Geospatial Information Science Degree
The Geography Department offers a wide variety of courses in Geospatial Information Science , including GIS, Remote Sensing and related geospatial technologies such as drones and GPS/GNSS. Your degree in Geography with a GIScience Area of Emphasis will include training with GIScience technologies and prepares your for a wide range of jobs in many industries. Earn your degree in the classroom or 100% online!
Bs In Geography With An Area Of Emphasis In Giscience
Students specializing in the Geospatial Information Science area of emphasis must complete the Geography Core Requirements and the following GIScience courses.
GIScience Area of Emphasis Courses
- Note: These courses required in addition to the Geography BS core requirements of GEO423 Cartography and GIS and GEO426 Principles of GIS.
- GEO 431 Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry
- Technologies: Choose at least six credits from: GEO 110 Basic GIS , GEO 111 Air Photos and Satellite lmagery , GEO 112 Smartphone GPS , GEO 113 Web GIS , GEO 433 GPS and Mobile Geospatial Technologies , GEO 454 Drones: Remote Sensing & GIS, GEO485-488 Independent Study
- Analysis and Applications: Choose a minimum of six credits from: GEO 429 Location Analysis and GIS , GEO 430 Environmental Raster Analysis , GEO 432 Enterprise GIS , GEO434 Flood Hazards and GIS , GEO 440 Spatial Statistics and GIS , GEO485-488 Independent Study , GEO 490 Internship
- Electives: Choose additional GIScience courses to reach a minimum of 21 credit hours beyond the Geography Core Requirements.
The Geography Department participates in an Undergraduate Minor in Geospatial Information Science, an Undergraduate Certificate in GIScience and two Graduate Certificates in GIScience.
Our latest Geospatial technology course features drones for Remote Sensing and GIS.
Meridians Or Lines Of Longitude
The prime meridian sits at 0 degrees longitude and divides the earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The prime meridian is defined as an imaginary line that runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, a suburb of London. The Eastern Hemisphere includes the continents of Europe, Asia, and Australia, while the Western Hemisphere includes North and South America. All meridians east of the prime meridian are numbered from 1 to 180 degrees east the lines west of the prime meridian are numbered from 1 to 180 degrees west . The 0 and 180 lines do not have a letter attached to them. The meridian at 180 degrees is called the International Date Line. The International Date Line is opposite the prime meridian and indicates the start of each day . Each day officially starts at 12:01 a.m., at the International Date Line. Do not confuse the International Date Line with the prime meridian . The actual International Date Line does not follow the 180-degree meridian exactly. A number of alterations have been made to the International Date Line to accommodate political agreements to include an island or country on one side of the line or another.
Don’t Miss: When Was Prodigy Math Game Made
What Is The Importance Of Elements In Our Life
1. Note that most living matter consists primarily of the so-called bulk elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfurthe building blocks of the compounds that constitute our organs and muscles. These five elements also constitute the bulk of our diet tens of grams per day are required for humans.
