Get Thoughts Off Your Mind And Onto Paper
Persistent worries can also cause some people to have difficulty falling asleep. If this happens to you, consider keeping a notepad beside your bed to jot down random thoughts that pop up. Writing down your thoughts can ease your mind, especially if you feel like you need to remember them for the next day.
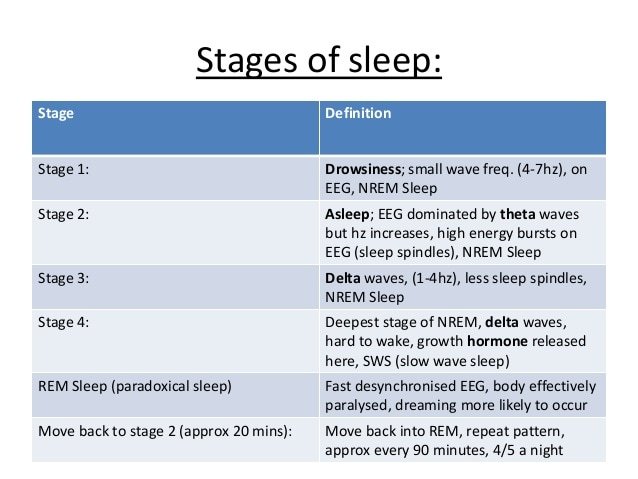
Stage 2 Sleep Is Characterized By The Appearance Of Both Sleep Spindles And K
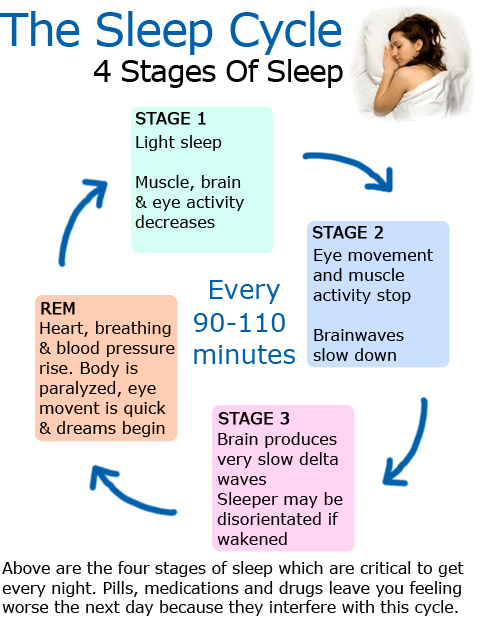
Stage 3 and stage 4 of sleep are often referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep because these stages are characterized by low frequency , high amplitude delta waves . During this time, an individuals heart rate and respiration slow dramatically. It is much more difficult to awaken someone from sleep during stage 3 and stage 4 than during earlier stages. Interestingly, individuals who have increased levels of alpha brain wave activity during stage 3 and stage 4 often report that they do not feel refreshed upon waking, regardless of how long they slept .
Why Is Early High School Start Later
have an easier time focusing in class. A multitude of students would rather sleep than go to school because they continuously fall asleep in class and are unable to pay attention. Robert Voronaan associate professor of medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical Schoolformerly suggested, Most of us in sleep medicine now believe that teenagers require nine-plus hours of sleep each night, and the consequences of insufficient sleep include excessive daytime sleepiness, mood disorders, and even potential suicidal
Don’t Miss: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Stage 5 Sleep Of The Sleep Cycle
Stage 5 of the sleep cycle, or REM sleep, is the stage of sleep associated with dreaming. It is very different physiologically from the other stages of sleep. The EEG resembles wake time. However, the skeletal muscles are atonic, or without movement. The breathing is more erratic and irregular. The heart rate often increases. It is theorized that muscle atonia evolved in order to protect the individual from injury during sleep.
