What Are 5 Main Ideas Of Freuds Personality Theory
Freud believed that the nature of the conflicts among the id, ego, and superego change over time as a person grows from child to adult. Specifically, he maintained that these conflicts progress through a series of five basic stages, each with a different focus: oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital.
What Is The Historical Background Of Neuropsychology
ROOTS OF THE WORD NEUROPSYCHOLOGY. In the post-Renaissance era, the words neurology and psychology, from which the term neuropsychology is derived, were introduced. In his Cerebri anatome of 1664, Thomas Willis , the most outstanding anatomist of the time, presented the word neurology in Greek.
Who was the first neuropsychologist?
Paul SollierPaul Sollier: the first clinical neuropsychologist.
Why Wundt is considered the father of psychology?
Indeed, Wundt is often regarded as the father of psychology. Wundt was important because he separated psychology from philosophy by analyzing the workings of the mind in a more structured way, with the emphasis being on objective measurement and control.
What was Wundts first experiment?
Wundt is credited with conducting the first formal experiment in psychology, where he tried to assess the speed of thought by measuring how long it took test subjects to make a judgment.
Who Was The First One To Use The Term Psychology
Volkmann, Philipp Melanchthon was the first author to have used the term psychology « als Vorlesungstitel »ã Volkmann s opinion was given wide currency a few years later by Rudolf Eucken in his authoritative Geschichte der philosophischen Terminologie , and then found its way in practically every standard
Also Check: Switching Circuits In Boolean Algebra
The Institute For Experimental Psychology At The University Of Leipzig
Wilhelm Wundt opened the first Institute for Experimental Psychology in 1879 at Leipzig University. Historians consider this event to be the beginning of modern psychology. Wundts research experience during his years in the physiology department with Hermann von Helmholtz was especially useful for this new project.
It wasnt long before his lab started to attract the attention of other doctors and students at German universities. So much so that many of them volunteered to participate in the institutes experiments. Wundt exposed them to different stimuli and then asked them to explain the sensations and thoughts they had. All of the data was objectively and carefully measured.
The results of these experiments provided valuable data on cognitive processes, human consciousness, volition, etc.
