Turbocharger And Its Major Types
Over the years, automotive technology is reaching new heights. The IC engines are becoming more powerful, more efficient, more reliable and are even less harmful to the environment. In this hustle and bustle came a small little thing called turbo that made a world of a difference. Turbochargers, as we know are still used in modern cars.
Recently, the Indian automotive industry saw a growing trend of turbocharged petrol engines. But why is turbo being introduced in the vehicles? whats so special about it? does it really make a difference? Well, in short, Yes! But what does this turbo do that it makes a small engine does big things? Lets find out.
Mechanically Actuated Electronically Controlled
While vacuum actuation is one method of variable geometry functionality, all turbochargers used in the pickup segment are electronically controlled, mechanically actuated units. This also means that both the electrical side and the mechanical side can fail. Mechanically, the actuator is susceptible to soot and carbon buildup hindering its performance and this type of issue is more common on engines equipped with exhaust gas recirculation . Although it isnt common for the electronic side of an actuator to burn up on Power Stroke or Duramax-powered trucks, the VGT solenoids do fail occasionallyand, luckily, are a relatively cheap fix. However, outright actuator failure is more common on the 6.7L Cummins .
Problem: Failed actuator/VGT controller
Symptom: Excessive smoke, high EGT, loss of power at low rpm, turbo or boost-related CEL
Reason: Excessive soot/carbon buildup
Fix: Cleaning or replacement of actuator or replacement turbo
What Is Variable Geometry Turbocharger Or Vgt
Variable Geometry Turbocharger or VGT is a type of turbocharger. It is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of air by compressing it. Another name for the Variable-Geometry Turbocharger is Variable Nozzle Turbines . VGT allows an effective aspect ratio for the turbocharger according to varying conditions. Therefore, manufacturers usually design VGTs to deliver refined performance.
Manufacturers employ VGT because the optimum aspect ratio at low engine speeds is very different from that at high engine speeds. If the aspect ratio is too large, then the turbocharger will not be able to create the required boost at low speeds. Conversely, if the aspect ratio is too small, the turbocharger will fill the engine with more air at high speeds. Thus, it results in high exhaust manifold pressures and high pumping losses. And, ultimately, it lowers the effectual power output.
Also Check: What Is Polar Molecule In Physics
Purchasing A Variable Geometry Turbocharger
The decision on whether or not to get an engine with VGT depends on what you will use your vehicle for and how much you can spend. Ultimately, we just present the facts and the decision to go VGT or not is up to you and your vehicle.
There may not even be options for the engine you need. Once you have an engine, you cannot convert a VGT engine to a non-VGT engine. Some conversion kits do exist for particular engines, but it is illegal to actually convert them and authorized repair shops will refuse to work on your engine after the conversion.
For more turbo questions, see our blog on common turbo problems and failures here.
If you have any additional questions about Variable Geometry, or any other general questions you need answered, please call our ASE Certified Techs at 215-3406. Or, you can request a quote online.
Originally Posted May 23, 2017 Edited October 1, 2019
Recent Articles
Applications Of Variable Geometry Turbocharger:

The two most common applications include a ring of aerodynamically-shaped vanes in the turbine housing at the inlet. Manufacturers use the first type in the passenger cars, race cars, and light commercial vehicles, which use light-duty engines. In this design, the vanes rotate in unison. As a result, they vary the swirl angle and the cross-sectional area of the turbine.
Manufacturers use the second type for heavy-duty engines, such as commercial vehicles. In this design, the vanes do not rotate. However, instead, an axially sliding wall mechanism selectively blocks the width of the turbo inlet. In this design, either this mechanism partially covers the vanes of a moving slotted shroud, or they somewhat move against a stationary slotted shroud. In addition, it varies the area between the tips of the vanes. Thus, it results in a variable aspect ratio.