Pody601 Week 1 Reflection Journal
How did I find the first week back into study? I am quite happy to say that I ended the first week of Semester two 2016 on a really good note. My expectations of the course were met as I have throughly enjoyed the content studied so far, been able to meet some of my fellow classmates and also be able to get a feel of the clinic practise during PODY601 tutorial and, the PCP1 tutorial. There was a huge build up of nerves and excitement during the beginning of the week and that excitement grew as
You May Like: What Does G Mean In Physics
What Are The Sleep Stages
There are four sleep stages one for rapid eye movement sleep and three that form non-REM sleep. These stages are determined based on an analysis of brain activity during sleep, which shows distinct patterns that characterize each stage.
| Sleep Stages | |
|---|---|
| REM Sleep | 10-60 minutes |
The breakdown of a persons sleep into various cycles and stages is commonly referred to as sleep architecture. If someone has a sleep study, this sleep architecture can be represented visually in a hypnogram.
The classification of sleep stages was by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine . Before that, most experts referred to five sleep stages, but today, the AASM definitions of the four stages represent the consensus understanding of the sleep cycle.
Sleep Patterns Change With Age
Sleep architecture changes continuously and considerably with age. From infancy to adulthood, there are marked changes in how sleep is initiated and maintained, the percentage of time spent in each stage of sleep, and overall sleep efficiency . A general trend is that sleep efficiency declines with age . Although the consequences of decreased sleep efficiency are relatively well documented, the reasons are complex and poorly understood. Exami nation of sleep characteristics by age, however, allows a closer understanding of the function of sleep for human development and successful aging.
Although there have been few systematic studies, there appear to be gender-based differences in sleep and circadian rhythms. Available evidence is strongest in adults however, gender differences have also been observed in infancy , childhood , and adolescence . In adults, men spend greater time in stage 1 sleep and experience more awakenings . Although women maintain longer than men, they complain more often of difficulty falling asleep and midsleep awakenings. In contrast, men are more likely to complain of daytime sleepiness .
Read Also: Algebra 1 Age Word Problems
How Much Time Should I Spend Asleep
How much sleep time we need varies from person to person, but most adults should aim for 7 to 9 hours of rest.
Your first sleep cycle will likely cover 70 to 100 minutes, while later sleep cycles should last 90 to 120 minutes. Your body cycles through the different stages about five times every night.
Our sleep calculator can help you determine your ideal bedtime. You simply count back from when you want to wake up, and factor in the time you need to fall asleep.
How Can You Have A Healthier Sleep Cycle
While you dont have full control of your sleep cycle, you can take steps to improve your chances of having a healthy progression through each sleep stage.
A key step is to focus on improving your sleep hygiene, which refers to your sleep environment and sleep-related habits. Achieving a more consistent sleep schedule, getting natural daylight exposure, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, and eliminating noise and light disruptions can help you get uninterrupted sleep and promote proper alignment of your circadian rhythm.
If you find that you have excessive daytime sleepiness or otherwise suspect that you might have a sleep disorder like sleep apnea, its important to talk with a doctor who can most appropriately guide your care. Addressing underlying issues may pave the way for more complete and restorative sleep cycles.
- Was this article helpful?
Read Also: Practice 2-4 Reasoning In Algebra Answers
What Affects Sleep Stages
While there is a typical pattern for sleep stages, there can be substantial individual variation based on a number of factors:
- Age: Time in each stage changes dramatically over a persons life. Newborns spend far more time in REM sleep and may enter a REM stage as soon as they fall asleep. As they get older, their sleep becomes similar to that of adults, normally reaching a comparable sleep architecture . On the other hand, elderly people tend to spend less time in REM sleep.
- Recent sleep patterns: If a person gets irregular or insufficient sleep over a period of days or more, it can cause an abnormal sleep cycle.
- Alcohol:Alcohol and some other drugs can alter sleep architecture. For example, alcohol decreases REM sleep early in the night, but as the alcohol wears off, there is a REM sleep rebound, with prolonged REM stages.
