Is There A Place With No Wind
Astronomers Find the Calmest Place On Earth 231
They have pinpointed the coldest driest calmest place on earth known simply as Ridge A 13 297 feet high on the Antarctic Plateau. Its so calm that theres almost no wind or weather there at all says study leader Will Saunders of the Anglo-Australian Observatory.
What Is Doldrum Short Answer
Textbook solution
The Intertropical convergence zone also called Doldrum is an atmospheric pressure belt that extends near the equator of the Earth. It is a major pressure belt of the Earth. Here the Earth receives direct rays of the sun which cause intense heating of the region. The air here is warm and hot.
Why Is There No Wind At The Equator
Theres science behind it. The effects of the Doldrums are caused by solar radiation from the sun, as sunlight beams down directly on area around the equator. This heating causes the air to warm and rise straight up rather than blow horizontally. The result is little or no wind, sometimes for weeks on end.
You May Like: Algebra 1 Eoc Practice Test
Where Are The Doldrums Winds
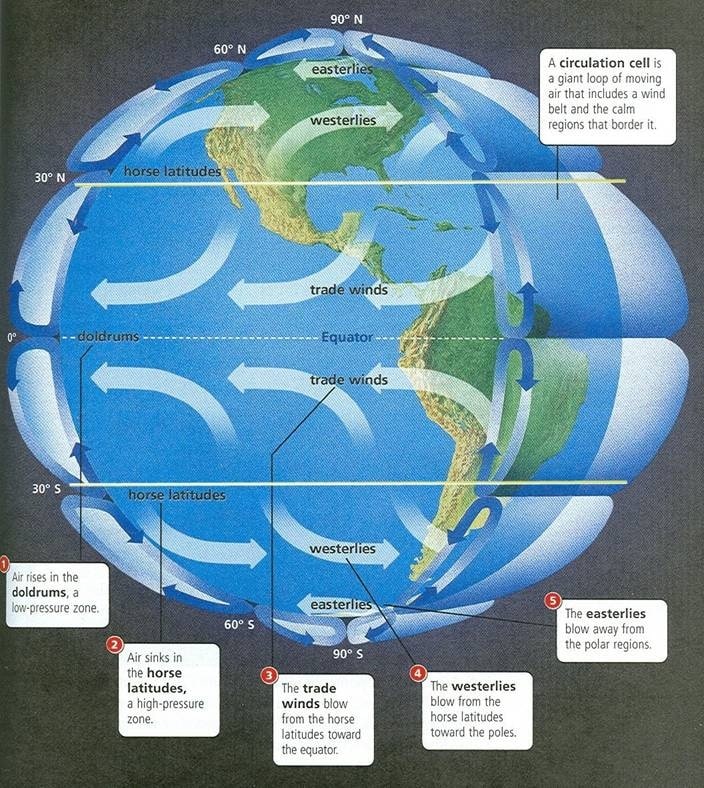
The Doldrums are located a little north of the equator but the effects can be felt from 5 degrees north of the equator to 5 degrees south of it. The trade winds border the Doldrums both to the north and south. Then there are the prevailing westerlies in the higher latitudes and the polar easterlies near both poles.
The Doldrums Is A Popular Nautical Term That Refers To The Belt Around The Earth Near The Equator Where Sailing Ships Sometimes Get Stuck On Windless Waters
This NASA satellite image shows the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone, known to sailors around the world as the doldrums.
Known to sailors around the world as the doldrums, the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone, , is a belt around the Earth extending approximately five degrees north and south of the equator. Here, the prevailing trade winds of the northern hemisphere blow to the southwest and collide with the southern hemispheres driving northwest trade winds.
Due to intense solar heating near the equator, the warm, moist air is forced up into the atmosphere like a hot air balloon. As the air rises, it cools, causing persistent bands of showers and storms around the Earths midsection. The rising air mass finally subsides in what is known as the horse latitudes, where the air moves downward toward Earths surface.
Because the air circulates in an upward direction, there is often little surface wind in the ITCZ. That is why sailors well know that the area can becalm sailing ships for weeks. And thats why they call it the doldrums.
Did you know?
Due to Earthâs rotation, the ITCZ shifts from season to season, causing both dry and rainy seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres.
Coral bleaching is prevalent in the ITCZ due to surface warming. NOAAâs Coral Reef Conservation Program monitors environmental conditions in coral reefs to identify areas at risk for bleaching.
