Daily Life In Mesopotamia
The daily life of the Mesopotamia was different depending on their social class. Upper class, such as priests and kings rejoice the power and responsibility, while the lowest class slaves were just an enchant of their master. The farmers, mostly lived outside the city walls.
The men in the family had more power than a woman. The men were responsible for trading, business, and were the master of the house. Womens stayed at home and serve the family doing the daily housekeeping and cooking.
Mesopotamian lived in a simple rectangle mud brick home up to level three. The mud brick acts as a good insulator to make the house cool during the hustling summer and make the house warmer in the winter.
Festivals were the commons among Mesopotamian. Most of the festival was related to agriculture. The Sumerian celebrated Akitu, the festival of sowing barley in the first month (March/April of the year. This festival was celebrated on the first day of the year in the Babylonian calendar. Hence, it is also known as a New Year festival.
King present was necessary for an important festival. Kings were taken as a god, and Mesopotamian think that the king present in the festival ceremony plays a religious role.
Timeline Of Ancient Mesopotamian Civilization
c. 5000-3500 BCE: The first city-states gradually develop in southern Mesopotamia. This is the achievement of the Sumerian people.
c. 3500: Writing begins to be developed. At first this is based on pictograms, and takes about a thousand years to evolve into a full cuneiform script.
c. 2300: King Sargon of Akkad starts conquering the first empire in world history. The empire reaches its height in c. 2220.
c. 2100: The city of Ur becomes the center of a powerful Mesopotamian state. It soon falls into decline. This marks the decline of the Sumerians as the Amorites, a nomadic people, start moving into Mesopotamia.
1792-49: King Hammurabi of Babylon conquers a large empire. Hammurabi is famous for the law code which he issues. His empire begins to decline immediately after his death.
c. 1530: Babylonia is conquered by the Kassites, who rule the area for 400+ years.
c. 1500: The Mitanni, an Indo-European people, conquer northern Mesopotamia, plus areas of Syria and Asia Minor. After 200 years the kingdom of Assyria conquers northern Mesopotamia from the Mitanni
From 1100: Nomadic peoples such as the Aramaeans and the Chaldeans overrun much of Mesopotamia. The kingdoms of Babylon and Assyria go into temporary decline.
Please see the article on Assyrian civilization for later developments within Mesopotamia.
Geography Of Southern Mesopotamia
Southern Mesopotamia was marshy land and many flat barren plains. Cities were developed along the rivers and irrigation was used in bundles to try and grow something on the infertile plains. Since the settlers in this area did not have any natural resources, they had to have much contact with settlers in other areas in order to trade and have enough food to support their families.
Southern Mesopotamia was also known as lower Mesopotamia. It was the home to the Chaldean marshes, the river of Babylon, the inland freshwater sea of Naja, and was surrounded by red sandstone cliffs standing high above the ground.
There was a primitive seaport named Eridu in the south of Ur on the western bank of Euphrates, but today this location is approximately 130 miles from the sea. Due to the silting up of the shore, the citys function as a harbor ceased to exist.
The first permanent settlements known was found in the lower Mesopotamia and this is why this place is known as the cradle of civilization. The land was so fertile that crops could be harvested twice a year and the third harvest was used for feeding the livestock owned by the inhabitants.
The population in both upper and lower Mesopotamia increased and the inhabitants changed the landscape from being a swamp not fit for human habitation to an extremely fertile area.
You May Like: Math Poems For High School Algebra
Ancient Mesopotamias Place In World History
Ancient Mesopotamia must surely be the most influential civilization in world history. For a start, it was the first. The Mesopotamians were the first to build cities, use the potters wheel, develop writing, use bronze in large quantities, evolve complex bureaucracies, organize proper armies, and so on.
All subsequent Western civilizations were ultimately built largely upon foundations laid here. Mesopotamian civilization deeply influenced societies in Syria, Palestine and Egypt. These in turn, especially via the Phoenicians and the Israelites, would provide the material, religious and cultural models on which the Greek, Roman and Islamic civilizations would later be constructed. A whole range of technologies and scientific advances were thus made in ancient Mesopotamia which eventually found their way to Medieval and Modern European civilization.
