Vsepr Geometry Of Hcn
The VSEPR geometry of a molecule of hydrogen cyanide is which of the following?
Correct Answer: B.Linear
This is a straightforward question. Drawing out the molecule, we see that there are no free electrons on N, meaning that it should be a linear, and not trigonal planar, configuration.
to receive the DAT Question of the Day delivered straight to your inbox every morning.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
What Is The Difference Between Symmetrical And Unsymmetrical
Answer: Symmetrical faults are those faults which involve with all the three phase. it simply means that symmetrical faults affect all the three phases. On the other side, unsymmetrical faults are those faults in which either one or two phase involve. In unsymmetrical faults the three phase lines become unbalanced.
Read Also: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Parents
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Hybridization Of Carbon In Hydrogen Cyanide
Carbon is triple-bonded to nitrogen, and so there are one sigma and two pi bonds.As per rule, the first bond between any two atoms is a sigma bond, and the second/third bonds are pi bonds)This means two p orbitals are required to be left over after hybridization.2 pi bonds = 2 leftover p orbitals.As a result, one of carbons p orbitals is available to hybridize
Also Check: What Is Figure Ground In Psychology
Definition Of Valence Bond Theory
The Valence Bond thoery simply explains the bond formation just like lewis dot structure, but instead it explains the bonding in terms of covalent bond by quantum mechanics. According to this theory, bond will form when
1) An orbital of one atom occupy another atom’s orbital, known as overlap.
2) number of electrons in both orbital is adds up to no more than two.
Just like forming a molecule with lewis dot structure, bonds between atoms complete when two electrons share same orbital together.
Bond strength depends on the the amount of overlap since electrons are attracted to nuclei of both atoms, more electrons will pull more nuceli thus increase bond strength. However, two orbitals can not contian more than two atoms due to the maximum capacity it can hold.
Also, because known atomic geometry can not be able to have effective overlap, atomic orbitals combine with each other and reconfigure themselves into a different configuration. This process is called hybrdization.
This formation of new hybrid orbital is possible by combining several types of orbitals .
Describe Hcn Molecular Bond By Using Valence Bond Theory
In HCN molecule, the C atom includes sp-hybridized orbital, since it will combine with only two other atoms to form HCN. One of the sp-hybrid orbitals of carbon atom overlaps with the 1s orbital of H atom, while the other sp-hybrid orabital mixes with one of the nitrogen’s atom’s three atomic p orbitals which were unhybridized. Because px orbital of C and N will form sigma bond, this leaves with two N atom p-orbitals which form two mutually perpendicular pi bonds to the two atomic p orbitals on the C atom. HCN thus has one single and one triple bond. The latter consists of a sigma bond from the overlap of a C atom sp hybrid orbital with a N atom p orbital, and two mutually perpendicular pi bonds are formed from parallel atomic p orbitals of carbon and nitrogen atoms.
Recommended Reading: Theory Of Everything Geometry Dash 2
What Is The Bond Angle Between Hydrogen Atoms In Nh4 +
Since NH4+ is a cation, the bond angle between 2 respective hydrogen atoms is 109.5 degrees instead of 90 degrees, which is as far away from one another as possible. A smart way to remember the structure of ammonium is that tetra stands for four, that is the number of bond pairs nitrogen makes in Ammonia.
What Is The Dat
The Dental Admission Test is a test administered by the American Dental Association . The test is four hours and 30 minutes long and contains four sections. The test is designed to assess your knowledge in: biology, chemistry, organic chemistry, perceptual ability, reading comprehension, and basic math.
Recommended Reading: What Is Elastic Force In Physics
Polarity Or Nonpolarity Of Hydrogen Cyanide
HCN, or hydrogen cyanide, is a polar molecule because there is a large electronegative difference between the N and H across the linear molecule. It consists of two polar bonds whose polarities line up in the same direction.
Thus conferring an overall partial positive charge on one end of the molecule and a partial negative on the other end.
The Lewis structure determines whether an entire molecule is polar or essentially nonpolar. Studies show that nonpolar molecules/nonpolar covalent bonds are symmetric. Meanwhile, polar molecules are asymmetric because they contain lone pairs of electrons on a central atom.
