What Is Studied In Geography
Therefore, Geography is the science that deals with the description of the Earths surface. Geography is a multi disciplinary fields that studies spatial patterns and phenomenon.
Geography is much more than cartography, the study of maps or simply knowing the capitals of every country. The field of geography not only investigates what is where on the Earth, but also why its there and not somewhere else, sometimes referred to as location in space.
Geography studies this whether the cause is natural or human. It also studies the consequences of those differences.
Connecting With Space And Place
Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments. Geographers explore both the physical properties of Earths surface and the human societies spread across it. They also examine how human culture interacts with the natural environment and the way that locations and places can have an impact on people. Geography seeks to understand where things are found, why they are there, and how they develop and change over time. Read More…
The Four Traditions Of Geography
There are some other ways to conceptualize the field of geography. Parkinson suggested that geography has four traditions: The Earth Science Tradition, Culture-Environment Tradition, Locational Tradition, and Area Analysis Tradition. Geographic techniques support these traditions. The chart below shows how selected subdisciplines fit within these four traditions.
Also Check: Does Mj Have Any Biological Kids
Defining Geography: What Is Where Why There And Why Care
History is the study of events through time. Basically, historians ask “What happened when and why then?” But many people, it seems, have a problem defining geography. Not enough people understand the nature of the discipline or its relevance to our everyday lives.
This brief essay presents an easily taught, understood, and remembered definition of geography. I have used it in my own teaching, public speaking, and professional writing for more than a decade. It works beautifully, and I believe that it will work for you and your students as well.
Geography Is What Geographers Do
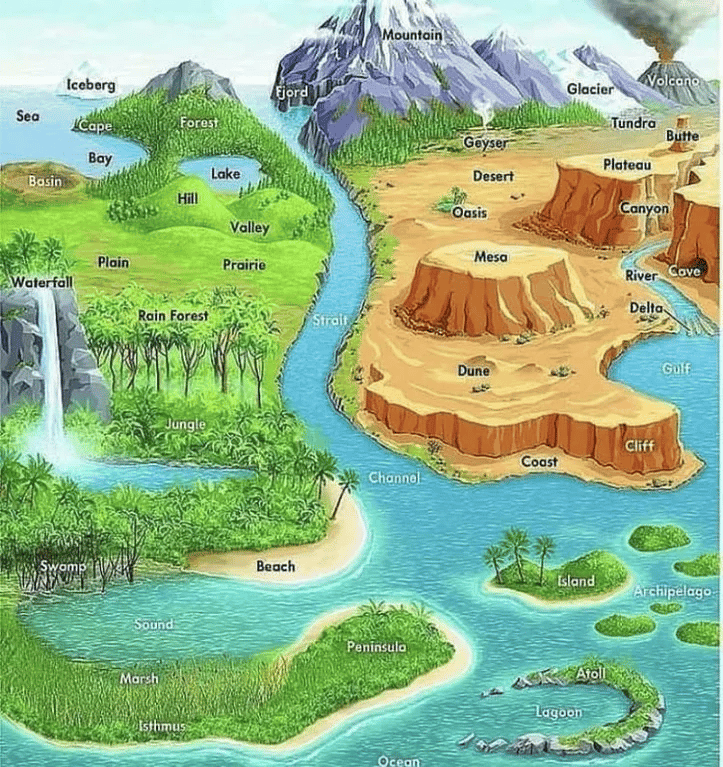
Everything that is happens in a space and time. Therefore, everything has ahistory and everything has a geography. There is no Pope in geography that sayswhat can and cannot be studied in geography, and since few people know what contemporary academic geography is, academic geographers are oftenfree to be interdisciplinary and study what they want. Thereforealmost anything can be and is studied within geography. If you visit theannual meetingof the Association of American Geographers, you cansee presentations on a very wide variety of topicsby a very heterogeneous collection of researchers.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Biology
The Popular Perception Of Geography
Unfortunately, the popular perception of geography is very different. I find the understanding of geography that I encounter on a daily basis to fit the stereotype that geographers refer to as place-name and location geography frighteningly often. Most people I encounter, regardless of their level of educational attainment, view geography as a body of discrete knowledge about the world that includes names and locations of countries, cities, bodies of water, and major geological features and facts about those places.
