Discussion And Study Questions
How Geography Has Shaped And Continues To Shape Russia
Russias lush green geography on the Western front has historically favoured aggressors, and modern Russia is trying to make amends through various steps.
As the Russian Federation continues the resurge following its drastic diminution from the days of the Cold War, Russias hard-handed political approach continues to raise questions about the motivation for such a belligerent foreign policy. The raison dêtre for such a policy, however, makes sense as soon as one catches a glance of a map of the modern Russian state and takes into account the history of the Russians in the past century.
Role of geographical borders
From a security viewpoint, one of the best assets a nation can have is a geographical barrier that doubles as a boundary for the country. Such an arrangement has ensured the security of numerous superpowers in the past and continues to do so in the present. The United States is insulated by two oceans, a frigid and friendly northern neighbour, and another ally to the south with an arid desert border to hamper any potential aggression from Central America.
The Russian disadvantage
Challenges faced by Russia
Present scenario and the future
Why Did Settlers Move To California
Commentary. Settlers flocked to the Far West for many reasons. They sought adventure, farmland, an escape from the constraints of civilization, and new starts. California was attractive because of its climate and the fact that the Spanish and Mexicans had begun to organize the territory through the mission system.
Read Also: Geometry Basics Unit 1 Test
What Geographic Disadvantages Does Russia Have
Russia also lacks rivers. The few it has flow in the wrong direction, or nowhere near urban areas. East of The Urals, the majority flow south to north, into the Arctic Ocean, which is useless for trade, and they dont pass through any cities. An exception is the Lena river, which passes through Yakutsk.
Russian History And Expansion
Russias current geographic landscape has been shaped by physical features, such as climate and topography, as well as historical events. Why is the capital of Russia Moscow, and why is its population so clustered in the west? In the 13th century, Moscow was actually an important principality, or city-state ruled by a monarch. The Grand Duchy of Moscow, or Muscovy as it was known in English, became a powerful state, defeating and surrounding its neighbors and claiming control over a large portion of Rus territory, an ancient region occupied by a number of East Slavic tribes. The Slavs represent the largest Indo-European ethno-linguistic group in Europe and include Poles, Ukrainians, Serbs, as well as Russians.
From the mid-1400s onward, the Muscovite territory expanded at an impressive rate . In 1300 CE, the territory occupied an area of around 20,000 square kilometers by 1462 CE, that number increased to 430,000 square kilometers. By 1584 CE, the territory had swelled to 5.4 million square kilometers.
During this time, Russias government shifted as well. In 1547 CE, Grand Duke Ivan IV, better known as Ivan the Terrible, crowned himself the first Tsar. The term tsar, also spelled czar, stems from the Roman title Caesar and was used to designate a ruler, much like the term king or emperor. Ivan IV nearly doubled the territory of Russia during his reign, conquering numerous surrounding ethnic groups and tribes.
Recommended Reading: June 2017 Algebra 2 Regents Answers With Work
Why Did The Early Californians Travel So Much
The earliest Californians were adventurous Asians who made their way across the Bering Straits to Alaska thousands of years ago when a warmer climate and a now-vanished land bridge made such travel easier. Mexican California In 1808, Spains American colonies, one by one, began to fight for independence.
Russias Climate And Geography
John Etty examines how far history has been moulded by enviroment.
Modern textbooks on Russian history often include an introductory chapter on the countrys climate and natural geography. Writers, it seems, believe Russias physical environment is either so significant or so widely misunderstood that students must receive an explicit description. Natural geography and climate are not always important in a regions history, however, and it is possible to overstate the impact that Russias geography has had on its history. The winter defeats of Napoleon and Hitler, for instance, were more than just seasonal coincidences. Nevertheless, the nature of Russias physical environment has undoubtedly had a significant impact on its history in recent centuries.
To continue reading this article you will need to purchase access to the online archive.
If you have already purchased access, or are a print & archive subscriber, please ensure you are logged in.
Please email if you have any problems.
Read Also: Abiotic Biology
Battle With Fate: Russia Geography And The Historical Cycle
BESA Center Perspectives Paper No. 953, September 20, 2018
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Russia under Putin falls neatly into the Russian historical cycle. When the old state is in decline, chaos ensues, and a new, powerful leader emerges to rebuild Russia. There are plenty of comparisons from Russian history that echo Putins rise and success but there are crucial differences, too, which help explain his inability to transform Russia into a truly global power.
Historical comparisons, when made judiciously, can help analyze current political realities. Russian history contains cycles that recur over centuries.
