What Is The Red Shift
Then in the early Twentieth Century, new discoveries showed that indeed that universe is definitely not static. Edwin Hubble showed that its expanding, at an increasing rate. Distant galaxies are flying away from us. And the faster theyre moving the redder they appear, as the wavelength of light is stretched out. Its so stretched out its color changes.
Hubble wasnt the first to suggest that universe was expanding based on the existence of the Red Shift. However, he did create a very specific mathematic constant, later named after him, the Hubble Constant that suggested that the rate of expansion was constant throughout the universe.
In other words, the Red Shift was a fundamental mathematical component that determines how the universe appears to us now and changes over time. In short, everything is expanding.
The Red Shift idea is not so different than things we experience here on Earth. Were all familiar with the Doppler shift, the way a siren changes pitch as it moves towards or away from you. As it comes towards you, the sound increases. As it moves away, the sound frequency gets stretched out and sounds lower in pitch to your ear.
While a siren moving away or towards you is just a local phenomenon, the Red Shift is the exactly same thing but at a vast, cosmological scale, the largest scale you can imagine.
Effects Due To Physical Optics Or Radiative Transfer
The interactions and phenomena summarized in the subjects of radiative transfer and physical optics can result in shifts in the wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation. In such cases the shifts correspond to a physical energy transfer to matter or other photons rather than being due to a transformation between reference frames. These shifts can be due to coherence effects or due to the scattering of electromagnetic radiation whether from charged elementary particles, from particulates, or from fluctuations in a dielectric medium. While such phenomena are sometimes referred to as “redshifts” and “blueshifts”, the physical interactions of the electromagnetic radiation field with itself or intervening matter distinguishes these phenomena from the reference-frame effects. In astrophysics, light-matter interactions that result in energy shifts in the radiation field are generally referred to as “reddening” rather than “redshifting” which, as a term, is normally reserved for the effects discussed above.
What Is Doppler Shift Formula
| \f_\) |
Where,
- c is the velocity of waves in the medium
- vr is the velocity of the receiver relative to the medium
- vs is the velocity of the source relative to the medium
- f is the observed frequency
- f0 is the emitted frequency
Above is the Doppler shift or Doppler effect formula explaining the relationship between observed frequency and the emitted frequency where the speed of source and receiver is lower than the velocity of the waves in the medium.
Following is the formula when the speeds of receiver and source are comparatively lower than the speed of the wave:
Observed frequency:
| \f_\) |
Change in frequency:
| \ |
Where,
Related Articles:
To know more about the doppler effect, click on the video below.
Read Also: Algebra 1 Age Word Problems
Red Shift Of Galaxy 8c1435+635
Reported in November 1994 in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society is a galaxy with a measured red shift of z=4.25 , a new record. This value for the z parameter corresponds to a recession speed of .93c. The galaxy 8C1435+635 was observed in a systematic search for faint, radio-emitting galaxies carried out by a team at Leiden Observatory led by George Miley. After discovery, the optical spectra was observed by the William Hershel Telescope in La Palma, Canary Islands. Two emission lines of ionized carbon and hydrogen were measured to obtain the red shift. This red shift corresponds to a distance of about 13 billion light years if one uses the current WMAP value of 71km/s/mpc for the Hubble parameter is used.
