Benefits Of Brain Plasticity
There are many benefits of brain neuroplasticity. It allows your brain to adapt and change, which helps promote:
- The ability to learn new things
- The ability to enhance your existing cognitive capabilities
- Recovery from strokes and traumatic brain injuries
- Strengthening areas if some functions are lost or decline
- Improvements that can promote brain fitness
Neuroplasticity Rehabilitation For Stroke Recovery
Neuroplasticity has been observed quite often in those recovering from strokes. Strokes often leave patients with brain damage, ranging from moderate to severe however, we have also seen amazing recovery from stroke patients.
According to the experts at stroke-rehab.com, the best way to encourage neuroplasticity in stroke recovery is to use two key methods:
In other words, learning a new skill or activity through specific, regular practice can result in significant changes in the brain. You may not be able to learn anything with repetition and specific practice, but you can certainly learn a lotand improvements in one area can often spill over into improvements in other abilities and skills.
Neuroplasticity In Everyday Life
The ability of the brain to change and grow in response to experience enables people to bounce back from setbacks and adversityto be resilient. They can bend without breaking.
The disruption of neuroplasticity by severe stress or adversity is characteristic of such conditions as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder. There is quite literally a loss of synapses. In those disorders, people get stuck in neural ruts of negative thinking/feeling/behaving or fear-based memories.
All psychotherapy is intended to foster resilience the goal is to help people examine distressing feelings and experience and redirect them into more functional patterns, restoring cognitive and behavioral flexibility.
Aging is thought to decrease resilience through the cumulative detrimental effects of stress on neuroplasticity. The dynamic capacity of the brain to rewire itself in response to experience makes a case for lifelong stimulation as a way to maintain optimal brain health and to decrease the risk of dementia and degenerative disorders like Alzheimers disease.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Key Facts Of Psychedelic Drugs And Hippocampal Neurogenesis
-
Neurogenesis is the birth of new neurons and occurs throughout the life span in specific regions in the mammalian brain, including the HPC. Neurogenesis occurs at higher rates in early years and declines with aging.
-
Hippocampal neurogenesis is critical in forming new memories. In fact, studies have shown that decreasing neurogenesis in the HPC severely impairs learning and memory tasks that are dependent on the HPC.
-
Many factors, including psychedelic drugs, can alter neurogenesis in the HPC. Physical exercise is one way to boost neurogenesis, whereas stress is one of the most potent ways to reduce neurogenesis.
-
Psychedelic drugs have potential therapeutic use in the treatment of specific conditions including depression, anxiety, PTSD, and drug dependence.
-
Stress effects on adult neurogenesis differ across sexes.
-
Stress-induced changes in adult neurogenesis may be linked to cognition, anxiety/stress regulation, and social behaviors associated with the hippocampus.
D.R. Vago, … L.S. Morris, in, 2017
What Is Brain Plasticity
The human brain is composed of approximately 86 billion neurons. Early researchers believed that neurogenesis, or the creation of new neurons, stopped shortly after birth. Today, it’s understood that the brain possesses the remarkable capacity to reorganize pathways, create new connections, and, in some cases, even create new neuronsa concept called neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity.
There are two main types of neuroplasticity:
- Functional plasticity: The brain’s ability to move functions from a damaged area of the brain to other undamaged areas
- Structural plasticity: The brain’s ability to actually change its physical structure as a result of learning
Recommended Reading: Lesson 9.5 Distance In Coordinate Geometry
Chronic Pain And Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity can also play an important role in helping people manage and treat chronic pain. After all, pain itself is experienced as a set or sequence of neuronal firingsif we can change the way our brains are wired, whats to stop us from changing the experience of pain?
A recent study on the subject found that there are at least four methods that can help your brain adapt and manage chronic pain:
In addition to these more intensive treatments, there are many things you can do to apply the principles of neuroplasticity to your experience of pain, and the good news is that most of them are things that we should all do to become more healthy anyway!
Adult Neurogenesis: Of Mice And Men
Our knowledge regarding neurogenesis in the adult human brain lags dramatically behind the numerous studies that characterized the neurogenic process in rodents and non-human primates. However, there is now solid evidence that new neurons are generated in the human brain in numbers comparable to those observed in rodents, at least in the hippocampal DG . In the human SVZ, the situation remains somewhat controversial, but current evidence suggests that neurogenesis in the SVZ/OB ceases during the early postnatal period, even though quiescent NSPCs may persist in the SVZ . In support of this, it has recently been found that striatal interneurons are generated throughout life in the human striatum and that turnover of this neuronal subtype is affected in Huntington’s disease .
