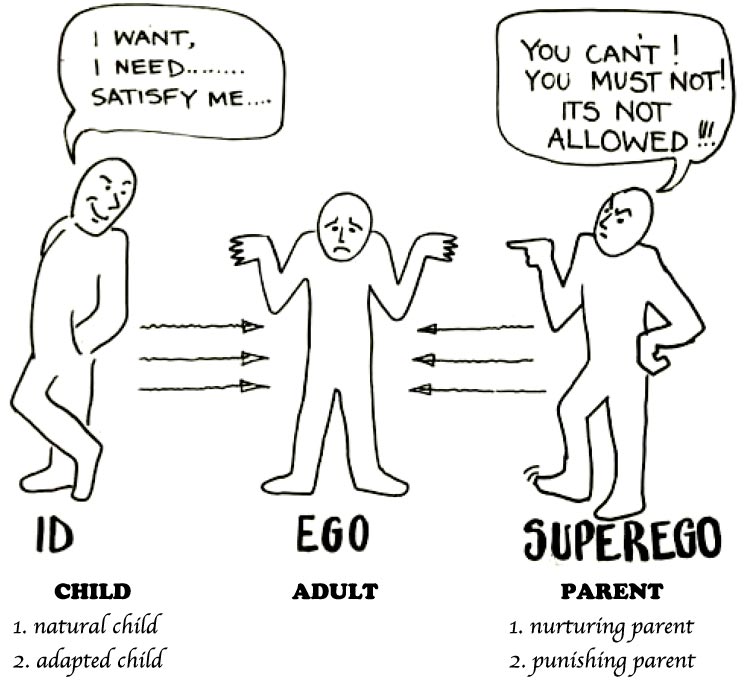
What Is The Id
The id is the primitive and instinctive component of personality. The id is a part of the unconscious that contains all the urges and impulses, including what is called the libido, a kind of generalized sexual energy that is used for everything from survival instincts to appreciation of art. The id is also kind of stubborn, for it responds only to what Freud called the pleasure principle , and nothing else.
It consists of all the inherited components of personality present at birth, including the sex instinct â Eros , and the aggressive instinct – Thanatos.
The id is the impulsive part of our psyche which responds directly and immediately to basic urges, needs, and desires. The personality of the newborn child is all id and only later does it develop an ego and super-ego.
The id remains infantile in its function throughout a person’s life and does not change with time or experience, as it is not in touch with the external world. The id is not affected by reality, logic or the everyday world, as it operates within the unconscious part of the mind.
The id operates on the pleasure principle which is the idea that every wishful impulse should be satisfied immediately, regardless of the consequences.When the id achieves its demands, we experience pleasure when it is denied we experience âunpleasureâ or tension.
How The Id Operates
The id acts according to the pleasure principle, which is the idea that needs should be met immediately. When you are hungry, the pleasure principle directs you to eat. When you are thirsty, it motivates you to drink. But of course, you can’t always satisfy your urges right away. Sometimes you need to wait until the right moment or until you have access to the things that will fulfill your needs.
When you are unable to satisfy a need immediately, tension results. The id relies on the primary process to temporarily relieve the tension. The primary process involves creating a mental image through daydreaming, fantasizing, hallucinating, or some other process. For example, when you are thirsty, you might start fantasizing about a tall, cold glass of ice water.
When you are hungry, you might start thinking about ordering your favorite dish from your favorite restaurant. By doing this, you are able to cope with the tension created by the id’s urges until you are realistically able to satisfy those needs.
What Does Ego Mean In Psychology
Ego is the holy grail in psychology. It is the stuff that psychologists try to fix whenever they are treating a patient. And almost all the psychological disorders are due to the faults in our egos.
It is ego that all the self-help experts are also trying to come to terms with in order to transcend its limits
So, can you guess now, how important the ego is?
Basically, ego is the center of our awareness. It is the form of our personality and the structure of our conscious existence.
Crudely, it can be said that ego is formed of our perceptions, thoughts, ideas, and memories.
In more academic terms, ego is a personality formation that deals with the external environment and the internal forces of ones psyche.