You May Like: Which Feature Of Athens’s Geography Most Affected Its Economy
How Does A Variable Geometry Turbocharger Work
The video shows us the inside of a typical variable vane turbocharger. It consists of a set of blades arranged around the exhaust turbine, the angle of which is controlled by an actuator. For example, there are other designs with paddles that move up and down they are more common in heavier machines such as trucks or other large vehicles.
Power Adders Can Kill Them
In the diesel truck segment, added fueling is both easy to come by and the simplest way to add considerable power. The only problem is that while an extra 100, 200, even 300-rwhp can be added without upgrading the factory turbocharger, it is often pushed way out of its map. The added fueling provides naturally aspirated gasoline-like responsiveness at low rpm, but thanks to extreme shaft speed and excessive drive pressure on the exhaust side a VGT can become a ticking time bomb.
You May Like: What Is Frictional Force In Physics
Holset Vgt Fixed Geometry And Wastegate Turbochargers
In 1998, Holset VGTTM, a pioneer in Variable Geometry , from Cummins Turbo Technologies, was developed for the commercial automobile industry. The Holset VGT has a large flow range, which enhances the pressure using a unique sliding nozzle ring, at lower engine speeds. VG technology provides the most efficient way to reduce NOx levels via short-haul gas recirculation .
The Holset VGT is unusual because the vanes axially move and so have less wearing and less moving components. This enhances the strength and dependability of this technology, which is critical for commercial diesel applications today. The world-class research and development of Cummins Turbo Technologies continue to expand on the successful current Holset VGT by increasing total operating costs and fuel economy.
Geometry fixed
The companys origins are fixed geometry, turbochargers that drive all the gas from the exhaust into the turbine to increase the power of the engine. Cummins Turbo Technologies has more than 60 years of experience in fulfilling the customers power demands and has shown its competence and manufactures some of the worlds most optimized, efficient, and reliable turbochargers today.
Wastegate
This state-of-the-art technology diversifies waste exhaust to fit most situations.
Fixed Geometry: Ol Reliable
On all Big Three applications , enthusiasts and owners fed up with VGT failure often make the switch to a fixed geometry turbocharger. The fixed geometry platform is known for its longevity and in the modern era a fixed geometry turbo can be specd to achieve adequate all-around performance. Dozens of aftermarket variable-to-fixed geometry turbo conversion kits exist, as well as dozens of turbo sizing options. In the photo above, the popular BorgWarner S467.7 sits in place of a failed factory Holset HE351VE on a 6.7L Cummins. Adding the S400 frame BorgWarner turbo was a bolt-on process thanks to BD Diesels new Rumble B Turbo Kit, which comes with everything needed to perform the swap .
Don’t Miss: Geometry For Class 4 Icse
Math For Those So Inclined
The treatment of the Honda Civic is an approximate one. The density of air was taken to be 1.18 kg/m3, the drag coefficient was assumed to be 0.32, which is less than the average for a passenger car, and the frontal area was approximated as a rectangle of the dimensions published in the 2001 Honda Civic owner’s manual. Drag power is given by the equation
Where Ï is the density of air, v is the vehicle speed, Cd is the drag coefficient, and A is the frontal area.
The power required to overcome air resistance works out to be about 10.3 kW , which I rounded up to 15 hp. The power an engine produces scales approximately linearly with increasing RPM, up to the peak power. Using this assumption, the Honda’s power at 65 MPH was estimated based on test data from Car and Driver magazine, where the peak occurs at 6300 RPM, and 65 MPH is 3100 RPM in fifth gear. Engine efficiency is given by
and pre-ignition cylinder pressure is given by
where CR is the engine’s compression ratio, γis the specific heat ratio , and P0 is the pressure inside the cylinder at its largest volume.
When Safety Provisions Fail
Even though the Garrett GT32 SST found on the 11-14 6.7L Ford Power Stroke features an internal wastegate, the drive pressure created via aggressive tuning can overwhelm it . When the wastegate cant rid itself of extreme drive pressure fast enough, that energy is used to spin the turbine wheel even quicker. So even though the GT32 SST is equipped with a wastegate, it is often the victim of overspeed failure.