The cycle runs this way: Russia sinks into chaos, rises from that chaos, returns as a regional and sometimes even global power, aspires to consolidate its gains through strongman rule and the addition of neighboring territories, and then collapses. Then the cycle begins anew.
One of the constants of Russias fateful historical cycle is its geography. Russia is vast, spanning almost the entire northern Eurasian landmass. However, far more than half the country is non-navigable . The climate is so harsh that it hinders any meaningful agricultural work beyond the Ural Mountains.
Three eras in Russian history demonstrate this recurrent pattern, which is rooted in Russias geography. This pattern can be seen in early 21st century Russia under the rule of Vladimir Putin.
BESA Center Perspectives Papers are published through the generosity of the Greg Rosshandler Family
Economics And Development In The Soviet Union
The Soviet Government, led by Lenin and later by Stalin, advocated a communist system. In a capitalist system, market forces dictate prices according to supply and demand. Those who control the means of production, known as the bourgeoisie in the Marxist philosophy, are much wealthier than the workers, known as the proletariat. In a communist system, however, the means of production are communally owned, and the intended result is that there are no classes of rich and poor and no groups of landowners and landless workers.
In the Soviet system, the government dictated economic policy, rather than relying on free market mechanisms and the law of supply and demand. This required the government to intervene at all levels of the economy. The prices of goods needed to be set by the central government, the production levels of goods needed to be determined, the coordination of manufacturers and distributors was needed everything that is traditionally accomplished through private individuals and companies in a capitalist model was the responsibility of the Soviet government.
To coordinate such a wide array of goods and services, long-term planning was needed. The Soviet government instituted a series of five-year plans which established long-term goals and emphasized quotas for the production of goods. This system lacked flexibility, however, and was often inefficient in its production and distribution of goods.
You May Like: 4 Goals Of Psychology Example
The Ethnicity Problem Do You Speak Russian
Russia found itself in a position it could not retreat from. If you compress the spring all the way to its limit, it will snap back hard
Vladimir Putin, March 2014, addressing the State Duma
How did Russia manage to get away with annexing Crimea? NATO has been known to intervene in non-NATO countries, so why not here? First, lets explain what happened.
Ukraine were playing both sides. They flirted with the west, whilst paying homage to Moscow. Putin tolerated this all he needed was a Ukraine that would act as a buffer zone against NATO, and one that would uphold Russias lease on Sevastopol. However, in 2014, Ukrainian president Viktor Yanukovych came close to signing a large trade deal with the EU, one that Putin decided could lead to eventual membership of the EU. For Russia, membership of the EU is simply a stalking horse for membership of NATO.
Putin simply couldnt allow Ukraine to join NATO. It would be a geotrategic disaster, and he therefore had to stop the trade deal. Putin pilled on the pressure, and offered a financial incentive to Yanukovych to cancel the deal. He made a pact with Moscow instead.
Street fighting erupted in Kiev, and on the 22nd February, Yanukovych fled. Anti-Russian fractions took over the government, which meant more fighting in the pro-Russian areas of Ukraine: the east. The Kremlin is compelled to protect ethnic Russians, and therefore told the world it was forced to annex Crimea.
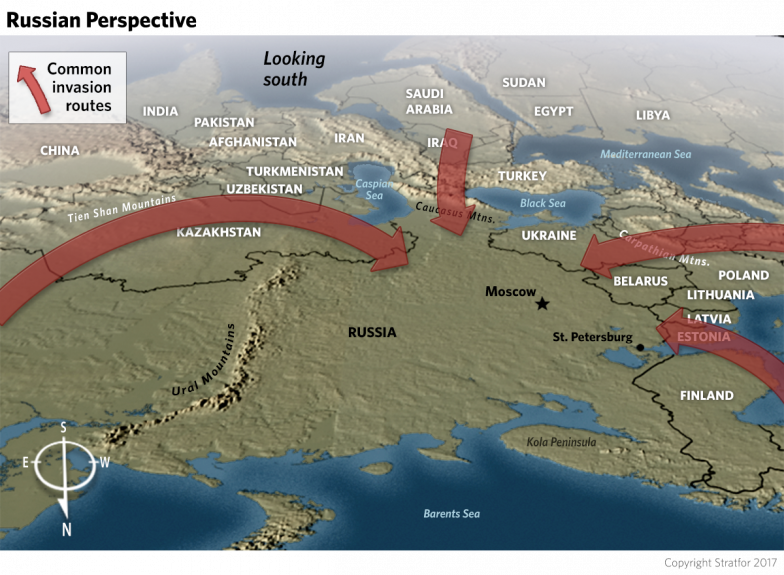
The Gap In Russias Natural Defences
There are many nations with geographic features that protect the nations border from invasion. Indeed, a lot of the success of some countries over others, depends upon how well their geography protects them. The USA for example has benefitted significantly from always being an ocean away from any nation that could threaten it. France is similarly fortunate. Their north-western border is protected by the English Channel, their western border by the Bay of Biscay, their southern border by the Pyrenees and the Mediterranean, their south-eastern border by the Alps, and their north eastern by the Rhine river. The eastern half of their northern border is however largely unprotected, a flaw Germany exploited in both world wars. Geography however concentrated attacks into a choke point, meaning they only had to fight on one front.