Read Also: Can Chemistry Be One Sided
Id: Meeting Basic Needs
The id is the most basic part of the personality. It also represents our most animalistic urges, like the desire for food and sex. The id seeks instant gratification for our wants and needs. If these needs or wants are not met, a person can become tense, anxious, or angry.
- Sally was thirsty. Rather than waiting for the server to refill her glass of water, she reached across the table and drank from Mr. Smith’s water glass, much to his surprise.
- A hungry baby cried until he was fed.
- A toddler who wanted another helping of dessert whined incessantly until she was given another serving.
- In line at the salad bar, Amy was so hungry that she shoved a handful of croutons in her mouth as she waited for the line to move.
- Bart was stuck in traffic. He just wanted his vehicle to move! Enraged at the situation, Bart pulled his car onto the shoulder and sped forward, not caring that he was clipping people’s side mirrors as he tried to get ahead of the cars in front of him.
Why Is Id In Psychology Important
The id is very important early in life because it ensures that an infant’s needs are met. If the infant is hungry or uncomfortable, they will cry until the demands of the id are satisfied. Young infants are ruled entirely by the id, there is no reasoning with them when these needs demand satisfaction.
Also Check: What Does Kn Stand For In Physics
Freud: Id Ego And Superego
Freud believed that most of our daily actions and behaviours are not controlled consciously but are the product of our unconscious mind.
The unconscious mind is where feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories outside our conscious awareness are stored. It holds unacceptable or unpleasant information, such as pain, anxiety, and conflicts.
The influence of the unconscious seeps into every part of our lives. The unconscious mind actively represses traumatic memories from reaching conscious awareness. These memories might cause anxiety therefore, the mind uses defence mechanisms to avoid discomfort.
Defence mechanisms are strategies we use unconsciously to protect ourselves from the anxiety caused by our unacceptable feelings and thoughts.
Freud outlined seven defence mechanisms: denial, sublimation, projection, displacement, undoing, isolation, and reaction formation.
Our unconscious tries to repress traumatic experiences. However, Freud believed traces of these experiences could reveal themselves in many different ways, such as through dreams, fantasies, slips of the tongue , creativity, and neurotic symptoms.
What Does Id In Psychology Stand For
The id is the impulsive part of our psyche which responds directly and immediately to basic urges, needs, and desires.
What kind of word is ID?
Id can be a noun or an abbreviation.
Which is correct ID or ID?
The correct one is Id. ID appears to be an acronym of two words, though there is only one word, identifier.
You May Like: Algebra 2 Chapter 3 Practice Workbook
How The Id Ego And Superego Interact
The id, ego, and superego dont function separately and independently. Instead, they overlap and interact in various ways to influence how people think, feel, and behave.
These forces are also dynamic and always shifting. Sometimes the demands of the id might take precedence. In other cases, it might be the superego that takes the lead. In every situation, the ego serves as the mediator trying to strike a balance between the demands of the id, the superego, and reality.
Ego strength is what Freud called the egos ability to manage these competing forces effectively. Having poor ego strength means that you might give in to your impulses more frequently, while having too much might mean an inability to adapt and compromise.
Read More: What Is a Type A Personality?
Advantages Of The Structural Model
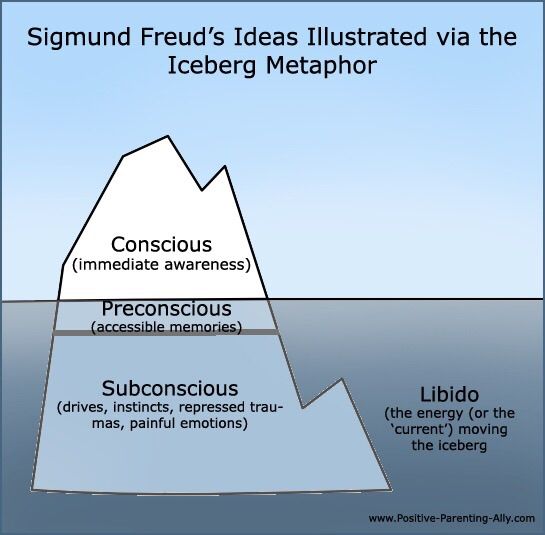
Freud’s earlier, topographical model of the mind had divided the mind into the three elements of conscious, preconscious, and unconscious. The conscious contains events that we are aware of, preconscious is events that are in the process of becoming conscious, and unconscious include events that we are not aware of. At its heart was “the dialectic of unconscious traumatic memory versus consciousness…which soon became a conflict between System Ucs versus System Cs.” With what Freud called the “disagreeable discovery that on the one hand ego and conscious and on the other hand repressed and unconscious are far from coinciding,” Freud took the step in the structural model to “no longer use the term ‘unconscious’ in the systematic sense,” and to rename “the mental region that is foreign to the ego… in future call it the ‘id’.” The partition of the psyche defined in the structural model is thus one that cuts across the topographical model’s partition of “conscious vs. unconscious”.