Question: Who Is The Father Of Psychology Quizlet
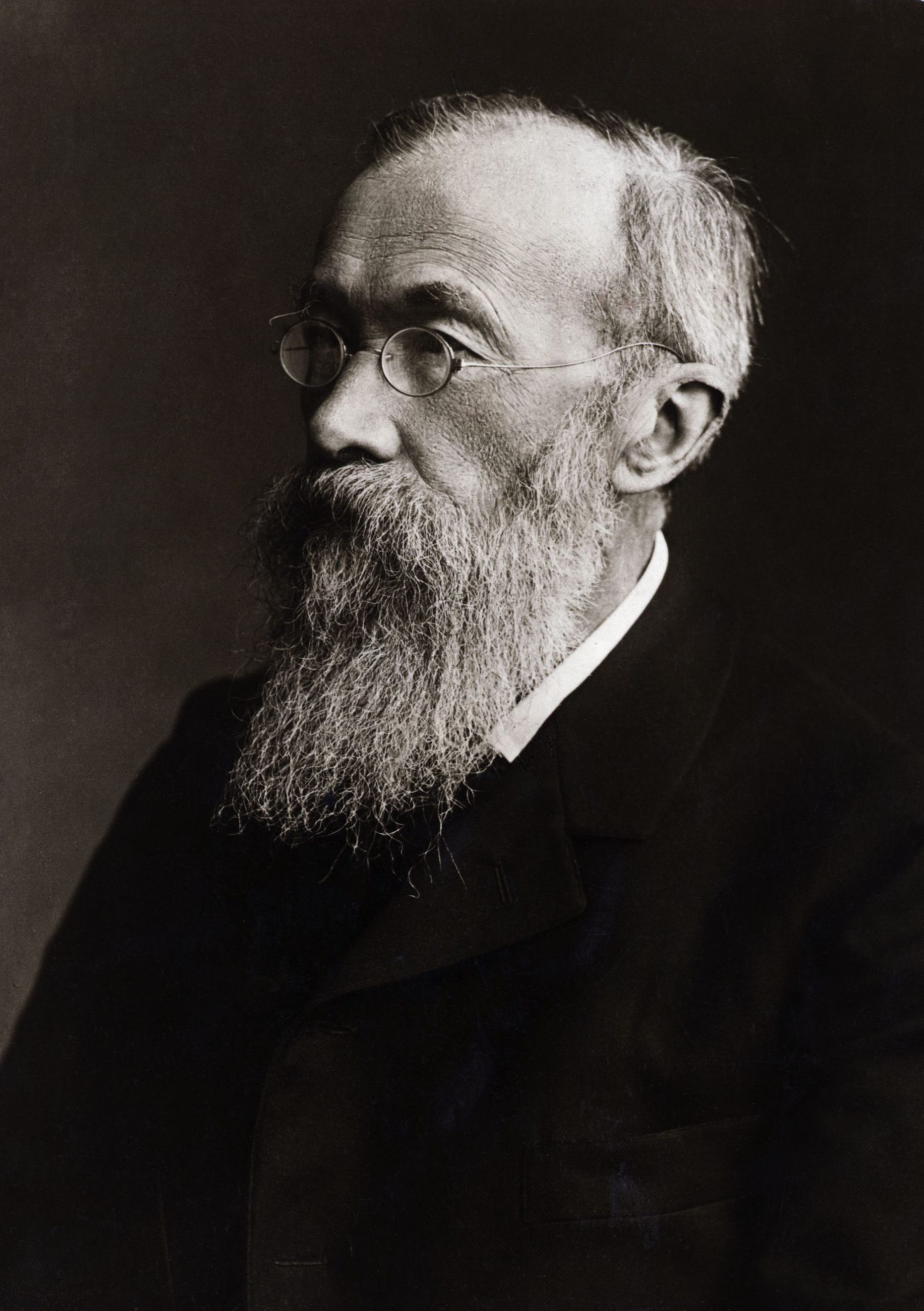

Wilhelm Wundt. Wilhelm Wundt opened the Institute for Experimental Psychology at the University of Leipzig in Germany in 1879. This was the first laboratory dedicated to psychology, and its opening is usually thought of as the beginning of modern psychology. Indeed, Wundt is often regarded as the father of psychology.
Contents
Also Check: What Is An Example Of Movement In Geography
Wundts Works In English
- 1894Lectures onhuman and animal psychology, J.G. Creighton and E.B. Titchener, London: Allen. Translation of Vorlesungen über dieMenschen- und Thier-Seele, 1863 .
- 1897Outlines ofPsychology, C.H. Judd , Leipzig: Wilhelm Engelmann,translation of Grundriss der Psychologie, 1896.
- 1901ThePrinciples of Morality and the Departments of the Moral Life,M.F. Washburn , London: Swan Sonnenschein New York:Macmillan. Translation of part of Ethik 1886.
- 1904Principles ofphysiological psychology, E.B. Titchener , London: Allen.Translation of Grundzüge der physiologischenPsychologie, 18734 but based mostly on the 5thedition.
- 1912AnIntroduction to Psychology, Rudolf Pintner , New York:MacMillan, translated from the 2nd edition ofEinleitung in die Psychologie. Leipzig: Engelmann.
- 1916Elements offolk-psychology: Outlines of a Psychological History of theDevelopment of Mankind, E.L. Schaub , London: Allen,translation of Elemente der Völkerpsychologie, 1912.
- 1973The Languageof Gestures, Approaches to Semiotics/Paperback Series, G.H. Meadet al. , T. Sebeok , The Hague: Mouton.
Misunderstandings Of Basic Terms And Principles
Wundt’s terminology also created difficulties because he had from today’s point-of-view given some of his most important ideas unfortunate names so that there were constant misunderstandings. Examples include:
- physiological psychology specifically not a scientific physiological psychology, because by writing the adjective with a small letter Wundt wanted to avoid this misunderstanding that still exists today for him it was the use of physiological aids in experimental general psychology that mattered.
- Self-observation not naive introspection, but with training and experimental control of conditions.
- Experiment this was meant with reference to Francis Bacon general, i.e. far beyond the scientific rules of the empirical sciences, so not necessarily a statistically evaluated laboratory experiment. For Wundt psychological experimentation primarily served as a check of trained self-observation.
