Who Invented The Periodic Table
No one person invented the periodic table of chemical elements. Rather, the current arrangement of elements on a periodic table was discovered and developed by several scientists over several decades.
The development of the modern periodic table of elements can be mainly credited to the following scientists:
Alexandre Béguyer de Chancourtoisâ de Chancourtois was a geologist who arranged the elements in a three-dimensional pattern using the vis tellurique published in 1862. This was based on the known atomic weights of the elements. As a result, elements with similar properties lined up in the diagram.
John Newlandsâ About four years before Mendeleev published his periodic table of chemical elements , Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves based on the similarities of elements that differ in weights by seven units. However, his system was awkward and did not provide any gaps for undiscovered elements. It was also criticised for being too arbitrary.
â Technically, Meyer could have been the one credited with the idea of the modern periodic table of chemical elements. However, his work was published much later than Mendeleevâs findings. Meyer grouped the elements based on their valency and in order of atomic weight. His table was very similar to Mendeleevâs table.
Fun Fact About The Noble Gases
Further Manifestations Of Periodicity
There are some other relationships throughout the periodic table between elements that are not in the same group, such as the diagonal relationships between elements that are diagonally adjacent . Some similarities can also be found between the main groups and the transition metal groups, or between the early actinides and early transition metals, when the elements have the same number of valence electrons. Thus uranium somewhat resembles chromium and tungsten in group 6, as all three have six valence electrons.
The first row of every block tends to show rather distinct properties from the other rows, because the first orbital of each type is significantly smaller than would be expected. The degree of the anomaly is highest for the s-block, is moderate for the p-block, and is less pronounced for the d- and f-blocks. There is also an even-odd difference between the periods that is sometimes known as secondary periodicity: elements in even periods have smaller atomic radii and prefer to lose fewer electrons, while elements in odd periods differ in the opposite direction. Thus, many properties in the p-block show a zigzag rather than a smooth trend along the group. For example, phosphorus and antimony in odd periods of group 15 readily reach the +5 oxidation state, whereas nitrogen, arsenic, and bismuth in even periods prefer to stay at +3.
You May Like: What Does Converse Mean In Geometry
What Is The Periodic Table Used For
The periodic table is used by chemists and other scientists as a comprehensive reference source.
Itâs very useful to know the relative properties of the elements and be able to predict their reactivity based on their positions in the periodic table.
For example, you can use the periodic table to predict and compare the ionisation energies of different elements. Specific details such as atomic weight and electronegativity values can also be found pretty easily.
Printed periodic tables can only contain a very limited amount of information without becoming extremely large and impractical. Digital periodic tables, however, are not limited by physical space. This means theyâre able to provide more information, including video content. Some digital periodic tables are also interactive and allow you to click on an element symbol to view further details.
Chemistry Glossary Definition Of Periodic Table
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements by increasing atomic number which displays the elements so that one may see trends in their properties. The Russian scientist Dmitri Mendeleev is most often credited with inventing the periodic table . The modern table is derived from Mendeleev’s periodic table, but with one significant different. Mendeleev’s table ordered the elements according to increasing atomic weight rather than atomic number. However, his table illustrated recurring trends or periodicity in the element properties.
