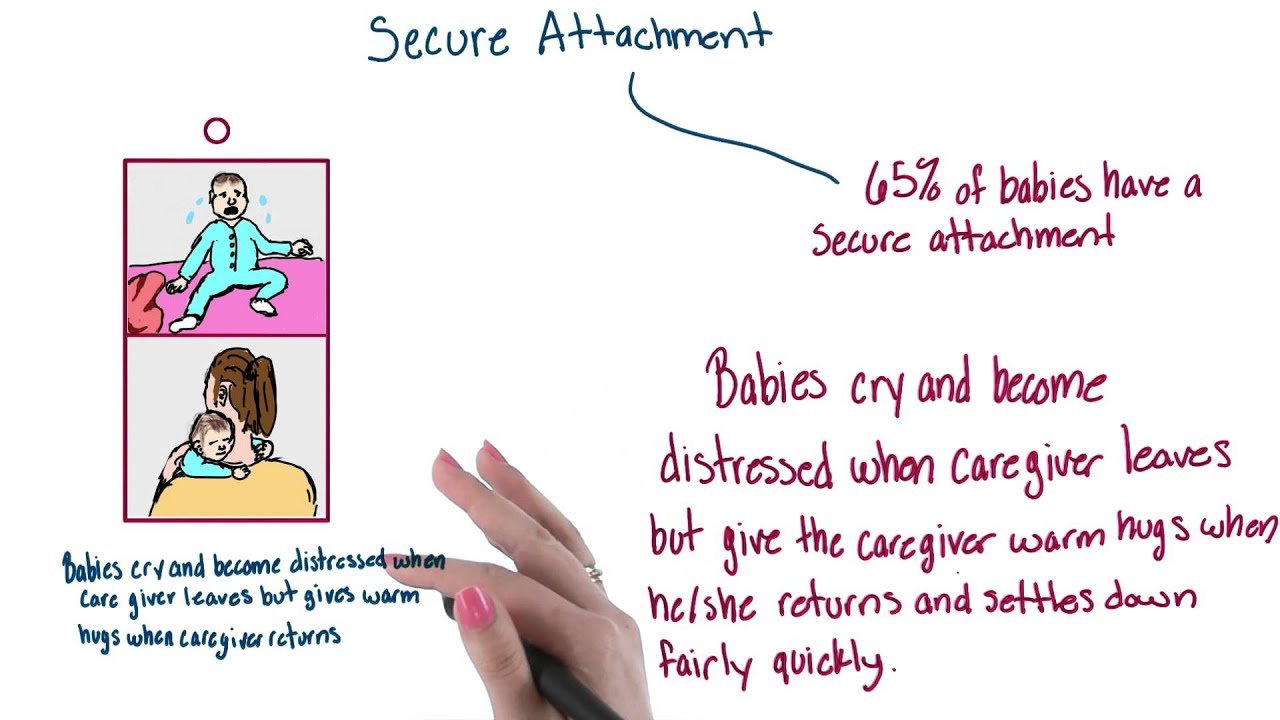
According to the theories of John Bowlby , a child is securely-attached if she is confident of her caregivers support. The attachment figure serves as a secure base from which the child can confidently explore the world.
Secure attachment is also associated with
- keeping track of the caregiver during exploration,
- approaching or touching the caregiver when anxious or distressed
- finding comfort in proximity and contact
And, in the long-term, kids with secure attachments seem to have opens in a new windowmany advantages emotional, social, medical, and cognitive.
But how can you know if researchers would classify your own baby as securely attached? How do they actually measure attachment security?
The original method, developed by the influential psychologist Mary Ainsworth, is the laboratory procedure called the Strange Situation .
Typically, the Strange Situation tests how babies or young children respond to the temporary absence of their mothers.
Heres how it works.