What Is Total Alkalinity
Total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water that can both attract and release Hydrogen ions. This interference with Hydrogen is why alkalinity buffers against change in pH. Total alkalinity is primarily bicarbonate, carbonate, and hydroxide, along with a few others like cyanurate alkalinity. When acid is added, these alkali have the ability to neutralize some of the acid. In simpler terms, total alkalinity is a measurement of the waters ability to resist change in pH. In particular, alkalinity slows the reduction of pH. Too much alkalinity is actually a source of rising pH. The more alkalinity you have, the more acid it takes to reduce pH.
Related: What is Alkalinity?
Total alkalinity is measured by its concentration in parts-per-million , and the ideal range is from 80-120 ppm, depending on the type of chlorine you use. For example, Trichlor has a low pH of 2.8, so given how acidic Trichlor is, a trichlor pool needs higher alkalinity. Another reason for more alkalinity in a trichlor pool is because the CYA in trichlor offsets alkalinity when doing LSI corrections.
Did you notice that total alkalinity is not measured on the pH scale?
Unified Absolute Ph Scale
In 2010, a new “unified absolute pH scale” has been proposed that would allow various pH ranges across different solutions to use a common proton reference standard. It has been developed on the basis of the absolute chemical potential of the proton. This model uses the Lewis acidbase definition. This scale applies to liquids, gases and even solids.
Preparation Occurrence And Applications
Phenyl groups are usually introduced using reagents that behave as sources of the phenyl anion or the phenyl cation. Representative reagents include phenyllithium and phenylmagnesium bromide . Electrophiles attack benzene to give phenyl derivatives:
- C6H6 + E+ C6H5E + H+
where E+ = Cl+, NO2+, SO3. These reactions are called electrophilic aromatic substitutions.
- Representative compounds containing phenyl groups
-
Atorvastatin , a blockbuster drug featuring two phenyl and one p-fluorophenyl groups. It is used to lower cholesterol in people with hypercholesterolaemia.
-
Fexofenadine , another blockbuster drug, which features a diphenylmethyl group as well as a p–phenylene group. It is an antihistamine used to treat allergies.
-
Phenylalanine, a common amino acid.
-
Biphenyl, consisting of two phenyl groups. The two rings tend not to be coplanar.
-
Chlorobenzene , a solvent.
Also Check: Who Is Khloe Kardashian’s Real Dad
Monoprotic And Polyprotic Bases
Bases with only one ionizablehydroxide ion per formula unit are called monoprotic since they can accept one proton . Bases with more than one OH- per formula unit are polyprotic.
The number of ionizablehydroxide ions present in one formula unit of a base is also called the acidity of the base. On the basis of acidity bases can be classified into three types: monoacidic, diacidic and triacidic.
Iupac Definition Of Ph
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry has a slightly different pH scale that is based on electrochemical measurements of a standard buffer solution. Essentially, the definition uses the equation:
pH = -log aH+
where aH+ stands for hydrogen activity, which is the effective concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. This might be slightly different from the true concentration. The IUPAC pH scale also includes thermodynamic factors, which may influence pH.
For most situations, the standard pH definition is sufficient.
You May Like: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate Answers
Site Evidence That Supports Excluding High Ph As A Candidate Cause
There are no site observations that specifically provide evidence of the absence of high pH. We strongly caution against using benchmarks of effects as evidence for excluding high pH from your initial list of candidate causes. Different species have different pH requirements, different sites have different naturally occurring levels of pH, and other agents may enhance the effects of pH.
Ph Of Acids And Bases
The pH of a solution varies from 0 to 14.
- Solutions having a value of pH ranging 0 to 7 on pH scale are termed as acidic and for the value of pH ranging 7 to 14 on pH scale are known as basic solutions.
- Solutions having the value of pH equal to 7 on pH scale are known as neutral solutions.
Solutions having the value of pH equal to 0 are known to be strongly acidic solutions. Further, the acidity decreases as the value of pH increases from 0 to 7 whereas, solutions with the value of pH equal to 14 are termed as strongly basic solutions.
The basicity decreases as the value of pH decreases from 14 to 7. The strength of acids and bases depends on the number of H+ and OH ions produced. Acids furnishing more number of H+ ions are known to be strong acids and vice versa.
The degree of ionisation of acids and bases differ for different acids and bases. It helps in the determination of the strength of acids and bases. The strength of an acid depends on the concentration of hydronium ion too. With the help of the comparison between the concentration of hydronium ion and the hydroxyl ion, we can distinguish between acids and bases.