To the east, powerful Mesopotamian influences flowed into India at the time of the Assyrians and Persians for example, the Sanskrit alphabet is based on the Aramaean script.
So, the Mesopotamians built long and well they were the giants upon whose shoulders later ages have stood. And given that they were the first people to have writing, and the first to record their deeds, their place in world history is, it is no exaggeration to say, as the ones who got it going!
How Was Trade In Mesopotamia
In the southern part of Mesopotamia docks were built along the sides of the rivers so that ships could easily dock and unload their trade goods. The merchants traded food clothing jewelry wine and other goods between the cities. To buy or trade these goods the ancient Mesopotamians used a system of barter.
You May Like: What Are Lysosomes In Biology
Sargon And The Akkadians
The Akkadian Empire existed from 2234-2154 B.C. under the leadership of the now-titled Sargon the Great. It was considered the worlds first multicultural empire with a central government.
Little is known of Sargons background, but legends give him a similar origin to the Biblical story of Moses. He was at one point an officer who worked for the king of Kish, and Akkadia was a city that Sargon himself established. When the city of Uruk invaded Kish, Sargon took Kish from Uruk and was encouraged to continue with conquest.
Sargon expanded his empire through military means, conquering all of Sumer and moving into what is now Syria. Under Sargon, trade beyond Mesopotamian borders grew, and architecture became more sophisticated, notably the appearance of ziggurats, flat-topped buildings with a pyramid shape and steps.
Why The Bank Of Tigris And Euphratesrivers
Content
A shift from hunters and gatherers to agriculture gave birth to the first civilization. It was the first time in history where a human could stay in the same place for a more extended period. It was known as the Neolithic revolution.
Agriculture flourished due fertile crescent and access of water from the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Most of the earliest civilizations, including Indus Valley Civilization and Ancient Egypt, also flourished on the bank of the river.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Change In Energy Chemistry
How Does Geography Impact The Development Of A Civilization
Geography is the single most important factor that decides if a civilization will prosper and survive throughout centuries. The most revolutionizing factor that caused humans to settle and develop a civilization was the ability to farm. The geographical features of a land will determine if it is suitable for farming.
When Did Mesopotamian Civilization Disappear
What caused such a robust civilization to decline and fall? What happened to the ancient Mesopotamians?
Despite the fact that Mesopotamian civilization experienced chaos and decline in the centuries either side of 1000 BCE, it did not vanish. Indeed, the cities of Mesopotamia, above all Babylon, carefully fostered their ancient heritage. The culture of the Assyrians, who came to dominate Mesopotamia after about 800 BCE, owed a huge amount to the ancient Mesopotamians, and they treated Babylon and other Mesopotamian cities with great respect.
Babylonian civilization under Nebuchadnezzar
The heritage of ancient Mesopotamia experienced a period of great revival in 6th century BCE, under the Babylonian empire of Nebuchadnezzar . By some interpretations, it was under Nebuchadnezzar that ancient Mesopotamia reached its peak. It had never been wealthier, its capital, Babylon, had never been more magnificent, and it had certainly never been more politically powerful. This is all reflected in its art and architecture. The ruins of Babylon which can be seen today mostly date from this phase in its history, and show what a splendid city it was at that time.
Under the Persian empire
The fall of the Babylonian empire to the Persians 539 BC brought Mesopotamia under foreign rule, and it was to remain so for more than a thousand years. In that time, the culture of the people of Mesopotamia was transformed.
Impoverishment
Alexander the Great and successors
Under the Parthians
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Growth And Development In Biology
Contributions To Human Development
Mesopotamia is called the cradle of civilization for numerous developments. Sumerian is considered to be Mesopotamias earliest language. Other languages spoken by the Mesopotamian population include Subartuan, Akkadian, and old Aramaic. Cuneiform was invented in the region, and it facilitated literacy efforts. Towns and temples in Mesopotamia boasted extensive libraries which enabled the population to learn and write. Numerous Babylonian literary works continue to be translated to date. Mesopotamian scholars made great strides in the field of mathematics, astronomy, art, medicine, technology, religion, and philosophy.
