The Levels Of Classification
Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms to construct internationally-shared classification systems with each organism placed into more and more inclusive groupings. Think about how a grocery store is organized. One large space is divided into departments, such as produce, dairy, and meats. Then each department further divides into aisles, then each aisle into categories and brands, and then, finally, a single product. This organization from larger to smaller, more-specific categories is called a hierarchical system.
Hierarchical models
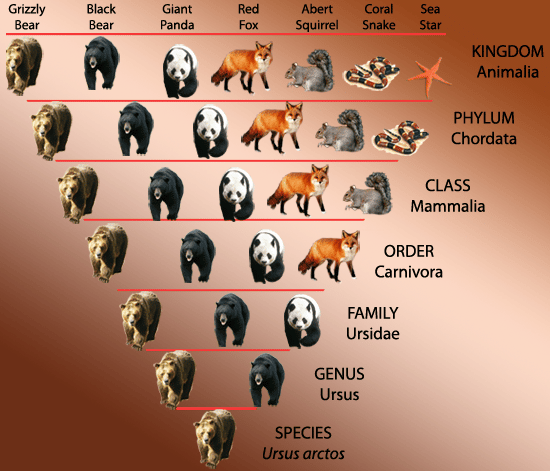
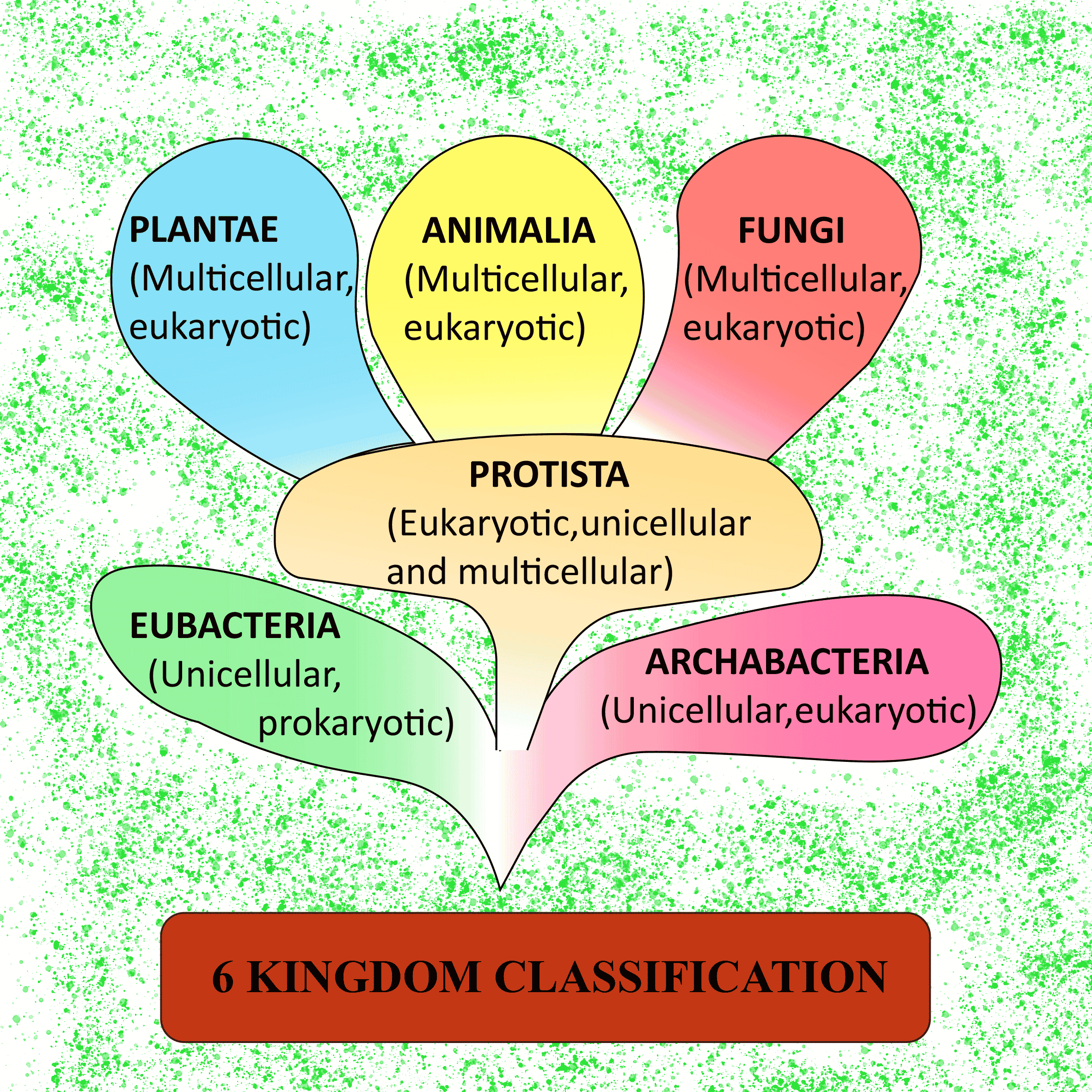
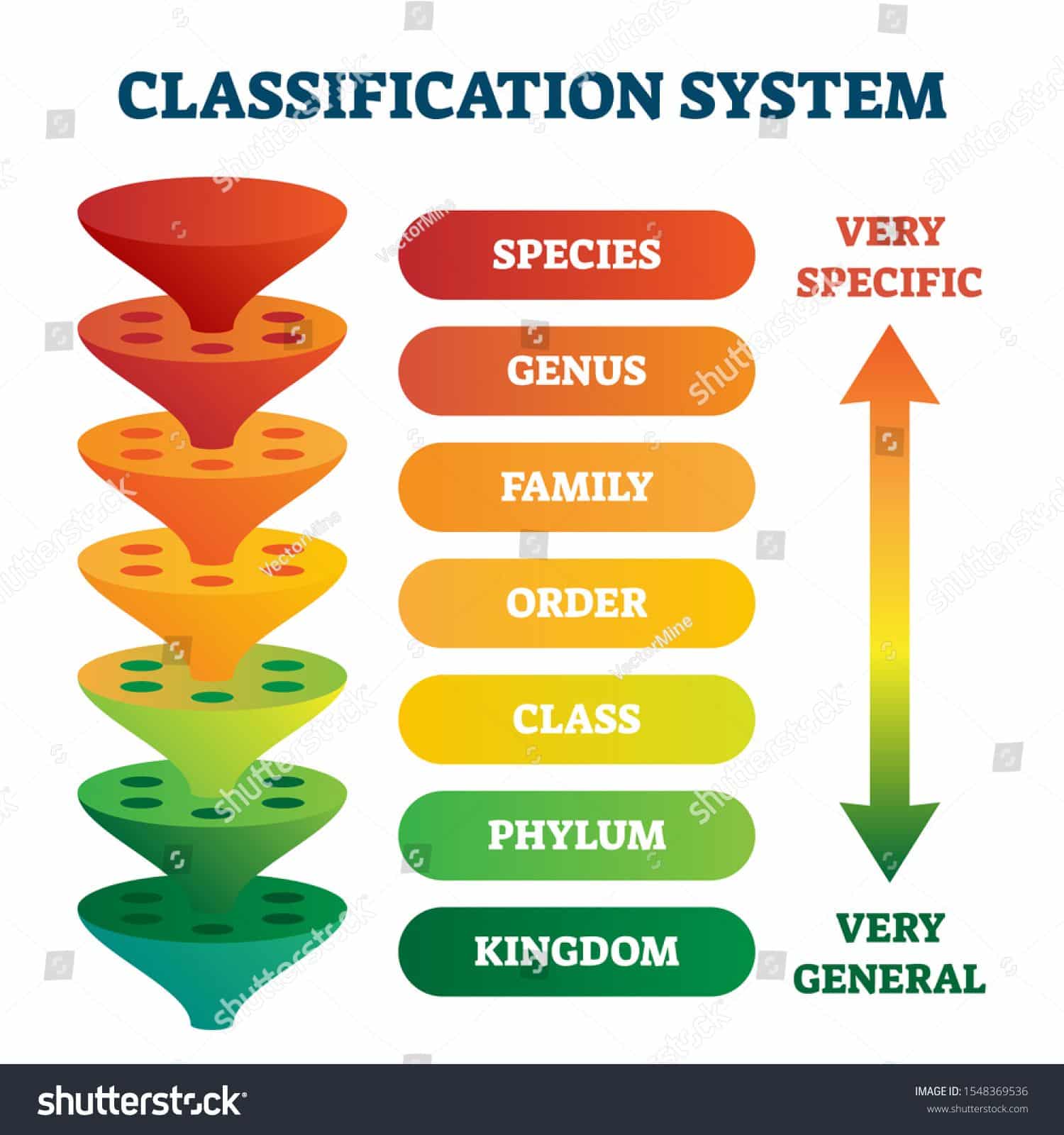
The taxonomic classification system uses a hierarchical model. Moving from the point of origin, the groups become more specific, until one branch ends as a single species. For example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
Levels in taxonomic classification
Dogs actually share a domain with the widest diversity of organisms, including plants and butterflies. At each sublevel, the organisms become more similar because they are more closely related. Historically, scientists classified organisms using physical characteristics, but as DNA technology developed, more precise phylogenies have been determined.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
Categories Of Generic Name
In zoological usage, taxonomic names, including those of genera, are classified as “available” or “unavailable”. Available names are those published in accordance with the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and not otherwise suppressed by subsequent decisions of the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature the earliest such name for any taxon should then be selected as the “valid” name for the taxon in question.