Lewis Structure Of Hcn
Some compounds have a very unique and different Lewis structure and HCN is one of those. Thus to understand the Lewis structure in-depth lets go step by step in understanding the concept.
First of all, to remind you Lewiss structure is a pictorial representation of different bonds and lone pair of electrons between two or more atoms of a compound.
Step 1: The foremost step of creating a Lewis structure is finding the valence electrons.
Here we have to find the valence electrons of all three atoms, hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen.
The number of valence electron is only 1 in Hydrogen because it is an exception atom which doesnt follow the octet rule and thus doesnt need 8 electrons to fill its octet but needs only 1.
Similarly, the valence electrons of Carbon are 4 and that of Nitrogen is 5.
The atomic number of Carbon is 6 so 2 electrons are filled in s orbital and the rest 4 are in the outer orbital that is why the valence number of electrons in carbon is 4.
For Nitrogen, its atomic number is 7, so after 2 electrons occupy s orbital, the rest 5 are in the outer orbital so the valence number of electrons is 5.
Now to find the total number of valence electrons we will add up the valence electrons of all three atoms:
=1+4+5 = 10 valence electrons.
Step 2: Now we will draw the Lewis dot structure of the compound. See the diagram below:
However, hydrogen is the least electronegative but it cant be a central atom because it has only one spare electron.
You May Like: Definition Of Reduction In Math
As A Poison And Chemical Weapon
In World War I, hydrogen cyanide was used by the French from 1916 as a chemical weapon against the Central Powers, and by the United States and Italy in 1918. It was not found to be effective enough due to weather conditions. The gas is lighter than air and rapidly disperses up into the atmosphere. Rapid dilution made its use in the field impractical. In contrast, denser agents such as phosgene or chlorine tended to remain at ground level and sank into the trenches of the Western Front’s battlefields. Compared to such agents hydrogen cyanide had to be present in higher concentrations in order to be fatal.