- Sleep disorders: Sleep apnea, Restless Leg Syndrome , and other conditions that cause multiple awakenings may interrupt a healthy sleep cycle.
Stages Of Sleep: The Sleep Cycle
There are five stages of sleep during the sleep cycle. Scientists categorized the stages of sleep based on the characteristics of the brain and body during sleep. Stage 1,2,3, and 4, are categorized as non-REM sleep, and the fifth stage, is REM sleep. Generally, brainwave frequencies and amplitudes from an electroencephelogram are used to differentiate the different stages of sleep, along with other biologic rhythms including eye movements and muscle movements .
Also Check: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
The Effects Of Sleep On Children And Adolescents
recorded having a sleep parasomnia, most of them being young children or adolescents. Parasomnias range from very common disorders such as sleepwalking, to a few some may have never heard of, for instance: sleep paralysis. Sleep parasomnias are disorders characterized by abnormal or unusual behavior of the nervous system during that occur during non-rapid eye movement sleep or rapid eye movement sleep . NREM sleep contains more common
What Is The Sleep Cycle
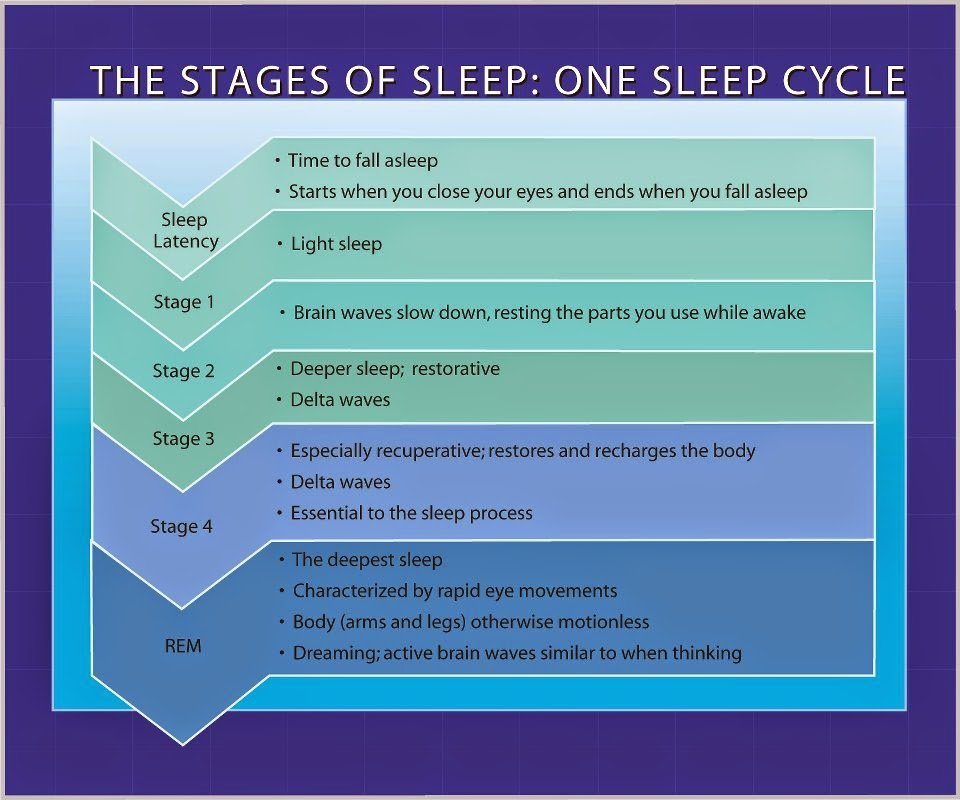
Sleep is not uniform. Instead, over the course of the night, your total sleep is made up of several rounds of the sleep cycle, which is composed of four individual stages. In a typical night, a person goes through four to six sleep cycles. Not all sleep cycles are the same length, but on average they last about 90 minutes each.