Also Known As: Periodic Chart, Periodic Table of the Elements, Periodic Table of the Chemical Elements
Also Check: How Does Geography Help Us Plan For The Future
How Are Elements Arranged In The Periodic Table
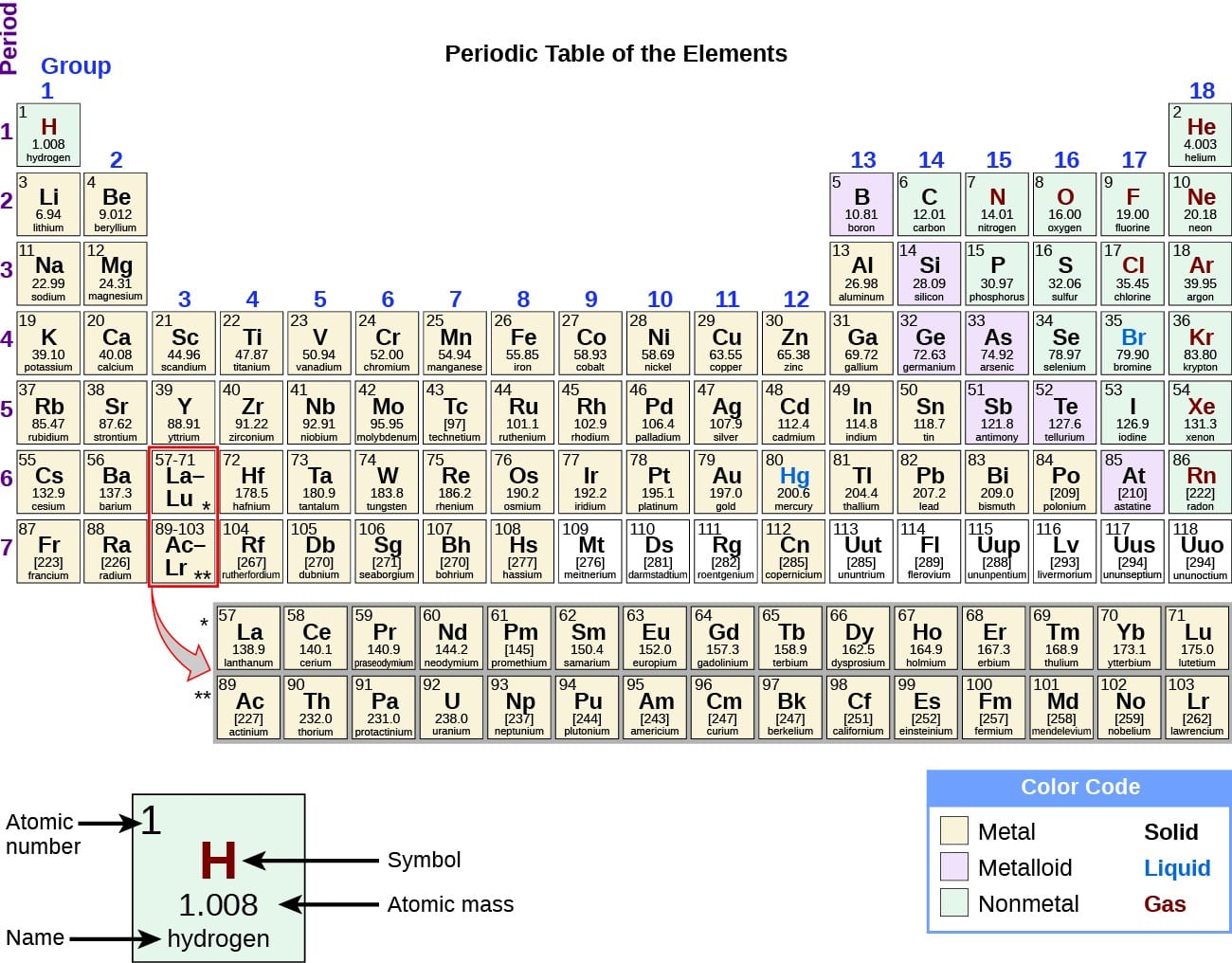
As the name suggests, the elements in the periodic table are arranged into periods, or rows, of increasing atomic number. There are seven periods.
There are also 18 âgroupsâ that are represented by the different columns. Each period exhibits certain trends, such as increasing electron affinity. The groups categorise elements based on their shared properties. For example, Group 15 is the column for noble gases, which are the least reactive elements.
The periods mainly represent the number of orbitals. Elements that belong to the same period have the same number of orbitals. This means you can also write the electron configuration of these elements. The electron configuration describes how the electrons are distributed among the orbitals.