A hydrogen cyanide concentration of 100200 ppm in breathing air will kill a human within 10 to 60 minutes. A hydrogen cyanide concentration of 2000 ppm will kill a human in about one minute. The toxic effect is caused by the action of the cyanide ion, which halts cellular respiration. It acts as a non-competitive inhibitor for an enzyme in mitochondria called cytochrome c oxidase. As such, hydrogen cyanide is commonly listed among chemical weapons as a blood agent.
The Chemical Weapons Convention lists it under Schedule 3 as a potential weapon which has large-scale industrial uses. Signatory countries must declare manufacturing plants that produce more than 30 metric tons per year, and allow inspection by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons.
Number Of Sigma Bonds In The Molecule
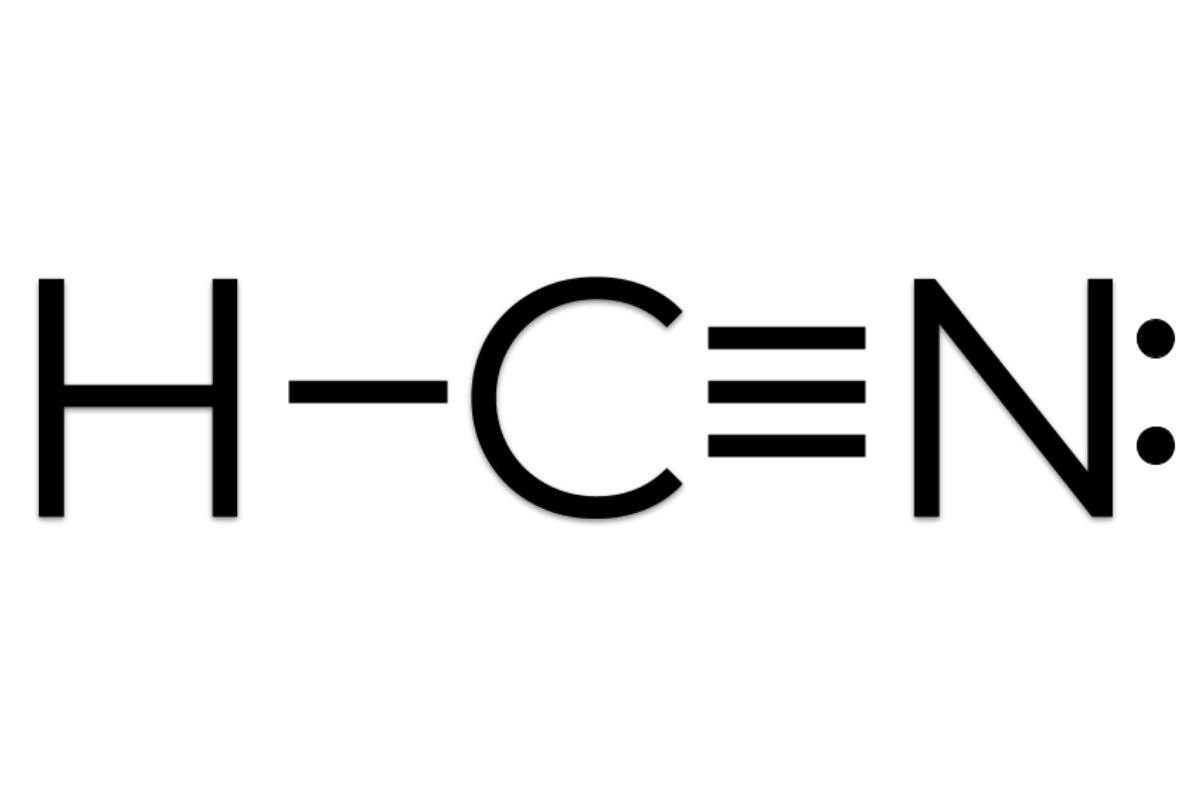
Another way to find out the hybridization of the molecule is to look at the number of sigma bonds formed. In HCN, there are two sigma bonds, C-H and C-N. The number of sigma bonds is equal to the number of hybrid orbitals formed. So the hybridization for HCN molecule is sp hybridization.
Concluding Remarks
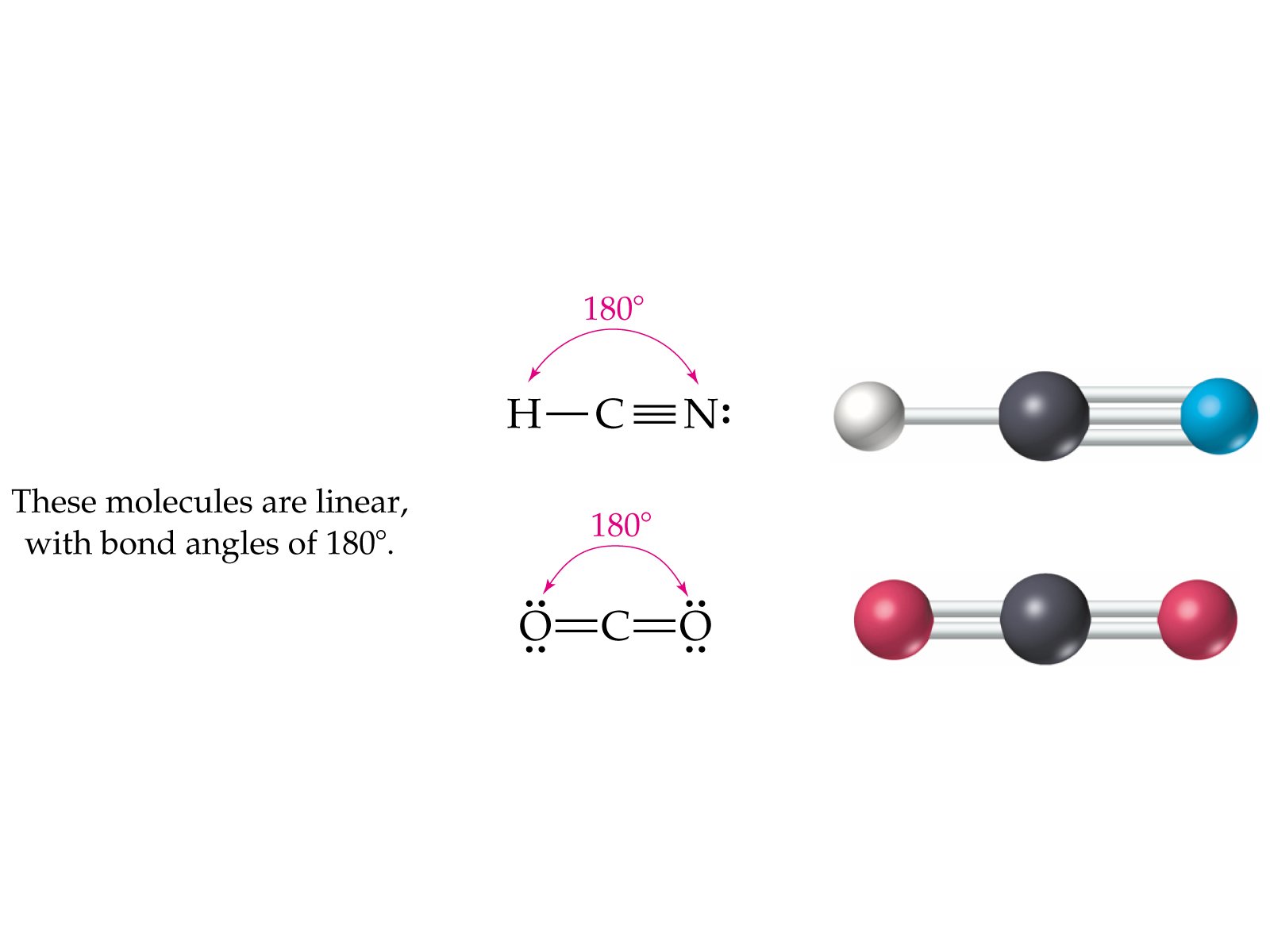
We can say that HCN, Hydrogen Cyanide, is a linear molecule with sp hybridization to conclude this blog post. The bond angles are 180°and two hybrid orbitals are formed for two sigma bonds formed in this molecule.
About Priyanka