Doppler Shift And Redshift
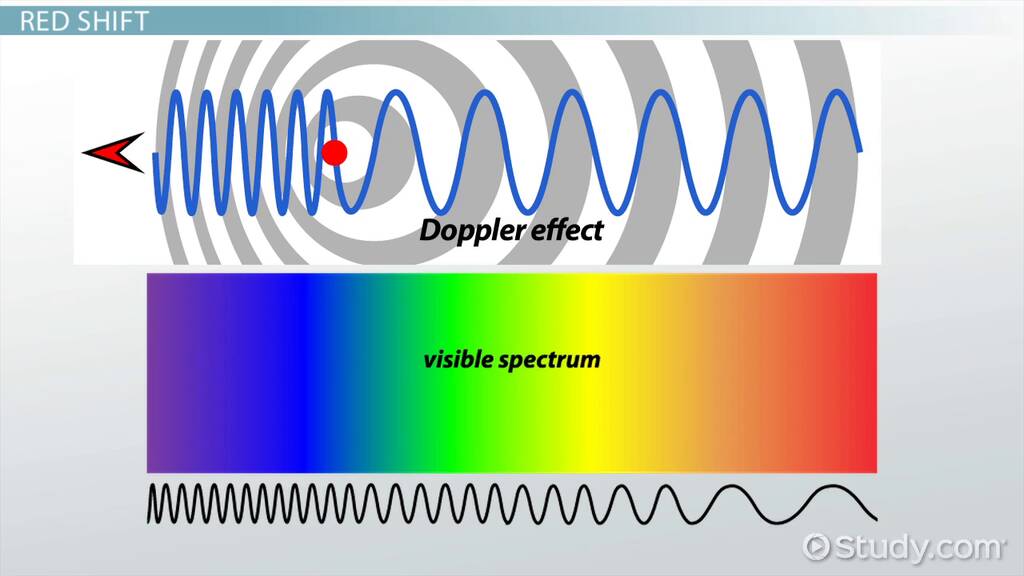
The Doppler Effect describes the change in the wavelength and frequency of waves emitted by a source which is in motion relative to the observer. As the source moves, each peak in the waveform it produces is emitted from a position which is closer or farther away . Because of this, the wavelength shifts and the frequency at which peaks arrive at the observer changes. The value of the shift is dependent on details of the material the waves are traveling in. Doppler shifts from the Doppler effect can be seen not only in sound waves , but in light waves as well.
When the velocity of the object is small compared to the speed at which the waves propagate, the magnitude of this blueshift or redshift, called z, is proportional to the shift in wavelength over the rest wavelength, rest. Furthermore, the magnitude of this blueshift or redshift z is proportional to the objects velocity v over the velocity at which the waves travel giving the equation z=v/c. These equations are given below. Doppler shifts in the spectrum of an object can usually be determined by comparing the wavelengths of features in the objects spectra, like absorption and emission lines, to expected wavelengths for certain elements and chemical compounds.
Also Check: Exponent Rules Review Worksheet
Measurement Characterization And Interpretation
Redshift may be characterized by the relative difference between the observed and emitted wavelengths of an object. In astronomy, it is customary to refer to this change using a dimensionless quantity called z. If λ represents wavelength and f represents frequency , then z is defined by the equations:
Calculation of redshift,
| v }} }}}} |
After z is measured, the distinction between redshift and blueshift is simply a matter of whether z is positive or negative. For example, Doppler effect blueshifts are associated with objects approaching the observer with the light shifting to greater energies. Conversely, Doppler effect redshifts are associated with objects receding from the observer with the light shifting to lower energies. Likewise, gravitational blueshifts are associated with light emitted from a source residing within a weaker gravitational field as observed from within a stronger gravitational field, while gravitational redshifting implies the opposite conditions.
Effects From Physical Optics Or Radiative Transfer
The interactions and phenomena summarized in the subjects of radiative transfer and physical optics can result in shifts in the wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation. In such cases, the shifts correspond to a physical energy transfer to matter or other photons rather than being by a transformation between reference frames. Such shifts can be from such physical phenomena as coherence effects or the scattering of electromagnetic radiation whether from chargedelementary particles, from particulates, or from fluctuations of the index of refraction in a dielectric medium as occurs in the radio phenomenon of radio whistlers. While such phenomena are sometimes referred to as “redshifts” and “blueshifts”, in astrophysics light-matter interactions that result in energy shifts in the radiation field are generally referred to as “reddening” rather than “redshifting” which, as a term, is normally reserved for the effects discussed above.