- For acidic solution: >
- For neutral solution: =
- For basic solution: <
Don’t Miss: Glencoe Geometry Practice Workbook Answers
Examples Of Ph In A Sentence
pHSmithsonian MagazinepHELLEpH oregonlivepH baltimoresun.compH ForbespH baltimoresun.compH clevelandpHUSA TODAY
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘pH.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Acid Solutions And Basic Solutions
Now that we have established a reference point for the basicity and acidity of solutions, we can discuss how acids and bases are defined. Acidic solutions are those solutions that have a greater H+ concentration than pure water, while basic solutions are those that have an H+ concentration lower than that of pure water. To put that another way:
Base = H+ concentration < 1 x 10^-7 M
Acid = H+ concentration > 1 x 10^-7 M
The concentration of hydrogen ions within a solution is usually given in pH terms, which is calculated as the inverse log of the hydrogen ion concentration for that given solution.
pH = -log10
So putting the hydrogen ion concentration of water into this formula would get you a value of 7.0, or the neutral pH on the pH scale. As you might be able to guess, substances made out of mainly water such as the cytosol found in cells or the blood in the human body, have pH values very near the neutral seven. Acids and bases can be added to a water-based solution, shifting the concentration of that solution away from the neutral pH point. Bases usually raise the pH level through the introduction of hydroxide into the environment, which collects the hydrogen ions and pulls them out of the solution. Meanwhile, acidic substances are those that increase hydrogen ion concentration by dissociating and introducing one of its hydrogen atoms into the solution.
Read Also: 4 Goals Of Psychology Example
What Does The Ph Scale Measure
The pH scale measures the relative acidity and alkalinity of solutions. Its a negative logarithmic scale of base ten that measures the potential of a solution to accept protons in the form of hydrogen ions. For example, a solution with pH level 8 is ten times more alkaline than pure water, which has a pH level of 7. This implies that the particular solute has ten times more potential to accept protons compared to water.
Therefore, basic or alkaline solutions have higher pH readings because of their potential to accept hydrogen ions. Acidic solutions already have high concentrations of hydrogen ions, which is why they have lower pH values. The rule of ten still applies here, though, with each integer value having a difference of ten times.
Although pH isnt the absolute criterion of acid or base strength, its a good measurement for the concentration of a particular acid or base solution. The strength of an acid or base is measured by the tendency of its ions to completely dissociate in aqueous solutions. This is measured by the dissociation constant, which is the ratio between the ions and the molecular form of the dissolved substance. An acid always yields hydrogen positive ions while a base always yields hydroxide negative ions .
Hydrogen ion concentration is calculated in an aqueous solution based on the molarity of the hydronium ions, which is measured in moles per litre. You need to know the molarity to calculate the pH. The formula is simple:
pH = log
What Ph Stands For
The term “pH” is used to mean the power of hydrogen within the solution. There is some debate within the scientific community of where the “p” comes from, but it now is indicative of the word “power.” It indicates the molar concentration of hydrogen ions within the solution and measures the acidity or alkalinity — also called the base — of the solution. The pH level is measured on a negative base-10 logarithm.
Recommended Reading: Ccl4 Molecular Structure
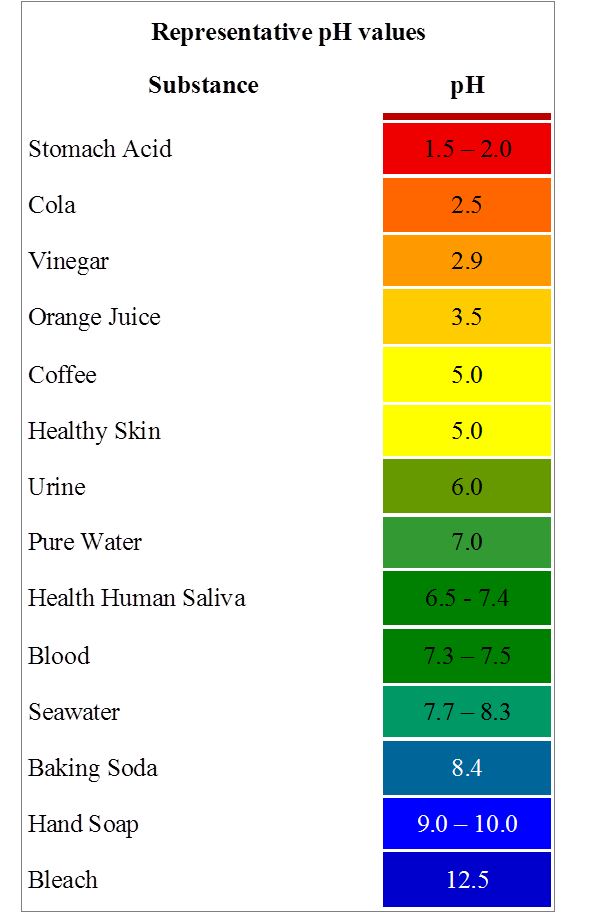
Examples Of Ph Values
The pH of a solution is a measure of the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution and as such is a measure of the acidity or basicity of the solution. The letters pH stand for “power of hydrogen” and numerical value for pH is just the negative of the power of 10 of the molar concentration of H+ ions.