Consequently, there will be more available names than valid names at any point in time, which names are currently in use depending on the judgement of taxonomists in either combining taxa described under multiple names, or splitting taxa which may bring available names previously treated as synonyms back into use. “Unavailable” names in zoology comprise names that either were not published according to the provisions of the ICZN Code, or have subsequently been suppressed, e.g., incorrect original or subsequent spellings, names published only in a thesis, and generic names published after 1930 with no type species indicated.
Prokaryote and virus codes of nomenclature also exist which serve as a reference for designating currently accepted genus names as opposed to others which may be either reduced to synonymy, or, in the case of prokaryotes, relegated to a status of “names without standing in prokaryotic nomenclature”.
Taxonomic Use Of Genus
A genus in one kingdom or domain is allowed to bear a name that is in use as a genus name or other taxon name in another kingdom. Although this is discouraged by both the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature, there are some 5,000 such names that are in use in more than one kingdom. For instance, Anura is the name of the order of frogs, but also is used for the name of a genus of plants Aotus is the genus of golden peas and night monkeys Oenanthe is the genus of wheatears and water dropworts and Prunella is the genus of accentors and self-heal .
Obviously, within the same kingdom, one generic name can apply to only one genus. This explains why the platypus genus is named OrnithorhynchusâGeorge Shaw named it Platypus in 1799, but the name Platypus had already been given to the pinhole borer beetle by Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Herbst in 1793. Since beetles and platypuses are both members of the kingdom Animalia, the name Platypus could not be used for both. Johann Friedrich Blumenbach published the replacement name Ornithorhynchus in 1800.
Homonyms are names with the same form but applying to different taxa. Synonyms are different scientific names used for a single taxon.
Don’t Miss: Year 10 Coordinate Geometry Test
What Are The Types Of Genus In Biology
A genus is a taxonomic category ranking used in biological classification that is below family and above species.Table 1: Difference between genus and species.
| Genus |
|---|
| Species example: H. sapiens |
How do you write genus and species examples?
What is a genus used for?
Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family.
What is a genus easy definition?
Genus, plural genera, biological classification ranking between family and species, consisting of structurally or phylogenetically related species or a single isolated species exhibiting unusual differentiation .
What Is A Genus Species
If the offspring cannot breed and produce offspring, then the original two organisms are classified as different species. For example, a donkey and a horse are different species, but they are capable of mating and reproducing an organism called a mule.
What are some examples of genus?genus: A group of closely related species. For example, the genus Canis which is Latin for dog includes all domestic breeds of dog and their closest wild relatives, including wolves, coyotes, jackals and dingoes. Homo: A genus of species that includes modern humans .
What is genus in simple terms?
: a group of related living things that ranks below the family in scientific classification and is made up of one or more species. genus. noun. ge·nus | \ j-ns , jen-s \
How do you write genus and species examples?
Genus and species: Names should always be italicized or underlined. The first letter of the genus name is capitalized but the specific epithet is not, e.g. Lavandula angustifolia. If the meaning is clear, the generic name can be abbreviated, e.g. L. angustifolia.
What is genus and example?
The genus is the generic name that includes closely related species the gray wolf, for example, is classified as Canis lupus and is a close relative of the coyote found in North America and designated as Canis latrans, their systematic relation indicated by their sharing the same genus name, Canis.
Recommended Reading: What Is Association In Chemistry
What Is Genus And Examples
The definition of a genus is a class of items such as a group of animals or plants with similar traits, qualities or features. An example of a genus is all the species of mushrooms that are part of the Amanita family. A group of organisms ranking above a species and below a family.
What is an example of species in biology?
Organisms may appear to be alike and be different species. For example, Western meadowlarks and Eastern meadowlarks look almost identical to one another, yet do not interbreed with each other thus, they are separate species according to this definition.