To read, write and know something new every day is the only way I see my day! Well, that rhymed. Hey folks, this is me, Priyanka, writer at Geometry of Molecules where I want to make Chemistry easy to learn and quick to understand. Having an MSc degree helps me explain these concepts better. I write all the blogs after thorough research, analysis and review of the topics. And if not writing you will find me reading a book in some cosy cafe!View all posts by Priyanka
Also Check: Imaginemath.com Login
What Is The Structure Of Nh4 Positive
Structure and bonding The lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom in ammonia, represented as a line above the N, forms the bond with a proton . Thereafter, all four NH bonds are equivalent, being polar covalent bonds. The ion has a tetrahedral structure and is isoelectronic with methane and borohydride.
What Is Dot Structure Of Hydrogen Sulfide
On both sides of the central sulfur atom in the H2S Lewis structure, there are two hydrogen atoms.The molecule bends due to the existence of two unbonded pairs of electrons.The molecule is slightly polar because sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen.In the case of H2S, the vectorial sum of the bond dipole moments results in a non-zero total dipole moment. As a result, dipole-dipole interactions are observed in hydrogen sulfide.
Read Also: Does Kamala Harris Have Children Of Her Own
How Do You Subject Yourself To Cyanide
- Consuming food, water etc. that has HCN in it could expose you to cyanide.
- As a product of both natural causes and human practices, cyanide enters water, soil, or air and is also present as gaseous HCN in the air.
- For those who do not work in cyanide-related sectors, smoking tobacco is potentially one of the main causes of cyanide toxicity.
Uses Of Hydrogen Cyanide
- Hydrogen cyanide is used in the preparation of acrylonitrile, which is used in the production of acrylic fibres, synthetic rubber, and plastics.
- Hydrogen cyanide and its compounds are used for many chemical processes, including fumigation, the case hardening of iron and steel, electroplating, and the concentration of ores.
