What Is Saturated Class 10
Compounds shaped by the linking of carbon by single bonds in between them are called saturated compounds. These compounds have hydrogen atoms that fill all of the different bonding orbitals of the carbon atoms. For example Alkanes are saturated compounds. The valency of hydrogen is 1 and that of carbon is 4.
What Makes A Solution Saturated
When the solution equilibrium point is reached and no more solute will dissolve, the solution is said to be saturated. A saturated solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved. At 20°C, the maximum amount of NaCl that will dissolve in 100. g of water is 36.0 g.
How Do You Know When A Solution Is Saturated
It’s easy to tell if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated by adding a very small amount of solute. If the solution is unsaturated, the solute will dissolve. If the solution is saturated, it won’t. If the solution is supersaturated, crystals will very quickly form around the solute you’ve added.
Also Check: What Does The Symbol K Mean In Chemistry
Affinity Of Nitrifying Bacteria For Ammonia And Nitrite
Saturation constants for growth range from 0.05 to 0.07 mM NH4+ and 0.015 to 0.178 mM NO2, for NH3 and NO2- oxidisers, respectively. Saturation constants for activity, measured on cell suspensions, are higher: 0.1214 mM NH4+ and 1.63.6 mM NO2, respectively. Thus, NH3 is unlikely to limit growth or activity of AOB in wastewater treatment systems, but will limit soil and aquatic NH3 oxidation, except in microenvironments with locally high concentrations. NO2-concentrations are close to detection levels in the majority of natural environments, and saturation constants therefore predict substrate-limited growth and activity of NO2 oxidisers. However, their greater biomass and potential for heterotrophic growth ensure that NO2 is used rapidly and rarely accumulates. It must be emphasised, however, that these growth parameters are difficult to obtain experimentally and quoted figures are based on relatively few studies.
Raymond H. de Wit, … Martine J. Smit, in, 2016
What Wont Make A Saturated Solution
There are two situations where a solute and solvent cant form a saturated solution.
Basically, to form an unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated solution you need a solute that is at least partially soluble in the solvent.
You May Like: How To Find My Biological Father
What Are Saturated Hydrocarbons
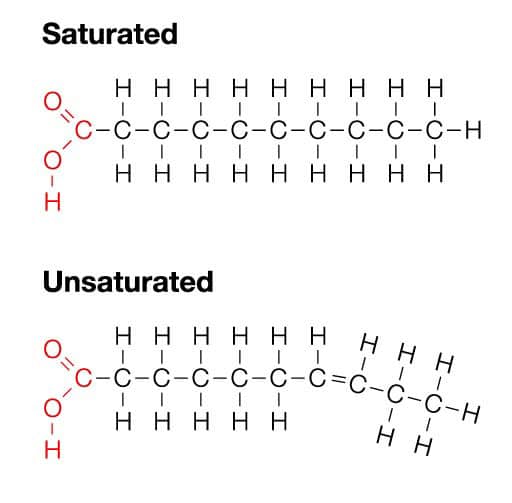
A Saturated hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon in which all the carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds. A hydrocarbon is an organic compound whose only constituents are carbon and hydrogen. As the name suggests, saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which all the carbon atoms are bonded to four other atoms and are saturated, implying that no carbon-carbon multiple bonds exist in these organic compounds.
Examples Of Saturated In A Sentence
saturatedsaturatedsaturated Alluresaturated Voguesaturated Washington Postsaturated Washington Postsaturated EW.comsaturated Better Homes & GardenssaturatedTown & CountrysaturatedForbes
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘saturated.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Recommended Reading: What Year Do You Take Chemistry
What Is Saturated In Biology
Saturated solutions happen when there is the maximum concentration of solute in an answer. Enzymes in biological techniques can also change into saturated with the substrate the molecule they paintings on. Saturation is additionally a term used to describe alkyl chains that experience the maximum number of carbon and hydrogen bonds.
