How Does Ingestion Affect Circadian Rhythm
Since your bodily functions give feedback to the SCN, eating at an appropriate time will help the SCN to maintain your daily rhythms. But what is the best time to eat? Active bodily functions are aligned with daylight hours. Therefore,specialists from the NIH recommendVerified SourceNational Library of Medicine Worlds largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible.View sourceeating with the sun as it will optimize your metabolic processeschemical reactions in our cells that balance energy. That means eating in the morning, afternoon, and early evening.
When we eat, our pancreas releases insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose to enter our bodys cells. Our cells then transform the glucose into energy. During the day, we are insulin sensitive, meaning our body uses glucose more effectively than at night. At night time, our bodys become insulin resistant, making it difficult for our cells to use glucose for energy. Instead, it is stored as fat.
What Can I Do To Alter My Circadian Type
There is no way to change your circadian type since it is genetically determined, though there is some natural change that occurs during your lifespan. For example, our circadian sleep phase tends to shift later during adolescence and advances earlier as we age .
If you find that your circadian sleep phase is out of sync with your desired schedule, you can either shift your social life to match your circadian rhythm, or try to shift your circadian rhythm to match your social life. It may be easier to try to shift your work and social life to your circadian rhythm: an example would be a person who has a delayed circadian rhythm and likes to sleep late and wake up late switching from a job with a 7 AM start time to a job which allows him or her to start working later around 10 AM. The other option would be talking to a sleep physician and doing ongoing work to try to shift your circadian rhythm to match your work and social life to an earlier wakeup time.
In general, the best way to improve your mood is to get a good nights sleep by matching your circadian rhythm to your sleep-wake cycle. Exposure to light in the morning helps synchronize the clock. Exposure to bright light at night, including bright artificial lights and screen time on laptops, tablets, and phones, can cause disruption in circadian rhythm and may contribute to worsening mood and negative consequences for health.
Anxiety And Circadian Rhythm
Misalignment of the circadian rhythm may also provoke anxiety. Shift work results in a sleep disorder when your nighttime work shifts affect your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep, causing you to have excessive sleepiness during the day that in turn results in distress and affects your ability to function normally. Nurses with shift work disorder have increased anxiety scores on questionnaires. In a study on jet lag, in which travel changes the time of the external environment so that it is no longer synchronized with the internal clock and disrupts sleep, travelers had elevated anxiety and depression scores.
Also Check: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
What Happens To Circadian Rhythms When There Is No Sunlight
As mentioned above, our master clock is highly sensitive to sunlight. Sunlight promotes alertness and can reset a disrupted circadian clock. A lack of sunlight, such as during the winter in the very far North, may result in lethargy in the day and energy at night. Artificial light may ease the effects of limited sunlight, but it does not emit nearly as much energy as the suns rays.
Is A Circadian Rhythm The Same As A Biological Clock
Biological clocks help regulate the timing of bodily processes, including circadian rhythms. A circadian rhythm is an effect of a biological clock, but not all biological clocks are circadian. For instance, plants adjust to changing seasons using a biological clock with timing that is distinct from a 24-hour cycle.
You May Like: How Does Quantum Physics Prove God
Ao: Evaluation Of Research Into Circadian Rhythms:
Strengths:
Point: There is research to support the interaction between endogenous pacemakers and exogenous zeitgebers in the control of circadian rhythms.Evidence/Example: For example, Aschoff and Wever placed participants in an underground WWII bunker with artificial light but no natural light and a complete lack of environmental and social cues. They found that most participants soon settled into a sleep/wake cycle of between 24 and 25 hours, although some rhythms were as long as 29 hours.In addition, David Lafferty remained in a cave for 127 days . Laffertys cycles appeared erratic at first, but then also began to settle at around 25 hours. Elaboration: This is a strength because, both pieces of research highlight the importance of internal factors in the control of circadian rhythms. In addition, such research also highlights that EPs and EZs work together in order to keep our body in line with the 24 hour external world .
Weaknesses:
What Are Biological Rhythms In Psychology
What are biological rhythms in psychology? Biological rhythm is a phrase often used interchangeably with circadian rhythm. These rhythms are a series of bodily functions regulated by your internal clock. They control cycles like sleep and wakefulness, body temperature, hormone secretion, and more.