- Element not in the sense of the smallest structure, but as a smallest unit of the intended level under consideration, so that, for example, even the central nervous system could be an “element”.
- Völkerpsychologie cultural psychology not ethnology.
- Apperception not just an increase in attention, but a central and multimodal synthesis.
- Voluntaristic tendency, voluntarism not an absolute metaphysical postulate, but a primary empirically-psychologically based accentuation of motivated action against the intellectualism and cognitivism of other psychologists.
You May Like: What Is Lithology In Geography
Which Perspective Would Focus On How An Individual
Which perspective would focus on how an individual interprets an event and applies it to their behavior? Cognitive Perspective Definition: The cognitive perspective is concerned with understanding. mental processes such as memory, perception, thinking, and. problem solving, and how they may be related to behavior.
Who Is The Father Of Modern Psychology As A Science
Since modern psychology is a scientific field, it might be best to look for another person to fill the role of father of modern psychology. Wilhelm Wundt The Father of Modern Psychology as a Science. Wilhelm Wundt rightfully holds the title as the father of modern psychology as a scientific pursuit.
Read Also: Ccl4 Electron Geometry
Read Also: What Does G Represent In Physics
Overview Of Wundt’s Work
Wundt was initially a physician and a well-known neurophysiologist before turning to sensory physiology and psychophysics. He was convinced that, for example, the process of spatial perception could not solely be explained on a physiological level, but also involved psychological principles. Wundt founded experimental psychology as a discipline and became a pioneer of cultural psychology. He created a broad research programme in empirical psychology and developed a system of philosophy and ethics from the basic concepts of his psychology bringing together several disciplines in one person.
Wundt’s epistemological position against John Locke and English empiricism was made clear in his book Beiträge zur Theorie der Sinneswahrnehmung published in 1862, by his use of a quotation from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz on the title page:
“Nihil est in intellectu quod non fuerit in sensu, nisi intellectu ipse.” . Nothing is in the intellect that was not first in the senses, except the intellect itself.
Principles that are not present in sensory impressions can be recognised in human perception and consciousness: logical inferences, categories of thought, the principle of causality, the principle of purpose , the principle of emergence and other epistemological principles.
Wundt’s most important books are:
Thereof Is Freud The Father Of Modern Psychology
who is the father of modern psychology,
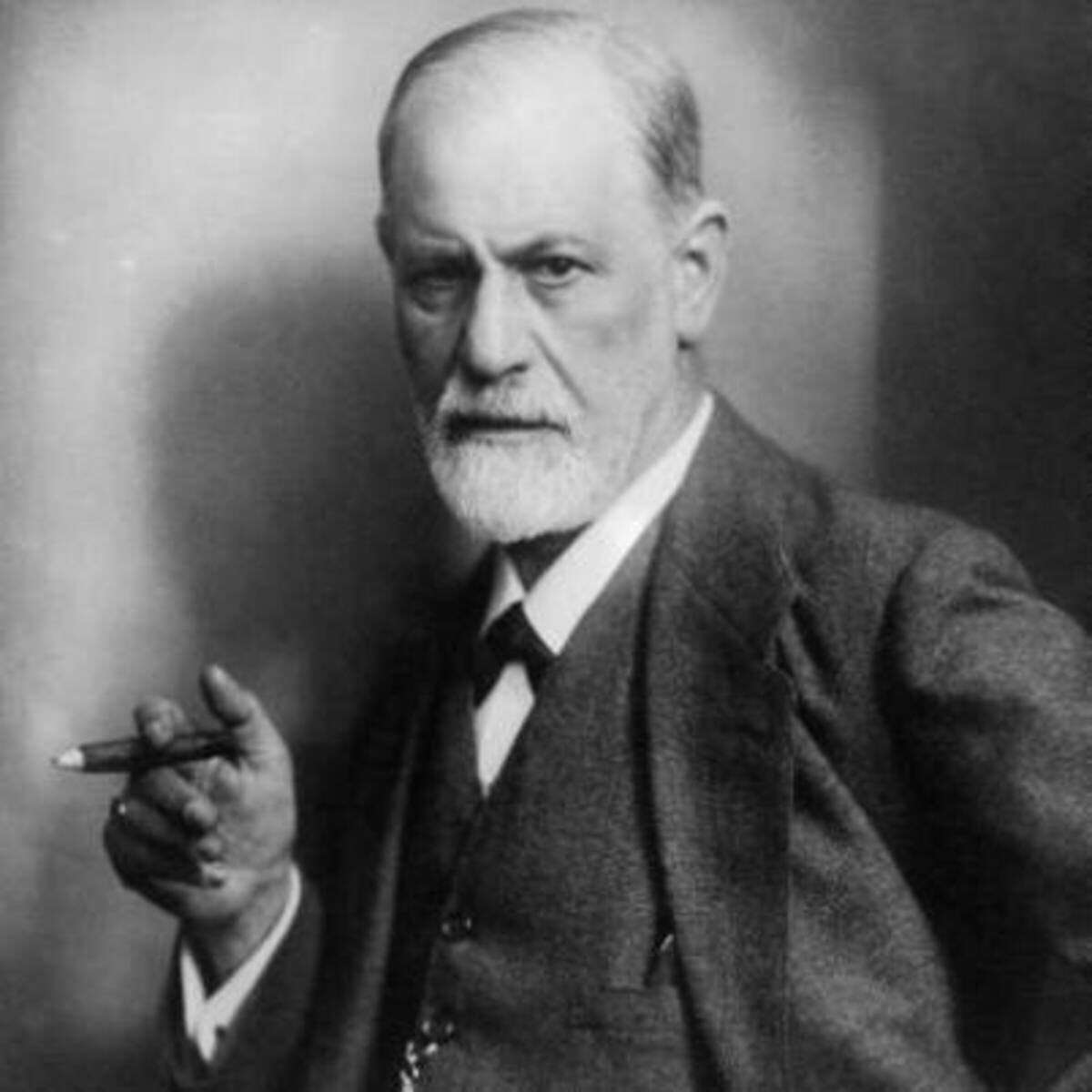
Sigmund Freud is a very well-known name. Many psychologists and others in the field continue to research and learn Freuds theories. While Freud worked, he had no means of studying and quantifying the mind or his theories by the scientific method.