The usual range of pH values encountered is between 0 and 14, with 0 being the value for concentrated hydrochloric acid , 7 the value for pure water , and 14 being the value for concentrated sodium hydroxide . It is possible to get a pH of -1 with 10 M HCl, but that is about a practical limit of acidity. At the other extreme, a 10 M solution of NaOH would have a pH of 15.
In pure water, the molar concentration of H+ ions is 10-7 M and the concentration of OH- ions is also 10-7 M. Actually, when looked at in detail, it is more accurate to classify the concentrations as those of + and -. The product of the positive and negative ion concentrations is 10-14 in any aqueous solution at 25°C.
An important example of pH is that of the blood. Its nominal value of pH = 7.4 is regulated very accurately by the body. The kidney regulates the pH by balancing the concentrations of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. If the pH of the blood gets outside the range 7.35 to 7.45 the results can be serious and even fatal.
Phenolpthalein is also a common indicator, being colorless in solution at pH below 8 and turning pink for pH above 8.
Site Evidence That Suggests Including Low Ph As A Candidate Cause
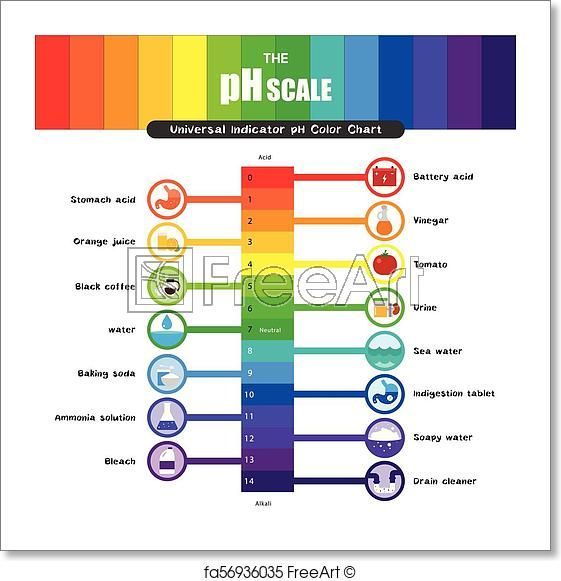
Figure 5
Low pH may be indicated by the presence of metal precipitates on stream substrate. Common metal precipitates observed in streams under acidic conditions include iron, manganese, and aluminum which have a yellow , black, or white color, respectively . Metal precipitates, notably iron, can result in a thick floc that smothers biota and degrades habitat quality to the point that many fauna are extirpated.
Black or brown water, common in southeastern U.S. swamps and bayous are typically acidic due to humic and other natural organic acids derived from peat and dissolved vegetative material.
Some filamentous algae are tolerant of low pH and may dominate acidified lakes and streams without heavy precipitates . They include the filamentous green algae Klebsormidium, Microspora, Mougeotia, Ulotrix and Stigeoclonium .
Also Check: Beth Thomas Child Of Rage Now
Ph Definition And Origin
pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration in a water-based solution. The term “pH” was first described by Danish biochemist Søren Peter Lauritz Sørensen in 1909. pH is an abbreviation for “power of hydrogen” where “p” is short for the German word for power, potenz and H is the element symbol for hydrogen. The H is capitalized because it is standard to capitalize element symbols. The abbreviation also works in French, with pouvoir hydrogen translating as “the power of hydrogen”.