Russia is not so fortunate. In their far east, geography protects them: theres not much to attack in Siberia except snow, and to reach Moscow youd need supply lines thousands of miles long, making you vulnerable to counter attack. Youd also have to pass over the Urals. Few armies of significant size could do so. Essentially, its impossible to reach Moscow through Siberia.
Coming from the south has a similar problem either you have to go through Kazakhstan, a Russian ally, or from the Middle East, over the Caucasus mountains, another mountain range few armies could pass over.
Wendover Production. Russias Geography Problem .
Don’t Miss: How Do Noise Cancelling Headphones Work Physics
How Did Geography And The Migrations Of Different Peoples Influence The Rise Of Russia
How did geography and migrations of different people influence the rise of Russia? How did geography and ethnic diversity contribute to the turmoil of eastern European history? Trade and migration led to turmoil because everyone wanted control. The location- the roads made trade and transportation easy.
Russian Multiculturalism And Tension
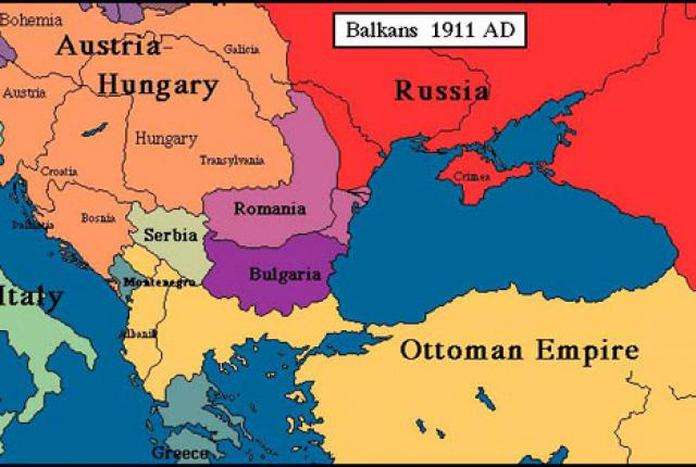
During the period of Russias expansion and development as an empire, and later during the time of the Soviet Union, Russias territory included not only ethnic Russians but other surrounding groups as well. Ethnicity is a key feature of cultural identity and refers to the identification of a group of people with a common language, ancestry, or cultural history. Many of these minority ethnic groups harbored resentment over being controlled by an imperial power.
Prior to the Bolshevik Revolution, the Russian Empires response to the non-Russian communities they controlled was known as Russification, where non-Russian groups give up their ethnic and linguistic identity and adopt the Russian culture and language. This type of policy is known as cultural assimilation, where one cultural group adopts the language and customs of another group. The Russian language was taught in schools and minority languages were banned in public places. Catholic schools were banned and instead, Russian Orthodoxy, part of the Eastern Orthodox Church, was taught at state-run schools. The Russian Empire essentially sought to make everyone in the territory Russian. This policy was only marginally successful, however, and was especially difficult to implement in the outer regions.
Read Also: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
Outline Of Russias Historical Geography
The Regions Early Heritage
Czarist Russia, 15471917
Figure 3.9 Moscow and the Moskva River
Behind the Borodinsky Bridge on the right are the government buildings of the Russian Federation.