More Information
Also Check: What Is Map Work In Geography
What Does The Doldrums Mean In English
Doldrums
doldrumsdold-rum
Definition of the doldrums in the English dictionary
The first definition of the doldrums in the dictionary is a depressed or bored state of mind. Other definition of the doldrums is a state of inactivity or stagnation.The doldrums is also a belt of light winds or calms along the equator.
How Do I Get Myself Out Of The Doldrums
The dictionary defines doldrums as a state of inactivity or stagnation, so it just makes sense to get moving to catapult yourself out of that state. Go for a brisk walk, engage in a yoga class, or do some simple stretches at home. Nothing chases the doldrums away faster than some exercise or even gentle movement.
Also Check: What Does Biome Mean In Geography
Itcz Over Oceans Vs Land
The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the northsouth migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not simply a response to just the surface convergence. Rather, it is modulated by a number of regional features such as local atmospheric jets and waves, proximity to the oceans, terrain-induced convective systems, moisture recycling, and spatiotemporal variability of land cover and albedo.
What Does The Doldrum Mean
Don’t Miss: What Does Capital M Mean In Chemistry
Where Are Doldrums Found
The Doldrums are regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans that have little if any wind. The Doldrums are located a little north of the equator, but the effects can be felt from 5 degrees north of the equator to 5 degrees south of it. The trade winds border the Doldrums both to the north and south.
What’s The Origin Of The Phrase ‘in The Doldrums’
The Doldrums is the region of calm winds, centered slightly north of the equator and between the two belts of trade winds, which meet there and neutralize each other. It is widely assumed that the phrase ‘in the doldrums’ is derived from the name of this region. Actually, it’s the other way about. In the 19th century, ‘doldrum’ was a word meaning ‘dullard a dull or sluggish fellow’ and this probably derived from ‘dol’, meaning ‘dull’ with its form taken from ‘tantrum’. That is, as a tantrum was a fit of petulance and passion, a doldrum was a fit of sloth and dullness, or one who indulged in such.
The term was used to mean ‘a general state of low spirits’ in the early 19th century for example, this piece from The Morning Herald, April 1811:
“I am now in the doldrums but when I get better, I will send you.”
In 1824, Lord Byron used the phrase in a nautical context in the verse tale The Island:
“From the bluff head where I watch’d to-day, I saw her in the doldrums for the wind Was light and baffling.”
‘In the doldrums’ came to refer specifically to sailing ships that were becalmed and unable to progress.
Please enable JavaScript
“The ‘equatorial doldrums’ is another of these calm places. Besides being a region of calms and baffling winds, it is a region noted for its rains.”
Read Also: What Are The Possible Benefits Of Studying Biology
Seven Things You Need To Know About The Doldrums
The teams have spent the last week hurtling south at breakneck speeds, huge stomach-twisting waves and with buckets of skinnumbing amounts saltwater gushing over the deck.
So far, so Volvo Ocean Race. But there’s another landmark on the horizon and it’s time for something altogether different.
Fickle winds coming and going, tropical rain spilling and stuttering from clouds as wide as cities, extreme thunderstorms cracking and warping the skyline yep, the boats are heading for the Doldrums, well-known by the world’s best sailors as an ocean parking lot around the Equator, and which could cause a complete fleet restart in Leg 2.
Here are seven things you need to know about the area which has tortured mariners for centuries…
There’s no wind here. The Doldrums is a low pressure area from 5°N to 5°S of the Equator. Winds are famously calm here, with prevailing breeze disappearing altogether at times, making it extremely difficult to navigate through.
It’s a place for trade winds to meet other trade winds. The Doldrums is also known as the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone , because it’s where two sets of trade winds meet and that’s why conditions can be so shifty. Previously, it was known as the Intertropical Front, but in the 1950s experts discovered the significance of wind field convergence, and renamed it.
South Pacific Convergence Zone
The South Pacific convergence zone is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is considered the largest and most important piece of the ITCZ, and has the least dependence upon heating from a nearby land mass during the summer than any other portion of the monsoon trough. The southern ITCZ in the southeast Pacific and southern Atlantic, known as the SITCZ, occurs during the Southern Hemisphere fall between 3° and 10° south of the equator east of the 140th meridian west longitude during cool or neutral El NiñoSouthern Oscillation patterns. When ENSO reaches its warm phase, otherwise known as El Niño, the tongue of lowered sea surface temperatures due to upwelling off the South American continent disappears, which causes this convergence zone to vanish as well.
