Comparison Between Brazilians And Canadians
To find out, the average scores on mental healths components and some variables of individual differences were compared using t-test for independent samples. The results of 354 Brazilian professors have been compared with those of 317 Canadian professors. presents the descriptive statistics for the two groups and the t-test for each variable.
TABLE 2
Since signification bilateral or p is smaller than 5% for all of these indicators, we reject the hypothesis null that the two samples are equals, and we accept the hypothesis alternative that the sample of Brazilian and Canadian professors are different for some variables. T-tests allowed us to observe that all the five components of mental health are statistically equal between Brazilian and Canadian university professors. However, T-tests allowed us to find mean differences in bias of conformity, gender and age. But, their effect sizes are small.
The effect size is used to determine the value of mean differences between the two groups. It is determined with the calculation of eta squared , using the formula below. The effect size for bias of conformity is 0.01 , for gender is 0.01 , and for age is 0.01 .
TABLE 3
It has to be noted that the gender and age of the respondents were not retained in the equation, suggesting that the perception of work-life balance is not a question of gender perception neither the age of respondents, but best explained by individual differences and attitudes toward mental health aspects.
If Youre Still Struggling Speak To A Professional For Help
For many, achieving psychological well-being isnât easy and they may need professional assistance to help them work toward wellness. If this is the case for you, donât be afraid to enlist the help of a psychological well-being practitioner. These practitioners are experts in mental health and psychological well-being and can help you find ways to manage anxiety, deal with your emotions, and find contentment in your life.
A common practice that people struggling with mental health can find helpful is meditation. Practicing mindfulness or meditation has also shown to lower physical health risks and improve your quality of life. Speak with your practitioner about what meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being might be beneficial for you.
Working with a life coach is another option to help you work on your psychological well-being. This person can help you evaluate your strengths, weaknesses, and point you in the right direction to fill certain gaps in your life, such as building relationships with others or having more confidence in yourself. While a life coach is not a substitute for a health practitioner, together the two roles can help you on your psychological well-being journey and keep you moving forward.
Theories Of Psychological Wellbeing
Theories about psychological wellbeing generally focus on understanding the structure of psychological wellbeing or the dynamics . The breakdown of psychological wellbeing into hedonic and eudaimonic components and Carol Ryffs model are widely accepted theories of the structure of PWB.
As far as the dynamics of PWB are concerned its important to recognise that, to some extent, PWB is relatively stable and will have been influenced by both previous experience and underlying personality. Stressful experiences can predispose people to subsequent mood and anxiety disorders but, on the other hand exposure to extremely traumatic events can help to build resilience and actually protect PWB. For example children exposed to moderately stressful events seem better able to cope with subsequent stressors . The same inoculating impact of stressful events has also been observed in working adults .
In summary, PWB theory proposes that early experience and underlying personality create a platform for psychological wellbeing but everyday experiences can help to maintain a good level of PWB or, if they are negative, reduce levels of PWB, leading, in turn, to poor health outcomes.
Read Also: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
Want To Grow Your Well
Well-being is the experience of health, happiness, and prosperity. It includes having good mental health, high life satisfaction, a sense of meaning or purpose, and ability to manage stress. More generally, well-being is just feeling well
Well-being is something sought by just about everyone, because it includes so many positive things feeling happy, healthy, socially connected, and purposeful. Unfortunately, well-being appears to be in decline, at least in the U.S. And increasing your well-being can be tough without knowing what to do and how to do it.
These are some of the reasons why I founded The Berkeley Well-Being Institute an organization that translates the science of well-being into simple tools and products that help you build your well-being. And they are the reasons why I wrote Outsmart Your Smartphone: Conscious Tech Habits for Finding Happiness, Balance, and Connection IRL, which helps people tackle new challenges that interfere with our well-being in the technology age.
Can You Actually Improve Your Well-Being?
Increasing your well-being is simple there are tons of skills you can build. But increasing your well-being is not always easy: Figuring out what parts of well-being are most important for you and figuring out how, exactly, to build well-being skills usually require some extra help.
How Long Does It Take to Improve Well-Being?
Butyou have to stick to it. If you are feeling better after five weeks, you can’t just stop there.
References
Definition Of Mental Health
The terms mental wellbeing and mental health are important concepts that are difficult to define.
The World Health Organization defines mental health in the following way:
- It is a state of wellbeing,
- in which the individual realizes their abilities,
- can cope with the normal stresses of life,
- can work productively and fruitfully, and
- can contribute to their community.
Other terms that might be used in the literature include positive mental health, mental capital, and wellbeing, which can be psychological, mental, or subjective .