Also Check: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
What Is The Color Shift If Light Passes Between Two Black Holes
If we observe light that originates X light years away, but it passes between black holes X/2 light years away, will it be normal or red shifted or blue shifted? What if the black holes were X/4 or 3X/4 light years away?
I have always wondered if the apparent red shift of distant galaxies must be due to relative velocity with us.
- $\begingroup$Why is it important that there be two or more black holes? Is there something you expect to happen in those cases that wouldn’t affect light that passes near a single, isolated black hole?$\endgroup$
There are two ways that light frequencies can be shifted. One is if the source of the light is moving toward or away from the observer. The other is if the light has fallen into, or climbed out of a gravitational potential on its way.
If light passes near a black hole, it will be blue-shifted since it is falling into a gravitational well. However, if the light makes it back out of the gravitational well and makes it to Earth, it will have to climb out of the same well, getting red-shifted an equal amount. So, on average there is no effect from having passed near the black hole.
The energy will be the same, but the direction may change since the black holes can act like a lens.
- $\begingroup$there are three ways that light frequencies can be shifted. Third is due to the space expansion.$\endgroup$
Astronomical Redshift And Hubble’s Law
In the early 20th century, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the spectra of distant galaxies were significantly redshifted . Hubble interpreted this shift in the spectrum as a Doppler shift, postulating that these distant galaxies were traveling away from our own. Hubble eventually determined that the velocity at which these galaxies were receding was proportional to how far away they were the further away the galaxies were, the higher their redshift was. This equation, Hubble’s Law, is written as v = H0d.
Hubble’s Law can be represented graphically by creating a plot of each observed galaxy . On the x-axis, we plot the distance d of each galaxy , and on the y-axis, we plot the velocity at which it is traveling away, the recessional velocity v . The slope of this line is called H0, pronounced H-naught, the Hubble constant, and is typically accepted to have a value of about 70 km/s/Mpc.
Furthermore, if we can look at galaxies nearby and far away and see how fast they are receding due to the expansion of spacetime, we have the varying rate for the expansion of the Universe. With the speed of something moving, varying or not, we can work backward to learn when the movement began. From Hubble’s observations, we can conclude how long ago the Big Bang occurred we can estimate the age of the Universe. From this and other methods, the age of the Universe is found to be 13.8 billion years.
Recommended Reading: Geometry Dash Practice Song Hack
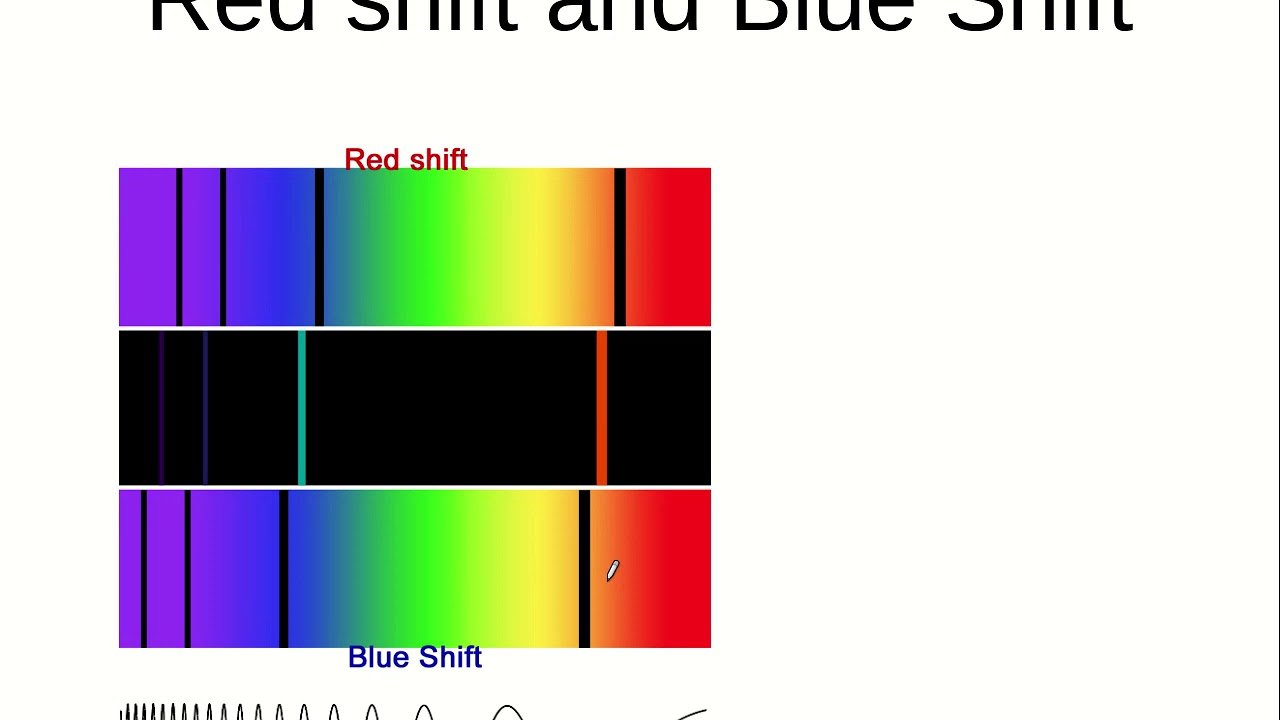
What Is ‘red Shift’
