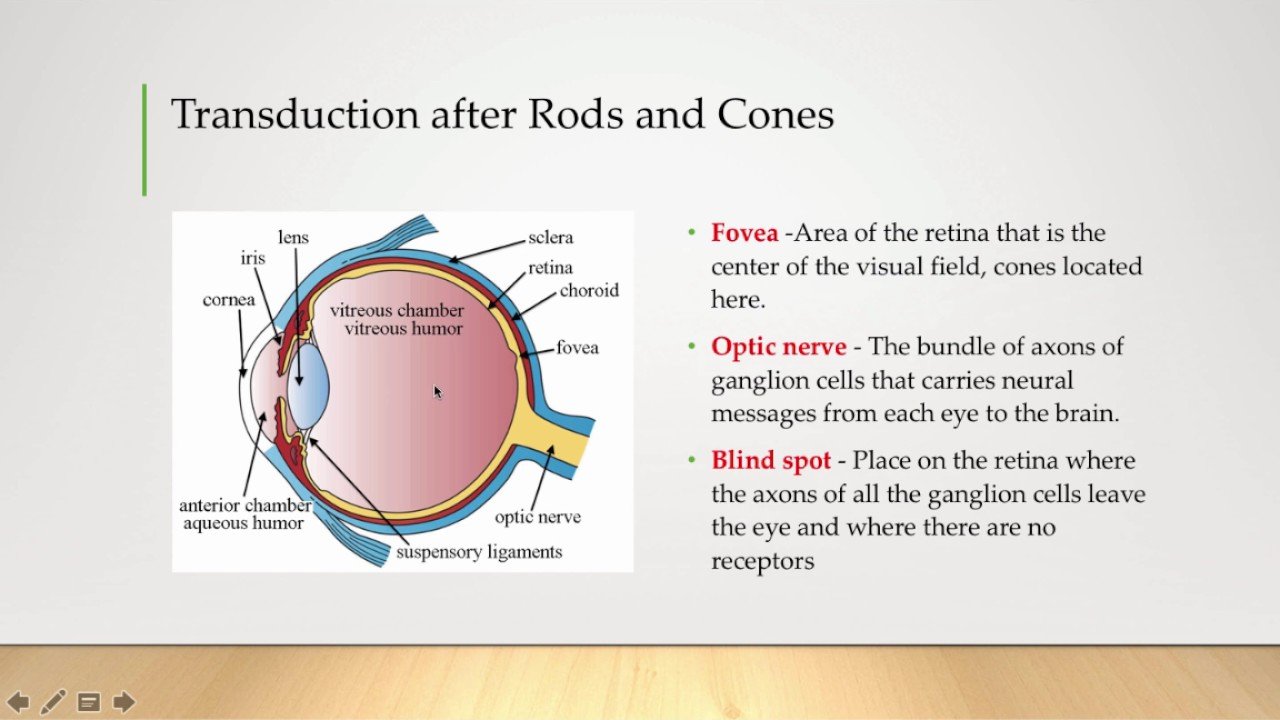
The Outer And Middle Ear
The visible part of the ear or pinna collects the changes in air pressure that carry sound and funnel them down the external auditory canal to the tympanic membrane or ear drum. The ear drum vibrates in response, which in turn moves three tiny bones in the Eustachian tube in succession. The end of the stapes, known as its footplate, presses onto the oval window of the snail-shaped, fluid-filled cochlea.
This round-about mechanism for the transmission of vibrational energy from air to the cochlea at first glance seems over-designed and prone to failure. Yet further scrutiny reveals the reason for such complexity. The surface of the tympanic membrane is several times larger than that of the stapes footplate, so the ossicles concentrate vibrational energy on it. The lengthened end of the incus acts as a lever in transmitting force to the stapes, which also concentrates the vibrational energy on the oval window. Thus the middle ear acts as a mechanical amplifier, so that by the time sound waves reach the organ of Corti, their amplitude is twenty-two times greater than that of the air impinging on the pinna.
Cochlea is Latin for snail
source:
Motivations Expectations And Perception
Motivation can also affect perception. Have you ever been expecting a really important phone call and, while taking a shower, you think you hear the phone ringing, only to discover that it is not? If so, then you have experienced how motivation to detect a meaningful stimulus can shift our ability to discriminate between a true sensory stimulus and background noise. The ability to identify a stimulus when it is embedded in a distracting background is called signal detection theory. This might also explain why a mother is awakened by a quiet murmur from her baby but not by other sounds that occur while she is asleep. Signal detection theory has practical applications, such as increasing air traffic controller accuracy. Controllers need to be able to detect planes among many signals that appear on the radar screen and follow those planes as they move through the sky. In fact, the original work of the researcher who developed signal detection theory was focused on improving the sensitivity of air traffic controllers to plane blips .