Read Also: Fsa Algebra 1 Eoc Review Packet Functions And Modeling Answers
Challenges To The Definition Of Mental Health
There are some challenges to the definition of mental health and what it means to be mentally healthy .
Mental health is framed as part of a larger set of behaviors that result in a healthy, happy, and meaningful existence . Together with physiological health, mental health is considered part of the broader concept of health. However, the determinants of physical health and psychological health are different.
Specifically, to be physically healthy typically implies the absence of illness . The World Health Organization states that mental health is not limited to the absence of mental illnesses or diseases. For example, just because an MRI scan shows that there are no abscesses or tumors present, it doesnt imply that someone is mentally healthy.
These two concepts mental wellbeing and mental illness are not dependent on each other . This implies that patients can present with mental illness and also have high levels of mental wellbeing.
At one point, mental health was considered a collection of symptoms of positive feelings and positive functioning . Keyes argued that mental health could be measured on a continuum: one end anchored with the presence of mental disorders, and the other, with mental wellbeing.
However, subsequent research now considers mental wellbeing as a separate concept from mental illness and mental distress .
Definitions of mental health are also influenced by social, cultural, and historical variables . Here are two examples:
Extrinsic And Intrinsic Psychological Needs
A study conducted in the early 1990s exploring the relationship between well-being and those aspects of positive functioning that were put forth in Ryffs model indicates that persons who aspired more for financial success relative to affiliation with others or their community scored lower on various measures of well-being.
Individuals that strive for a life defined by affiliation, intimacy, and contributing to ones community can be described as aspiring to fulfil their intrinsic psychological needs. In contrast, those individuals who aspire for wealth and material, social recognition, fame, image, or attractiveness can be described as aiming to fulfil their extrinsic psychological needs. The strength of an individuals intrinsic aspirations as indicated by rankings of importance correlates with an array of psychological outcomes. Positive correlations have been found with indications of psychological well-being: positive affect, vitality, and self-actualization. Negative correlations have been found with indicators of psychological ill-being: negative affect, depression, and anxiety.
Also Check: Draw The Lewis Structure For Ccl4.
Mental Health And Social Justice
Mental health is another domain that evinces social justice concerns. Even though mental health is typically understood as an individual trait, macrolevel patterns in psychological well-being have been observed across demographic groups. These relationships appear nuanced by specific disorder and demographic characteristic . For example, a positive correlation between economic status and mental health has been observed for decades . Studies have also demonstrated that women tend to be overrepresented among depression sufferers, while men tend to be overrepresented among schitzophrenics . In some cases, class has demonstrated to exacerbate race and gender associations with mental health: in one study, working-class women were observed as more likely to be depressed than middle-class women .
Frank Neuner, … Verena Ertl, in, 2015
What Are Some Correlates Of Well
Countries differ substantially in their levels of well-being.4, 70 Societies with higher well-being are those that are more economically developed, have effective governments with low levels of corruption, have high levels of trust, and can meet citizens basic needs for food and health.4, 5 Cultural factors also play a role in national estimates of well-being.70