‘Red shift’ is a key concept for astronomers. The term can be understood literally – the wavelength of the light is stretched, so the light is seen as ‘shifted’ towards the red part of the spectrum.
Something similar happens to sound waves when a source of sound moves relative to an observer. This effect is called the ‘Doppler effect’ after Christian Andreas Doppler, an Austrian mathematician who discovered that the frequency of sound waves changes if the source of sound and the observer are moving relative to each other.
If the two are approaching, then the frequency heard by the observer is higher if they move away from each other, the frequency heard is lower.
There are many everyday examples of the Doppler effect – the changing pitch of police and ambulance sirens, or train whistles and racing car engines as they pass by. In every case, there is an audible change in pitch as the source approaches and then passes an observer.
Everyone has heard the increased pitch of an approaching police siren and the sharp decrease in pitch as the siren passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener’s ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes.
Since light travels at such a great speed relative to everyday phenomena we do not experience this red shift in our daily lives.
Application Of Doppler Effect
Sirens
The principle behind the siren is that it starts at a higher pitch than its stationary pitch when it slides down from the observer, and again when it recedes from the observer, it continues from the lower pitch than its stationary pitch. It is used in emergency vehicles. Sirens velocity is given as \ where is the angle between the objects line of sight and the forward velocity.
Astronomy
In astronomy, Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves of light results in either red-shift or blue-shift. With the help of Doppler effect and radial velocity, one can measure the speed at which stars or galaxies are receding or approaching from us.
Velocity Profile Measurement
Ultrasonic Doppler Velocimetry is used to measure the real-time completion velocity profile of any liquids containing suspended particles like dust, emulsions and gas bubbles. The flow can be pulsating, laminar or turbulent, oscillating or stationary.
Also Check: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
In The Hydrogen Spectrum
In 1947, Hans Bethe was the first to explain the Lamb shift in the hydrogen spectrum, and he thus laid the foundation for the modern development of quantum electrodynamics. Bethe was able to derive the Lamb shift by implementing the idea of mass renormalization, which allowed him to calculate the observed energy shift as the difference between the shift of a bound electron and the shift of a free electron.The Lamb shift currently provides a measurement of the fine-structure constant to better than one part in a million, allowing a precision test of quantum electrodynamics.
Three Types Of Redshift
At least three types of redshift occur in the universe from the universe’s expansion, from the movement of galaxies relative to each other and from “gravitational redshift,” which happens when light is shifted due to the massive amount of matter inside of a galaxy.