Figure 7. In the Müller-Lyer illusion, lines appear to be different lengths although they are identical. Arrows at the ends of lines may make the line on the right appear longer, although the lines are the same length. When applied to a three-dimensional image, the line on the right again may appear longer although both black lines are the same length.
Dark And Light Adaptation
Humans have the ability to adapt to changes in light conditions.;As mentioned before, rods are primarily involved in our ability to see in dim light. They are the photoreceptors responsible for allowing us to see in a dark room. You might notice that this night vision ability takes around 10 minutes to turn on, a process called dark adaptation. This is because our rods become bleached in normal light conditions and require time to recover. We experience the opposite effect when we leave a dark movie theatre and head out into the afternoon sun. During light adaptation, a large number of rods and cones are bleached at once, causing us to be blinded for a few seconds. Light adaptation happens almost instantly compared with dark adaptation. Interestingly, some people think pirates wore a patch over one eye in order to keep it adapted to the dark while the other was adapted to the light. If you want to turn on a light without losing your night vision, dont worry about wearing an eye patch, just use a red light; this wavelength doesnt bleach your rods.
Read Also: Copulation Definition Biology
Nearly One Third Of Participants In A Study Did Not Notice That A Red Cross Passed On The Screen Because Their Attention Was Focused On The Black Or White Figures
Motivation can also affect perception. Have you ever been expecting a really important phone call and, while taking a shower, you think you hear the phone ringing, only to discover that it is not? If so, then you have experienced how motivation to detect a meaningful stimulus can shift our ability to discriminate between a true sensory stimulus and background noise. This motivational aspect of expectation in conversation additionally may be why such strong inattentional blindness has been found in relation to cell phone use. The ability to identify a stimulus when it is embedded in a distracting background is called signal detection theory.
Signal;detection theory:;A theory explaining explaining how various factors influence our ability to detect weak signals in our environment.
Exercise And Critical Thinking
References
Chisolm, T. H., Willott, J. F., & Lister, J. J. . The aging auditory system: Anatomic and physiologic changes and implications for rehabilitation. International Journal of Audiology, 42, 2S32S10.
Corey, D. P., García-Añoveros, J., Holt, J. R., Kwan, K. Y., Lin, S.-Y., Vollrath, M. A., Amalfitano, A.,Zhang, D.-S. . TRPA1 is a candidate for the mechano-sensitive transduction channel of vertebrate hair cells. Nature, 432, 723730. Retrieved from
Dettman, S. J., Pinder, D., Briggs, R. J. S., Dowell, R. C., & Leigh, J. R. . Communication development in children who receive the cochlear implant younger than 12 months: Risk versus benefits. Ear and Hearing, 28, 11S18S;
Dorman, M. F., & Wilson, B. S. . The design and function of cochlear implants. American Scientist, 92, 436445.
Kochkin, S. . MarkeTrak VII: Hearing loss population tops 31 million people. Hearing Review, 12 1629.
Middlebrooks, J. C., & Green, D. M. . Sound localization by human listeners. Annual Review of Psychology, 42, 135159.
Tennesen, M. . Gone today, hear tomorrow. New Scientist, 2594, 4245.
Also Check: Afda Mean Median Mode Range Practice Answer Key
When A Transduction Psychology Textbook Says You Cant Do It What Should You Do
The Transduction Psychology Handbook is the latest in a series of books that have become a cottage industry for transduction researchers and teachers alike.
The book has been praised for its clarity and clarity of intent, its rigorous scientific reasoning, its emphasis on how to use transduction as a way to better understand the world, and its wide array of examples that show how transduction can be applied to everyday problems.
Its also the book that most likely to put your brain on autopilot.
In this post, Im going to explore what you should do if you find yourself stuck on a transference problem, whether youre a teacher, a teachers assistant, a researcher, a parent, a colleague, or just an anxious parent.
If you want to learn more about how transference works and how to implement transduction in your teaching or research, read on.
Transduction as an approach to learning Transduction is a field that is mostly a theoretical one.
Most researchers in the field think transduction is an approach that we can learn from, or should use.
It is, after all, the process of integrating ones thoughts and feelings into the physical world.
So why shouldnt we use transference as a tool to learn from it?
There are a number of reasons for this.
Transference is an attempt to apply what we know about the world to the world we live in, and it is a way of using science to understand how things work.
It allows us to learn things that we might not be able to otherwise learn from the world.