- Hydrogen cyanide is an excellent solvent for many salts, but it is not widely used as a solvent because of its toxicity.
Recommended Reading: Copulation Biology
Historical Methods Of Production
The large demand for cyanides for mining operations in the 1890s was met by George Thomas Beilby, who patented a method to produce hydrogen cyanide by passing ammonia over glowing coal in 1892. This method was used until Hamilton Castner in 1894 developed a synthesis starting from coal, ammonia, and sodium yielding sodium cyanide, which reacts with acid to form gaseous HCN.
What Is Hydrocyanic Acid
Hydrocyanic acid is a liquid of hydrogen cyanide in water. The chemical formula of Hydrocyanic acid is HCN. Hydrocyanic acid is a colorless liquid whose vapor is lighter than air and dissipates rapidly. It is usually sold commercially as an aqueous solution containing 2 to 10% hydrogen cyanide.The aqueous solutions of hydrogen cyanide decomposes slowly to form ammonium formate. It is very poisonous colourless gas with a characteristic fragrance of bitter almonds. It is a dangerous transparent liquid its storage and transport are prohibited.
Other names Prussic acid, acetonitrile, formonitrile
| HCN |
You May Like: How Do You Do Percent Error In Chemistry
How To Draw Lewis Structure Of Oxygen
In the O2 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between two oxygen atoms.Oxygen is a diatomic nonpolar molecule with bond angles of 180 degrees.In its molecule, both oxygen atoms have the same electronegativity value and both atoms share equal ratios of bonded shared electrons and the overall O2 molecule turns out to be nonpolar.
Hcn And The Origin Of Life
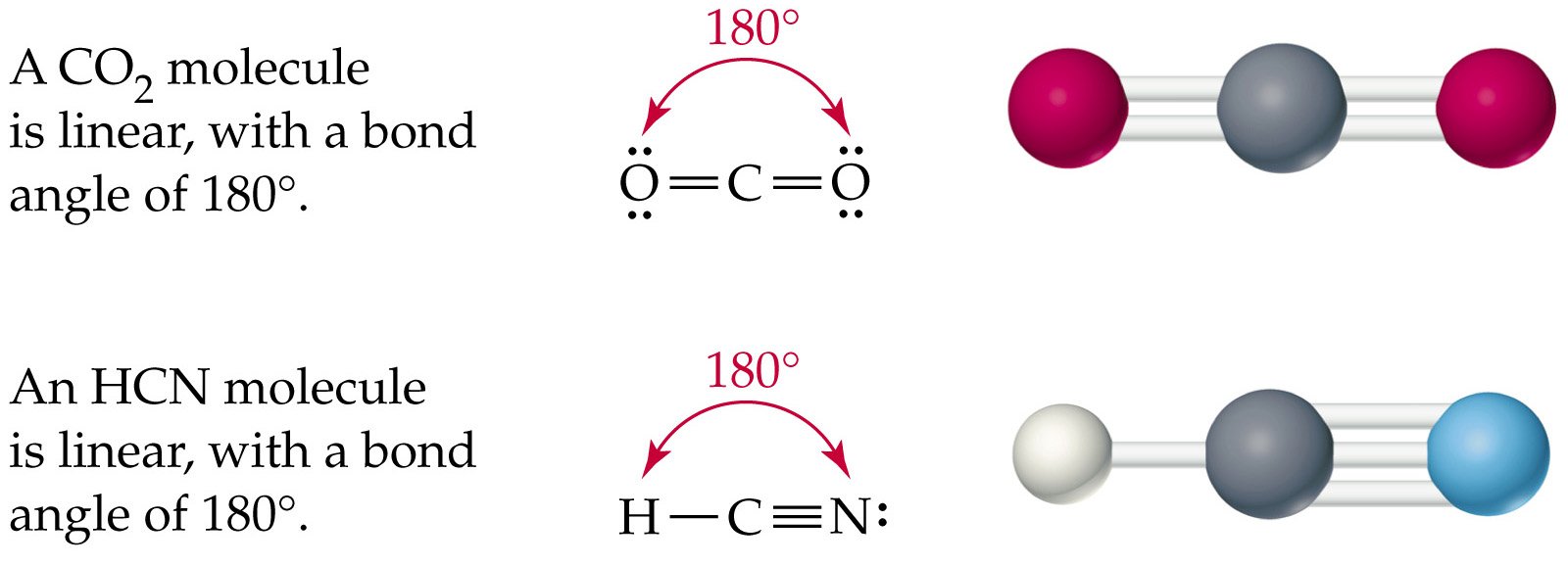
Hydrogen cyanide has been discussed as a precursor to amino acids and nucleic acids, and is proposed to have played a part in the origin of life. Although the relationship of these chemical reactions to the origin of life theory remains speculative, studies in this area have led to discoveries of new pathways to organic compounds derived from the condensation of HCN .