What are biological rhythms and what are some examples? Biological rhythms are everywhere. The daily changes in sleep and wakefulness, annual bird migration, and the tidal variations in behavior of coastal animals: these are all examples of biological rhythms.
What are types of biological rhythms? There are four biological rhythms: circadian rhythms: the 24-hour cycle that includes physiological and behavioral rhythms like sleeping. diurnal rhythms: the circadian rhythm synced with day and night. ultradian rhythms: biological rhythms with a shorter period and higher frequency than circadian rhythms.
What is biological rhythm theory? Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. These natural processes respond primarily to light and dark and affect most living things, including animals, plants, and microbes. Chronobiology is the study of circadian rhythms.
Don’t Miss: Renate Blauel 2018
How To Maintain A Healthful Circadian Rhythm
There are several important factors to consider when maintaining a healthful circadian rhythm.
If possible, go to bed and wake up at the same time each day. Setting a regular time may help the body set its rhythms around these times. Some choose to set a morning alarm to wake up at the same time each day. This may help the body adjust and encourage tiredness when they need to sleep to wake up on time.
This regular sleep-wake schedule also includes days off from work, such as weekends.
As light can disrupt the circadian rhythms, it is important to choose when to limit exposure. The CDC note that the 2 hours before a person falls asleep appear to be most crucial. Avoiding blue light at this time may help ensure a regular circadian rhythm, which includes limiting screen time and any bright sources of white or blue light, such as in shops.
Other tips may help promote a healthful circadian rhythm, including:
- going outside or in bright light in the morning
- avoiding caffeine late in the day
- taking small naps in the early afternoon if a person needs to nap
- avoiding long naps or napping later in the day
- avoiding heavy meals
- performing calming activities before bed, such as reading or doing gentle stretches
Some calming herbal teas or supplements may help promote a sleepy state in people with trouble falling asleep. However, talk with a doctor before taking products with active ingredients.
Poor quality sleep or sleep deprivation can lead to health complications, including:
Laboratory Research On Unconscious Visual Processing
Dr. Tony Ro is a professor of psychology at the City University of New York. He started studying the connection between consciousness and brain processing more than 20 years ago, and he was one of the earliest researchers to apply TMS technology to the study of visual perception.
In one study, Dr. Ro and graduate students Jennifer Boyer and Stephenie Harrison used TMS technology to see if normal people could process features of visual stimuli without conscious awareness of those stimuli. In other words, they wanted to know if they could they create temporary blindsight in normal subjects in a laboratory.
Remember that blindsight involves unconscious awareness of features of objects and events, such as the shape of an object or the direction of its movement. This study focused on two visual features: orientation and color. You and I see orientation or color as part of the experience of some object. A line is horizontal. A box is red. For a person with blindsight, horizontal is experienced without any shape associated with it. Red is experienced without awareness of the thing that is red. This is the blindsight condition that Dr. Ro and his colleagues wanted to reproduce in the laboratory with the help of volunteer subjects.
Lets walk through the experiment to understand how it was designed and conducted.
Recommended Reading: Segment Addition Postulate Practice
How Does Your Circadian Rhythm Impact Your Mood
An irregular circadian rhythm can have a negative effect on a persons ability to sleep and function properly, and can result in a number of health problems, including mood disorders such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and seasonal affective disorder.
A recent study suggested that the night-owl type might have a greater predisposition to psychological disturbances. The authors found that the different circadian types were likely to have different coping styles to emotional stressors, and the ones adopted by the morning larks seemed to result in better outcomes and fewer psychological problems. This was a correlational study, so the reason for adopting different styles wasnt explained, but this study emphasizes the great impact circadian rhythms have on health and functioning.
Light And The Biological Clock
Light resets the biological clock in accordance with the phase response curve . Depending on the timing, light can advance or delay the circadian rhythm. Both the PRC and the required illuminance vary from species to species, and lower light levels are required to reset the clocks in nocturnal rodents than in humans.
You May Like: Subfields In Psychology Worksheet Answers
What Happens When There Is No Sunlight
There has been a considerable amount of research on what happens to circadian rhythms when natural sunlight patterns are interrupted.
Clinical research has shown that individuals who are blind from birth frequently have difficulty with their sleep-wake cycle because of the complete lack of environmental light cues. Those who perform shift-work or travel frequently are also subject to having their natural circadian rhythms disrupted.