Natural Resources And Land Use
Russia holds the greatest reserves of mineral resources of any country in the world. Though they are abundant, they are in remote areas with extreme climates, making them expensive to mine. The country is the most abundant in mineral fuels. It may hold as much as half of the world’s coal reserves and even larger reserves of petroleum. Deposits of coal are scattered throughout the region, but the largest are located in central and eastern Siberia. The most developed fields lie in western Siberia, in the northeastern European region, in the area around Moscow, and in the Urals. The major petroleum deposits are located in western Siberia and in the Volga-Urals. Smaller deposits are found throughout the country. Natural gas, a resource of which Russia holds around forty percent of the world’s reserves, can be found along Siberia’s Arctic coast, in the North Caucasus, and in northwestern Russia. Major iron-ore deposits are located south of Moscow, near the Ukrainian border in the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly this area contains vast deposits of iron ore that have caused a deviation in the Earth’s magnetic field. There are smaller deposits in other parts of the country. The Ural mountains hold small deposits of manganese. nickel, tungsten, cobalt, molybdenum and other iron alloying elements occur in adequate quantities.
Recommended Reading: Why There Are Different Branches Of Chemistry
We Need More Rivers The Reasons Behind Russias Lack Of Money
Russia is a land of superlatives. Almost twice as large as the next largest country Canada, its size can at least partially explain some of the problems it faces today. It is over 70 times larger than the UK, and yet thats about the only league table Russia tops the UK on. Russias GDP per capita of $8,748 is similar to that of The Bahamas, and significantly below the UKs figure of $42,609. Both the UK, and indeed The Bahamas are far smaller, and so we can deduce that Russias sheer size is likely a limiting factor in its economy.
Historically, naval power equalled power. There was no better way for a country to project their power and grow their economy, than to have a powerful naval and merchant fleet. Many of the worlds most powerful nations today, like the UK and Japan, are ones that once had the worlds most powerful navies. Theres a good reason why none of the ten largest economies in the world are landlocked. Maritime shipping is still the cheapest way to transport goods long distance. But Russia, despite its 23,000 miles of coastline, has no warm water, ice free ports, with direct access to an ocean.
The majority of Russias north coast is deep inside the Arctic Circle, and therefore frozen for much of the year. When its not, any ship carrying cargo would need an icebreaker to accompany it out of the Arctic Sea, although this is beginning to change as I explain in The Russian Ocean. Moreover, any sea port on the north coast is also in Siberia.
The Modern Russian Landscape
The collapse of the Soviet Union had far-reaching effects on the Russian landscape and even today, Russia is affected by the legacy of the Soviet Union. The remnants of Soviet bureaucracy, for example, affect everything from the cost of road building to the forms needed to get clothes dry cleaned. After the immediate collapse of the Soviet Union, the government transitioned to a market economy. In many cases, those who had positions of power within the Soviet government gained control over previously state-owned industries creating a wealthy class often called a Russian oligarchy. Despite some setbacks and global economic downturns, Russias economy has improved significantly since the end of the Soviet Union and Russia now has the sixth-largest economy in the world. Poverty and unemployment rates have also fallen sharply in recent decades. Although Russias population fell sharply following the Soviet Unions collapse, it has rebounded somewhat in recent years.
a biome characterized by very cold temperatures and limited tree growth
soil that is consistently below the freezing point of water
a biome characterized by cold temperatures and coniferous forests
a biome characterized by treeless, grassland plains
areas near the center of a continent that experience more extremes in temperature due to their location away from bodies of water
an ethno-linguistic group loctaed in Central and Eastern Europe that includes West Slavs , East Slavs , and South Slavs
Also Check: Common Core Worksheets 2nd Grade
Global Position And Boundaries
Kaliningrad Oblast, westernmost part of Russia along the Baltic Sea, is about 9,000 km apart from its easternmost part, Big Diomede Island in the Bering Strait. This distance spans about 6,800 kilometres , to Nome, Alaska. From north to south, the country ranges from the northern tip of the Russian Arctic islands at Franz Josef Land to the southern tip of the Republic of Dagestan on the Caspian Sea, spanning about 4,500 kilometres of extremely varied, often inhospitable terrain.
Extending for 57,792 kilometres , the Russian border is the world’s longest. Along the 20,139-kilometre land frontier, Russia has boundaries with 14 countries: Poland and Lithuania , Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, the People’s Republic of China, Mongolia, and North Korea.
Approximately two-thirds of the frontier is bounded by seawater. Virtually all of the lengthy northern coast is well above the Arctic Circle except for the port of Murmanskwhich receives currents that are somewhat warmer than would be expected at that latitude, due to the effects of the Gulf Streamthat coast is locked in ice much of the year. Thirteen seas and parts of two oceansthe Arctic and Pacificwash Russian shores. It is separated by close sea, making it a . It also shares one with Japan.