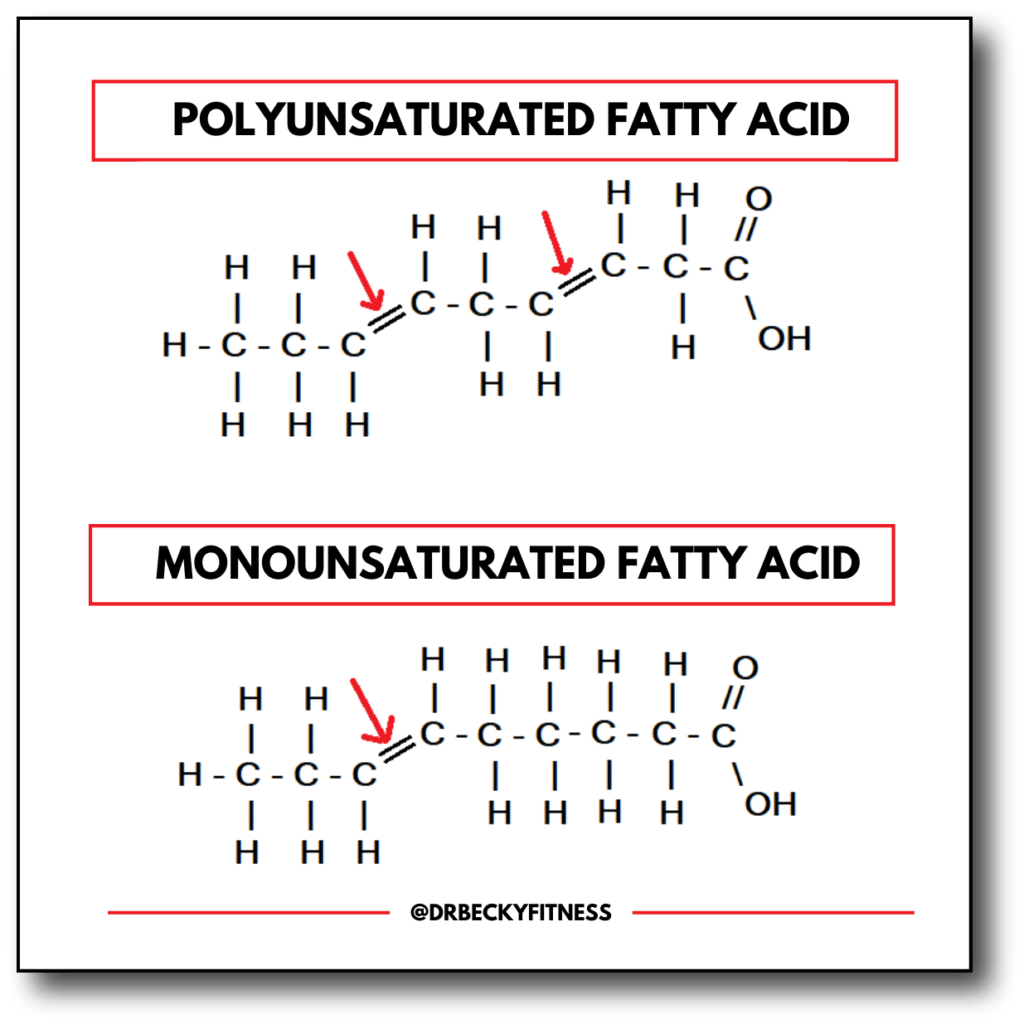
Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Unsaturated hydrocarbons feature at least one double or triple bond between two adjacent carbon atoms. The key differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons are tabulated below.
| Saturated Hydrocarbons | |
| All carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized in these compounds. | They contain sp2 or sp hybridized carbons. |
| Contain more hydrogen atoms than the corresponding unsaturated hydrocarbons. | Contain fewer hydrogens than the corresponding saturated hydrocarbons. |
| Examples include alkanes and cycloalkanes. | Examples include alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. |
| They have a relatively low chemical reactivity | They are more reactive than their saturated counterparts. |
| They generally burn with a blue flame | These generally burn with a sooty flame. |
Read Also: What Are Probes In Biology
What Are The Uses Of Saturated Hydrocarbons
Alkanes are widely used as fuels, heating oils, and solvents. A few other uses of saturated hydrocarbons are listed below.
- Methane is used as a fuel in several automobiles, water heaters, and ovens. In its refined form, liquid methane can also serve as rocket fuel.
- Several cryogenic refrigeration systems use ethane as a refrigerant. It is also used in the production of ethylene.
- The propellant used in several aerosol sprays is a saturated hydrocarbon known as propane. This compound is also used as a fuel for hot air balloons.
- Cycloalkanes also find use in motor fuels, diesel, petroleum gas, and other heavy oils.
- The manufacture of rubber and nylon also involves the use of cycloalkanes.
What Is A Saturated Solution
A saturated solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved under the condition at which the solution exists.
In chemistry, after studying solutions and properties of the solution, one can understand that a solution can reach a status of saturation. This state is when the solution has reached a point in which no more solute can be added. Addition of solute after this point would result in a solid precipitate or gas being released. Such a mixture is called a saturated solution.
Read Also: Introduction To 3 Dimensional Geometry
What Do The Terms Saturated And Unsaturated Mean Biology
Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms whilst in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain. Saturated fat have a tendency to be forged at room temperature and from animal assets whilst unsaturated fat are generally liquid and from plant resources.