Recommended Reading: How Does Structure Affect Function In Biology
Major Types Of Turbochargers
You might be thinking, which turbo is installed in your vehicle. Well, there are two main turbochargers through which an engine breath. A Fixed Geometry Turbo or an A Variable Geometry Turbo .
-
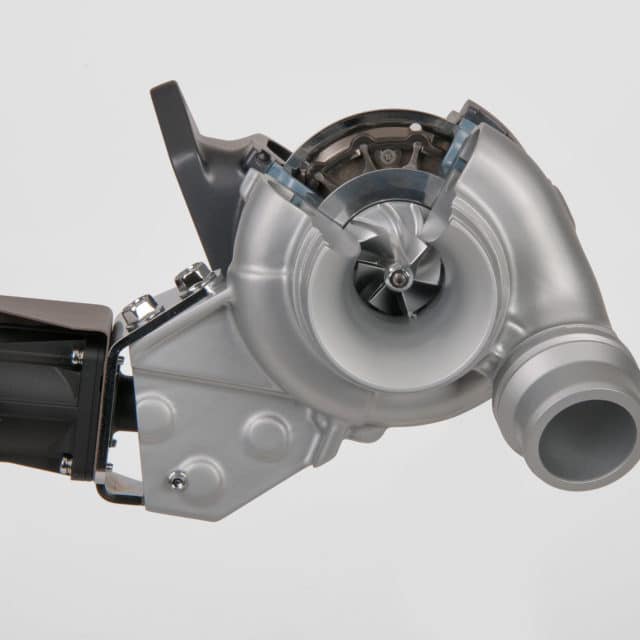
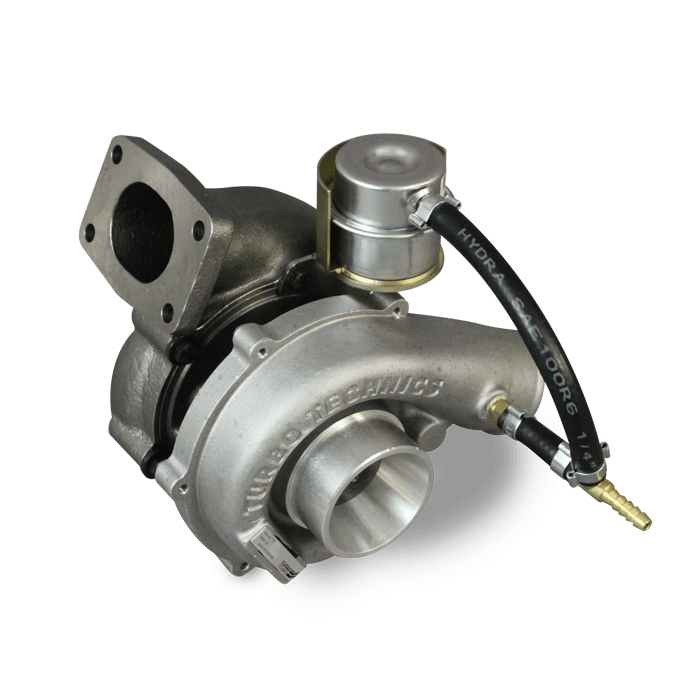
Variable Geometry Turbo
Variable Geometry Turbocharger | Image Source:
Not going into the very detail, long story short, a VGT can function at a wider RPM range. The most common problem with a turbocharger is the turbo lag. With a VGT it can be controlled to some extent.
- As the name suggests, a variable geometry uses vanes to control the amount of air entering the turbine.
- These vanes are connected to an actuator that either opens them or closes them.
- Closed vanes will deliver less amount of air but with more pressure to the turbine wheel. This reduces the turbo lag at low speeds as the exhaust gasses are pressurised.
- Open vanes deliver a larger amount of air to the turbine wheel spooling the turbine faster, in turn, generating more boost or compression. Well, the pressure is not a problem as the exhaust gasses at high RPMs are expelled with force.