- Period 1: one orbital, two elements
- Period 2: two orbitals, eight elements
- Period 3: three orbitals, eight elements
- Period 4: four orbitals, 18 elements
- Period 5: five orbitals, 18 elements
- Period 6: six orbitals, 32 elements
- Period 7: seven orbitals, 32 elements
Why Does The Periodic Table Split
The periodic table has two rows at the bottom that are usually split out from the main body of the table. These rows contain elements in the lanthanoid and actinoid series, usually from 57 to 71 and 89 to 103 , respectively. There is no scientific reason for this. It is merely done to make the table more compact.
Recommended Reading: Apex Learning Answer Key Algebra 2 Sem 1
What Is The Periodic Table
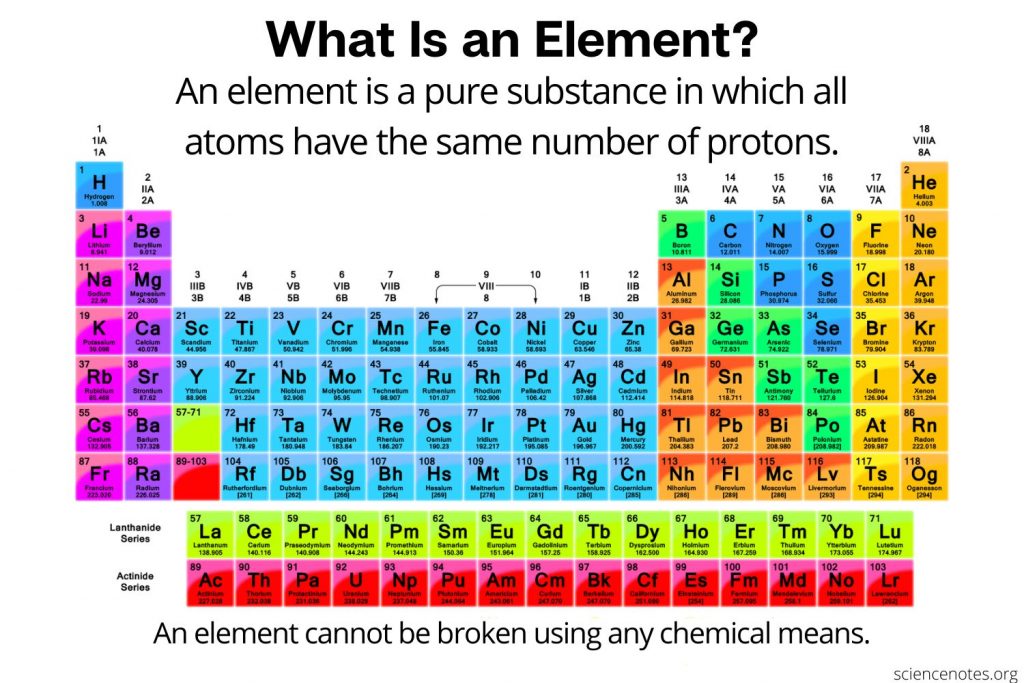
The periodic table is a tabular array of the chemical elements organized by atomic number, from the element with the lowest atomic number, hydrogen, to the element with the highest atomic number, oganesson. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Hydrogen has 1 proton, and oganesson has 118.
The History Of The Periodic Table
The original periodic table was created by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev. He wrote it almost 30 years before Thomson discovered the electron, close to 45 years before Rutherford found the nucleus of an atom and over 50 years before scientists determined that the proton and neutron made up the nucleus of the atom!
Mendeleev proposed a primitive version of todays periodic table as he was writing a textbook on general chemistry. Through his research he was struck by the fact that the elements chemical properties varied with the atomic mass, so he drew up a table to show these relationships.
Mendeleevs 1871 Periodic Table,
In a stroke of genius, he left gaps for elements that had not yet been discovered and even went so far as to predict the properties of those missing elements. And amazingly, when these elements were finally discovered the properties were very similar to what Mendeleev had predicted!