Most people I talk to consider map reading and wayfinding to be the only skills that geography teaches, and if they are aware that one can study geography at an advanced level or practice geography professionally, they believe the focus of that geography is mapmaking.
From the perspective of geography education, the popular perception of geography is as pernicious as it is widespread. People are increasingly aware that factual knowledge is of limited value in the Internet age, so it is difficult to have a productive conversation about the value of geography education with someone who believes geography is about factual understanding and thinks its usefulness for careers is limited to the obscure profession of cartography. Unfortunately, it can be very difficult to change this perception of geography, especially in a single conversation, when the individual has had no personal exposure to systematic geographic reasoning or problem solving.
Early Definitions Of Geography
Geography, a study of Earth, its lands, and its people, started in ancient Greece, with the study’s name defined by the scholar and scientist Eratosthenes, who calculated a relatively close approximation of the circumference of Earth. Thus, this academic field started with mapping the land. Greco-Roman astronomer, geographer, and mathematician Ptolemy, living in Alexandria, Egypt, in 150 defined its purpose as providing “‘a view of the whole’ earth by mapping the location of places.”
Later, Islamic scholars developed the grid system to make maps more accurately and discovered more of the planet’s lands. Then, another major development in geography included the use in China of the magnetic compass for navigation, the earliest known recording of which is 1040. European explorers started using it in the century to follow.
Philosopher Immanuel Kant in the mid-1800s summed up the difference between history and geography as history as being when something happened and geography being where certain conditions and features are located. He thought of it more descriptive than a hard, empirical science. Halford Mackinder, a political geographer, included people in his definition of the discipline in 1887, as “man in society and local variations in environment.” At the time members of Britain’s Royal Geographic Society wanted to ensure that it was studied in schools as an academic discipline, and Mackinder’s work aided that aim.
Read Also: More Work With The Quadratic Formula Common Core Algebra 2
Five Themes Of Geography
The Five Geography Themes began as a framework for making geography accessible to children from kindergarten to high school. They describe a simple, effective method for parents and educators to teach children about geography and how it relates to nature, civilization, and other topics. More: Five Themes of Geography Explained
Though the National Geographical Standards replaced these themes in 1994, they remain a simple and effective way to teach children about geography.
Who Cares About What Human Geography Is
A dictionary is a compilation of the terms of a language, as well as directions on how to write them properly, what their description is. Dictionaries show prototype sentences to elaborate how the words are utilized. An outstanding dictionary should have as much examples as possible.
A dictionary book is a useful data feed for authors of prose or poetry, who have to utilize expressions in their particular context. It is also beneficial for decoding of languages, who try to interpret from one language into another.
Recommended Reading: What Does Denominator Mean In Math
Defining Geography For Education
Odds are that if I ask you and the person in the next office to describe the field of geography, I will get pretty different answers. And if I were to ask other members of your familyyour mother, your brother, your spouseI would get an even broader range of answers. And if I were to ask the people next to you on your morning commute, the answers would be more diverse still.
This diversity is, of course, an inherent property of human psychology. We all carry around our own personal understanding of words and concepts that result from our own particular set of experiences.
In most cases, the fact that there is such a broad range of definitions for the field of geography isnt a problem, but there is one place where it is a serious issuein conversations about geography education.
In more than a decade of talking to people about how to improve geography education, I have learned that it is important to be explicit about the definition of geography that I am using.
While there are, of course, as many definitions of geography as there are people, there are three clusters that are important for discussions about geography education. I call these clusters of definitions geographers geography,the popular perception of geography, and school geography.