In some major studies of circadian rhythms, participants stayed in underground units for weeks or even months at a time. Deprived of all-natural light cues, the circadian rhythms of the participants began to shift toward a 25-hour schedule rather than the standard 24-hour pattern. Many of the bodys previously synchronized circadian rhythms shifted as well.
When exposed to environmental sunlight signals, many of the body’s rhythms operate on a very similar schedule. When all-natural light cues are removed, these body clocks begin to operate on completely different schedules.
What Disrupts Circadian Rhythm
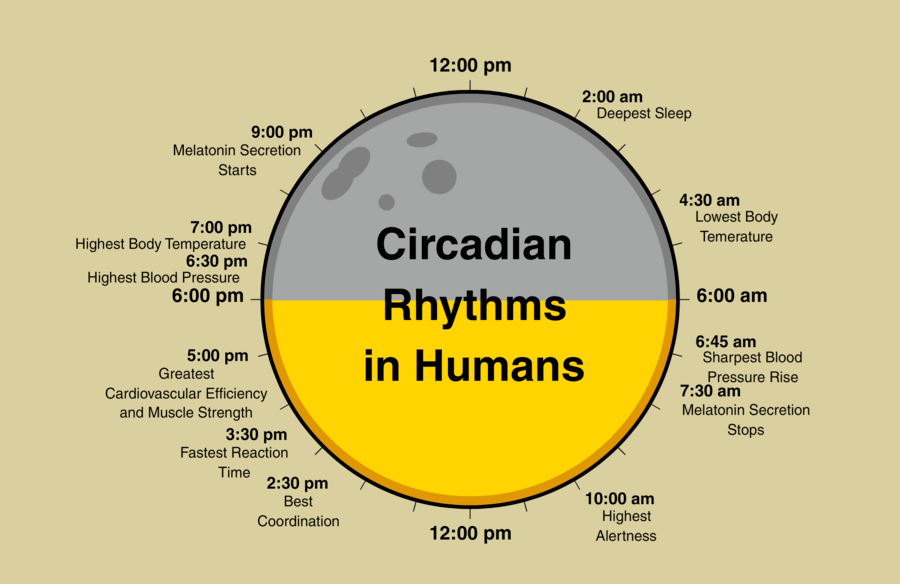
Our biological clocks innately align our physical, mental, and behavioral processes with day and night. For instance, we are biologically wired to be productive during the day but rest at night.
Disruptions to our day-night cycle can throw off our entire circadian rhythm, negatively affecting our coordination, energy, digestive system, sleep patterns, and much more. So how do you know if your circadian rhythm is off? The most obvious sign of a disrupted circadian rhythm is lethargy, but you may also experience the following:
- Sleepiness during the day
- Tension headaches
Recommended Reading: Who Is Generally Recognized As The Founder Of American Psychology
The Best Time For Activities
The reality is that the demands of daily life such as school, commuting, work, and social events can all throw the body’s natural cycles out of whack. The way we organize our daily activities is sometimes in direct contrast to our body’s own inclinations.
Altering your schedule might not always be easy, but there are clear benefits to doing so. In addition to making better use of your time, there are also potential health implications. Circadian rhythm disruptions have been linked to a range of negative health outcomes including depression and diabetes.
When is the best time to tackle certain tasks?
Limit Nightly Screen Use
Weve discussed the effects of morning light on your circadian rhythm, and light in the evening works the same way. Household light, from both lamps and blue light emitted from laptops, smartphones and tablets, can trick your brain into thinking its still daytime, causing it to suppress melatonin production. Bright light wakes up your brain, Dr. Schwartz says.
Start dimming lights about two hours before bedtime and resist scrolling through social media in bed. If you work a night shift or need to use screens in the evenings, you can wear glasses that block blue light or install a blue light filter app on your device.
Maintaining a regular circadian rhythm is crucial for healthy sleep. If daytime drowsiness is interfering with your daily activities, you may have a sleep disorder. Schedule an appointment with the INTEGRIS Sleep Disorders Center of Oklahoma to discuss your symptoms and find a treatment plan to help you sleep better.
You May Like: The Founder Of Behaviorism Was:
Effect Of Lightdark Cycle
The rhythm is linked to the lightdark cycle. Animals, including humans, kept in total darkness for extended periods eventually function with a free-running rhythm. Their sleep cycle is pushed back or forward each “day”, depending on whether their “day”, their endogenous period, is shorter or longer than 24 hours. The environmental cues that reset the rhythms each day are called zeitgebers . Totally blind subterranean mammals are able to maintain their endogenous clocks in the apparent absence of external stimuli. Although they lack image-forming eyes, their photoreceptors are still functional they do surface periodically as well.