Subsequently, question is, who is the founder of modern psychology in India? Narendra Nath Sen Gupta was a Harvard-educated Indian psychologist, philosopher, and professor, who is generally recognized as the founder of modern psychology in India along with Indian Scientist Gunamudian David Boaz.
Also asked, who are the fathers of psychology?
When hearing the names Sigmund Freud, Carl Jung, Alfred Adler, and William James, one thinks of the founding fathers of psychology. They are the most well-known pioneers and early founders who contributed their endeavors of better understanding to the psychological frailties.
You May Like: What Is Symmetry In Biology
The Father Of Modern Psychology
Wilhelm Wundt is the man most commonly identified as the father of psychology. Why Wundt? Other people such as Hermann von Helmholtz, Gustav Fechner, and Ernst Weber were involved in early scientific psychology research, so why are they not credited as the father of psychology?
Wundt is bestowed this distinction because of his formation of the world’s first experimental psychology lab, which is usually noted as the official start of psychology as a separate and distinct science.
In addition to making psychology a separate science, Wundt also had a number of students who went on to become influential psychologists themselves. Edward B. Titchener was responsible for establishing the school of thought known as structuralism,
James McKeen Cattell became the first professor of psychology in the United States, and G. Stanley Hall established the first experimental psychology lab in the U.S.
Wilhelm Wundt’s Career In Psychology

Wilhelm Wundt graduated from the University of Heidelberg with a degree in medicine. He went on to study briefly with Johannes Muller and later with the physicist Hermann von Helmholtz. Wundt’s work with these two individuals is thought to have heavily influenced his later work in experimental psychology.
Wundt later wrote the Principles of Physiological Psychology , which helped establish experimental procedures in psychological research. After taking a position at the University of Leipzig, Wundt founded the first experimental psychology lab in the world.
Although another psychology lab already existedWilliam James had established a lab at Harvard a few years beforeJames’ lab was focused on offering teaching demonstrations rather than experimentation. After studying with Wundt, G. Stanley Hall founded the first American experimental psychology lab at John Hopkins University.
Wundt is often associated with the theoretical perspective known as structuralism, which involves describing the structures that compose the mind.
Structuralism is regarded as the very first school of thought in psychology. He believed that psychology was the science of conscious experience and that trained observers could accurately describe thoughts, feelings, and emotions through a process known as introspection.
