What Is Polarity In Chemistry
We know there are many physical properties of compounds like density, melting and boiling points, solubility, volume etc. One of the significant properties of molecules is polarity. The polarity of molecules disturbs other physical properties of the molecules. The polarity of a molecule depends on the type of chemical bonding in the molecule and also on the bonded atoms.
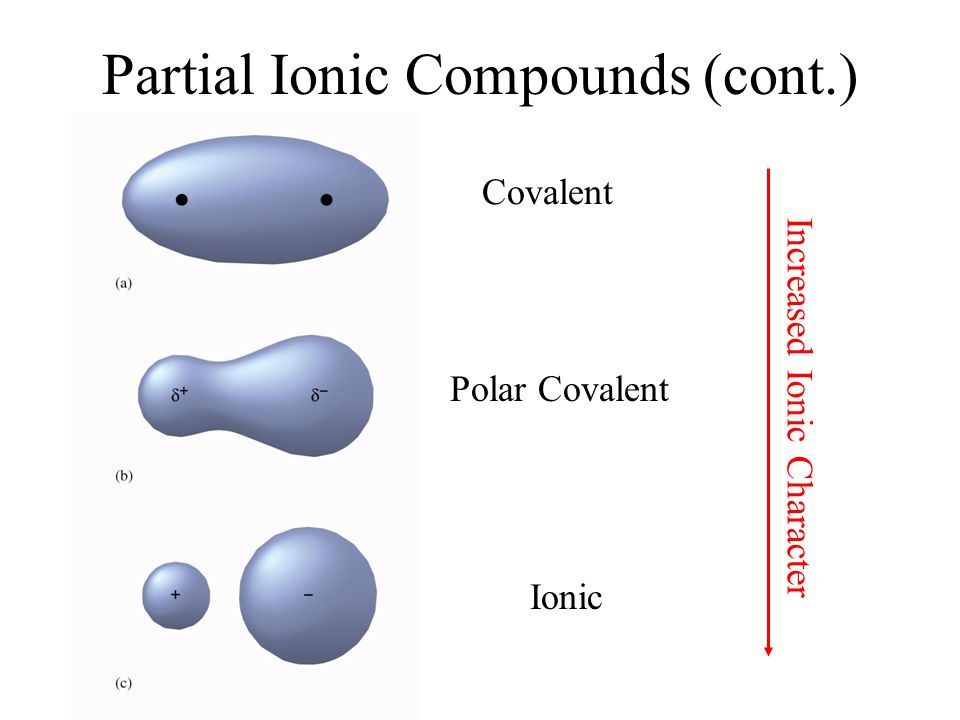
If there is a clear separation of charges, we assume that there is polarity in the molecule. Polarity can be with an ionic and covalent bond. Several of the molecules have polar chemical bonds but are still non-polar in nature due to the equal arrangement of the chemical bonds. Polarity, in common, refers to the physical properties of compounds such as boiling point, melting points, and their solubility. The polarity of bonds mainly arises from the space between molecules and atoms with difference in electronegativities. Moving on, usually, the term Polarity is used in areas like magnetism, electricity, and signaling of electronic devices. Consider an electromotive force or an electric potential, acting between two poles.. The pole having more electrons has a negative polarity whereas the other end has a positive polarity.
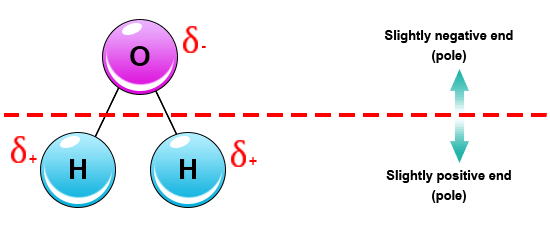
Discussing polarity in Chemistry, well it is mostly the separation of an electric charge which leads a molecule to have a positive and negative end. Consider the below illustration-
What Makes A Bond Non
Non-polar bonds are also a type of covalent bond. Unlike polar bonds, non-polar bonds share electrons equally. A bond between two atoms or more atoms is non-polar if the atoms have the same electronegativity or a difference in electronegativities that is less than 0.4. An example of a non-polar bond is the bond in chlorine. Chlorine contains two chlorine atoms. The electrons are shared equally because the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is zero.
Examples Of Polar And Non
A molecule may be polar or non-polar. A non-polar molecule has a structure of its atoms lined up in a way that the orbital electrons in the outer region cancel out the electronegativity.