Ancient Mesopotamia In A Nutshell
Civilization Name: Mesopotamia
Period: 3500 BC -500 BC
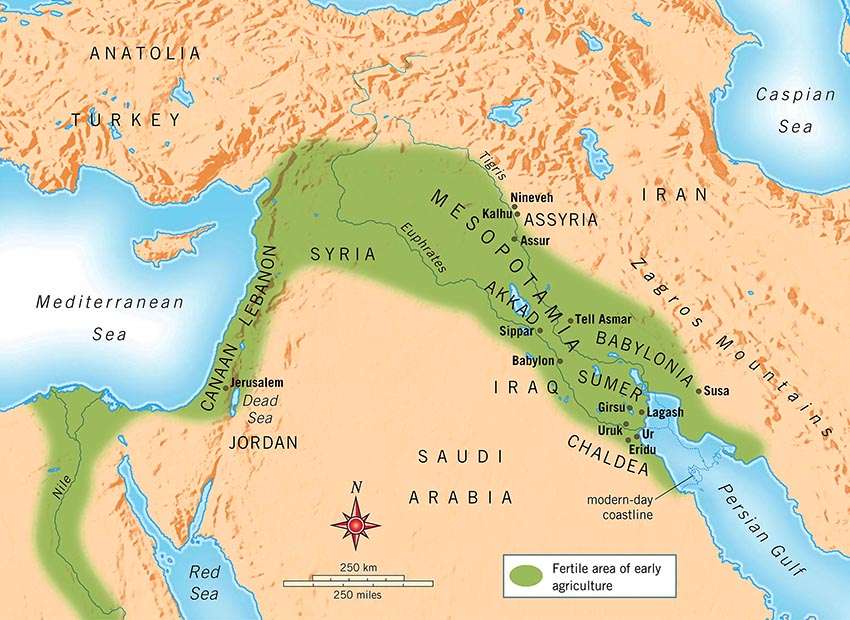
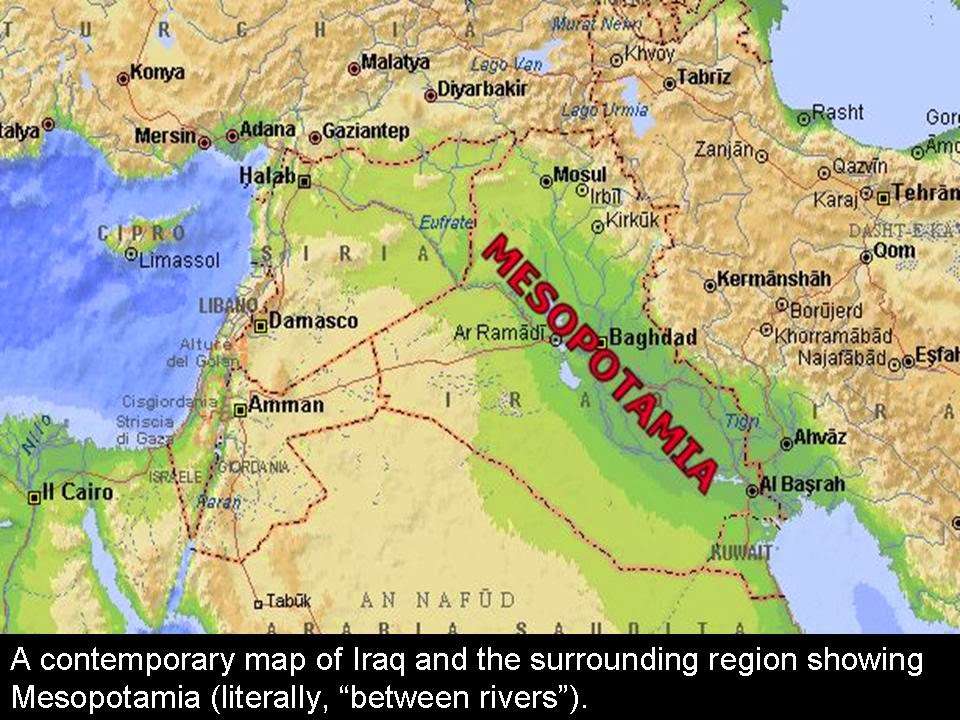
Originated Location: northeast by the Zagros Mountains, southeast by the Arabian Plateau
Current Location: Iraq, Iran, Syria, and Turkey
Meaning: land between rivers
Major Highlights: First civilization in the world
Mesopotamian was the worlds earliest civilization between the land of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. It was bounded by Zagros Mountains in the northeast and Arabian Plateau in the southeast. The irrigation and farming were easier because of the fertile land, and the tremendous water supply from two rivers. The early settlers started to gather in a small group forming small village and town. The small village and town started to transform in the larger town, and the world first civilization Mesopotamia emerged.
