Limitations Of Vsepr Theory:
Some significant limitations of the VSEPR theory include:
- This theory fails to explain isoelectronic species . The species may vary in shapes despite having the same number of electrons.
- The VSEPR theory does not shed any light on the compounds of transition metals. The structure of several such compounds cannot be correctly described by this theory. This is because the VSEPR theory does not take into account the associated sizes of the substituent groups and the lone pairs that are inactive.
- Another limitation of VSEPR theory is that it predicts that halides of group 2 elements will have a linear structure, whereas their actual structure is a bent one.
Vsepr Shapes Of Molecules And Geometry
We’ve learned that VSEPR uses the number and arrangement of valence electrons to predict the geometry of a molecule. We’ll now focus on the different shapes caused by varying numbers of pairs of electrons, starting with molecules with just two pairs and working up to those with six. We’ll start with the basic shape of each molecule, which occurs when all of the pairs of electrons are bonded pairs, before exploring the effect of swapping some of them for lone pairs.
Complexes With Strong D
Some transition metal complexes with low d electron count have unusual geometries, which can be ascribed to d subshell bonding interaction.Gillespie found that this interaction produces bonding pairs that also occupy the respective antipodal points of the sphere. This phenomenon is an electronic effect resulting from the bilobed shape of the underlying sdxhybrid orbitals. The repulsion of these bonding pairs leads to a different set of shapes.
| Molecule type |
|---|
| W6 |
The gas phase structures of the triatomic halides of the heavier members of group 2, , are not linear as predicted but are bent, . It has been proposed by Gillespie that this is also caused by bonding interaction of the ligands with the d subshell of the metal atom, thus influencing the molecular geometry.
Read Also: Algebra 2 Pre Assessment Test
Solved: What Does Vsepr Stand For In Vsepr Theory What Determines Theshape Of The Molecule
So, according to the Vesper theory, it is the electron groups around the central Adam that, um, determines thumb molecular geometry. So, for example, there are two bounds around the center. Adam. So this structure is a tribunal planer. Yes, one of them is not occupied. Means a long pair, and two of them is occupied. So there are still three electron groups around Sentra. Adam, eh? So the Elektronik geometry or the electron geometry is still tribunal planner. But the molecular geometry we only consider in this part. And its a bends. So it is the electron groups around central Adam, and whether theyre occupied or no unoccupied determines thie molecular geometry in a molecule.
VSEPR Chart Use our handy VSEPR chart to obtain the 3-D geometric VSEPR shapes of molecules and ions. Find out about VSEPR theory and shapes like trigonal planar or square pyramidal. VSEPR means valence covering electron pair repulsion.
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is a model used to predict 3-D molecular geometry based on the number of valence shell electron bond pairs among the atoms in a molecule or ion. This model assumes that electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion effects from one another. In other words, the electron pairs are as far apart as possible.
Video advice: VSEPR Theory Basic Introduction
Presentation On Theme: What Does Vsepr Stand For Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Presentation Transcript:
1 What does VSEPR stand for? Valence Shell Electron Pair RepulsionVSEPR THEORYWhat does VSEPR stand for?Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
2 VSEPR lets us determine the shape of covalent molecules and ionsVSEPR THEORYWhat does VSEPR mean?VSEPR lets us determine the shape of covalent molecules and ions
3 VSEPR THEORYWhy is this important to know?It explains how molecules and ions behave.
4 VSEPR THEORYFor example:It explains why water molecules are so good at dissolving ionic substances even though water does not have an ionic bond.
5 How do we determine the shapes of molecules and ions?VSEPR THEORY:How do we determine the shapes of molecules and ions?
6 VSEPR THEORY:Procedures to determine Geometry1) Determine the central atom .
7 VSEPR THEORY: Procedures to determine Geometry2) Draw the electron dot structure3) Determine the electronic geometry Electron density = all bonded atoms and unbonded electron pairs connected to the central atom
8 VSEPR THEORY: Procedures to determine Geometry4) Determine the molecular geometry
9 Common shapes you should knowVSEPR THEORYCommon shapes you should knowTetrahedral: Tetrahedral molecules look like pyramids with four faces. Each point on the pyramid corresponds to an atom that’s attached to the central atom. Bond angles are degrees.
11 VSEPR THEORYTrigonal planar: It looks like the hood ornament of a Mercedes automobile, or like a peace sign with that bottom-most line gone. The bond angles are 120 degrees.