- In general, pyramid-shaped and V-shaped molecules are said to be polar. Whereas the Linear molecules are said to be non-polar in nature.
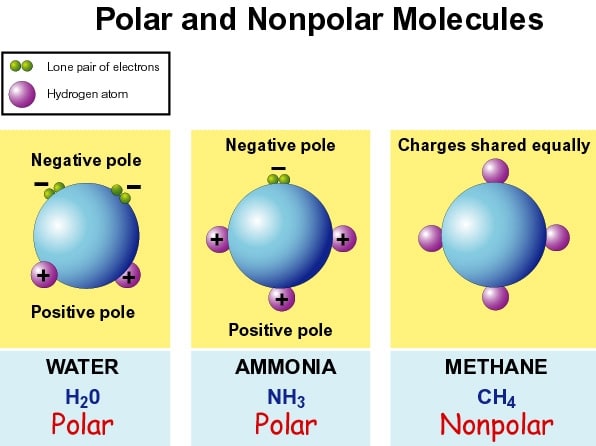
- Water is said to be a polar molecule due to the difference in the electronegativities between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen. Oxygen is a highly electronegative atom when compared to hydrogen.
- Fats, petrol, oil, and gasoline are said to be non-polar molecules as they do not dissolve in water and nonpolar is insoluble in water.
- Glucose is one more example of a polar molecule based on the arrangement of the oxygen and hydrogen atoms in it.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Psychological Approach To The Study Of Law
What Is Polar And Nonpolar Solvents
Let us understand the concept of polar and non-polar solvents.
Polar solvent is a type of solvent that has large partial charges or dipole moments. The bonds between the atoms have very different but measurable electronegativities. A polar solvent can dissolve ions and other polar compounds.
It is possible because of the electrical charges pulling on different parts of the solute molecules. The positively charged ions of the solid compound are attracted by the negatively charged side of a solvent molecule and vice versa. This enables the polar compound to be soluble in the polar solvent. Due to this activity, the ions are evenly distributed throughout the solvent. As for the polarity of the solvent, it basically emerges due to the existing bonds of the atoms with different electronegativity values that leads to the formation of the molecule.
Water is a popular example of a polar solvent. What makes it a polar solvent? If we look at the molecules of water it has a unique structure with two hydrogen bonds. Further, there is a large difference in the electronegativity between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms. As such, the large oxygen attracts the electrons close together and gets negatively charged. The hydrogen atoms each get a smaller share of the shared electrons and thus gains a positive charge. This is the very reason for water becoming a very strong dipole molecule.
Also Read: Hydrogen Bonding
Was this answer helpful?
Polar Molecule Definition And Examples
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A polar molecule is a molecule containing polar bonds where the sum of all the bond’s dipole moments is not zero. Polar bonds form when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms participating in a bond. Polar molecules also form when the spatial arrangement of chemical bonds leads to a more positive charge on one side of the molecule than the other.
Don’t Miss: What Does G Mean In Physics
To Summarize To Be Polar A Molecule Must:
Steps to Identify Polar Molecules
Example \:
Label each of the following as polar or nonpolar.
Solution
Exercise \
Label each of the following as polar or nonpolar.
a. SO3
How Cold Are Ultracold Polar Molecules
Ultracold polar molecules have been created by research scientists. These “molecules” consist of \ and \ atoms excited by lasers to form a type of \ compound where the \ has a positive charge and the \ has a negative charge. The material is formed at temperatures extremely close to absolute zero. The researchers believe these techniques will help them make new reactions and new materials.
You May Like: What Is Ucr In Psychology
Show Students Examples Of Water Molecules Attraction For One Another
Remind students that in Chapters 1 and 2, they investigated the behavior of water at different temperatures and explored the state changes of water. Many of the explanations were based on the idea that water molecules are attracted to one another. Remind students that in Chapter 4 they looked at the covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen, which creates the water molecule. Now students will look more closely at the details of the covalent bonds in a water molecule to understand why water molecules are attracted to one another.
Point out that the water is able to stay together in these arcs because water molecules are very attracted to each other.
Explain
First Frame of the Animation
- Electrons are shared between atoms in a covalent bond.
- Remind students how the shared electrons in a water molecule are attracted to the protons in both the oxygen and the hydrogen atoms. These attractions hold the atoms together.
