Albert Bandura And His Model
The psychological theory of self-efficacy grew out of the research of Albert Bandura. He noticed that there was a mechanism that played a huge role in peoples lives that, up to that point, hadnt really been defined or systematically observed. This mechanism was the belief that people have in their ability to influence the events of their own lives.
Bandura proposed that perceived self-efficacy influences what coping behavior is initiated when an individual is met with stress and challenges, along with determining how much effort will be expended to reach ones goals and for how long those goals will be pursued .
He posited that self-efficacy is a self-sustaining trait when a person is driven to work through their problems on their own terms, they gain positive experiences that in turn boost their self-efficacy even more.
Bandura also identified four sources of self-efficacy, but well get to those later.
To learn more about Banduras original self-efficacy theory, check out this PDF of his chapter in Ramachaudrans Encyclopedia of Human Behavior .
Edited By Shane J Lopez And Cr Snyder
- Print Publication Date:
- Psychology, Social Psychology, Clinical Psychology
- Online Publication Date:
- or copy the link directly:https://www.oxfordhandbooks.com/view/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780195187243.001.0001/oxfordhb-9780195187243-e-031The link was not copied. Your current browser may not support copying via this button.Link copied successfully
date: 27 December 2021
What Is The Meaning Of Self
Self-efficacy is the belief we have in our own abilities, specifically our ability to meet the challenges ahead of us and complete a task successfully . General self-efficacy refers to our overall belief in our ability to succeed, but there are many more specific forms of self-efficacy as well .
Although self-efficacy is related to our sense of self-worth or value as a human being, there is at least one important distinction.
Read Also: Laws Of Exponents Worksheets 8th Grade
What Is The Self Sufficiency Path
The two paths to development are. Self–sufficiency and international trade. Key ideas for the self sufficiency path are. Barrier limit the import of goods, fledgling businesses are nursed to success, investment is spread equally, and incomes in the country keep pace with incomes in the city. You just studied 22 terms!
How To Improve Self

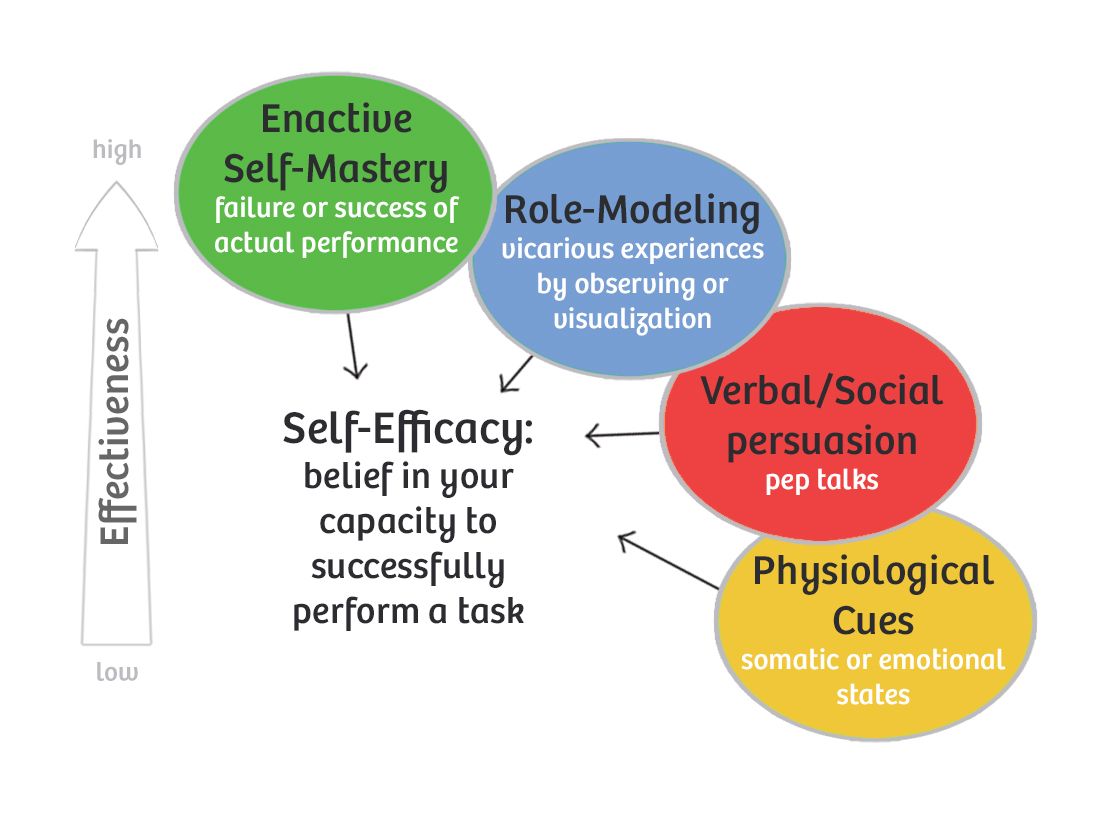
According to Bandura, there are four main sources of self-efficacy beliefs:
Mastery experiences refer to the experiences we gain when we take on a new challenge and succeed. The best way to learn a skill or improve our performance by practice part of the reason this works so well is that we are teaching ourselves that we are capable of acquiring new skills.