You May Like: What Is Statistical Mechanics In Physics
The Trigonal Planar Domain
When the central atom is connected to one of the groups by a double bond or has an empty p-orbital, we get the trigonal planar domain. There are less shapes associated with this domain than with the tetrahedral though, so it makes it easier to remember.
The figure above shows only the cases with the double bonds. Well discuss the examples with empty orbitals later in this course. Structures with empty orbitals are very unstable, so were only going to see those as highly reactive compounds or intermediates in reactions.
How Can The Vsepr Theory Be Used To Predict The Shapes Of Molecules
The strength of the repulsion between a lone pair and a bond pair of electrons lies in between the repulsion between two lone pairs and between two bond pairs. The order of repulsion between electron pairs is as follows:
Lone Pair- lone pair > Lone Pair- bond- pair > Bond Pair- bond pair.
1. Total number of electron pairs around the central atom = ½
- For negative ions, add the number of electrons equal to the units of negative charge on the ions to the valence electrons of the central atom.
- For positive ions, subtract the number of electrons equal to the units of positive charge on the ion from the valence electrons of the central atom.
2. The number of Bond pair = Total number of atoms linked to central atom by single bonds.
3. Number of lone pairs = Total number of electron No of shared pair
The electron pairs around the central atom repel each another and move so far apart from each another that there are no greater repulsions between them. This results in the molecule having minimum energy and maximum stability.
Also Check: Is Paris Jackson Biologically Related To Michael Jackson
These Independent Clauses Are Joined By A Conjunction
These independent clauses are joined by a conjunction . Vsepr is an acronym that stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion. What does vsepr stand for? Basically, a compound contains two simple sentences. Throughout the chapters, david They are considered the developers of the vsepr theory. Study.com has answers to your toughest chemistry homework questions with detailed step by step explanations. Vocabulary antonyms, synonyms language usage testing reading comprehension of a poem through as global question factual questions vocabulary in the text conveyed in the text inferential questions Feb 17, 2022 · bf3, also known as boron trifluoride, is an inorganic chemical compound which is a colorless gas with a pungent smell. The model was proposed by nevil sidgwick and herbert powell in 1940. Ronald gillespie and ronald nyholm then developed the model into their theory published in 1957 Aug 24, 2016 · 4/6 = 2/3 of a sandwich each, students often find this type of question difficult at first, until they realise that the question is the answer! Jun 02, 2021 · a compound sentence has two independent clauses.
They are considered the developers of the vsepr theory. Jun 02, 2021 · a compound sentence has two independent clauses. Rarr 12/4 = 3 but in this case we are sharing a smaller number between a What is 12 divided by 4? These independent clauses are joined by a conjunction .
Molecular Formulas And Nomenclature
The content that follows is the substance of General Chemistry Lecture 33. In this lecture we introduce the shapes and reasoning behind VSEPR.
VSEPR Valence covering electron pair repulsion theory is really a model utilized in chemistry to calculate the geometry of person molecules from the amount of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. The idea centers around the concept that the clouds of electrons that surround nuclei and flow within the bonds that link atoms together repulse one another. And so the structures that form in the repulsions is going to be individuals that increase the distances between your atoms as well as their bonds.
Also Check: Algebra Lesson 4.7 Patterns On The Multiplication Table
S Used To Find The Shape Of The Molecule
To sum up there are four simple steps to apply the VSEPR theory.
Why Is The Water Molecule Bent Like That
The characteristic bent shape of the water molecule shown above was a puzzling discovery for scientists at first. The shape allows the molecule to be polar, increasing its boiling point and making it possible for life on earth to exist as we know it. But what makes it bend? The structure is almost the same as carbon dioxide which is known to be a gas at room temperature, why not water too?
Putting atoms together to form compounds can be done on paper or in the lab. However, when the shape of the molecule made in the lab is different from the shape of the molecule drawn on paper, then we need to rethink our ideas and find better explanations.
Read Also: What Is Ap Human Geography
Molecular Structure For Multicenter Molecules
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space . A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Bond distances are measured in Ångstroms or picometers .
Postulates Of Vsepr Theory:
The postulates of the VSEPR theory are listed below
- In polyatomic molecules , one of the constituent atoms is identified as the central atom to which all other atoms belonging to the molecule are linked.
- The total number of valence shell electron pairs decides the shape of the molecule.
- The electron pairs have a tendency to orient themselves in a way that minimizes the electron-electron repulsion between them and maximizes the distance between them.
- The valence shell can be thought of as a sphere wherein the electron pairs are localized on the surface in such a way that the distance between them is maximized.