Despite these seminal data showing that neurogenesis clearly persists in distinct areas of the adult human brain, one must keep in mind that the mechanisms of neurogenesis and disease associations described herein are largely and sometimes exclusively based on animal research. To overcome this apparent gap between animal and human studies, a number of groups currently aim to develop novel methods to measure levels of neurogenesis in the human brain, for example by using non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging .
Read Also: Law Of Figure And Ground
Benefits Neuroplasticity Has On The Brain
Building on the studies we just mentioned, there are tons of ways that neuroplasticity benefits the brain. In addition to the improvements and advantages outlined above, these are some of the other ways your brain benefits from brain adaptation:
So, how can we apply neuroplasticity and get these benefits?
Adult Neurogenesis: Beyond Learning And Memory
Annual Review of Psychology
Vol. 66:53-81 First published online as a Review in Advance on September 19, 2014
Heather A. Cameron1 and Lucas R. Glover1,2
1Section on Neuroplasticity, National Institute of Mental Health, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892 email:
2Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX1 3UD United Kingdom
Recommended Reading: Simplifying Radicals Imaginary Numbers Worksheet Kuta Software
What Is The Meaning Of Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity refers to the brains ability to adapt. Or, as Dr. Campbell puts it:
It refers to the physiological changes in the brain that happen as the result of our interactions with our environment. From the time the brain begins to develop in utero until the day we die, the connections among the cells in our brains reorganize in response to our changing needs. This dynamic process allows us to learn from and adapt to different experiences
Celeste Campbell .
Our brains are truly extraordinary unlike computers, which are built to certain specifications and receive software updates periodically, our brains can actually receive hardware updates in addition to software updates. Different pathways form and fall dormant, are created and are discarded, according to our experiences.
When we learn something new, we create new connections between our neurons. We rewire our brains to adapt to new circumstances. This happens on a daily basis, but its also something that we can encourage and stimulate.
Can Adult Neurogenesis Be Increased
Research on the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus suggests that different factors can modulate adult neurogenesis. QBI researchers, for example, have found that exercise increases neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus, resulting in the increased production of newborn neurons.
Conversely, depression has been found to decrease neurogenesis, and adult neurogenesis has also been shown to decline with age.
Neuroscientists are now interested in developing ways to harness the brains reservoir of neural stem cells and progenitor cells to enhance hippocampal neurogenesis. By increasing production of newborn neurons, neuroscientists may be able to treat age-associated cognitive decline, neurodegenerative diseases including dementias, and mental illnesses.
Don’t Miss: Blanket Jackson Biological Father
What Is Human Development According To Psychology
Human development refers to the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development of humans throughout the lifespan. … Cognitive development involves learning, attention, memory, language, thinking, reasoning, and creativity. Psychosocial development involves emotions, personality, and social relationships.
Hippocampal Neurogenesis And Mdd
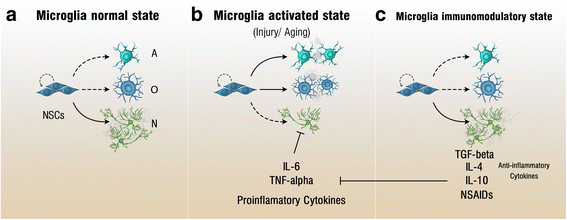
Dysregulated neurogenesis may contribute to MDD, anxiety and other neuropsychiatric disorders . Due to the lack of precise animal models of MDD, studies utilize different stressors to induce depressive-like states. In rodents, both acute psychosocial stress , as well as chronic stress reduce hippocampal neurogenesis . Similarly, social isolation-stress in primates decreases hippocampal neurogenesis and concurrently induces depressive and anxiety-like phenotypes, including anhedonia and self-defeating behavior . Moreover, the lasting effects of chronic stress during early life include the inhibition of adult neurogenesis , and potentiation of anxiety-like behaviors . However, stress-related effects are dose-dependent, and a short exposure to weaker stressors may not affect hippocampal neurogenesis .