This latter redshift is the subtlest of the three, but in 2011 scientists were able to identify it on a universe-size scale. Astronomers did a statistical analysis of a large catalog known as the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, and found that gravitational redshift does happen exactly in line with Einstein’s theory of general relativity. This work was published in a Nature paper.
“We have independent measurements of the cluster masses, so we can calculate what the expectation for gravitational redshift based on general relativity is,” said University of Copenhagen astrophysicist Radek Wojtak at the time. “It agrees exactly with the measurements of this effect.”
The first detection of gravitational redshift came in 1959, after scientists detected it occurring in gamma-ray light emanating from an Earth-based lab. Previous to 2011, it also was found in the sun and in nearby white dwarfs, or the dead stars that remain after sun-sized stars cease nuclear fusion late in their lives.
Read Also: Molecular Shape Of Ccl4
Notable Uses Of Redshift
Redshift helps astronomers compare the distances of faraway objects. In 2011, scientists announced they had seen the farthest object ever seen a gamma-ray burst called GRB 090429B, which emanated from an exploding star. At the time, scientists estimated the explosion took place 13.14 billion years ago. By comparison, the Big Bang took place 13.8 billion years ago.
The farthest known galaxy is GN-z11. In 2016, the Hubble Space Telescope determined it existed just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. Scientists measured the redshift of GN-z11 to see how much its light had been affected by the expansion of the universe. GN-z11’s redshift was 11.1, much higher than the next-highest redshift of 8.68 measured from galaxy EGSY8p7.
Scientists can use redshift to measure how the universe is structured on a large scale. One example of this is the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall light takes about 10 billion years to go across the structure. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is an ongoing redshift project that is trying to measure the redshifts of several million objects. The first redshift survey was the CfA RedShift Survey, which completed its first data collection in 1982.
Editor’s note: This article was updated on Aug. 7, 2019 to reflect a correction. Radio waves shifted into the ultraviolet part of the spectrum are blueshifted, not redshifted.
Are You Expanding Too
Since we live in an expanding universe you can also imagine that youre expanding all the time too. Its fun as a meditation technique to see yourself moving throughout the cosmos. Even if you think youre standing still, youre really moving at a cosmic speeds! Youre expanding and flying through the universe at an ever-faster velocity and in many different directions at once. And the best part about it is that universe is doing all the work for you. Even when you seem to be standing still, youre flying around at breathtaking speeds.
So while the galactic Red Shift is about something vast and cosmological, you can still use it to help you with visualization, meditation, or just pondering how huge our universe really is.
Recommended Reading: Figure Ground Perception Psychology
Update: Hubble’s Law Of Redshifted Light And The Expansion Of The Universe
Coming back to the OP, the question specifically refers to redshifted light and “deciding the universe was expanding”. So I’ll try a quick explanation .
About a hundred years ago, Hubble formulated his law which said that light from distant galaxies was redshifted, and the more distant the galaxy, the more redshifted the light. Where galaxies were close enough to be measured directly, they turned out to be receding from Earth.
Now, this might have meant they were all travelling outward at extreme velocities from some common centre, but could have many other meanings: one theory suggested matter was being created continually to replace it .
So although the Big Bang was conceptualised, there actually wasn’t much evidence and it was only several decades later that other overwhelming evidence gradually ended up supporting the Big Bang theory.
We are now extremely sure, from many different kinds of observation and knowledge, that light from distant galaxies is redshifted to lower frequencies because of the expansion of space, and the Cosmic Microwave Backgroundcan be detected and identified as an extremely redshifted form of light from excited hydrogen atoms emitted at the dawn of our universe, when it was about 370,000 years old.
However, once modern cosmological ideas of the Big Bang began to be taken seriously as a theory, the detailed evidence gained through redshifted radiation became crucial evidence for both of these ideas and for much of modern cosmology.