Interesting Fact: The name came from the Greek word between rivers. Mesopotamia lied between the Tigris and Euphrates River.
Also Check: What Does Hierarchy Mean In Biology
Mesopotamia In Modern Day
The war between Iran and Iraq in the 1980´s was one of the many conflicts in this area. Oil is another reason for conflicts. Perhaps the future will hold something better for the cradle of civilization. Only time will tell, but the geography and the history of Mesopotamia show that the possibility to change the land once more to its state of prime and fertility is not impossible and hopefully this will happen sooner than later.
Weather And Climate In Mesopotamia
The weather in Mesopotamia was no doubt similar to th weather in Iraq today. In Iraq the weather in Iraq varies according to elevation and location but generally is mild in the winter, very hot in the summer and dry most of the year except for a brief rainy period in the winter. Most of the country has a desert climate. The mountainous areas have temperate climates. Winter and to a lesser extent spring and autumn are pleasant in much of the country.
Precipitation is generally scarce in most of the Iraq and tends to fall between November and March, with January and February generally being the rainiest months. The heaviest precipitation usually falls in the mountains and on the windward western sides of the mountains. Iraqi receives relatively little rain because the mountains in Turkey, Syria and Lebanon block the moisture carried by winds from the Mediterranean Sea. Very little rain comes in from the Persian Gulf.
In the desert regions rainfall can vary greatly from month to month and year to year. The amount rainfall generally diminishes as one travels westward and southward. Baghdad gets only about 10 inches of rain a year. The barren deserts in the west get around 5 inches . The Persian Gulf area receives little rain but can oppressively humid and hot. Iraq suffers from occasional droughts.
Also Check: How To Solve For Concentration In Chemistry
How Cyrus The Great Turned Ancient Persia Into A Superpower
The Hittites pulled out shortly after sacking Babylon, and the Kassites took control of the city. Hailing from the mountains east of Mesopotamia, their period of rule saw immigrants from India and Europe arriving, and travel sped up thanks to the use of horses with chariots and carts.
The Kassites abandoned their own culture after a couple of generations of dominance, allowing themselves to be absorbed into Babylonian civilization.
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
history of Mesopotamia, history of the region in southwestern Asia where the worlds earliest civilization developed. The name comes from a Greek word meaning between rivers, referring to the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, but the region can be broadly defined to include the area that is now eastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, and most of Iraq. The region was the centre of a culture whose influence extended throughout the Middle East and as far as the Indus valley, Egypt, and the Mediterranean.
This article covers the history of Mesopotamia from the prehistoric period up to the Arab conquest in the 7th century ce. For the history of the region in the succeeding periods, seeIraq, history of. For a discussion of the religions of ancient Mesopotamia, seeMesopotamian religion. See alsoart and architecture, Mesopotamian.
Also Check: How To Write An Assessment Report For Psychological
Dna Study On Links Between Marsh Arabs Of Modern Iraq And Ancient Mesopotamians
N. Al-Zahery wrote: To shed some light on the paternal and maternal origin of this population, the Male Specific region of the Y chromosome and mitochondrial DNA variation was surveyed in 143 Marsh Arabs and in a large sample of Iraqi controls. Analyses of the haplogroups and sub-haplogroups observed in the Marsh Arabs revealed a prevalent autochthonous Middle Eastern component for both male and female gene pools, with weak South-West Asian and African contributions, more evident in mtDNA. A higher male than female homogeneity is characteristic of the Marsh Arab gene pool, likely due to a strong male genetic drift determined by socio-cultural factors .