Wundt also established the psychology journal Philosophical Studies. In a 2002 ranking of the most influential psychologists of the 20th century, Wundt was ranked at number 93.
Recommended Reading: What Does Psychology Degree Involve
The 1st Wave: The Disease Model
During the second half of the 19th century and the early part of the 20th, psychology was concerned with curing mental disorders, such as schizophrenia and human complexes of various kinds .
And why not? There has always been, and will perhaps always be, a significant incidence of mental illness in all communities, irrespective of race or religion, caste or creed.
The attempt of psychologists to cure these ailments was quite natural and laudable, and the work of early psychologists, such as Sigmund Freud, Adler, and Carl Jung was indeed very effective. .
Over time, this disease focus pushed psychology towards the dark recesses of the human mind and away from the deeper well-springs of human energy and potential. As highlighted by Martin Seligman, in his 2008 TED talk on Positive Psychology, the negative focus of psychology resulted in three major drawbacks for the field:
Why Did Sigmund Freud Marry His Mother
In an effort to understand the nature of hysteria, he imagined that his father had abused him and some of his siblings. He came to realize that, as a boy, he had wanted to marry his mother, and saw his father as a rival for her love. Freud understood his own wishes to be universal among all boys in all cultures.
You May Like: Best Mice For Geometry Dash
Wundts Contributions To Psychology Summary
Wundt accomplished much in psychology. He contributed several things that no one else had touched on:
- He established psychology as its field, separate from biology and philosophy.
- He named the new field of psychology, and its practitioners psychologists.
- He founded the first psychology research lab.
- He devised some of the earliest techniques for studying psychology in a lab setting.
- His work led to his students formation of the first school of thought in psychology.
Wundt also made contributions that werent necessarily unique to psychology but helped establish him as an important force in this new field. These included:
- Writing a scholarly book on his methods and findings.
- Founding a psychology journal.
- Teaching students who went on to impact psychology significantly.
What Does it Mean to be the Father of a Field?
The title of father of psychology is simply a poetic way of describing a persons founding of a particular subject, and summarizing what people who study in that subjector were impacted by itfeel was a large and important contribution to it. This means that Freud was an early pioneer in the field, making him the father of psychology.
Reception By His Contemporaries
The psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin described the pioneering spirit at the new Leipzig Institute in this fashion: “We felt that we were trailblazers entering virgin territory, like creators of a science with undreamt-of prospects. Wundt spent several afternoons every week in his adjacent modest Professorial office, came to see us, advised us and often got involved in the experiments he was also available to us at any time.”
The internal consistency of Wundt’s work from 1862 to 1920, between the main works and within the reworked editions, has repeatedly been discussed and been subject to differing assessments in parts. One could not say that the scientific conception of psychology underwent a fundamental revision of principal ideas and central postulates, though there was gradual development and a change in emphasis. One could consider Wundt’s gradual concurrence with Kant’s position, that conscious processes are not measurable on the basis of self-observation and cannot be mathematically formulated, to be a major divergence. Wundt, however, never claimed that psychology could be advanced through experiment and measurement alone, but had already stressed in 1862 that the development history of the mind and comparative psychology should provide some assistance.
Read Also: How To Prepare Geography For Prelims
Wundt Is Bestowed This Distinction Because Of His Formation Of The Worlds First Experimental Psychology Lab Which Is Usually Noted As The Official Start Of Psychology As A Separate And Distinct Science
Who is considered the father of modern psychology. Wilhelm Wundt is typically considered the father of modern psychology. We live in the PR reality but not many of us know how it all came about. Freud is known for Psychoanalysis Wilhelm Wundt is the Father of Modern Psychology.
View this answer Kurt Lewin 1890-1947 was a German-American psychologist known as the father of modern social psychology. Wilhelm Wundt opened the Institute for Experimental Psychology at the University of Leipzig in Germany in 1879. He is widely seen as the father of contemporary positive psychology About Education 2013.
Wundt established the first psychology lab in Germany and introduced the scientific method to psychology. He founded the first experimental psychology lab in 1879 at the University of Leipzig in Germany. George Alexander Kelly April 28 1905 March 6 1967 was an American psychologist therapist educator and personality theorist.