Free-running organisms that normally have one or two consolidated sleep episodes will still have them when in an environment shielded from external cues, but the rhythm is not entrained to the 24-hour lightdark cycle in nature. The sleepwake rhythm may, in these circumstances, become out of phase with other circadian or ultradian rhythms such as metabolic, hormonal, CNS electrical, or neurotransmitter rhythms.
Recent research has influenced the design of spacecraft environments, as systems that mimic the lightdark cycle have been found to be highly beneficial to astronauts.Light therapy has been trialed as a treatment for sleep disorders.
What Is Biological Night
Biological night has been described as the time when the circadian clock promotes sleep.4 Importantly, humans vary as to when they tend to be awake and asleep in the course of 24 hours. This is evinced and captured by the chronotype which depends on factors such as genes, sex, age and environmental light.
Read Also: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
What Controls Circadian Rhythms
Almost all known plants and animals exhibit circadian rhythms. For instance, the microscopic single-celled aquatic plant, Gonyaulax polyedra, is phosphorescent, lighting up at night, and dimming in the day. In 1958, Hastings and Sweeney demonstrated that Gonyaulax showed peaks and troughs of luminescence even in constant darkness, but the peak time of luminescence shifted a little later each day. If the plant was exposed to brief pulses of light, the peak of luminescence could be shifted to almost any time of day, depending on when the light pulse was given. Thus, light reset the Gonyaulax clock.
The analogy of the SCN to an orchestra conductor is inadequate, however, because the cells of the SCN do not act as a single multioscillator unit. Welsh et al. demonstrated that SCN cells grown in culture oscillate at different rates: this means that each single SCN neuron functions as an independent circadian clock.
R.M. Voigt, … A. Keshavarzian, in, 2016
What Affects Circadian Rhythm
Light is the major outside factor controlling the bodys circadian rhythms. It keeps the circadian rhythm in sync with the Earths natural 24-hour cycle. In addition, other environmental cues may help synchronize the circadian rhythm, including food intake and activity level. However, many things can disrupt this process.
While circadian rhythms occur naturally, several factors may affect them across the day.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Geography Of Paraguay
The Master Clock And Biological Clocks
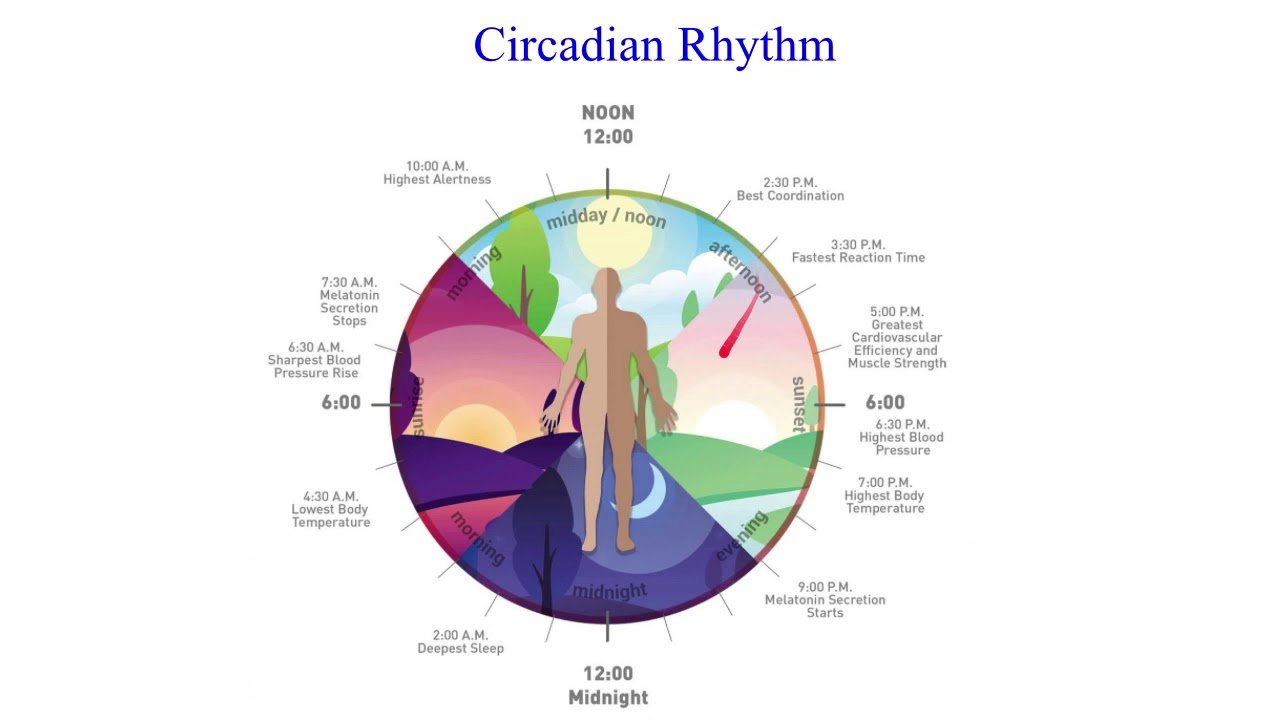
Our brain contains a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus , sometimes called the circadian pacemaker. As the master clock, our SCN directs otherbiological clocksVerified SourceOxford AcademicResearch journal published by Oxford University.View sourcelocated in peripheral tissues.