- Water molecules are neutral.
- Be sure students realize that no protons or electrons are gained or lost. The water molecule has a total of 10 protons and 10 electrons . Since it has the same number of protons and electrons, the water molecule is neutral.
Ask students:
Examples Of Molecules With Polar Covalent Bonds
Water is a polar bonded molecule. The electronegativity value of oxygen is 3.44, while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 2.20. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the bent shape of the molecule. The oxygen “side” of the molecule has a net negative charge, while the two hydrogen atoms have a net positive charge.
Hydrogen fluoride is another example of a molecule that has a polar covalent bond. Fluorine is the more electronegative atom, so the electrons in the bond are more closely associated with the fluorine atom than with the hydrogen atom. A dipole forms with the fluorine side having a net negative charge and the hydrogen side having a net positive charge. Hydrogen fluoride is a linear molecule because there are only two atoms, so no other geometry is possible.
The ammonia molecule has polar covalent bonds between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. The dipole is such that the nitrogen atom is more negatively charged, with the three hydrogen atoms all on one side of the nitrogen atom with a positive charge.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Six Essential Elements Of Geography
What Are The Factors That Determine Whether A Molecule Is Polar
-
If the molecule or atom is perfectly symmetric, the molecule will not be polar even if there are polar bonds present.
-
Polar bonds are formed when one atom in the bond has a much tougher pull towards electrons than the other atom. The difference in strength can be expected by comparing electronegativity values. If one electronegativity value is greater, that atom will pull the electron closer and develop a partial negative charge, while the other atom develops a partial positive charge.
Polar Versus Nonpolar Molecular Geometry
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
The two main classes of molecules are polar molecules and nonpolar molecules. Some molecules are clearly polar or nonpolar, while others fall somewhere on the spectrum between two classes. Here’s a look at what polar and nonpolar mean, how to predict whether a molecule will be one or the other, and examples of representative compounds.
You May Like: How Did The Geography Of Greece Affect Its Development
Electrical Deflection Of Water
Contrary to popular misconception, the electrical deflection of a stream of water from a charged object is not based on polarity. The deflection occurs because of electrically charged droplets in the stream, which the charged object induces. A stream of water can also be deflected in a uniform electrical field, which cannot exert force on polar molecules. Additionally, after a stream of water is grounded, it can no longer be deflected. Weak deflection is even possible for nonpolar liquids.
Factors On Which The Polarity Of Bonds Depend
-
Relative Electronegativity of Participating Atoms or Molecules- Since the bond polarity involves dragging of electrons towards itself, a more electronegative element will be able to attract the electrons more towards itself. As a result, the electrons will absolutely move towards the more electronegative element. The amount of their transfer will depend upon the relative electronegativity of the participating atoms.
-
The Spatial Arrangement of Various Bonds in the Atom or Molecule- The shared pair of electrons also experience dragging force from the other bonded and non-bonded pair of electrons. This results in different bond polarity among the same participating atoms that are present in other molecules. For e.g. Bond Polarity of O-H bond in an H2O molecule and acetic acid molecule is much different. This is due to the different spatial arrangement of many bonds in the molecule.
Don’t Miss: Saxon Algebra 1 Third Edition Answers
Which Elements Form Polar Bonds
Polar covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms that have sufficiently different electronegativities from each other. Because the electronegativity values are slightly different, the bonding electron pair isn’t equally shared between the atoms. For example, polar covalent bonds typically form between hydrogen and any other nonmetal.
The electronegativity value between metals and nonmetals is large, so they form ionic bonds with each other. Usually hydrogen acts as a nonmetal rather than as a metal.
Examples Of Polar In A Sentence
polarpolar oppositesMen’s Healthpolar Detroit Free Presspolar Better Homes & Gardenspolar USA TODAYpolar San Diego Union-Tribunepolar CNNpolar WSJpolar NBC NewspolarNew York Timespolar CNNpolar New York Timespolar NBC Newspolar CNNpolar Smithsonian Magazinepolar Popular Sciencepolar National Review
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘polar.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Also Check: What Is K+ In Chemistry
But Aren’t Ionic Bonds Polar
In ionic bonds, the electrons in the bond are essentially donated to one atom by the other . Ionic bonds form between atoms when the electronegativity difference between them is greater than 1.7. Technically ionic bonds are completely polar bonds, so the terminology can be confusing.