- Should the central atom of the molecule be surrounded by bond pairs of electrons, then, the asymmetrically shaped molecule can be expected.
- Should the central atom be surrounded by both lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons, the molecule would tend to have a distorted shape.
- The VSEPR theory can be applied to each resonance structure of a molecule.
- The strength of the repulsion is strongest in two lone pairs and weakest in two bond pairs.
- If electron pairs around the central atom are closer to each other, they will repel each other. This results in an increase in the energy of the molecules.
- If the electron pairs lie far from each other, the repulsions between them will be less and eventually, the energy of the molecule will be low.
Also Check: What Is Chromosome In Biology
What Do I Do Now
In every scientists life comes that moment when you realize that you were wrong. Sometimes you think about a problem and recognize where you went astray. Other times you find out when you go into the lab and the experiment doesnt work . What has to happen then is a change in direction. The good scientist sees the problem and comes up with a new answer. Then that answer has to be tested to see how it works.
In 1956, British scientists R.J. Gillespie and R.S. Nyholm recognized that the current model for explaining bond angles did not work well. The theory at that time relied on hybrid orbitals to explain all aspects of bonding. The problem was that the theory gave incorrect prediction of bond angles for many compounds. They developed a new approach based on earlier work by other scientists that incorporated a consideration of electron pairs in predicting three-dimensional structure.
How Do We Apply The Vsepr Theory
The premise of the VSEPR is the idea that the electron pairs & bonds will distribute themselves as far from each other as possible around the central atom. Think about a bunch of balloons tied to a single point. That would be a pretty accurate description of the approach.
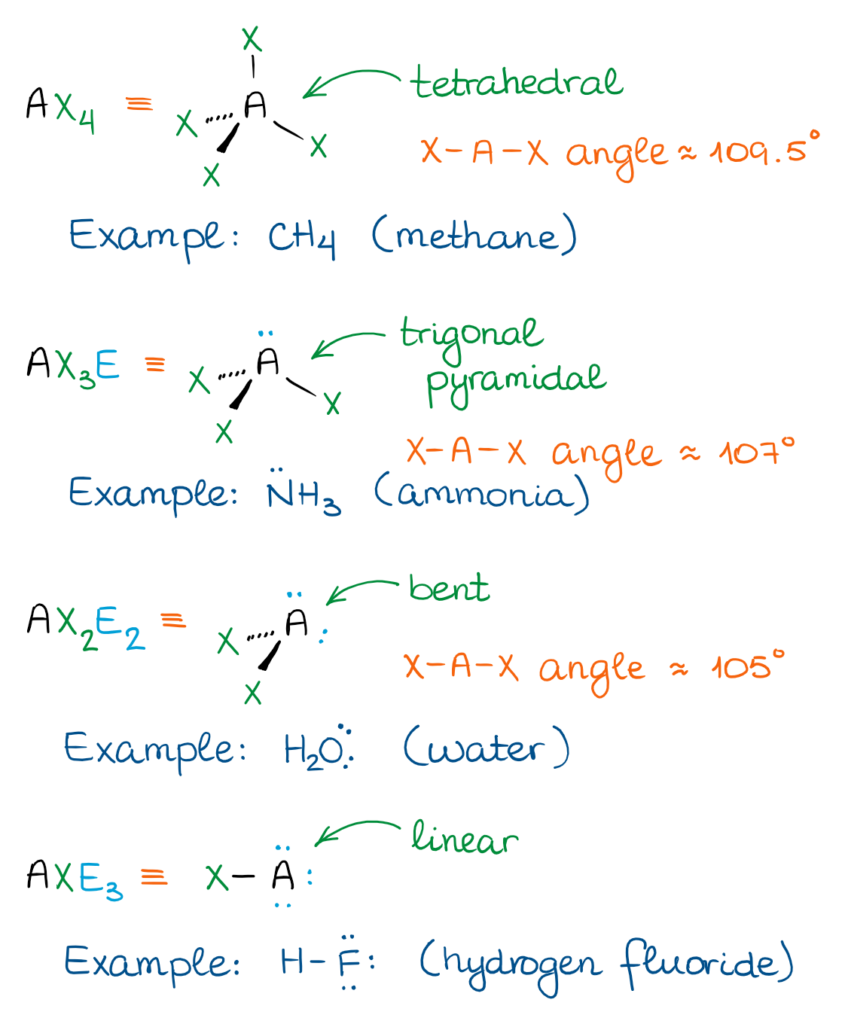
While there are quite a few electronic domains and, thus, 3D shapes, we only focus on three shapes in organic chemistry.