Main Difference Genus Vs Species
Genus and species are two taxonomic ranks, which are used in the biological classification of the organisms on earth. The main difference between genus and species is that genus is a lower classification level that lies below family and above species, whereas species is the fundamental category of closely related organisms that lies below the genus. Organisms in each taxonomic rank consist of similar characteristics. An organism of a particular taxonomic ranking, genus or species cannot interbreed with another taxonomic ranking to produce a fertile offspring. In the binomial nomenclature of organisms, the genus is the first part of the binomial name whereas the species is the second part.
Recommended Reading: What Is Qc In Chemistry
Biology Of Genus Boswellia
You can also search for this author inPubMed
You can also search for this author inPubMed
You can also search for this author inPubMed
You can also search for this author inPubMed
-
This would be the first comprehensive book on Boswellia
-
It has all the species and their distribution
-
Richly illustrated with over 40 color photographs
-
Includes a special chapter on genetic analysis and data for analysis of these species
-
Fully referenced for further reading
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution.
Are Dogs A Species
Instead, genetic analyses tell us that all dogs are the same species, Tseng said. But, by those standards, dogs and gray wolves are also the same species, as the two share most of the same genes.
Are birds a species?
Bird, , any of the more than 10,400 living species unique in having feathers, the major characteristic that distinguishes them from all other animals.
Also Check: Geometry Angle Pairs Worksheet Answers
What Is A Genus Class 9
Examples of taxonomic ranks are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain, etc. Species:The lowest taxonomic rank, and the most basic unit or category of biological classification. Genus: Any of the taxonomic groups into which a family is divided and which contains one or more species.
What Is A Species
A species refers to a closely related group of organisms, which comprise similar characteristics and interbreed to produce a fertile offspring. It is considered as the fundamental unit of the classification of organisms. Some hybrid species are also fertile. In order to define a particular species, the similarities in the DNA sequences, morphological, and ecological features can be considered. Sometimes, a particular species may consist of different breeds with great variations.
Figure 3: Panthera tigris amoyensis
Most of the times, similar species live in similar habitats since they originate from a common ancestor. The defining of a species may become difficult due to variation within the species. A south Chinese tiger , which is a species of tiger is shown in figure 3.
Also Check: What Is Location 5 Themes Of Geography
Genus And Species Definition And Classification
Taxonomists decide the makeup of a genus. Since there are no definite codified criteria for genus classification, various authorities frequently create different classifications for genera.
However, there are some common practises, such as the suggestion that a newly identified genus should meet these three conditions in order to be concisely beneficial:
-
Monophyly – All descendants of an ancestral taxon were placed together in monophyly .
-
Fair Compactness A genus must not be overly extended.
-
Distinctness In terms of evolutionarily applicable parameters such as ecology, anatomy, or biogeography DNA sequences are a result instead of a cause of diverging evolutionary lineages unless they specifically impede gene flow .
Furthermore, genera should be made up of the very same phylogenetic units as other genera.
How Many Different Genus Groups Are There
This section presents a list of all genus-group names applied to Culicidae from Linnaeus . It contains 441 genus-group names: 209 currently valid names and 232 synonyms. In addition to the 41 extant genera and 162 extant subgenera, the valid names include 5 genera of fossil mosquitoes and one nomen dubium.
Read Also: How Do You Find Percent Yield In Chemistry
Which Is An Example Of A Group Of Related Species
Which is higher a genus or a family?
Classification system. Genus is a taxonomic rank among the eight major taxonomic ranks in a biological classification. It is below the family and above the species. A genus may be comprised of one or more species. A family, in turn, consists of a genus or several genera.
What Is The Genus Of A Human
HomoHuman/Genus
What genus means?
Genus refers to a taxonomic category which comprises a group of closely related plants and animals. E.g., Panthers leo is lion. Panthers is a genus which has less common characters than species.
Which is an example of a genus in biology?
1. biology any of the taxonomic groups into which a family is divided and which contains one or more species. For example, Vulpes is a genus of the dog family
How is a genus related to a taxa?
A genus is a group of species that are closely related through common decent. A genus represent one of several hierarchical categories called taxa include only a small group of species which evolved from a relatively recent common ancestor.