You May Like: How To Find Math Worksheet Answers
Presentation On Theme: Welcome To The Doldrums Presentation Transcript:
1 WelcometotheDoldrums
2 Sailors sometimes have difficulty when sailing in the doldrumsSailors sometimes have difficulty when sailing in the doldrums. Winds will be light causing boats to come to a standstill, sometimes for days. Only sudden storms with strong winds allow sailors to move on.
3 Doldrums
4 The doldrums are between the northeast trades of the northern hemisphere and the southeast trades in the southern hemisphere. The doldrums vary each year, but never extend far south of the equator.The doldrums are also known as Intertropical Convergence Zone .
5 In the doldrums, the winds are light or do not exist at all, the weather is hot and sticky, and thunderstorms can appear with little warning. Sometimes the warm air that rises causes these sudden storms. Sailors will seek out these sudden storms to get out of the doldrums they will go from storm to storm until they are finally able to leave the area of the doldrums.
6 Web Resources Works Cited“doldrums.” The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. © 1994, 2000, 2001, 2002 on Infoplease.com. © 2002 Family Education Network. 3 Dec < Schrope, Mark. “The Doldrums: Sailing’s Dead Zone.” The Volvo Ocean Race National Geographic Society. 03 Dec <
Why Do The Winds Curve To The East Between 30 60 Degrees
The Coriolis effect is the apparent curvature of global winds, ocean currents, and everything else that moves freely across the Earths surface. The curvature is due to the rotation of the Earth on its axis. Between thirty and sixty degrees latitude, the winds that move toward the poles appear to curve to the east.
Don’t Miss: Do You Know Your Geography Worksheet Answers
Solved Question For You
Q.1 In which direction the doldrums or ITCZ moves during the summer of the northern hemisphere?
A.1 The Correct answer is A towards the north. Due to the tilt in the earth axis, the doldrums move towards the north during the summer season in the northern hemisphere
What Is Doldrums In Geography
The doldrums is a popular nautical term that refers to the belt around the Earth near the equator where sailing ships sometimes get stuck on windless waters. The rising air mass finally subsides in what is known as the horse latitudes where the air moves downward toward Earths surface.Feb 26 2021
You May Like: What Does Flashpoint Mean In Chemistry
What Are The Doldrums
The Doldrums are regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans that have little if any wind.
This was a particular problem for sailors in the past when they depended on the winds to propel their ships, a problem that could be potentially deadly.
The Doldrums are caused by solar radiation from the sun, as sunlight beams down directly on area around the equator.
This heating causes the air to warm and rise straight up rather than blow horizontally.
The result is little or no wind, sometimes for weeks on end.
The Doldrums are located a little north of the equator, but the effects can be felt from 5 degrees north of the equator to 5 degrees south of it.
The trade winds border the Doldrums both to the north and south.
Then there are the prevailing westerlies in the higher latitudes and the polar easterlies near both poles.
The rising moist air in the Doldrums can spawn tropical storms and hurricanes.
Nearly every Atlantic hurricane arises in or near the Doldrums.
The unpredictability of the weather, either no winds or potential hurricanes, made the Doldrums one of the least favorite sailing lanes back when all that ships had to power them across the ocean was their sails.
Reason For The Doldrums
With regards,ISC Editor.Studyvillage editor.A group of donkey led by a lion can defeat a group of lion led by a donkey.
| 4 |
Doldrums are also known as ‘Equatorial Calms’. The north of Equator are the areas where Doldrums occur and it is caused when winds from northen and southern hemisphere come together.Due to intense heating the air gets warm and rises in the equatorial region causing equatorial low pressure belt which extends from the equator to about 10’N and S. This belt is characterized by extremely low pressure with calm conditions. Surface winds are generally absent and thus vertical currents are found. This equatorial low pressure belt is called Doldrum due to extremely calm movements. The areas that doldrum effect are Atlantic oceans, Indian oceans and Pacific oceans.Thanks,
| 1 |
HIDoldrums are used to denote inactive or stagnant things. It also refers to an equitorial zone encircling the earth.