Also Check: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Conceptual Foundations And Empirical Indicators
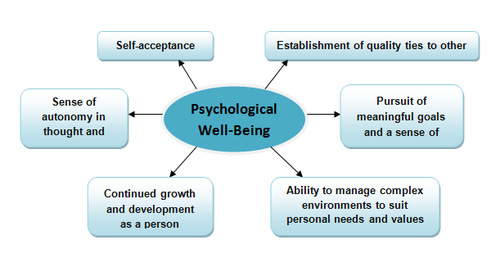
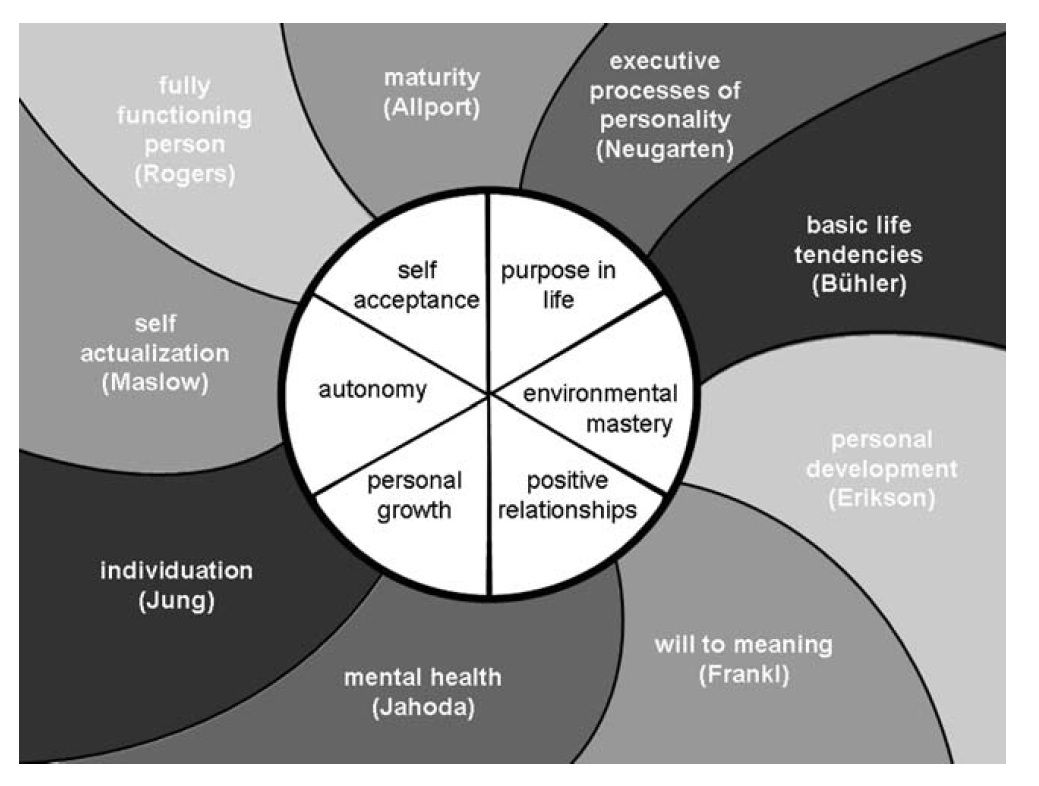
Although considerable empirical research in the 1980s was concerned with well-being – as studied in national surveys and segments of psychology – such endeavors focused largely on reports of happiness, life satisfaction and positive affect. Minimal attention was given to the deeper question, namely, what constitutes essential features of well-being? The neglect was puzzling, given the deep philosophical roots of happiness dating back to the ancient Greeks along with the pervasive interest shown in humanistic, existential, developmental and clinical psychology in distilling positive human functioning . These differing conceptions revealed overlapping themes in articulating what it means to be self-actualized, individuated, fully functioning or optimally developed. Such points of convergence became the basis for distilling 6 key components of well-being . Following the construct-oriented approach to personality assessment , definitions of high and low scorers were then generated for each dimension, and self-report items were written to operationalize the definitions.
Fig. 1
Core dimensions of psychological well-being and their theoretical foundations.
Table 1
Definitions of theory-guided dimensions of well-being
What Is Cdc Doing To Examine And Promote Well
CDCs Health-Related Quality of Life Program has led an effort since 2007 to examine how well-being can be integrated into health promotion and how it can be measured in public health surveillance systems.55 A number of studies have examined the feasibility of existing scales for surveillance, including application of item-response theory to identify brief, psychometrically sound short-form that can be used in public health surveillance systems.72,73 CDC and three states collected data using the Satisfaction with Life Scale and other well-being measures on the 2010 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.74 CDC also led the development of overarching goals related to quality of life and well-being for the Healthy People 2020External initiative.
Recommended Reading: Exponential Growth And Decay Worksheet Answer Key Algebra 1
Diener And Swb Theory
Professor Ed Diener is one of the worlds foremost SWB researchers, coining the construct in his seminal 1984 article: Subjective Well-Being.
Ever since, he has continued studying the subject from a positive psychology perspective with a career spanning more than 25 years, his vast contributions to the field have earned him the nickname Dr. Happiness.
What Are Some Findings From These Studies
- Data from the NHANES I , found that employed women had a higher sense of well-being and used fewer professional services to cope with personal and mental health problems than their nonemployed counterparts.53
- Data from the 2001 NHIS and Quality of Well-Being scale, a preference based scale which scores well-being between 0-1, found that males or females between the ages of 2039 had significantly better well-being compared with males or females 40 years of age or older .54
- Data from the 2005 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System found that 5.6% of US adults reported that they were dissatisfied/very dissatisfied with their lives.48
- Data from the 2005 BRFSS found that about 8.6% of adults reported that they rarely/never received social and emotional support ranging in value from 4.2% in Minnesota to 12.4% in the US Virgin Islands.47
- Based on 2008 Porter Novelli HealthStyles data.55
- 11% of adults felt cheerful all of the time in the past 30 days.
- 15% of adults felt calm and peaceful all of the time in the past 30 days.
- 13% of adults felt full of life all of the time in the past 30 days.
- 9.8% of adults strongly agree that their life is close to their ideal.