Do You Realized What The Definition Of Human Geography Is
Have you been puzzled by the definition of the word and the answer to the question what does Human Geography mean? The language is like that, it grants to all the letters and sounds a meaning and a idea which is sometimes elaborated to recognizewhat it is. You already experienced the definition of human geography, but besides language, beyond a certain terminology we find more, we have vocabulary books, philologers and their work that develop the meanings and supervise how the populace of the mother tongue use terms such as HUMAN GEOGRAPHY.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Physical Geography
Do You Perceive A Little Better What Human Geography Means
Terms, like human geography, are an idea, one of the principal ones. The word word is far more antique than any other in the records of the human race, dating back to about the 40th century BC . But there is no substantial written testimony of that stage of antiquity.The word word may have been passed on by word of mouth, like prevailing culture. primitive humans applied terminologies to talk to each other and pass on information. Words were a significant part of human society across its evolution.
Negative Impacts Of Regeneration

Whilst there are expected positive impacts of regeneration from restoring or developing an area, there are negative impacts of regeneration.
Gentrification is the regeneration of an urban area that is subject to environmental and socio-economic decline. It attracts wealthy investors to clear and prepare brownfield sites to make way for high-value properties.
From the perspective of the “trickle down” theory, local governments see gentrification as benefitting the community. The theory is that the investors in gentrification projects will invest in local services and businesses, the workers would spend their disposable income in the local area and the investors and businesses would pay more taxes which then can be spent on local services and improvements. This would benefit everyone in the local area.
However, there are negative impacts such as house prices increasing rapidly so that low-cost tenants are forced to leave and are replaced by high-income tenants. This creates a social division between the existing communities and the new residents . Neighbourhoods can lose their identity as they start to look similar to other gentrified places. It is contested whether gentrification improves an area when there is a displacement of one social group, forcing another less affluent social group to migrate elsewhere.
Graffitti fighting against gentrification, Wikimedia
Recommended Reading: What Is Conjugation In Chemistry
Measuring The Success Of Regeneration
Measuring the success of regeneration can be varied and can depend on what is focused on improving.
-
Economic regeneration = This can be measured through the growth of the local economy’s size, comparison of employment rates, industrial productivity and before and after schemes.
-
Social improvements = Measurements include an increase in life expectancy, decreased applicants for social housing, literacy rates and reductions in social tensions.
-
Improvements in the living environment = This can be measured through improved air quality, abandoned land being utilised and an increase in green, open spaces.
A Basic Overview Of The Discipline Of Geography
- M.A., Geography, California State University – Northridge
- B.A., Geography, University of California – Davis
Since the beginning of humankind, the study of geography has captured the imagination of the people. In ancient times, geography books extolled tales of distant lands and dreamed of treasures. The ancient Greeks created the word “geography” from the roots “ge” for earth and “grapho” for “to write.” These people experienced many adventures and needed a way to explain and communicate the differences between various lands. Today, researchers in the field of geography still focus on people and cultures , and the planet earth .
Recommended Reading: Geometry Arc Length And Sector Area Worksheet Answer Key
What Are The Three Types Of Geography
It is an all-round discipline that explains an understanding of the earth and its human, physical and environmental complexities. Geography can be divided into three main branches or types. These are human geography, physical geography and environmental geography.
What are the five areas of geography?
What is the importance of studying geography?
Studying geography can provide an individual with a holistic understanding of our planet and its systems. Those who study geography are better prepared to understand topics impacting our planet such as climate change, global warming, desertification, El Nino , water resource issues, among others.
What are the uses of geography?
The main purpose of geography and geographers is to see and understand patterns in our world. To determine patterns. Geographers work in environmental managements, education, disaster response, city and county planning and much more. Geography itself is the study of place and space.
New Frontiers In Geography
Geographers plan new communities, decide where new highways should be placed, and establish evacuation plans. Computerized mapping and data analysis are known as Geographic Information Systems , a new frontier in geography. Spatial data is gathered on a variety of subjects and input onto a computer. GIS users can create an infinite number of maps by requesting portions of the data to plot.
There’s always something new to research in geography: new nation-states are created, natural disasters strike populated areas, the world’s climate changes, and the Internet brings millions of people closer together. Knowing where countries and oceans are on a map is important but geography is much more than the answers to trivia questions. Having the ability to geographically analyze allows us to understand the world in which we live.