“The new terminology which he introduced has a highly clarifying effect and so made further clinical advances possible.” Its value lies in the increased degree of precision and diversification made possible: Although the id is unconscious by definition, the ego and the super-ego are both partly conscious and partly unconscious. What is more, with this new model Freud achieved a more systematic classification of mental disorder than had been available previously:
Read Also: What Does Fg Mean In Physics
Why Dont I Understand Myself
Every individual has a goal of nurturing values and making choices that are consistent with their true self. Some internalize the values of their families or culture, even though they dont align with their authentic self. This conflict can drive dissatisfaction and uncertainty. Reflecting on ones values can spark change and a more fulfilling life.
Examples Of The Superego
For example, if you give in to the urges of the id, the superego is what will cause you to feel a sense of guilt or even shame about your actions. The superego may help you feel good about your behavior when you suppress your most primal urges.
Other examples of the superego include:
- A woman feels an urge to steal office supplies from work. However, her superego counteracts this urge by focusing on the fact that such behaviors are wrong.
- A man realizes that the cashier at the store forgot to charge him for one of the items he had in his cart. He returns to the store to pay for the item because his internalized sense of right and wrong urge him to do so.
- A student forgot to study for a history test and feels an urge to cheat off of a student sitting nearby. Even though he feels like the chances of getting caught are low, he knows that cheating is wrong, so he suppresses the urge.
You May Like: What Is Heuristic In Psychology
When Does The Id Emerge
Freud compared personality to an iceberg. What you see above the water is actually just a tiny piece of the entire iceberg, most of which is hidden under the water. The tip of the iceberg above the water represents conscious awareness.
The bulk of the iceberg below the water symbolizes the unconscious mind where all of the hidden desires, thoughts, and memories exist. It is in the unconscious mind that the id resides.
The id is the only part of the personality that is present at birth, according to Freud. He also suggested that this primitive component of personality existed wholly within the unconscious. The id acts as the driving force of personality. It not only strives to fulfill the most basic urges that people have, many of which are tied directly to survival, it also provides all of the energy necessary to drive personality.
During infancy, before the other components of personality begin to form, children are ruled entirely by the id. Satisfying basic needs for food, drink, and comfort is of the utmost importance.
Key Takeaways: Id Ego And Superego
- Sigmund Freud originated the concepts of the id, the ego, and the superego, three separate but interacting parts of the human personality that work together to contribute to an individual’s behavior.
- While Freuds ideas have often been critiqued and labeled unscientific, his work continues to be highly influential in the field of psychology.
You May Like: What Is Radius In Math
Freud’s Theory Of The Id In Psychology
By Charlotte Nickerson, published May 12, 2022 | Fact Checked by Saul Mcleod, PhD
The id, first conceived of by the psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud , is the part of the personality that is driven by instinctual needs and desires.
The id is the primary source of motivation for all human behavior, namely basic needs, such as hunger, emotional expression, and sex.
The id operates on the pleasure principle, which means that it seeks to gratify its needs and desires in any way possible.
Psychodynamic Theories Of Personality: The Role Of The Unconscious
One of the most important psychological approaches to understanding personality is based on the theorizing of the Austrian physician and psychologist Sigmund Freud , who founded what today is known as the psychodynamic approach, an approach to understanding human behaviour that focuses on the role of unconscious thoughts, feelings, and memories. Many people know about Freud because his work has had a huge impact on our everyday thinking about psychology, and the psychodynamic approach is one of the most important approaches to psychological therapy . Freud is probably the best known of all psychologists, in part because of his impressive observation and analyses of personality . As is true of all theories, many of Freuds ingenious ideas have turned out to be at least partially incorrect, and yet other aspects of his theories are still influencing psychology.