Also Check: Ccl4 Valence Electrons
Resist The Urge To Scroll
Although you may enjoy lying in bed and scrolling through social media, research has shown that using electronic devices for at least before sleeping can result in poor sleep quality. If you think this contributes to your sleep struggles, consider having a no device in the bedroom policy to see if that helps.
What Can Interrupt Your Cycle
Interrupted sleep is the term used to describe sleep that is not continuous throughout the night. When this happens, your sleep cycle can be disrupted. An in-progress sleep stage may be cut short and a cycle may repeat before finishing.
There are a number of issues that can interrupt your sleep cycles. Depending on which one is at play, this may happen occasionally or on a chronic basis.
Some factors that are associated with interrupted sleep and, therefore, may affect your sleep stages include:
- Older age: Sleep naturally becomes lighter and you are more easily awoken.
- Nocturia: Frequently waking up with the need to urinate
- Sleep disorders, including obstructive sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome
- Pain: Difficulty falling or staying asleep due to acute or chronic pain conditions, like fibromyalgia
- Mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder
- Other health conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, heart disease, and asthma
- Lifestyle habits: Little/no exercise, cigarette smoking, excessive caffeine intake, excessive alcohol use
Any time you have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep at night, your sleep cycle will be affected.
Read Also: Lesson 9.5 Geometry Answers
Curfews Should Be Allowed
A teenagers mind is still not fully developed, meaning that they are still learning and don’t make the brightest decisions. A curfew of 10 p.m. on weekdays and midnight on weekends is a good decision. Curfews will keep teenagers out of trouble because they are less likely to drink and drive, have more time for homework, and they’re not quite mature enough to handle so much responsibility. Curfews will keep teenagers away from drinking and driving. Most people come home past midnight after
Your Brain While You Sleep
Several parts of the brain are involved in sleep and wakefulness. These areas include the thalamus, hypothalamus, basal forebrain, pineal gland, and portions of the brainstem. When a person sleeps is determined by the interaction of their bodys circadian rhythm and sleep homeostasis. The circadian rhythm acts as the bodys internal clock and is controlled by circadian oscillator cells in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus. It roughly corresponds to a 24 hour cycle, although it is affected by external light and temperature. Sleep homeostasis, or sleep drive, determines the length of wakefulness and the intensity of sleep when it occurs. Although the exact mechanism controlling this drive is poorly understood, it is thought to be related to the release of the neurotransmitters GABA and adenosine from the basal forebrain and other surrounding areas.
Although the thalamus, basal forebrain, and brainstem promote wakefulness through release of stimulatory hormones, the hypothalamus in particular drives the awake state with hormones such as glutamate, histamine, and orexin. However, as the time for sleep approaches based on the circadian rhythm and sleep drive, these hypothalamic signals decrease to allow sleep to begin. The central autonomic system and the pineal gland are also influenced by the sleep drive to appropriately affect the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems for the changes in bodily functions seen during the stages of sleep.
You May Like: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Tips For Improved Sleep
All stages of sleep are important and your body naturally regulates your sleep cycles to make sure you get what you need.
Tools like the Oura Ring can help you monitor your sleep patterns and generate a Sleep Score each night to help you improve your sleep.
Check out these patterns to see if your sleep is being disrupted:
- Increase in deep sleep after a hard workout: Exercise can increase your bodys prioritization of deep sleep the night after an intensive workout.1
- Higher REM rebound after sleep deprivation: When you recover from a period of sleep deprivation, your body prioritizes deep sleep for the first few nights to repair your body and prepare for action. After several nights of sufficient deep sleep, REM sleep rebounds to focus on your brain.
- Interrupted sleep cycles after caffeine:Caffeine can increase the time it takes for you to fall asleep, cutting your sleep period short. Shorter sleep periods disproportionately cut down on your total REM sleep, as REM cycles are more likely to occur in later sleep cycles.