So, a VGT delivers the convenience of both worlds, controlled lag at low RPMs and uncompromised performance at high RPMs.
Also, read 10 Things to Keep in Check when Driving a Typical Manual Transmission
Because the FGT is not as versatile as VGT, it is used mainly in city cars or vehicles with low power output. The advantage of an FGT is that it is fairly cheap to manufacture.
Diving Into The Distinctions Between Turbo Types
Turbochargers, like other mechanical devices like engines, have a technical history where subsequent innovations developed into new technical iterations, or types, built upon the previous generation. Nearly all main turbo types fall into a turbo family free floating, wastegate, variable nozzle turbine and most recently, electric turbos .
In this article, we will review these different turbocharger types beginning with the simplest/earliest types to most recent.
Free Floating: A turbocharger with a single, fixed area-to-radius is called a free-floating or fixed geometry turbo, because it has no integral control over speed or boost pressure. Turbo control is entirely dependent on the engine and its systems providing the correct amount of energy in the exhaust gas to power to the turbine. The turbocharger is precisely matched to the engine during the engine development phase, where the optimum A/R turbine housing is selected.
Wastegate: The wastegate or turbine bypass was introduced onto our turbochargers many years ago, to improve turbo and engine performance. These types of devices were used as early as the 1940s in the Wright R-1820 Cyclone engine found on the famous B-17 Flying Fortress .
A pneumatic actuator may be powered by air pressure or vacuum and controlled by a hose from the compressor outlet or by a control valve in the vehicles vacuum circuit. An electric actuator responds to commands from the vehicles own Electronic Control Unit.
Don’t Miss: What Is B In Math
What Is The Difference Between A Fixed Geometry Turbocharger
In a conventional fixed geometry turbocharger, the exhaust gases pass through a turbine and spin it, which spins an attached compressor that creates boost for the engine. At low RPM, the engine does not generate enough exhaust flow to spin the turbine and create significant levels of boost. At this point, the system is said to be below the boost threshold.
Once the engine reaches RPM high enough to generate thrust, it still takes some time to spin the turbine up to the right speed this is known as turbo lag. Turbo lag and boost threshold are higher for larger turbos that need more power to spin. However, these higher flow turbines are capable of generating more power. It’s a compromise, like so many other things in engineering.
What Is Wastegate
This feature of the Variable Geometry Turbocharger consists of a bypass valve built into the turbine housing. The waste-gate bypasses some part of the exhaust gases going through this valve to the turbine. It is as shown in the diagram.
The waste-gate arrangement reduces the high boost pressure created by the compressor and limits it to the desired value. Thus, it obtains the optimum engine performance with controlled peak cylinder pressure. As a result, Cummins and Holset are some of the worlds most popular manufacturers of Variable Geometry Turbochargers.
Also Check: What Is Radiation In Chemistry
How Does It Work
The variable geometry turbocharger, as previously mentioned, helps create more boosts of exhaust gas across the entire rev range. During low boost operations, the variable geometry turbochargerknown as a variable turbine geometry turbocharger or the variable nozzle turbinehas small movable vanes that direct exhaust flows into turbine blades.
An actuator adjusts the angles of the vanes. As a result, vane angle affects the engine RPM range and optimizes turbine behavior. As the path increases for the turbine, it allows for greater flow and increases the boost at a higher RPM.
The Basics Of Fixed Geometry Turbochargers
In a previous blog, we covered the details of what makes a variable geometry turbocharger different from other turbochargers. Today, we are going to cover a different type of turbocharger known as the fixed geometry turbocharger. While there are some similarities between the two, there are also differences. For a deeper look at the basics of fixed geometry turbochargers , continue reading the material provided below.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Say Biology In Spanish
Advantages Of Variable Geometry Turbochargers
Compared with a fixed geometry turbocharger, a variable geometry turbocharger has the following advantages:
|
Image: Boost pressure comparison |
AVNTTM Advanced Variable Nozzle Turbocharger
Studies performed by Garrett Engine Boosting Systems shows significant improvements in the torque curve of the engine, thanks to an improved control of the air-fuel ratio. For a given powertrain, the clutch engagement torque increased up to 45 % and the peak torque with over 30 %. These two improvements are directly related to the increased intake air flow generated by the AVNTTM at low engine speeds.