Everyday Examples Of Saturated Solution

- Beverages are one of the most widely used and loved saturated solutions. In these drinks, water is a solvent and carbon is bombarded as a solute until the point of saturation is reached.
- In the kitchen, many cooking recipes involves dissolving of salt, sugar and other household ingredients into the water. This procedure is temperature-dependent. As the temperature of water increases the solubility of the solute increases. After the point of saturation is reached the solute forms a visible layer on top of the solvent.
- Soil present on the earth surface can also be called as a saturated mixture which consists of nitrogen. Once the saturation point is reached the excess nitrogen is let out into the air in the form of gas.
Also Check: How To Do Powers In Math
Effects Of Saturation On Life
The minimum saturation of 85% does provide a guide to the life of the battery under normal operating conditions. Given a starting saturation of 97% and an end-of-life saturation of 85% it can be calculated, from the normal water loss due to grid corrosion and recombination inefficiencies, whether the saturation is a life-limiting factor regarding thermal runaway in a particular cell design and for a specific duty.
Saturation level also affects battery capacity as shown in Figure 10. Low rate capacities such as the 25 A reserve capacity are directly proportional to the saturation and consequently reduce in a linear manner with saturation. The high rate capacity, on the other hand, shows a very nonlinear behavior. This is due to the effect of reduced saturation producing a marked increase in the separator resistance and iR losses becoming very significant at these high currents. This is illustrated in Figure 11, where the increase in resistance is shown to mirror the decrease in saturation.
Figure 10. Effect of saturation on reserve capacity at 25 A.
Figure 11. Effect of saturation on high rate capacity.
Notes: Results are for a 12 V battery. Conductivity ratio is the battery conductivity compared to the conductivity at 100% saturation.
The 30 s voltage refers to the battery discharged at the rated cold cranking current at 0 °F, i.e., 18 °C. After 30 s on discharge the requirement is that the battery voltage be in excess of 7.2 V.
DONALD J. PIETRZYK, CLYDE W. FRANK, in, 1979
Hls And Hsv Colour Models
The HLS colour model, whose parameters represent hue, lightness and saturation, is based on the Ostwald colour system. This model consists of a double pyramid, as shown in Figure 10.9. Analogous to the HSV system , the hue H is given by the angle around the vertical axis of the double pyramid, occupying red at the origin . Saturation is represented by the distance from a colour to the vertical neutral axis. Lightness ranges from 0 to 1, from black to white, respectively.
Figure 10.9. HLS colour model.
A. Das, … S. Makhija, in, 2010
Don’t Miss: How To Name Compounds In Chemistry
What Are Some Uses Of Alkanes
To learn more about saturated hydrocarbons and other related concepts in organic chemistry , register with BYJUS and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Factors That Affect Saturation
The amount of solute that dissolves in a solvent depends on multiple factors. Some of the key factors affecting solubility are:
- Temperature: Increasing temperature increases solubility, up to a point. For example, more salt dissolves in hot water than in cold water. A saturated solution at a cold temperature has a lower concentration than a saturated solution at a higher temperature.
- Pressure: Increasing pressure forces more solute into solution. One application is dissolving gases into liquids, such as carbon dioxide into soda.
- Chemical Composition: The nature of the solute and solvent affect solubility. So does the present of other compounds in the solution. For example, you can dissolve more sugar in water than salt in water.
- pH: The acidity or basicity of a solution affects whether or not ions dissociate, so it influences solubility.
Also Check: Slader Big Ideas Math Geometry
Saturated Vs Supersaturated Solutions
Controlling these factors allows for supersaturation. A supersaturated solution is an unstable solution that contains more solute than should dissolve in the solvent. For example, if you prepare a saturated solution of sugar in hot water and then cool the solution, it becomes supersaturated when the temperature changes. Disturbing the solution or adding a nucleation point induces crystal growth.
How To Prepare A Saturated Solution
A saturated solution is prepared by continuously adding solute to the solution until a stage is reached where the solute appears as a solid precipitate or as crystals to form a highly saturated solution.
Don’t Miss: What Does P Stand For In Math
How Do You Know If A Solution Is Saturated
It’s easy to tell if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated by adding a very small amount of solute. If the solution is unsaturated, the solute will dissolve. If the solution is saturated, it won’t. If the solution is supersaturated, crystals will very quickly form around the solute you’ve added.