Even though our modern-day table looks quite a bit different from what Mendeleev drew, we still give him credit for the original idea of the periodic table.
Recommended Reading: How To Find Volume In Chemistry
Key Concepts And Summary
The discovery of the periodic recurrence of similar properties among the elements led to the formulation of the periodic table, in which the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number in rows known as periods and columns known as groups. Elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties. Elements can be classified as metals, metalloids, and nonmetals, or as a main-group elements, transition metals, and inner transition metals. Groups are numbered 118 from left to right. The elements in group 1 are known as the alkali metals those in group 2 are the alkaline earth metals those in 15 are the pnictogens those in 16 are the chalcogens those in 17 are the halogens and those in 18 are the noble gases.
Periodic Trends In The Electronegativities Of Elements
As we move across a period from left to right the nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases, therefore the value of electronegativity increases across a period in the modern periodic table. For example, the electronegativity trend across period 3 in the periodic table is depicted below.
There is an increase in the atomic number as we move down the group in the modern periodic table. The nuclear charge also increases but the effect of the increase in nuclear charge is overcome by the addition of one shell. Hence, the value of electronegativity decreases as we move down the group. For example, in the halogen group as we move down the group from fluorine to astatine the electronegativity value decreases and it is shown in the diagram below.
It is a general observation that metals show a lower value of electronegativity as compared to the non-metals.Therefore, metals are electropositive and non-metals are electronegative in nature. The elements in period two differ in properties from their respective group elements due to the small size and higher value of electronegativity.
The elements in the second period show resemblance to the elements of the next group in period three. This happens due to a small difference in their electronegativities. This leads to the formation of a diagonal relationship.
Read Also: Geometry Dash Demon Key Hack
The Periodic Table Of Chemical Elements
Kate Onissiphorou
The periodic table of chemical elements is like the alphabet of chemistry. Similar to letters in the alphabet, elements can combine and react in many ways.
In fact, the permutations of all possible chemical combinations of elements are greater than the estimated number of atoms in the visible universe!
If we include the noble gases in the permutations, there would be 6.62×10184 possibilities. From these possibilities, the complex chemistry of life arose. In comparison, the estimated total upper number of atoms in the universe is only about 1×1082, or one hundred thousand quadrillion vigintillion atoms.
You can predict some reactions and combinations of elements if you know their properties based on the periodic table. And if youâre familiar with how the table is organised, you can describe at least some of the properties of an element by just looking at its position in the table.
In this post:
How We Can Share The Periodic Table In Our Homeschool
Here’s how we share the periodic table throughout the years:
- In the elementary years, I introduce the idea of the periodic table, along with a simplified view of the groups.
- During the middle school years, I teach the basic relationships that the periodic table can show us, along with the periods and groups.
- And finally, for the high school years, the student can focus on learning the chemical principles and mathematics that the periodic table shows us.
Teaching this foundation of chemistry in this manner allows our students to learn about the elements and the periodic table at a level they will understand as they build upon it throughout the years.
You can introduce the periodic table informally through books and then use games to help your students learn the included elements, or you can choose to study chemistry more formally using a pre-planned program. Below are several of the options we have used along the way for homeschool science.
The following books are a few of my favorites to learn more about the periodic table:
You May Like: Does Adderall Permanently Change Brain Chemistry
Length Of Periodic Tables
An important condition for the emergence of periodicity of chemical behavior under ambient conditions is a well-structured atomic orbital level scheme, in particular with gaps, above 1s and 2p to 6p. This quantum-mechanical phenomenon determines the period lengths of 2, 8, 8, 18, 18, 32. At the bottom of common Periodic Tables, four changes happen together, accidentally: The high number Z of electrons occupy orbitals with high principal quantum numbers n, with small energy gaps. The value of the Coulomb coupling constant causes different screenings of the s, p, d, and f orbitals by the large atomic cores that smooth out the shell structure at large Z. The actual value of the fine structure constant causes additional orbital splitting of qualitative chemical relevance via spin-orbit coupling at the bottom of the table. The actual values of the coupling constants of particle physics let the nuclear lifetimes decrease at the end of the second 32-period to values below the time limit required for the existence of a chemical substance.