Vicarious experience isquite simplyhaving a role model to observe and emulate. When we have positive role models who display a healthy level of self-efficacy, we are likely to absorb some of those positive beliefs about the self.
Vicarious experiences can come from a wide range of sources, including parents, grandparents, aunts and uncles, older siblings, teachers, and administrative staff, coaches, mentors, and counselors.
The verbal persuasion factor describes the positive impact that our words can have on someones self-efficacy telling a child that she is capable and face any challenge ahead of her can encourage and motivate her, as well as adding to her growing belief in her own ability to succeed.
Paying attention to your own mental state and emotional well-being is a vital piece of the self-efficacy puzzle.
When overcoming the challenge in front of you and meeting your goals feels so real you can taste it , its hard not to feel empowered and capable.
Read Also: Algebra 2 Chapter 4 Test Form A
What Types Of Assessment Tools Are Available
There are several types of assessments one can use to measure self-efficacy. One of these is the New General Self-Efficacy Scale by Chen, Gully, and Eden .
This scale provides a measure of self-efficacy that serves as an improvement to the original self-efficacy scale of 17 items created by Sherer et al. in 1982. Although this scale is considerably shorter it is thought to have a higher construct validity that the General Self-efficacy Scale.
The eight-item measure scale assesses ones belief that they can achieve their goals, despite whatever difficulties they may encounter or have.
Researchers have used this measure with African-Americans living on a low income, European Americans who were homeless, Latin-American, first generation Latinx college students and college students as well as professionals in the U. S. and abroad.
Pay Attention To Your Thoughts And Emotions
If you find yourself getting stressed out or nervous before a challenging event, you might feel less sure of your ability to cope with the task at hand.
Another way to boost your self-efficacy is to look for ways to manage your thoughts and emotions about what you are trying to accomplish.
Do you feel anxious? Looking for ways to ease your stress levels can help you feel more confident in your capabilities. Do you find yourself dwelling on negative thoughts? Look for ways to replace negativity with positive self-talk that promotes self-belief.
Read Also: What Was The Geography And Climate Of New England
What Is Self Efficacy Examples
Some examples of strong selfefficacy include: A student who feels confident that she will be able to learn the information and do well on a test. A woman who has just accepted a job position in a role she has never performed before but feels that she has the ability to learn and perform her job well.
What are the 4 sources of self efficacy?
According to Bandura, there are four main sources of self-efficacy beliefs:
Watching Others Experiences Of Mastery
A second source of efficacy beliefs comes from vicarious experience of mastery, or observing others successes . Simply seeing someone else succeed at a task, in other words, can contribute to believing that you, too, can succeed. The effect is stronger when the observer lacks experience with the task and therefore may be unsure of his or her own ability. It is also stronger when the model is someone respected by the observer, such as a students teacher, or a peer with generally comparable ability. Even under these conditions, though, vicarious experience is not as influential as direct experience. The reasons are not hard to imagine. Suppose, for example, you witness both your teacher and a respected friend succeed at singing a favorite tune, but you are unsure whether you personally can sing. In that case you may feel encouraged about your own potential, but are likely still to feel somewhat uncertain of your own efficacy. If on the other hand you do not witness others singing, but you have a history of singing well yourself, it is a different story. In that case you are likely to believe in your efficacy, regardless of how others perform.