Naturally Occurring Ph Indicators
Many plants or plant parts contain chemicals from the naturally colored anthocyanin family of compounds. They are red in acidic solutions and blue in basic. Anthocyanins can be extracted with water or other solvents from a multitude of colored plants and plant parts, including from leaves flowers berries and stems . Extracting anthocyanins from household plants, especially red cabbage, to form a crude pH indicator is a popular introductory chemistry demonstration.
Litmus, used by alchemists in the Middle Ages and still readily available, is a naturally occurring pH indicator made from a mixture of lichen species, particularly Roccella tinctoria. The word litmus is literally from ‘colored moss’ in Old Norse . The color changes between red in acid solutions and blue in alkalis. The term ‘litmus test’ has become a widely used metaphor for any test that purports to distinguish authoritatively between alternatives.
Hydrangea macrophylla flowers can change color depending on soil acidity. In acid soils, chemical reactions occur in the soil that make aluminium available to these plants, turning the flowers blue. In alkaline soils, these reactions cannot occur and therefore aluminium is not taken up by the plant. As a result, the flowers remain pink.
Another useful natural pH indicator is the spice Turmeric. It turns yellow when exposed to acids and reddish brown when in presence of an alkalis.
| Indicator |
|---|
Read Also: Punchline Bridge To Algebra 2nd Ed Answer Key
Finding A Balance: Ph And The Human Body
Whats better for you: sucking on a lemon or snacking on a bunch of bananas? To answer this question, you first need to understand the impact of pH on your body and how to manage its delicate balance.
The fine line between acidic and alkaline
The human body has a natural pH of 7.4 and it needs to maintain this level in order to function at its peak. Everything we consume has its own pH level. So our bodies are constantly working to restore the fragile balance thats temporarily disrupted whenever we eat or drink something thats too acidic or alkaline. This process is called cellular homeostasisthe bodys ability to maintain balance in the face of external challenges.
What Is The Ph Scale
Lucy Bell-Young
The pH scale is a precise way of classifying the acidity, basicity or neutrality of a solution. As a logarithmic scale, 1 pH unit is ten times stronger, or ten times weaker, than the one below or above it, depending on its position: a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 5, but ten times weaker than a pH of 3. Continue reading for an in-depth look at what the pH scale measures, how it works, and how to use it.
In this post:
You May Like: How To Calculate The Percent Error In Chemistry
Why Is Ph Important
Some chemical reactions only take place under certain pH conditions. Sometimes this is because H+ or OH acts as a reactant in the reaction. In other cases, acid or base can catalyze a reaction, meaning that they affect the rate of the reaction.
Living organisms rely on a wide variety of biochemical reactions and processes, most of which require specific pH ranges. As a result, ecosystems like lakes and rivers thrive under the pH conditions that are favorable to the biochemistry of the local flora and fauna.
Like an ecosystem, the human body has a certain pH that allows the proper functioning of the different tasks that our body performs. We require one value in our blood, and a totally different one in our digestive fluids. Otherwise, normal biochemistry could break down, causing serious health issues. Luckily, humans and many other creatures have blood that is buffered, so that the pH cannot change easily. This is why if you drink a bottle of alkaline water or acidic soda, your blood will stay nearly the same, keeping you safe from the effects of imbalance!
Another consequence of this safety net built into your blood is that the common health benefits associated with alkaline water are mostly made-up. Even if your blood were somehow too acidic, drinking some water with pH 8 would barely change it!
What Causes High Ph In Water
The cause of the unbalanced pH is the soil, bedrock, or other underlying composition from which the water source comes. High alkaline water is a consequence of rocky areas with a lot of calcareous. It contains compounds of carbonate, bicarbonate, and hydroxide that dissolve and migrate with the water, increasing its pH.
Don’t Miss: Span Linear Algebra Definition
The Basis For The Ph Scale
Even if youre not intimately familiar with the concepts of acids and bases, you certainly have some exposure to them. Basic substances are things like baking soda, while acidic substances are things like orange juice and soda. Substances are classified as a base or an acid-based upon the concentration of hydrogen ions that the substance has. The H in pH represents the level of hydrogen ion activity in a given solution. So its possible to define acidic and basic solutions this way:
An acidic solution is a solution with levels of hydrogen ions greater than the amount found in pure water . A basic solution, in contrast, has a hydrogen ion concentration lower than that of water.
In terms of the number of hydrogen ions produced through autoionization, the amount is equal to 1 x 10^-7 M . The notation refers to moles per liter of water. The number of ionized water molecules is an incredibly small percentage of the total number of water molecules found in any amount of pure water.