Recommended Reading: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Pattern Separation As A Cognitive Marker Of Adult Neurogenesis
The ability to discriminate and store similar, but not identical, inputs of sensory information into distinct representations is referred to as pattern separation. This function is notable for its dependence on hippocampal adult neurogenesis . In fact, rodents with ablated neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus display impairments in pattern separation ability . In contrast, increasing hippocampal neurogenesis leads to enhanced pattern separation ability in animals . Hippocampal neurogenesis is also implicated in a variety of additional processes, including cognitive flexibility , hippocampus-dependent memory functions , spatial memory , memory encoding , and executive function . However, whether its role is required for these functions remains to be determined . A significant challenge in this research is determining the magnitude of pattern separation demanded by each of these cognitive task. It is those tasks that manipulate the level of sensory discrimination by altering the degree of similarity among study items that appear to most strongly correlate with neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus .
During Which Stage Of Development Is Plasticity Possible
The window of developmental plasticity extends from conception to early childhood, and even beyond to the transition from juvenility to adolescence, and could be transmitted transgenerationally. It involves epigenetic responses to environmental changes, which exert their effects during life history phase transitions.
Also Check: What Is K+ In Chemistry
Using Neuroplasticity To Help With Anxiety
The same principles apply to manage and treat anxiety disordersour brains are also perfectly capable of rewiring and remodeling to improve our ability to manage anxiety.
However, as life coach and clinician Ian Cleary says:
Any brain changes are at the expense of other changes. The development of these parts of our brain that effortlessly trigger anxiety, it is at the detriment of the ones that aid calmness & confidence it is not enough to just stop anxiety in any given moment which is often peoples focus. The anxiety wiring is still there and waiting to be triggered. We need to create competitive wiring. We need to create specific wiring of what we want to achieve which is competitive wiring to the problem. Without this we loop endlessly in anxiety with no neural pathway to take us forward.
Basically, neuroplasticity can be applied to help you manage, treat, and perhaps even cure anxiety, but it takes some time and effort! These more permanent brain changes can be achieved through adapting and changing thought patterns, through recall and memory patterning, breathing exercises, eye patterning, modifying postural habits, increasing body awareness, and targeting sensory perception .
Neurogenesis In The Hippocampus
C.L. Beites, … A.L. Calof, in, 2009
Neurogenesis in olfactory and vomeronasal sensory epithelia proceeds through two phases: primary neurogenesis, an early morphogenetic phase in which neural stem cells are established and expanded, and established neurogenesis, in which cell proliferation and differentiation are balanced to maintain constant neuron number. Together with secreted signals , stage-specific transcription factors direct progressive restrictions in developmental potential that occur as neuronal stem cells and committed progenitor cells produce terminally differentiated neurons during each phase of neurogenesis. Olfactory epithelium neurogenesis is regulated by a negative feedback circuit in which endogenous cytostatic factors regulate the size of the stem/progenitor cell pool and total neuron number, endowing the olfactory epithelia with the ability to rapidly respond to neuron loss with regeneration.
Erika Sarno, … Alfred J. Robison, in, 2021
Recommended Reading: Psychology Figure Ground
How Neurogenesis Occurs
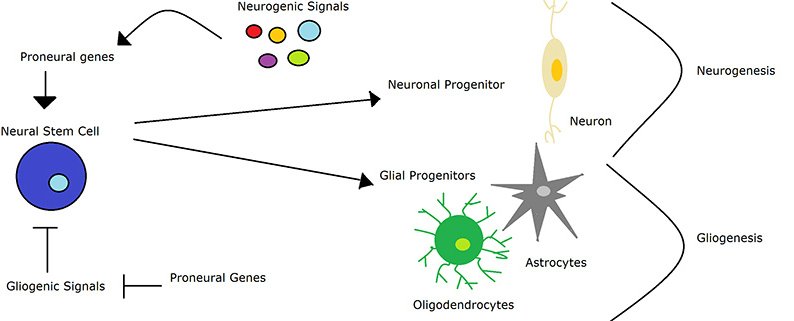
The process of neurogenesis in the brain starts off by getting triggered by neurogenic signals. These could arise from a number of factors such as stimulated activity in certain brain regions. This then helps to develop and stimulate neural stem cells.
These stem cells with then either divide indefinitely to produce more stem cells, or they will differentiate to give rise to neural progenitor cells. Neural progenitor cells are a stage between stem cells and fully formed neurons.
At this stage, the neural progenitor cells also differentiate to develop specific types of neurons.Likewise, glia cells, which are cells which have supportive functions in the CNS, are triggered by gliogenic signals to help stimulate neural stem cells.