Recommended Reading: Span In Linear Algebra
What Are Some Examples Of Self
Examples of High Self–Efficacy
- A man who is struggling to manage his chronic illness but feels confident that he can get back on track and improve his health by working hard and following his doctor’s recommendations.
- A student who feels confident that she will be able to learn the information and do well on a test.
Alternative Approaches To Research On Self
Although direct recommendations may be premature given the need for further research, we offer the following suggestions to illustrate the potential implications of the self-efficacy-as-motivation argument. First, the vast literature in which self-efficacy is predictive of health-related behaviours , as well as research on how to change self-efficacy ratings , should not be ignored even if the measures of self-efficacy in this literature are confounded with motivation. Instead, self-efficacy assessments may be viewed as an alternative assessment of motivation , with the vast literature on self-efficacy and health-related behaviour reinterpreted to indicate that motivationnot merely perceived capabilityis predictive of health-related behaviour. Can-do motivation would then be positioned as the most proximal determinant of behaviour, as is currently the case with behavioural intention , with the caveat that can-do motivation and behavioural intention may often be largely redundant .
According to the self-efficacy-as-motivation argument, I can do is colloquially interpreted as motivation . Accordingly, self-efficacy should be relabelled and repositioned as can-do motivation in the context of health behaviour theories such as social cognitive theory, the theory of planned behaviour, and protection motivation theory.
Also Check: Chapter 7 Test Algebra 1 Answer Key
Social Messages And Persuasion
A third source of efficacy beliefs are encouragements, both implied and stated, that persuade a person of his or her capacity to do a task. Persuasion does not create high efficacy by itself, but it often increases or supports it when coupled with either direct or vicarious experience, especially when the persuasion comes from more than one person .
For teachers, this suggests two things. The first, of course, is that encouragement can motivate students, especially when it is focused on achievable, specific tasks. It can be motivating to say things like: I think you can do it or Ive seen you do this before, so I know that you can do it again. But the second implication is that teachers should arrange wherever possible to support their encouragement by designing tasks at hand that are in fact achievable by the student. Striking a balance of encouragement and task difficulty may seem straightforward, but sometimes it can be challenging because students can sometimes perceive teachers comments and tasks quite differently from how teachers intend. Giving excessive amounts of detailed help, for example, may be intended as support for a student, but be taken as a lack of confidence in the students ability to do the task independently.
The Interaction Of Self

According to Bandura , two levels of efficacy interact with two types of environment to produce the following four predictive variables:
Success – A person with a high level of self-efficacy in a responsive environment will be successful. Their positive attitude toward their abilities coupled with environmental change promotes success and improves long-term motivation.
Depression – A person with a low level of self-efficacy in a responsive environment may fall into a depressed state. They know the environment will change but their lack of belief in their own abilities stops them from trying and succeeding.
Apathy and helplessness – A person with low self-efficacy and an unresponsive environment will feel helpless and decide that all efforts are pointless thus causing them to be completely inactive.
Effort intensification or change of course – A person with high self-efficacy in an unresponsive environment will either increase their efforts toward change or decide they need to change their goals.
Also Check: What Is Surface Area In Geometry
Research And Studies On The Concept
Self-efficacy has been a popular topic in general psychology and received another boost in attention once positive psychology got off the ground. Accordingly, there is tons of research on the subject, including what it is, how it relates to similar constructs, how it can be improved, and how it impacts people in various contexts.
Locus Of Control Explained
To put self-efficacy in other terms, you might say that those with high self-efficacy have an internal locus of control.
The locus of control refers to where you believe the power to alter your life events resides: within you or outside of you .
If you immediately have thoughts like, I only failed because the teacher graded unfairlyI couldnt do anything to improve my score or She left me because shes cold-hearted and difficult to live with, and Im not, you likely have an external locus of control. That means that you do not have a solid sense of belief in your own abilities.
In juxtaposition to the external locus of control is the internal locus of control, in which an individual is quick to admit her own mistakes and failures, and is willing to take the credit and blame whenever it is due to her.
Self-efficacy and an internal locus of control often go hand-in-hand, but too far in either direction can be problematic those who blame themselves for everything are not likely to be healthy and happy in their lives, while those who dont blame themselves for anything are likely not completely in touch with reality and may have trouble relating to and connecting with others.
Read Also: Algebra 1 Chapter 7 Review Answer Key
National Indices Of Happiness
The creation of various national indices of happiness have broadened and expanded the field of positive psychology to a global scale.