Read Also: How To Study For Ap Human Geography
What Is The Lewis Structure Of Bef2
Now by taking the above structures as examples we can draw the Lewis dot structure of $Be_}$ and it is as follows. From the above Lewis dot structure we can easily say that each fluorine atom has three lone pairs of electrons and beryllium has zero lone pair of electrons in Beryllium difluoride molecules.
Uses Of Hydrocyanic Acid Hcn
- Used as a fugiment to kill pests such as rodents in warehouses, grain storage bins, greenhouses and holds of ships where its high toxicity and ability to penetrate obscure spaces are advantageous.
- Used in the manufacture of cyanide salts, acrylonitrile and dyes. It is also used as a horticultural fumigant.
- Used as a highly valuable precursor in the production of several chemicals.
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz
You May Like: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
What Are Its Properties
Hydrogen Cyanide or HCN becomes a colorless liquid when placed at room temperature with an oily odor. However, it may become flammable and poisonous due to the instability of the triple bond. HCN is acidic and has a melting point of 13.29 °C or 8.08 °F. On the other hand, it has a boiling point of 26 °C or 79 °F.
Its acidity is 9.21 PKA, and it has ten valence electrons. However, when exposed to a temperature of 25 °C, its vapor pressure becomes 100 kPa. According to Molecular Geometry, the HCN features a polarity bond of 2.98 D and has a linear molecular shape.
Structure And General Properties
Hydrogen cyanide is a linear molecule, with a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. The tautomer of HCN is HNC, hydrogen isocyanide.
Hydrogen cyanide is weakly acidic with a pKa of 9.2. It partially ionizes in water solution to give the cyanide anion, CN. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water, represented as HCN, is called hydrocyanic acid. The salts of the cyanide anion are known as cyanides.
HCN has a faint bitter almond-like odor that some people are unable to detect owing to a recessive genetictrait. The volatile compound has been used as inhalation rodenticide and human poison, as well as for killing whales. Cyanide ions interfere with iron-containing respiratory enzymes.
Don’t Miss: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
Molecular Geometry For Hcn
- 6
- Molecular geometry for HCN- Drawing of Lewis structure
Draw the Lewis structure & Molecular geometry for HCN: explain the configuration in the molecule of valence electrons around the atoms
A chemical compound with the formula HCN is hydrogen cyanide. It is also called prussic acid. It is a liquid that is colorless, highly toxic, and flammable in nature. HCN is a particularly valuable predecessor of numerous chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals and is processed on an industrial scale.
HCN has a slight bitter almond-like smell due to a recessive genetic mutation that certain individuals are unable to identify. The explosive agent has been used for rodenticide inhalation and human venom, as well as for the slaughter of whales. Cyanide ions interact with respiratory enzymes containing iron as well.
In a variety of plants, this HCN chemical is present in small amounts, particularly in stone fruits such as cherries, as well as in the roots of cassava. Prolonged exposure to a small quantity of cyanide can contribute to chronic health problems in individuals whose diet includes large concentrations of cassava.
Since it prevents cellular oxidative processes, hydrogen cyanide is extremely toxic. Without severe effects, an adult person can tolerate 50 to 60 parts of hydrogen cyanide per million parts of air for an hour, but exposure to concentrations of 200 to 500 parts per million of air for 30 minutes is typically lethal.