Recommended Reading: Geometry 3.5 Worksheet Answers
Names Of Botanical Taxa
Taxa at the rank of genus and above have a botanical name in one part those at the rank of species and above have a botanical name in two parts all taxa below the rank of species have a botanical name in three parts ” rel=”nofollow”> infraspecific name). To indicate the rank of the infraspecific name, a “connecting term” is needed. Thus Poa secunda subsp. , where “subsp.” is an abbreviation for “subspecies”, is the name of a subspecies of Poa secunda.
Hybrids can be specified either by a “hybrid formula” that specifies the parentage, or may be given a name. For hybrids receiving a hybrid name, the same ranks apply, prefixed with notho , with nothogenus as the highest permitted rank.
Outdated names for botanical ranks
If a different term for the rank was used in an old publication, but the intention is clear, botanical nomenclature specifies certain substitutions:
What Is A Genus
A genus refers to a principle taxonomic classification, which ranks below family and above species. It consists of a collection of different species with similar characteristics. In binomial nomenclature, the name of the genus comes first, and it is followed by the name of the species. For example, the scientific name of the modern human is . is the genus of humans whereas sapiens sapiens is the species name.
Figure 1: Biological Classification
Three criteria are used to define a genus.
Figure 2: Aster
Aster is a genus of flowering plants. The members of the genus Aster is shown in figure 2.
You May Like: Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Workbook Answers
Numbers Of Accepted Genera
The numbers of either accepted, or all published genus names is not known precisely Rees et al., 2020 estimate that approximately 310,000 accepted names may exist, out of a total of c. 520,000 published names as at end 2019, increasing at some 2,500 published generic names per year. “Official” registers of taxon names at all ranks, including genera, exist for a few groups only such as viruses and prokaryotes, while for others there are compendia with no “official” standing such as Index Fungorum for Fungi,Index Nominum Algarum and AlgaeBase for algae, Index Nominum Genericorum and the International Plant Names Index for plants in general, and ferns through angiosperms, respectively, and Nomenclator Zoologicus and the Index to Organism Names for zoological names.
Totals for both “all names” and estimates for “accepted names” as held in the Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera are broken down further in the publication by Rees et al., 2020 cited above. The accepted names estimates are as follows, broken down by kingdom:
- Animalia: 239,093 accepted genus names
- Plantae: 28,724 accepted genus names
- Fungi: 10,468 accepted genus names
- Chromista: 11,114 accepted genus names
- Protozoa: 3,109 accepted genus names
- Bacteria: 3,433 accepted genus names
- Archaea: 140 accepted genus names
- Viruses: 851 accepted genus names
Names Of Zoological Taxa
- A taxon above the rank of species has a scientific name in one part .
- A species has a name composed of two parts : generic name + specific name for example Canis lupus.
- A subspecies has a name composed of three parts : generic name + specific name + subspecific name for example Canis lupus italicus. As there is only one possible rank below that of species, no connecting term to indicate rank is needed or used.
Recommended Reading: Xef2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry
Categories Of Generic Name:
Taxonomic names, along with those of genera, are listed as “available” or “unavailable” in zoological terminology. Appropriate names are those that have been reported in compliance with the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and have not been prohibited by subsequent decisions of the ICZN the latest known term for any taxon should therefore be chosen as the “true” title for the taxon in question.
How Are Species Named
Scientists use a two-name system called a Binomial Naming System. Scientists name animals and plants using the system that describes the genus and species of the organism. The first word is the genus and the second is the species. The first word is capitalized and the second is not.
Recommended Reading: How To Learn Name Reactions In Organic Chemistry
What Is A Genus In Biology
The genus-species format is essential in naming an organism. The genus is the generic name whereas the species is the specific name in a binomial nomenclature. For example, Allium cepa . The Allium is the generic name whereas the cepa is the specific name.
What is a genus species?Genus and species are two taxonomic rankings of the biological classification of organisms. Species is the fundamental taxonomic rank of organisms, which contains a group of closely-related organisms, interbreeding to produce a fertile offspring. A genus is a closely-related group of several species.
What is a species example?
If the offspring cannot breed and produce offspring, then the original two organisms are classified as different species. For example, a donkey and a horse are different species, but they are capable of mating and reproducing an organism called a mule.
What is a genus example?
genus: A group of closely related species. For example, the genus Canis which is Latin for dog includes all domestic breeds of dog and their closest wild relatives, including wolves, coyotes, jackals and dingoes. Homo: A genus of species that includes modern humans .
What is genus and example?
genus: A group of closely related species. For example, the genus Canis which is Latin for dog includes all domestic breeds of dog and their closest wild relatives, including wolves, coyotes, jackals and dingoes. Homo: A genus of species that includes modern humans .