Nearly every organ and tissue within our body contains a biological clock made from genes and proteins the most crucial proteins being CLK and PER . CLK and PER proteins have a seesaw effect because they enable and disable one another, keeping each other in a cyclic balance. This seesaw cycle helps to keep clocks on time.
However, our external environment affects circadian rhythms as well. Cues from light, ingestion, temperature, noise, and physical activity maintain or disrupt the 24-hour cycles. These external cues are called ZeitgebersGerman for givers of time. Light and ingestion are the most impactful Zeitgebers.
How Does Circadian Rhythm Change With Age
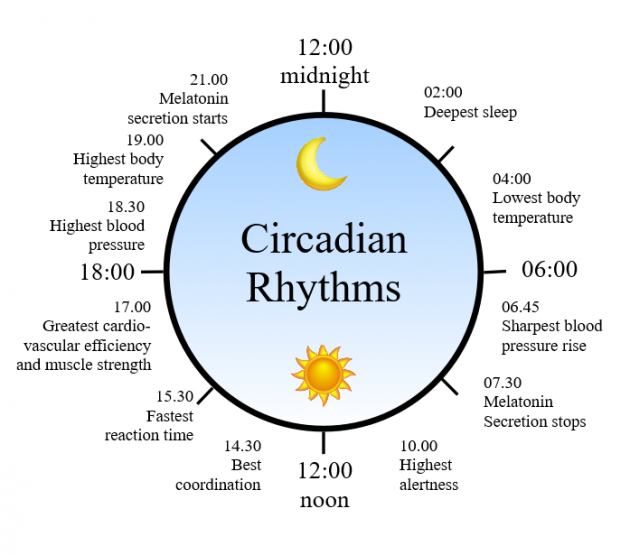
Older adults tend to have more trouble sleeping, including falling asleep, staying asleep, and remaining alert throughout the day. Research suggests that this may be because the brain area responsible for the circadian clock shows weaker electrical activity as we age, sending muffled messages to the rest of the body.
Read Also: How To Find Ksp Chemistry
Ao: Evaluation Of Ultradian Rhythm Research:
Strengths:
Point: The research into ultradian rhythms can be praised for being conducted in controlled laboratory settings. Evidence/Example: For example, research looking at the stages of sleep uses EEG and ERP mechanisms to measure the waves occurring in the brain. Elaboration: This is a strength because, research from Dement and Kleitman and Rechtschaffen and Kales can be seen to produce scientific and objective measures that allow research to draw firm conclusions about the specific characteristics associated with the different stages of sleep which increased internal validity.
Weaknesses:
Point: Due to the fact that research is conducted in the control setting of a laboratory, the sleep environment can be criticised for its artificial nature. Evidence/Example: For example, sleep research involves individuals sleeping under circumstances that dont usually reflect their typical nights sleep. Participants sleep with electrodes attached to their body/head, are often woken up a numbers of times throughout the night in order to report dreams etc Furthermore, they are sleeping in a lab setting not their usual bedroom setting. Elaboration: This is a weakness because the research can be criticised for lacking ecological validity and not reflecting an individuals true sleep behaviour.