Tests For Saturated And Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Saturated hydrocarbons can be distinguished from unsaturated hydrocarbons in the laboratory because saturated hydrocarbons are less chemically active than unsaturated hydrocarbons. This means alkenes and alkynes more likely to readily react with a chemical reagent than an alkane.
For a qualitative test for unsaturation, a test for the presence or absence or unsaturation, we want to choose a chemical reaction that produces an effect that is easy to observe, a colour change for example.
Two common reagents used to detect whether a hydrocarbon is saturated or unsaturated are:
- bromine water, Br2 : a yellow to brown colour depending on concentration
- potassium permanganate solution, KMnO4 : a pink to purple colour depending on concentration
Recommended Reading: How To Find Kp In Chemistry
What Does It Mean Saturated And Unsaturated
Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms, while in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain. Saturated fats tend to be solid at room temperature and from animal sources, while unsaturated fats are usually liquid and from plant sources.
Saturated Solution Definition And Examples
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A saturated solution is a chemical solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent. The additional solute will not dissolve in a saturated solution.
The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent to form a saturated solution depends on a variety of factors. The most important factors are:
- Temperature: Solubility increases with temperature. For example, you can dissolve much more salt in hot water than in cold water.
- Pressure: Increasing pressure can force more solute into solution. This is commonly used to dissolve gases into liquids.
- Chemical Composition: The nature of the solute and solvent and the presence of other chemicals in a solution affects solubility. For example, you can dissolve much more sugar in water than salt in water. Ethanol and water are completely soluble in each other.
Read Also: What Does Coordinate Mean In Math
Interconversion Of Saturated And Unsaturated Solution
Saturated solution on heating becomes unsaturated whereas an unsaturated solution becomes saturated upon cooling. On heating the saturated solution, the solubility of that particular solute increases in the given solvent. As a result of this, more solute can be dissolved into the solvent. However, in the case of cooling a solution, the solute particles which were initially dissolved in the solvent separate out as crystals.
Things That Will Not Form Saturated Solutions
If one substance will not dissolve into another, you cannot form a saturated solution. For example, when you mix salt and pepper, neither dissolves in the other. All you get is a mixture. Mixing oil and water together will not form a saturated solution because one liquid does not dissolve in the other.
Also Check: What Is Bachelor Of Psychology
Factors Affecting The Point Of Saturation
- With an increase in temperature the solubility of ionic solutions increases, except mixtures which are made up of compounds containing anions.
- Solutes which are finely divided possess greater solubility.
- The rate of crystallization is dependent upon the amount of solute at the crystal surface.
- The solution is said to be saturated if the rate of crystallization and the rate of solubility are the same.
- The net dissolving rate can be increased by stirring the solution which prevents the build-up of solute.
- The response of the equilibrium system is predicted using Le Chateliers principle which depends upon the change in pressure, concentration or temperature.
Plotting Saturation Binding Data
Saturation binding experiments measure specific binding at equilibrium at various concentrations of the radioligand to determine receptor number and affinity. Use of drug concentrations that allow binding to approach saturation is crucial for accurate examination of the interaction between the drug and receptor. The next consideration is that of nonspecific binding. As mentioned above, a good rule of thumb is to use a concentration of unlabeled ligand at 100 times the Kd. When examining binding in the presence of 100 × Kd, the amount of detected is considered nonspecific, and as shown in Figure 4 is linear with respect to free ligand concentration. Total binding is the amount of detected in parallel samples without this competitor included in the incubation. The difference is the specific binding, and is the data that should conform to the law of mass action. It is this binding that we will examine in more detail.
One of the criteria stated previously for a physiologically relevant receptor is that the binding sites are saturable. To assess saturability, the characteristics of binding as a function of increasing concentrations of radioligand are determined. The saturation-binding curve can be described by eqn
R.A. Chapman, in, 2007
Read Also: How Did The Field Of Psychology Emerge
Other Saturated And Unsaturated Organic Compounds
The term “saturated” can be applied to any organic molecule that contains only single bonds between the carbon atoms , even if another functional group is present in the molecule.
So, for example, we can have
- saturated alcohols, alkanes in which 1 or more hydroxyl functional groups has substituted for a hydrogen atom in the parent alkane.
Saturated And Unsaturated Solutions
A saturated solution is one that contains the maximum amount of solute capable of being dissolved, whereas unsaturated solutions contain less than the maximum amount of solute capable of being dissolved. Because carbonated water is saturated with carbon, it emits carbon through bubbles. Sand in water is an example of an unsaturated.
You May Like: Who Uses Math In Their Job
How To Make A Saturated Solution
There’s more than one way to make a saturated solution. You can prepare it from scratch, saturate an unsaturated solution, or force a supersaturated solution to lose some solute.