In a January 2000 academic article published in American Psychologist, psychologist Ed Diener proposed and argued for the creation of a national happiness index in the United States. Such an index would provide measurements of happiness, or subjective well-being, within the United States and across many other countries in the world. Diener argued that national indices would be helpful markers or indicators of population happiness, providing a sense of current ratings and a tracker of happiness across time. Diener proposed that the national index include various sub-measurements of subjective well-being, including “pleasant affect, unpleasant affect, life satisfaction, fulfillment, and more specific states such as stress, affection, trust, and joy.”
Additional national well-being indices and reported statistics include the Gallup Global Emotions Report, Gallup Sharecare Well-Being Index, Global Happiness Council’s Global Happiness and Well-being Policy Report,Happy Planet Index, Indigo Wellness Index,OECD Better Life Index, and UN Human Development Reports.
How Self Efficacy Beliefs Are Created
Individuals form their self-efficacy beliefs by interpreting information from four sources. The most influential source is the interpreted result of one’s previous performance, or mastery experience. In addition to interpreting results of their actions, people form their self-efficacy beliefs through the vicarious experience of observing others. Individuals then also create and develop self-efficacy beliefs as a result of social persuasions they receive from others and somatic and emotional states such as anxiety, stress, arousal, and mood states .
Also Check: Who Is The Founder Of Behaviorism
Does Experimental Manipulation Of Outcome Expectancy Influence Self
According to self-efficacy theory, expected outcomes of a target behaviour should not causally influence self-efficacy ratings . Instead, a causal influence of outcome expectancy on self-efficacy ratings is consistent with the self-efficacy-as-motivation argument, suggesting that self-efficacy ratings reflect the broader concept of motivation, rather than perceived capability. We located three studies in which an experimental manipulation focused exclusively on changing expected outcomes of the target behaviour showed effects on subsequent assessments of self-efficacy.
First, tested the causal effects of outcome expectancy on self-efficacy ratings among college student smokers. Participants first responded to the questions could you shoot a basketball through a basket from and could you quit cigarette smoking for . They then rated whether they could perform those same tasks in the context of hypothetical monetary incentives . Participants were more likely to say that they could quit smoking or make basketball shots under the hypothetical incentive scenario. The effect of incentives was greater for ratings of smoking self-efficacy than basketball self-efficacy thus indicating that the causal effects of outcome expectancy on self-efficacy is stronger for behaviours that involve regulation of behaviour rather than specialized physical skills .
Teachers Need High Self
Teachers with a high sense of efficacy about their teaching capabilities may have an easier time motivating their students and enhancing their cognitive development. These teachers may also be able to rebound from setbacks and more willing to experiment with new ideas or techniques. Low efficacious teachers may rely more on a controlling teaching style and may be more critical of students. and )
“Schools in which staff members collectively judge themselves capable of promoting academic success imbue their schools with a positive atmosphere for development that promotes academic attainments regardless of whether they serve predominantly advantaged or disadvantaged students.”
Read Also: Exponential Modeling With Percent Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 2 Homework
Pedagogic Strategies That Foster Self
It is particularly exciting to note that teaching strategies used in the classroom can and do make a difference to students’ self-efficacy.
Research shows that the type of learning environment and teaching method can improve self efficacy in the classroom ). A similar result was reported by Fencl and Scheel . They describe a required, nonmajors’ physics course where the effects of different teaching methods on the classroom climate and self-efficacy were measured. The students’ response indicated that a question and answer format, inquiry-based lab activities and conceptual problems had a significant effect on creating a positive climate in the classroom. In addition to those pedagogies, collaborative learning and the use of electronic applications showed a positive correlation with increased self-efficacy in their student sample. Fencl and Scheel point out that the teaching methods that showed a measurable positive effect share the common feature of engaging students in a comfortable or creative manner. Moreover, pedagogies such as collaborative learning and inquiry-based activities have also been shown to have a strong correlation with how well students learn physics .
Other pedagogies for improving self-efficacy include:
What Is Self Efficacy In Psychology
SelfefficacySelfefficacy
What is meant by self efficacy?
Psychologist Albert Bandura has defined selfefficacy as ones belief in ones ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task. Ones sense of selfefficacy can play a major role in how one approaches goals, tasks, and challenges.
what are the two types of self efficacy?efficacyways
Contents
Also Check: Behaviorism Was Founded By