The neural stem cells with gliogenic signals will then become glial progenitors, which then differentiate to become support cells such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
This process is known as gliogenesis, rather than neurogenesis.Neurons within mammalsâ CNS have been shown to originate from three classes of stem and progenitor cells: neuroepithelial cells, radial glial cells, and basal progenitors.
The onset of neurogenesis transforms the neuroepithelial cells into radial glial cells, which are responsible for producing all the neurons in the CNS, including supportive cells – astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
Adult Neural Stem Cells
Neural stem cells are the self-renewing, multipotent cells that generate the main phenotypes of the nervous system. In 1992, Reynolds and Weiss were the first to isolate neural progenitor and stem cells from the striatal tissue, including the subventricular zone one of the neurogenic areas – of adult mice brain tissue . Since then, neural progenitor and stem cells have been isolated from various areas of the adult brain, including non-neurogenic areas, such as the spinal cord, and from various species including human . Epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor are mitogens for neural progenitor and stem cells in vitro, though other factors synthesized by the neural progenitor and stem cells in culture are required for their growth . It is hypothesized that neurogenesis in the adult brain originates occurs from NSCs. The origin and identity of NSCs in the adult brain remain to be defined.
You May Like: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Where Does Neurogenesis Occur In The Brain
NSCs reside in specific regions of the brain known as neurogenic niches. These regions have molecular and cellular characteristics that create a microenvironment that allows neuronal development to occur . In adult mammals, there are two canonical neurogenic regions where NSCs reside: the subventricular zone lining the lateral ventricles , and the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus .
Neurogenesis outside these two regions is generally considered to be very restricted in the adult mammalian brain. However, non-canonical sites of neurogenesis have been reported in different species , including the neocortex, striatum, amygdala, hypothalamus, substantia nigra, cerebellum and brain stem .
Most research on adult neurogenesis has focused on the DG area of the hippocampus. Hippocampal adult neurogenesis has been observed in all mammalian species studied to date. In the adult human brain, neurogenesis appears to occur in the hippocampus, a brain area that is particularly important for cognitive functions such as learning and memory, and for emotions, mood, anxiety, and stress response .
Neural stem cells give birth, if needed, to new cells that replace dead or dying ones in the dentate gyrus, where adult neurogenesis might support processes involved in storing and retrieving memories.
Plasticity Can Cause Problems
Brain changes are often seen as improvements, but this is not always the case. In some instances, the brain might be influenced by psychoactive substances or pathological conditions that can lead to detrimental effects on the brain and behavior.
Voss P, Thomas ME, Cisneros-Franco JM, de Villers-Sidani É. Dynamic brains and the changing rules of neuroplasticity: implications for learning and recovery. Front Psychol. 2017 8:1657. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01657
-
Doidge N. The Brain That Changes Itself: Stories of Personal Triumph From the Frontiers of Brain Science. New York: Viking 2007.
-
Hockenbury SE, Nolan SA, Hockenbury D. Discovering Psychology. 7th ed. New York, NY: Worth Publishers 2016.
-
Hoiland E. Brain plasticity: What is it? Chudler EH, ed. Neuroscience for Kids. University of Washington.
-
James W. The Principles of Psychology. Classics in the History of Psychology. Green CD, ed. 1890.
-
Kolb B, Gibb R. Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain. Clarke M, Ghali L, eds. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2011 20:265-276.
Don’t Miss: Explain Why There Are Different Branches Of Chemistry
Starting The Day Off With Chocolate Could Have Unexpected Benefits
Chronic vicarious social defeat stress attenuates new-born neuronal cell survival in mouse hippocampus
Increasing evidence has shown that adult hippocampal neurogenesis is closely related to the pathophysiological condition of depressive disorders. Recently, chronic social defeat stress paradigms have been regarded as important animal models of depression, accompanied with neural plastic changes in the hippocampus. However, little is known about influences of non-physical stress on neurogenesis.
In the present study, we focused on the chronic vicarious social defeat stress paradigm and examined the effect of psychological stress on mouse hippocampal neurogenesis. Immediately after the chronic psychological stress, the cell survival rate in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus was significantly diminished without modifying the cell proliferation rate.
The decreased ratio in cell survival persisted for 4 weeks after the stress-loading period, while the differentiation and maturity of new-born neurons were identical to control groups. Furthermore, treatment with the chronic antidepressant fluoxetine reversed the social behavioral deficits and promoted new-born neurons survival.
These results demonstrate that emotional stress in the vicarious social defeat stress paradigm influences neuronal cell survival in the hippocampus, which reinforces its validity as an animal model of depression.