Freud was influenced by the work of the French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot , who had been interviewing patients who were experiencing what was at the time known as hysteria. Although it is no longer used to describe a psychological disorder, hysteria at the time referred to a set of personality and physical symptoms that included chronic pain, fainting, seizures, and paralysis.
Don’t Miss: What Is N In Physics
How Are The Id Ego And Superego Related To One Another
Freud believed that each of these three components of personality represents a distinct component, but they interact with one another to form an individuals personality and direct behavior. The id provides the drives for behavior, the superego strives for moral perfection, and the ego works to strike a balance between those two needs and the demands of reality.
A healthy, well-functioning personality is all about striking a need between the id, ego, and superego.
What Causes The Superego
The superego develops primarily from parental instructions and rules, and encourages the individual to rise above his or her base instincts and drives. It works in direct counterbalance to the id. Freud believed that the superego is formed during the Oedipus complex after a boy learns to identify with his father.
You May Like: What Is Lattice In Chemistry
What Is An Identity Crisis
The idea of an identity crisis emerged from psychologist Erik Erikson, who delineated eight stages of crises and development, a concept later expanded upon by others. Although not a clinical term, an identity crisis refers to facing a challenge to ones sense of self, which may center around politics, religion, career choices, or gender roles.
How To Be Authentic
A hunger for authenticityguides us in every age and aspect of life. It drives our explorations of work, relationships, play, and prayer. Teens and twentysomethings try out friends, fashions, hobbies, jobs, lovers, locations, and living arrangements to see what fits and what’s “just not me.” Midlifers deepen commitments to career, community, faith, and family that match their self-images, or feel trapped in existences that seem not their own. Elders regard life choices with regret or satisfaction based largely on whether they were “true” to themselves.
Authenticity is also a cornerstone of mental health. Its correlated with many aspects of psychological well-being, including vitality, self-esteem, and coping skills. Acting in accordance with one’s core selfa trait called self-determinationis ranked by some experts as one of three basic psychological needs, along with competence and a sense of relatedness.
Read Also: How To Use Percentages In Math
What Happens If There Is An Imbalance
According to Freud, the key to a healthy personality is a balance between the id, the ego, and the superego.
If the ego is able to adequately moderate between the demands of reality, the id, and the superego, a healthy and well-adjusted personality emerges. Freud believed that an imbalance between these elements would lead to a maladaptive personality.
For example, an individual with an overly dominant id might become impulsive, uncontrollable, or even criminal. Such an individual acts upon their most basic urges with no concern for whether their behavior is appropriate, acceptable, or legal.
On the other hand, an overly dominant superego might lead to a personality that is extremely moralistic and judgmental. A person ruled by the superego might not be able to accept anything or anyone that they perceive to be “bad” or “immoral.”
The Interaction Of The Id Ego And Superego

When talking about the id, the ego, and the superego, it is important to remember that these are not three separate entities with clearly defined boundaries. These aspects are dynamic and always interacting to influence an individual’s overall personality and behavior.
With many competing forces, it is easy to see how conflict might arise between the id, ego, and superego. Freud used the term ego strength to refer to the ego’s ability to function despite these dueling forces.
A person who has good ego strength can effectively manage these pressures, while a person with too much or too little ego strength can be unyielding or disruptive.
You May Like: How To Differentiate In Physics
How Did Freud Understand Identity
According to Freuds psychoanalytic framework, the mind was composed of the id, driven by instinct and desire, the superego, driven by morality and values, and the ego which moderates the two and creates ones identity. Many features contribute to ego functioning, including insight, agency, empathy, and purpose.
How Do I Live Authentically
Everyone subconsciously internalizes conventions and expectations that dictate how they believe they should think or behave. The decision to examine or challenge those assumptions, even though its difficult, is the first step to living more authentically. This set of 20 steps can guide you through that process.
Read Also: What Is The Unit For Distance In Physics