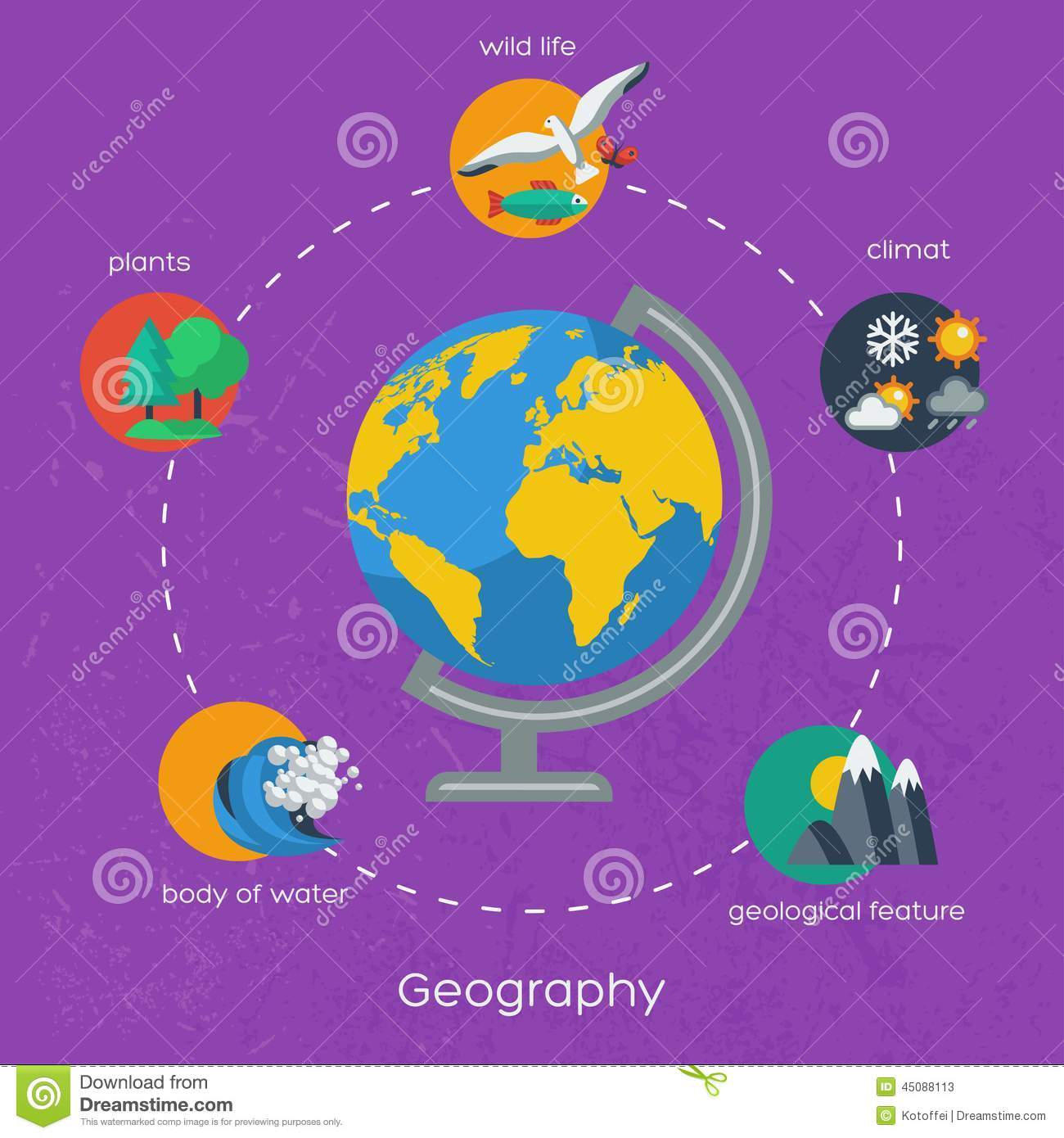
The Six Essential Elements Of Geography

The Merriam-Webster dictionary describes geography as a science that deals with the description, distribution, and interaction of the diverse physical, biological, and cultural features of the earths surface. Simply put, we will learn about the features of the earth and how living things interact and change the earth. Scholars have divided the study of geography into six parts called The Six Essential Elements of Geography. A geographically informed person knows:
Read Also: What Is Allele In Biology
What Are The Six 6 Elements Of Living Organisms And Where Does Each Occur In The Environment
The six most common elements in organic moleculescarbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfurtake a variety of chemical forms. They may be stored for long or short periods in the atmosphere, on land, in water, or beneath the Earths surface, as well as in the bodies of living organisms.
Defined By A Common Characteristic The Corn Belt
Functional RegionA place connected by movement between places. Example – the greater Houston Metropolitan area, DFW. People move from home-work-home for jobs, entertainment, etc.
Functional Region
Central place and the surrounding area linked to it Houston and its suburbs are linked by highways
Perceptual Region A place defined by popular feelings & images rather than by objective data. Example the term Heartland refers to a central area where traditional values are believed to be predominate.
PERCEPTUAL REGION
With a perceptual region, the exact area that the region describes can differ based on perceptions. There is NO real defined area.