Reading The Periodic Table
The periodic table contains an enormous amount of information:
Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is referred to as the atomic number of that element. The number of protons defines what element it is and also determines the chemical behavior of the element. For example, carbon atoms always have six protons hydrogen atoms always have one and oxygen atoms always have eight. Different versions of the same element, called isotopes, can have a different number of neutrons also an element can gain or lose electrons to become charged, in which case they are called ions.
Atomic symbol: The atomic symbol is an abbreviation chosen to represent an element . These symbols are used internationally and are sometimes unexpected. For example, the symbol for tungsten is “W” because another name for that element is wolfram. Also, the atomic symbol for gold is “Au” because the word for gold in Latin is “aurum.”
Atomic mass: The standard atomic weight of an element is the average mass of the element written in atomic mass units . Even though each atom has roughly a whole number of atomic mass units, you will notice that the atomic mass on the periodic table is a decimal that’s because the number is a weighted average of the various naturally-occurring isotopes of an element based on their abundance. An isotope is a version of an element with a different number of neutrons in its nucleus. from the atomic mass.)
Multiply the abundance of the isotope by its atomic mass:
Recommended Reading: Is Psychology Bsc Or Ba
Why The Periodic Table Was Developed:
In 1869, Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev wanted to see if there was a pattern to the chemical properties of the elements he knew. He found a pattern, listing elements by their increasing atomic number and arranging them in a chartcreating the first periodic table. This structure helped Mendeleev and other scientists identify similarities and differences among elements to help predict future chemical reactions.
Mendeleevs periodic table included 63 elements. He anticipated others would one day be discovered, so he left open spaces in his table for additions. Today, the 118 chemical elements identified on the periodic table include the materials that make up all known objects in the universe.
Did you know? The most abundant element making up Earth3 is Iron .2 Oxygen is the most common element in the Earths crust.3
Why Is Atomic Number Important
Atomic number is called the number of protons in an atom. This number is very important, because it is unique to a given elements atoms. An elements atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms.
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz
You May Like: How To Make Psychology Notes
Rare Earth Metals: Actinides
Actinides are another family of rare earth metals. Like the lanthanides, these elements are highly reactive. They also have high electropositivity and are radioactive. Additionally, these elements contain paramagnetic, pyromorphic, and allotropic properties. Physically, they are very similar to lanthanides. They are silvery metals that are soft, malleable, and ductile.
Periodic Table Metals Non
The final way of structuring the periodic table that we’ll look at today involves splitting the table with a zigzagging line. It starts to the left of boron and meanders its way down and to the right, sneaking between silicon and germanium, then between arsenic and antimony and tellurium and polonium. Finally, it splits astatine from tennessine, before finishing off to the left of oganesson.
This line has various names: the metal-nonmetal line, the amphoteric line, the metalloid line, and the staircase. It divides the table into metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
- The elements to the left of the line are classified as metals.
- The elements to the right of the line are classified as non-metals.
- Some of the elements touching the line are classified as metalloids.
Metals, non-metals, and metalloids in the periodic table. Based on a StudySmarter Original by Olive Odagbu
Recommended Reading: What Is Radiation In Chemistry
Groups Of The Periodic Table
As previously mentioned, the vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups. There is eighteen groups on the periodic table in total, and each periodic table group contains elements with the same number of valence electrons.
The number of valence electrons present dictates the properties of an element. The reason for this is that the valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell, are the ones taking part in chemical reactions. These electrons are either donating, accepting, or sharing. Moreover, the more filled the valence shell is, the more stable the element.