- 19% of adults strongly agree that they are satisfied with their life.
- 21% of adults strongly agree that their life has a clear sense of purpose.
- 30% of adults strongly agree that on most days they feel a sense of accomplishment from what they do.
Recommended Reading: Eoc Fsa Practice Test Algebra 2 No Calculator Portion Answers
Global Impact Of Mental Illnesses And Disorders
Mental health is as important as general physical health . Of the global prevalence of illnesses, mental disorders and illnesses make up 14% of the burden of disease .
The World Health Organization estimates that the prevalence of mental illnesses has increased substantially and that approximately 20% of youth experience mental disorders .
To measure the impact of mental illnesses and disorders, we can use the concept of disability-adjusted life years . This measurement is the total number of years that someone spent living with a disability or that were lost to living with consequences of certain illness .
Higher numbers are more serious and indicate a higher impact. It is estimated that by 2030, the percentage of disability-adjusted life years that can be attributed to mental, behavioral, and neurological disorders will be almost 15% globally, but this pattern of prevalence will differ among high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries .
The prevalence will be highest among high-income countries, with mental, behavioral, and neurological disorders accounting for approximately 30% of disability-adjusted life years. Additionally, it is estimated that the number of disability-adjusted life years attributed to mental, behavioral, and neurological disorders in older adults will increase by 79.5% in 2030 .
Specific mental illnesses and disorders that are expected to contribute to disability-adjusted life years include the following:
Summary Observations And Future Directions
As illustrated above, the eudaimonic approach to psychological well-being has become a flourishing arena of scientific inquiry and clinical practice. Why this has occurred merits reflection. Presumably, it stems from the fact that these phenomenological indicators capture core aspects of what it means to be human: that is, to strive, to be proactive, to make meaning and, as articulated by Aristotle over 2,000 years ago, to pursue the highest good that is within us. These ideals about human functioning, along with refinements from existential, humanistic, developmental and clinical psychology, paved the way for new empirical targets in scientific research . Measures designed to operationalize eudaimonic well-being have now been incorporated into many fields as tools to evaluate people’s negotiations through the challenges and transitions of adulthood and aging as well as their management of work, family and community life. Psychological well-being, it seems, is becoming as foundational to defining who we are as were personality traits some decades ago.
Read Also: Math Aids Mean Median Mode
Biopsychosocial Model Of Wellbeing
The biopsychosocial model of wellbeing emphasises the modifiable components needed for an individual to have a sense of wellbeing,. These are:
- healthy environments
- developmental competencies
- sense of belonging
- education and skills, and
- governance.
Personal well-being is a particularly important dimension which we define as how satisfied we are with our lives, our sense that what we do in life is worthwhile, our day to day emotional experiences and our wider mental wellbeing.“
The ONS then introduced four questions pertaining to wellbeing in their 2011 national survey of the UK population, relating to evaluative well-being, eudemonic well-being, and positive and negative affect. They later switched to referring to the construct being measured as “personal well-being”.
Work And Other Life Engagements
The interface between work and family has been extensively studied. Work-family conflict, particularly as it relates to the demands of caregiving, has been linked with poorer well-being . Alternatively, positive spillover from work to family and from family to work is associated with better well-being outcomes . Changing expectations about how to fulfill work and family roles has been linked with cohort differences in how such roles are tied to well-being . For example, older women and younger men who adjusted their work schedules to meet family demands had higher self-acceptance, whereas older men and midlife or younger women had lower self-acceptance if they cut back on paid employment to accommodate family demands. Invoking comparisons between Korean and US adults, positive work to family spillover was associated with better adult well-being, but not for Korean women. Alternatively, negative work to family spillover was linked with poorer well-being, especially among US women , while family to work spillover was also linked with poorer mental health, particularly among Korean men.
Don’t Miss: Ccl4 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry
Affective Commitment And Job Performance
The concept of organizational commitment was first initiated by sit-bet theory in the early 1960s . Organizational commitment is defined as the psychological connection of employees to the organization and involvement in it . It is also defined as the belief of an individual in his or her organizational norms the loyalty of an employee toward the organization and willingness of an employee to participate in organizational duties .
Organizational commitment is further categorized into three correlated but distinct categories , known as affective, normative and continuance. In affective commitment, employees are emotionally attached to their organization. In normative commitment, employees remain committed to their organizations due to the sense of obligation to serve. While in continuance commitment, employees remain committed to their organization because of the costs associated with leaving the organization . Among the dimensions of organizational commitment, affective commitment has been found to have the most substantial influence on organizational outcomes . It is a better predictor of OCB , low turnover intention and job performance .
H2.
Affective commitment positively predict employee job performance.