In addition, higher power ratings of up to 6 % have also been evaluated due the ability of the AVNTTM to reduce the boost levels at high engine speeds, thus reducing the engine cylinder firing pressure and thermal loading of the charge air cooler.
Fuel economy improvements, on the dynamometer, have also been demonstrated. The ability to optimize air-fuel ratio, minimize pumping losses and operate at higher efficiencies, all influence break specific fuel consumption in a positive way.
On diesel engines, at low engine speeds, smoke emissions can be reduced significantly due to the ability of the turbocharger to adjust the air-fuel ratio. NOx emissions can also be reduced thanks to the increased backpressure in the exhaust manifold. Negative pressure difference across the engine increases the exhaust gas flow into the intake manifold.
What Cars Accept It
There are a considerable number of diesel-powered vehicles that use variable geometry turbochargers. For example, the Porsche 718 models and the Suzuki Swift Sport carry turbochargers. If you want to get your hands on a preinstalled VGT, youre in luck.
Finding the right turbocharger doesnt have to cost your patience and time. If youre in the market for Mitsubishi turbochargers for sale, look no further than us at TurboTurbos. MHI turbos maintain a compact, reliable, and high-tech design that maximizes your vehicles performance. You can find the perfect Mitsubishi turbocharger through our online platform and explore our comprehensive catalog. If you have any questions, reach out to us today.
You May Like: What Is Remote Sensing In Geography
Find Out How A Turbocharger Works
A turbocharger is turbine-driven. It is a forced induction mechanical device. First, it compresses the incoming air. Then, it pumps the air into the engine cylinder at high pressure. Thus, it increases the engines efficiency and power output. It is about 30% to 40% more efficient than naturally aspirated engines.
Furthermore, both Petrol and Diesel engines use turbo-chargers to enhance power. However, they considerably differ in critical areas. These include operating temperatures and combustion pressures. Besides, they differ in volume of air and operating RPM range. A Supercharger is a similar device that works on the same principle. However, it uses engine power.
Fluid Flow Through A Pipe
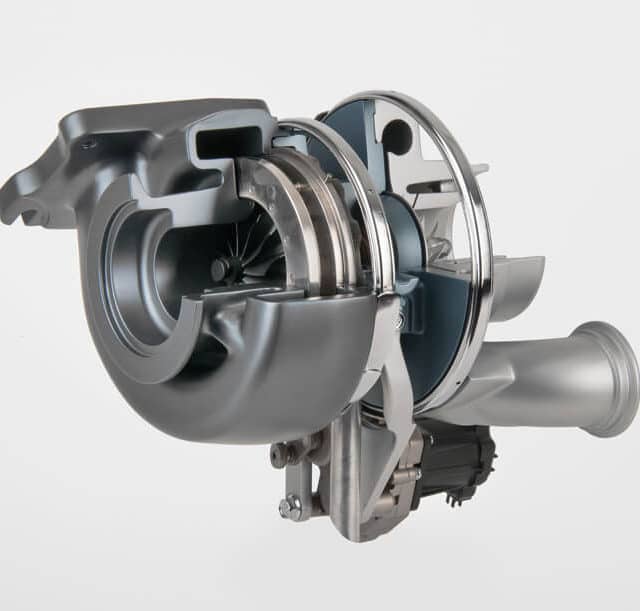

In order to understand the working principle of a variable geometry turbocharger , we need to recall some hydrodynamics laws.
Imagine you have a pipe with variable diameter along its length.
Image: Continuity of fluid flow
A area
|
In a nutshell, variable geometry turbochargers are combining the benefits of a small A/R ratio and a large A/R ratio into one unit, bringing together the advantages of both types.
Don’t Miss: What Does S Stand For In Chemistry