Read Also: Who Is The Mother Of Biology
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
geography, the study of the diverseenvironments, places, and spaces of Earths surface and their interactions. It seeks to answer the questions of why things are as they are, where they are. The modern academic discipline of geography is rooted in ancient practice, concerned with the characteristics of places, in particular their natural environments and peoples, as well as the relations between the two. Its separate identity was first formulated and named some 2,000 years ago by the Greeks, whose geo and graphein were combined to mean earth writing or earth description. However, what is now understood as geography was elaborated before then, in the Arab world and elsewhere. Ptolemy, author of one of the disciplines first books, Guide to Geography , defined geography as a representation in pictures of the whole known world together with the phenomena which are contained therein. This expresses what many still consider geographys essencea description of the world using maps but, as more was learned about the world, less could be mapped, and words were added to the pictures.
To most people, geography means knowing where places are and what they are like. Discussion of an areas geography usually refers to its topographyits relief and drainage patterns and predominant vegetation, along with climate and weather patternstogether with human responses to that environment, as in agricultural, industrial, and other land uses and in settlement and urbanization patterns.
Geography As A Three Key Issues
Rubenstein defines geography as addressing three key issues:
| How do geographers address where things are? | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Also Check: Who Is Kaepernick’s Biological Father
The Nature Of Geography
Immanuel Kant, writing some two centuries ago, may have been the first scholar to identify clearly and succinctly the unique nature of both history and geography. He observed that:
- History organizes and analyzes events in terms of when they occurred .
- Geography focuses upon Earth’s features and conditions by asking where they are found .
Both history and geography, then, are methodologiesunique ways of thinking about our world and its events, conditions, patterns, and consequences. If “When?” is the realm of history, then “Where?” is the primary focus of geographic inquiry.
But what is “spatial analysis”? When most people think of space, they associate it with astronomy, not geography. In a geographic context, “space” is defined as a portion of Earth’s surface. Location, place, area, region, territory, distribution, and pattern are all closely related spatial concepts.
The Definition In Practice

This definition of geography works well for several reasons. First, it emphasizes that geography is a methodology. It stresses the geographic way of organizing and analyzing information pertaining to the location, distribution, pattern, and interactions of the varied physical and human features of Earth’s surface. All geographic inquiry should begin with the question, “Where?” Geographers and all other scientists ask “Why?” And, of course, most major Earth-bound events, features, and conditions can and often do have some impact on our lives, thereby begging the question, “Why care?”
An example on the global scale, petroleum resources in the Middle East certainly have contributed to a host of conflicts, and “petro-politics” surely will be a major issue for decades to come. Oil production, distribution, consumption, and trade all impact the lives of several billion people daily.
The definition I describe is clear and concise. It places no limitation on what geographers study it clearly identifies the discipline’s unique methodologythe spatial dimension of features, including where they are, in what patterns they occur, what important relationships exist, and so forth.
*Charles F. Gritzner, “What Is Where, Why There, and Why Care?,” Journal of Geography, 101, no. 1 , pp. 3840.
Recommended Reading: How To Study Chemistry For Class 12 Hsc
The Breadth Of Geography
As you can see from the definitions, geography is challenging to define because it is such a broad and all-encompassing field. It is far more than the study of maps and the physical features of the land because people are influenced and influence the land as well. The field can be divided into two primary areas of study: human geography and physical geography.
Human geography is the study of people in relation to the spaces they inhabit. These spaces can be cities, nations, continents, and regions, or they can be spaces that are defined more by the physical features of the land that contain different groups of people. Some of the areas studied within human geography include cultures, languages, religions, beliefs, political systems, styles of artistic expression, and economic distinctions. These phenomena are analyzed with statistics and demographics in relation to the physical environments in which people live.
Physical geography is the branch of the science that is probably more familiar to most of us, for it covers the field of earth science that many of us were introduced to in school. Some of the elements studied in physical geography are climate zones, storms, deserts, mountains, glaciers, soil, rivers and streams, the atmosphere, seasons, ecosystems, the hydrosphere, and much, much more.
This article was edited and expanded by Allen Grove.