Balance And The Vestibular System
The inner ear isnt only involved in hearing; its also associated with our ability to balance and detect where we are in space. The vestibular system is comprised of three semicircular canalsfluid-filled bone structures containing cells that respond to changes in the heads orientation in space. Information from the vestibular system is sent through the vestibular nerve to muscles involved in the movement of our eyes, neck, and other parts of our body. This information allows us to maintain our gaze on an object while we are in motion. Disturbances in the vestibular system can result in issues with balance, including vertigo.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Tongue And Taste Buds
The sense of taste is transduced by taste buds, which are clusters of 50-100 taste receptor cells located in the tongue, soft palate, epiglottis, pharynx, and esophagus. The tongue is the main sensory organ of the gustatory system. The tongue contains papillae, or specialized epithelial cells, which have taste buds on their surface. There are three types of papillae with taste buds in the human gustatory system:
- fungiform papillae, which are mushroom-shaped and located at the tip of the tongue;
- foliate papillae, which are ridges and grooves toward the back of the tongue;
- circumvallate papillae, which are circular-shaped and located in a row just in front of the end of the tongue.
Each taste bud is flask-like in shape and formed by two types of cells: supporting cells and gustatory cells. Gustatory cells are short-lived and are continuously regenerating. They each contain a taste pore at the surface of the tongue which is the site of sensory transduction. Though there are small differences in sensation, all taste buds, no matter their location, can respond to all types of taste.
Taste Buds: A schematic drawing of a taste bud and its component pieces.
The Process Of Hearing
Hearing begins with pressure waves hitting the auditory canal and ends when the brain perceives sounds. Sound reception occurs at the ears, where the pinna collects, reflects, attenuates, or amplifies sound waves. These waves travel along the auditory canal until they reach the ear drum, which vibrates in response to the change in pressure caused by the waves. The vibrations of the ear drum cause oscillations in the three bones in the middle ear, the last of which sets the fluid in the cochlea in motion. The cochlea separates sounds according to their place on the frequency spectrum. Hair cells in the cochlea perform the transduction of these sound waves into afferent electrical impulses. Auditory nerve fibers connected to the hair cells form the spiral ganglion, which transmits the electrical signals along the auditory nerve and eventually on to the brain stem. The brain responds to these separate frequencies and composes a complete sound from them.
Structural diagram of the cochlea: The cochlea is the snail-shaped portion of the inner ear responsible for sound wave transduction.
Also Check: What Type Of Math Is On The Ged
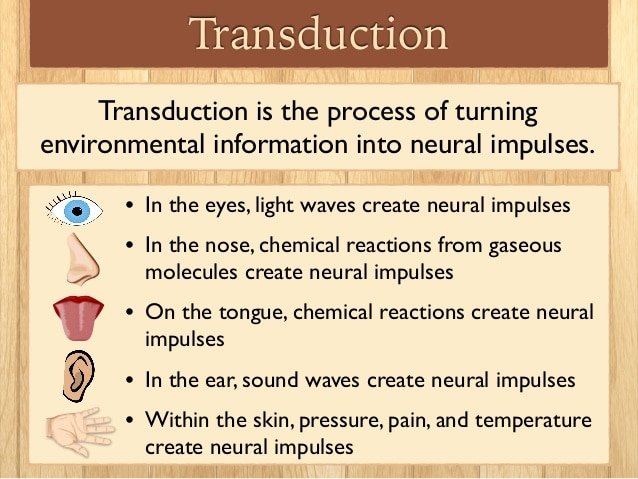
In Sensation The Transforming Of Stimulus Energies Such As Sights Sounds And Smells Into Neural Impulses Our Brains Can Interpret
Transduction psychology definition. Terms in this set 22 Transduction. The conversion of the energy of a stimulant into an alteration within the electric potential across the membrane of a receptor cell. According to Jean Piagets theories on cognitive development transductive reasoning or transductive logic is the primary form of reasoning used during the preoperational stage of development.
Psychology definition for Transduction in normal everyday language edited by psychologists professors and leading students. Start studying AP Psychology Unit 4 sensation and transduction. See Article History Transduction a process of genetic recombination in bacteria in which genes from a host cell a bacterium are incorporated into the genome of a bacterial virus bacteriophage and then carried to another host cell when the bacteriophage initiates another cycle of infection.
This stage occurs approximately from the ages of 2-7. Transduction is the process by which sensory cells in the sensory organs translate external signals from stimuli into neural signals that are sent to. Conversion of one form of energy into another.
Transduction definition is the action or process of transducing. Through visual transduction images on the retina are transformed into signals which are sent to the brain to be interpreted. Transduction can be affected by our experiences such as through adaptation.
Help us get better.