Just remember a polar bond refers to a type of covalent bond where electrons aren’t equally shared and electronegativity values are slightly different. Polar covalent bonds form between atoms with an electronegativity difference between 0.4 and 1.7.
Nonpolar Molecules Have No Separation Of Charge
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A nonpolar molecule has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are formed. In other words, the electrical charges of nonpolar molecules are evenly distributed across the molecule. Nonpolar molecules tend to dissolve well in nonpolar solvents, which are frequently organic solvents.
In a polar molecule, one side of the molecule has a positive electrical charge and the other side has a negative electrical charge. Polar molecules tend to dissolve well in water and other polar solvents.
There are also amphiphilic molecules, large molecules that have both polar and nonpolar groups attached to them. Because these molecules have both polar and nonpolar character, they make good surfactants, aiding in mixing water with fats.
Technically, the only completely nonpolar molecules consist of a single type of atom or of different types of atoms that display a certain spatial arrangement. Many molecules are intermediate, neither completely nonpolar nor polar.
Also Check: What Does Origin Mean In Math Terms
Polarity And Mixing Solutions
If you know the polarity of molecules, you can predict whether or not they will mix together to form chemical solutions. The general rule is that “like dissolves like”, which means polar molecules will dissolve into other polar liquids and nonpolar molecules will dissolve into nonpolar liquids. This is why oil and water don’t mix: oil is nonpolar while water is polar.
It’s helpful to know which compounds are intermediate between polar and nonpolar because you can use them as an intermediate to dissolve a chemical into one it wouldn’t mix with otherwise. For example, if you want to mix an ionic compound or polar compound in an organic solvent, you may be able to dissolve it in ethanol . Then, you can dissolve the ethanol solution into an organic solvent, such as xylene.
Examples Of Polar Molecules
- Water is a polar molecule. The bonds between hydrogen and oxygen are distributed so that the hydrogen atoms are both on one side of the oxygen atom rather than evenly spaced. The oxygen side of the molecule has a slight negative charge, while the side with the hydrogen atoms has a slight positive charge.
- Ethanol is polar because the oxygen atoms attract electrons because of their higher electronegativity than other atoms in the molecule. Thus the -OH group in ethanol has a slight negative charge.
- Ammonia is polar.
- Sulfur dioxide is polar.
- Hydrogen sulfide is polar.
Carbon dioxide is made up of polar bonds, but the dipole moments cancel each other out. Therefore it is not a polar molecule.
You May Like: What Is Ba Psychology Course
Give Each Student An Activity Sheet
Students will record their observations and answer questions about the activity on the activity sheet. The Explain It with Atoms & Molecules and Take It Further sections of the activity sheet will either be completed as a class, in groups, or individually, depending on your instructions. Look at the teacher version of the activity sheet to find the questions and answers.
Key Takeaways: What Is A Polar Bond In Chemistry
- A polar bond is a type of covalent bond in which the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. In other words, the electrons spend more time on one side of the bond than the other.
- Polar bonds are intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. They form when the electronegativity difference between the anion and cation is between 0.4 and 1.7.
- Examples of molecules with polar bonds include water, hydrogen fluoride, sulfur dioxide, and ammonia.
Don’t Miss: Algebra 2 Conics Review Worksheet
Key Takeaways: Polar And Nonpolar
- In chemistry, polarity refers to the distribution of electric charge around atoms, chemical groups, or molecules.
- Polar molecules occur when there is an electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.
- Nonpolar molecules occur when electrons are shared equal between atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out.
How To Tell If Something Is Polar Or Non
Polarity describes the tendency of a substance to have a molecular dipole, or a positively and a negatively charged end. Polar molecules are made of elements with different electronegativities, or electron attractions, meaning that one element possesses the shared electrons more often than the other. This gives the more electronegative element a partially negative charge and the more electropositive element a partially positive charge. If these elements are arranged symmetrically, so that these charges cancel one another, the molecule is non-polar. If they are arranged asymmetrically, however, they form a polar molecule.
You May Like: Common Core Geometry Module 2
What Is Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the measurement of how much an atom wants to bond to another atom. Electronegativity increases from left to right and down each column on the periodic table. The Pauling scale describes the electronegativity of an element, with a scale from 0.7 to 4. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, with an electronegativity of 4. Cesium is the least electronegative element with an electronegativity of 0.7.