Its interesting that this notable scientist a man who laid the foundations for the field of psychology is completely unknown to most people. Wilhelm Wundt is the man most commonly identified as the father of psychology. He is considered the father of cognitive clinical psychology and is best known for his theory of personality personal construct psychology.
Who is the father of modern psychology. He was also the main figure in promoting the field of biological psychiatry which sees mental illness as a biological issue. SIGMUND FREUD 1 Sigmund Freud.
Who Is The Father Of Modern Psychology And Why
Wilhelm Wundt opened the Institute for Experimental Psychology at the University of Leipzig in Germany in 1879. This was the first laboratory dedicated to psychology, and its opening is usually thought of as the beginning of modern psychology. Indeed, Wundt is often regarded as the father of psychology.
Recommended Reading: What Is The R Constant In Chemistry
Who Were The Pioneers Of Psychology In India
Turning now to the academic psychology that was transplanted from the West, we may note two pioneers: Narendra Nath Sengupta of the Calcutta University, who was trained in experimental psychology with Hugo Munsterberg at Harvard, and his successor Girindra Shekhar Bose, who became a self-taught psychoanalyst to be
Also Check: How Old Are Elton Johns Kids
Distinguished Psychology As A Science
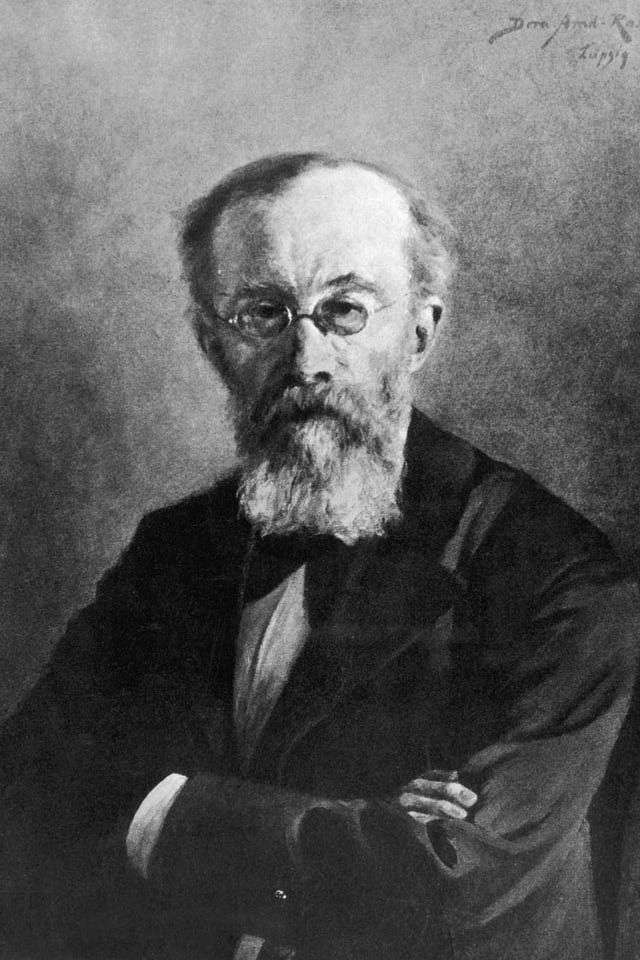
Before Wilhelm Wundt, there was no science known as psychology. People who studied the mind did so by learning about biology and philosophy. Wundt also started with these two subject areas, but he melded them together to create a distinct science of psychology that was more complete than the sum of its parts. Wundt was the first person to label himself a psychologist to study psychology.
Founded First Experimental Psychology Lab
Publications and Psychological Journals
Wundts book Principles of Physiological Psychology, published in 1874, detailed the experimental techniques hed developed for psychology research at that time. Wundt also established the first psychology journal, titled Philosophical Studies, which reported on experimental psychology findings as well as general concepts of psychology.
Contributions of Students
Structuralism involved breaking down the processes of the human mind to study them separately. Structuralism was also devoted to studying the overall mind structure, and how each individual part worked together to form a conscious thought.
If none of Wilhelm Wundts students had ever done anything significant in the new psychology field, Wundts contributions would have been enough to earn him his title. However, that wasnt the case his students became significant contributors in their own rights. These included:
Don’t Miss: What Does K Stand For In Math