How Does A Stimulus Reach The Brain
A withdrawal reflex starts when sensory nerves in your skin receive a stimulus from outside the body. That stimulus starts a nerve impulse along the cell membrane. Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and nerves.
Recommended Reading: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
The Key To The Senses: Transduction
Heres probably the most basic question in all of sensory neuroscience . How does a ray of light enter our nervous system, to eventually become something that we see? How in fact does anything external get turned into something internal .
The answer is simple, so simple in fact that it is one word:Transduction.
It’s about this simple…
OK fine, its a simple answer if you know what transduction means. So Im going to explain it to everyone now.
In a sentence, transduction is the conversion of one form of energy into another. Try to think back and remember the different types of energy:
They might have missed a couple out…
- Kinetic
- Gravitational potential
- Elastic Potential
Now lets lay these out in relevance to our 6 senses .
Touch:
- Elastic potential
Taste and Smell:
Self :
- Elastic potential.
These are all the main types of energy that we can sense. Now heres the problem:
The nervous system only uses one type of energy, and that is electric.
Therefore if we the brain is what allows us to sense the outside world, all of these energies we mentioned previously have to be converted into electrical energy so they can enter the brain. That is where transduction come in.
In all of our sense organs there are nerve endings which contain hundreds and thousands of receptors. Each organ will have different types of receptors that will react differently to each type of energy.
There you go, now if anyone ever asks you how we can sense things, just say: Transduction!
Smell And Taste: The Chemical Senses
The two most underappreciated senses can be lumped into the broad category of chemical senses. Both olfaction and gustation require the transduction of chemical stimuli into electrical potentials. I say these senses are underappreciated because most people would give up either one of these if they were forced to give up a sense. While this may not shock a lot of readers, take into consideration how much money people spend on the perfume industry annually . Many of us pay a lot more for a favorite brand of food because we prefer the taste. Clearly, we humans care about our chemical senses.
Also Check: What Kind Of Math Is On The Ged Test
Examples Of Transduction In A Sentence
transductionQuanta Magazinetransduction Quanta Magazinetransduction Ars TechnicatransductionWIRED
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘transduction.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
The Basilar Membrane And Tonotopic Mapping
All of this is to get you to the point of understanding what happens to the strip of tissue that separates the vestibular and tympanic canals and thus bends with the transfer of pressure from one side to the other. Known as the basilar membrane, it is fixed at the base of the cochlea and free to move at the apex. Any vibration impinging on it creates what is known as a traveling wave. You have probably created a traveling wave yourself. Imagine that you want to shake out a wet towel. You grasp it with both hands across a narrow end, and give it a shake. A wave runs down it from your hands to the end. That is a traveling wave. It is much more readily appreciated in a moving one, of which the Internet affords us a rich selection, such as the general one at Wikipedias Periodic travelling wave or the particular one created on the basilar membrane at Mammano & Nobilis Cochlea site.
There is one way in which the basilar membrane is very different from a towel, however. A towel is of uniform width and stiffness throughout its length. The basilar membrane is not; it is narrower and stiffer at the base, and wider and more flexible at the apex. This is much easier to grasp if the cochlea is uncoiled into a straight tube, as in the figure below:
Fig. 40 Cochlea uncoiled to show shape of basilar membrane
Fig. 41 The basilar membrane as a xylophone
You May Like: Imagine Math Login
In Physiology As Relates To Psychology
Transduction in physiology also has a meaning that relates to psychology when discussing the biological origins of the mind: that is, transduction meaning the transportation of stimuli to the central nervous system, when physical signals from the environment are transformed into electrical or neural signals.Receptor cells produce an electrical change in response to a physical stimulus.
The New College Professor
This activity;is a personal favorite, and it might be because it is adapted from a party game and can be used as a springboard to discuss multimodality, multimedia, popular culture, or literacy.;This assignments requires students to transduct and circulate from peer-to-peer, drawing on the ways in which meaning is potentially stable or changed through transduction and;circulation.
What is transduction? Transduction is moving meaning from one mode/medium to another mode/medium. One example of tranduction is a novel turned into a movie, or a saying hello versus waving hello versus writing hello.
Comic Book
Blockbuster Movie
What is;circulation?;Circulation describes how something moves from person-to-person. One example of this is the phrase YOLO which began with Drakes song The Motto and then moved to Facebook, and Twitter. The user determines the deliverance, because they could say something like, Just booked a flight to Paris. YOLO! or ironically, as in My cat just died YOLO.
Explicit, show with discretion
Classroom appropriate
Directions for Students:;
- Fold paper twice .
- RULE: You can only look at he sentence or drawing your partner made last.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answer Key