- The linear shape means that all three atoms are making a linear string of 3 atoms in a line. Thus, the X-A-X bond angle is 180º.
- The trigonal planar shape has a central atom in the middle of the molecule, while the rest of the groups are making a perfect triangle around it. This gives a X-A-X bond angle of 120º.
- The tetrahedral shape resembles a trigonal pyramid with all sides being perfect triangles. The X-A-X bond angle is a little more difficult to calculate, but it is approximately 109.5º.
The most important domains for us are going to be the AX3 and AX4. Those are the two most common shapes well see in organic molecules.
Recommended Reading: What Is Human Biology Class Like
What Are The Limits Of Vsepr
Some significant limitations of the VSEPR theory include: This theory fails to explain isoelectronic species . The species may vary in shapes despite having the same number of electrons. The VSEPR theory does not shed any light on the compounds of transition metals.
What are limitations of VBT?
Limitations of Valence Bond Theory They are: It fails to explain the tetravalency of carbon. This theory does not discuss the electrons energies. The assumptions are about the electrons being localized to specific locations.
What is described by the VSEPR theory?
VSEPR and valence bond theory are two theories in chemistry that are used to explain properties of covalent compounds. The VSEPR theory explains the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule. This theory uses the repulsions between lone electron pairs and bond electron pairs in order to predict the shape of a certain molecule.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. The theory centers around the idea that the clouds of electrons that surround nuclei and flow in the bonds that link atoms together repulse each other. Therefore the structures that form from the repulsions will be those that maximize the distances between the atoms and their bonds.
The Theory uses the letter A to represent central atoms and X to represent peripheral atoms and E to represent lone pairs to describe the structure of the molecule.
For Example: The ClO3- Ion has the following structure:
There is one central atom and 3 peripheral Oxygen atoms and one lone pair of electrons so the VSEPR code would be AX3E.
Read Also: Does Kamala Have Biological Children
Square Planar Ml4 Complexes
The Kepert model predicts that ML4 transition metal molecules are tetrahedral in shape, and it cannot explain the formation of square planar complexes.:542 The majority of such complexes exhibit a d8 configuration as for the tetrachloroplatinate ion. The explanation of the shape of square planar complexes involves electronic effects and requires the use of crystal field theory.:5624
What Is Vsep Number
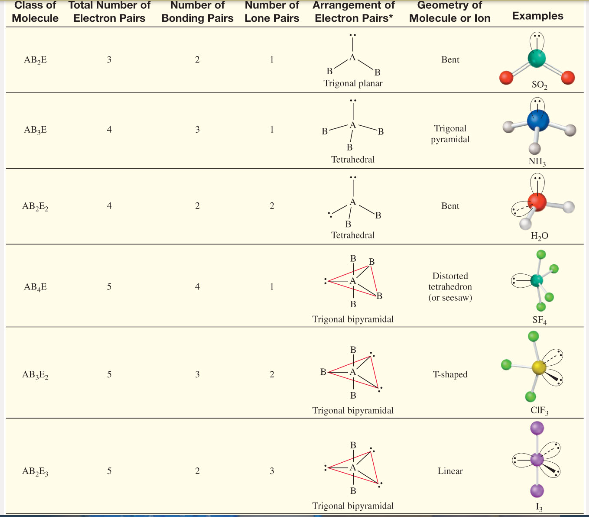
The VSEP number describes the shape of the molecule, as described in the table provided below.
| VSEP Number | |
| 7 | Pentagonal Bipyramidal |
Each of these corresponding shapes can also be found in the illustration provided earlier. However, the VSEPR theory cannot be used to obtain the exact bond angles between the atoms in a molecule.
Now, we will discuss each shape in detail:
Also Check: What Are The Psychological Effects Of Incarceration
What Does Vsepr Theory Tell You
The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory states that electron pairs repel each other whether or not they are in bond pairs or in lone pairs. Thus, electron pairs will spread themselves as far from each other as possible to minimize repulsion.
Why is VSEPR important?
Clearly it is very important to know the shape of a molecule if one is to understand its reactions. It is also desirable to have a simple method to predict the geometries of compounds. For main group compounds, the VSEPR method is such a predictive tool and unsurpassed as a handy predictive method.
How can VSEPR theory be used to predict the shape?
The VSEPR predicted shapes of molecules can be found in a systematic way by using the number of electron pairs to determine the shape of the molecules. To predict the shape of the molecules, first draw out the Lewis structure of the molecule. On the Lewis diagram, identify the central atom.