The sample consists of 143 healthy unrelated males, mainly from the Al-Hawizah Marshes J1 sub-clades was also investigated in four samples from Kuwait , Palestine , Israeli Druze and Khuzestan as well as in more than 3,700 subjects from 39 populations, mainly from Europe and the Mediterranean area but also from Africa and Asia. ||||
Geography Of Ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a Greek word meaning Land between the Rivers. The region is a vast, dry plain through which two great rivers, the Euphrates and Tigris, flow. These rivers rise in mountain ranges to the north before flowing through Mesopotamia to the sea. As they approach the sea, the land becomes marshy, with lagoons, mud flats, and reed banks. Today, the rivers unite before they empty into the Persian Gulf, but in ancient times the sea came much further inland, and they flowed into it as two separate streams.
Map of Mesopotamia in about 3500 BCE
The land has too little rainfall to grow many crops on. As a result, much of it has been and is still home to herders of sheep and goat. These nomads move from the river pastures in the summer to the desert fringes in the winter, which get some rain at this time of year. At various times they have had a large impact on Mesopotamian history.
Near the rivers themselves, the soil is extremely fertile. It is made up of rich mud brought down by the rivers from the mountains, and deposited over a wide area during the spring floods. When watered by means of irrigation channels, it makes some of the best farmland in the world.
The marshy land near the sea also makes very productive farmland, once it had been drained. Here, the diet is enriched by the plentiful supply of fish to had from the lagoons and ponds.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Rdw Process In Math
Where Was Mesopotamia Located
Mesopotamia is a term used to refer to a medieval region located on the banks of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, which now lies in the modern-day Middle East. The region corresponds to most parts of modern day Iraq as well as parts of Iran, Kuwait, Syria, and Turkey. Mesopotamia is important in history for being the cradle of civilization as it was the site of significant developments throughout history.
Activity : The Geography Of Mesopotamia
Ancient Civilizations
- Label the Tigris River.
- Label these bodies of water: the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, and the Persian Gulf
- Label the cities of Ur, Uruk, Ashur, and Babylon
Page 2 Answer Key:
- Why do you think so many groups of people successfully settled and thrived in this area?Your child may mention that being near rivers enabled them to effectively grow crops and have water for drinking or that the rivers and seas may have made trade easier.
- What natural resources do you think might be available in this area? Your child may mention fertile land, access to rivers and seas, clay, bronze, and iron.
- How would those natural resources be useful?Answers will vary, but your child may mention the need for fertile land for growing crops rivers for drinking water, irrigation, and transportation access to the sea for trade clay for making pottery or buildings metals for making tools, weapons, and other objects.
Optional Extension: Mesopotamia Today
Geography of the World
Recommended Reading: Function Notation Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Government In Ancient Mesopotamia
One of the most remarkable things about Mesopotamian civilization is that here, right at the dawn of recorded history, we find states which organized their populations more tightly than all but a very few in subsequent ages. In truth, this situation is the result of gradual steps taken over hundreds, even thousands, of years, and only appears to arrive fully formed as written records begin to shed their light however, the sheer scope of the states control over the lives of the people is astonishing.
Politically, the each Sumerian city formed its own city-state, composed of the city itself and the farmland for several miles around. These city-states were fiercely independent from one another, and warfare between them was frequent.
Priests and bureaucrats
In early Sumerian cities, the temple stood at the very center of public life, both political and religious. The god of the city was held to own the city in practice, this translated into the temple controlling the productive land of the city-state. There are indications that the common people brought what they grew to the temple, and received back what they needed to live on from the priests. If this is correct, then we have here as near a communist state as we ever get in history.
Whatever the true situation the temple acted as a major center of distribution: receiving, storing and disbursing the food as needed, and keeping back stocks for years of poor harvest or floods.
Kings
Larger states
Administration
Law
Warfare