Also Check: How To Tutor 6th Grade Math
Relation Of Global Wind Circulation
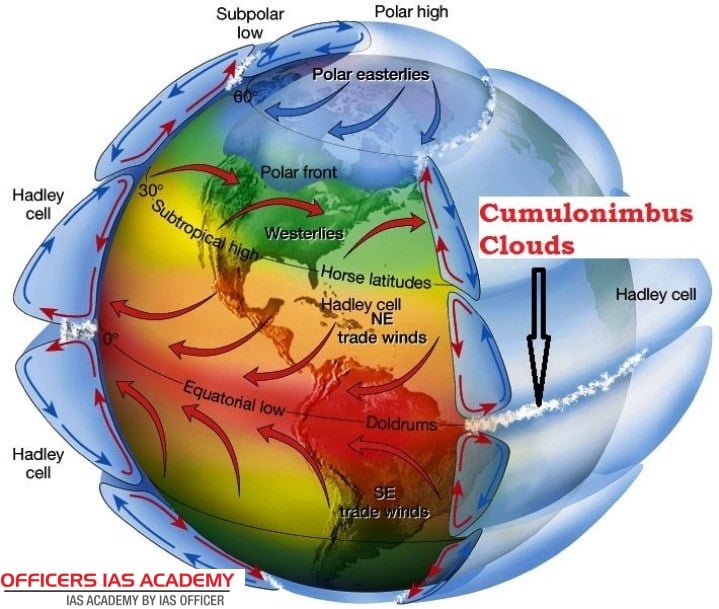
They fit perfectly in the global pattern of the atmospheric circulation of wind that involves three cells in each hemisphere.
Also, the cells involve zones of major wind belts, separated from each other by zones of relatively lighter winds in which the air sinks or rises.
In addition, they separate the trade winds of the southern hemisphere from the trade wind of northern hemisphere.
At the doldrums, the warm air rises and flows away from the equator to about 30 degrees south and north latitude where it descends respectively.
From this wind, some of the warm air moves towards the westward direction in the form of trade winds. On the contrary, the remaining portion blows towards the east, creating the dominant westerlies.
After that, the air again rises to around 60 degrees in latitude from the boundary between westerlies and the polar easterlies and finally sinks once more at the poles.
Role In Tropical Cyclone Formation

One of the six conditions for tropical cyclogenesis is low-level vorticity, which the ITCZ offers as a region of wind shift and speed, also known as horizontal wind shear. Increasing Coriolis force makes the development of tropical cyclones within the ITCZ more likely as it migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes, and even beyond, during the respective hemisphere’s summer season.
Don’t Miss: What Is Sensory Restriction Psychology
Doldrums Vs Horse Latitudes
Doldrums and horse latitudes are ocean regions on the Earth. Specifically, doldrums are ocean belts near the equator. The region is characterized as having little to no wind. This lack of wind has been a problem in sea exploration in the last centuries since ships cannot move if there is no wind.
Doldrums can be found in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Doldrums are located five degrees to the north and five degrees to the south near the equator. The lack of wind in the doldrums can last for a long period of time. This happens because the suns intense heat contributes to the warming of the air, and it climbs into the atmosphere.
Due to the rising moist air, doldrums can also develop into extreme weather like massive storms, squalls, thunderstorms, or hurricanes. This resulting weather also disrupts a ships movement and journey. Both the lack of wind and extreme weather cause casualties at sea by prompting low supplies, starvation, sickness, and eventually death.
The term doldrums originated from the dull or slow-moving experiences of sailors in this area during the 18th century. These adjectives were later adapted and used to describe the place.
On the other hand, horse latitudes are also two ocean belts located near the equator. They are placed at exactly 30 degrees north and south latitude. Like doldrums, the areas of horse latitudes have clear skies with little or low airflow.
What Are Doldrums
The “doldrums” is a nautical word for the belt around the Earth above the equator where sailing ships will get stuck in windless waters sometimes. Low atmospheric pressure and a lack of substantial wind characterize the region. In addition, the region’s weather is cloudy and rainy.
The convergence zone, or ITCZ , is the name given to this zone or region. Furthermore, they are precisely situated between the latitudes of five degrees north and five degrees south. The Doldrums are a few degrees north of the equator, but their impact can be felt anywhere from 5 degrees north to 5 degrees south. This was a particular concern for sailors who relied on the wind to power their ships in the past. It was a crisis with the potential to be deadly.
The hot, moist air is drawn up into the atmosphere like a hot air balloon due to extreme solar heating above the equator. When the air rises, it cools, resulting in a ring of showers and storms around the Earth’s center. In the horse latitudes, where the air travels downward toward the Earth’s surface, the increasing air mass finally subsides. In the ITCZ, there is typically no surface wind since the air circulates upward. This is why the region will keep sailing ships at bay for weeks. That’s why it’s known as the doldrums.
You May Like: What Can You Do With An Associate’s In Psychology