We all have those days when we just need our coffee. However, taking a look at your nightly patterns and acting on your desire to improve your sleep can help you face those days well rested.
References
What Does A Normal Night Look Like
The amount of each phase of sleep can vary significantly between nights and individuals. During an ideal nights sleep, your body has enough time to go through four to five 90-minute cycles that sample different phases of sleep as the night progresses.
In general, each cycle moves sequentially through each stage of sleep: wake, light sleep, deep sleep, REM, and repeat. Cycles earlier in the night tend to have more deep sleep while later cycles have a higher proportion of REM. By the final cycle, your body may even choose to skip deep sleep altogether.
Overall, your body spends the majority of the night in light sleep. How much time you spend in REM or deep can vary widely by individual but below are the averages you can expect for each stage in a single night.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Repair Work In Progress
During deep sleep , your cells repair and rebuild, and hormones are secreted to promote bone and muscle growth. Your body also uses deep sleep to strengthen your immunity so you can fight off illness and infection.
It’s important to realize that sleep does not progress through the four stages in perfect sequence.
When you have a full night of uninterrupted sleep, the stages progress as follows:
Once REM sleep is over, the body usually returns to NREM stage 2 before beginning the cycle all over again.
Time spent in each stage changes throughout the night as the cycle repeats .
Sleep architecture refers to the exact cycles and stages a person experiences in a night. A sleep specialist may show you this information on what’s known as a hypnograma graph produced by an EEG.
What Are The Stages Of Sleep
Each night you take a rollercoaster ride through the different phases of sleep. Though youre unaware of what goes on while youre snoozing, your brain and body are in an active state.
Each stage of sleep plays a different role in how you feel the next day. Read on to learn which stage helps your brain, which restores your body, and if youre striking a good balance between the stages each night.
Recommended Reading: Behaviorism Was Founded By
Evaluating Factors Affecting Bodily Rhythms
Internal
External
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
- Key parts of a Neuron
2 pages
- Key parts of a Neuron
Garden City Community College PSYCH 101
Axon Terminal copy.docx
Garden City Community College PSYCH 101
depression.docx
Garden City Community College PSYCH 101
Chapter 4 Review.docx
Garden City Community College PSYCH 101
Chapter 3 Review.docx
Garden City Community College PSYCH 101
Chapter 5 Review.docx
Recommended Reading: Road Trip Math Project Answer Key
Key Takeaways: Stages Of Sleep
- Sleep is comprised of four stages in two categories .
- The hypothalamus is the major driving force for wakefulness and sleep through circadian rhythm and sleep homeostasis.
- Non-REM sleep is a progression from the lightest to the deepest stage of sleep with slowing of heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and muscle activity.
- REM sleep is a more active stage of sleep associated with dreams and faster brain wave activity.
- Tips for improving your sleep include setting a schedule, avoiding stimulating activities near bedtime, performing relaxation techniques before bed, and exercising regularly during the day.
How To Improve Your Habits For Healthier Sleep
The amount of sleep required per day varies depending on a persons age and ranges from up to 18 hours for infants, 9-10 hours for school-age children, to 7-9 hours for adults. Although sleep has drastic importance for our health and well-being, most people dont receive the recommended requirement per night. A 2016 CDC study found more than 33% of adult Americans received less than 7 hours of sleep a night. Lack of sleep has been associated with higher risks of chronic diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, stroke, and mental illness.
In order to improve your sleep habits, you can follow these tips recommended by the NIH. First, follow a regular schedule for daily bedtime. This step will help set your bodys circadian rhythm and make it easier to fall asleep at a regular time. Second, avoid stimulating activities close to bedtime, including those with bright lights and sounds or with exposure to screens. Similarly, avoiding consumption of caffeinated or alcoholic beverages close to bedtime is generally recommended, as these increase hormones that stimulate the body. Finally, exercise for 20 to 30 minutes daily but not fewer than a few hours before bedtime to further promote healthy circadian rhythm patterns.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4