Paris
Read Also: What Is Standard Deviation In Psychology
Parallels Or Lines Of Latitude
Figure 1.4 Noted Lines of Latitude
The equator is the largest circle of latitude on Earth. The equator divides the earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and is called 0 degrees latitude. The other lines of latitude are numbered from 0 to 90 degrees going toward each of the poles. The lines north of the equator toward the North Pole are north latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter N. The lines south of the equator toward the South Pole are south latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter S. The equator is the only line of latitude without any letter following the number. Notice that all lines of latitude are parallel to the equator and that the North Pole equals 90 degrees N and the South Pole equals 90 degrees S. Noted parallels include both the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, which are 23.5 degrees from the equator. At 66.5 degrees from the equator are the Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle near the North and South Pole, respectively.
Connecting With Space And Place
Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments. Geographers explore both the physical properties of Earths surface and the human societies spread across it. They also examine how human culture interacts with the natural environment and the way that locations and places can have an impact on people. Geography seeks to understand where things are found, why they are there, and how they develop and change over time. Read More…
Recommended Reading: What Is Human Geography The Study Of
The Earth And Graticule Location
When identifying a region or location on the earth, the first step is to understand its relative and absolute locations. Relative location is the location on the earths surface with reference to other places, taking into consideration features such as transportation access or terrain. Relative location helps one compare the advantages of one location with those of another. Absolute location, on the other hand, refers to an exact point on the earths surface without regard to how that point is related to any other place. Absolute location is vital to the cartographic process and to human activities that require an agreed-upon method of identifying a place or point.
Just as you were taught in geometry that there are 360 degrees in a circle or a sphere, the earth also has 360 degrees, and they are measured using a grid pattern called the graticule. Lines of latitude and longitude allow any absolute location on the earth to have an identifiable address of degrees north or south and east or west, which allows geographers to accurately locate, measure, and study spatial activity.
Figure 1.3 Basic Lines of Longitude and Latitude
The World In Spatial Terms
a. How to use maps and other geographic representations, tools, and technologies to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective
b. How to use mental maps to organize information about people, places, and environments in a spatial context
c. How to analyze the spatial organization of people, places, and environments on earths surface
Also Check: What Is Frictional Force In Physics
Give To Cambridge College
Cambridge Colleges promise depends on the ongoing support of people like you. You can make a difference. Every gift large or small is important in helping the College provide higher education for a diverse population of working adults.
You can use your MasterCard or Visa to make a quick, easy, and secure online donation.
Thank you for your vote of confidence that a Cambridge College education matters!
“Cambridge College took me from a beginner real estate property manager to a lifelong career as a property owner/manager. Additionally, CC gave me and my wife Leslie, a speech-language pathologist, the ability to spend 30 years in the Malden Public Schools working with autistic and special needs students. We couldnt have done it without learning the skills we did at Cambridge College. We both love Cambridge College, and we hope President Jackson, a superior person and leader, stays for years!
For people struggling to survive financially my hope is that they can enhance their career with a degree from Cambridge College. Your gift of support during this Golden Anniversary can make their dreams come true.“
Presentation On Theme: The 6 Elements Of Geography Presentation Transcript:
1 The 6 Elements of GeographyPart 1
2 6 ElementsMany geographers use the six essential elements to organize their study.The World in Spatial TermsPlaces and RegionsPhysical SystemsHuman SystemsEnvironment & SocietyUses of Geography
3 The World in Spatial TermsGeographers look at where things are on the Earths surface.Changes in settlement patterns over time are also important.
4 The World in Spatial TermsIt tells us where this place is in relation to other places?Or, its LOCATION
5 The World in Spatial TermsWhere are we?Absolute Location:Latitude and longitude Sugar Land is located at 29°N, 96°WStreet address
6 The World in Spatial TermsRelative Location:Described by landmarks, time, distance from one place to another, etc.Sugar Land is southwest of HoustonCollege Station is 1 hr 45 min awayIsrael is next to Lebanon & Jordan
16 Title-Describes what the map shows
17 Orientation -refers to directions shown by compass rose* cardinal directions = N, S, E, & W* intermediate dir. = NW, NE, SW, & SE* must have at least North
18 Date & Author -helps us judge accuracy of the mapDate usually down here, too
20 Scale -shows relationship between map measurementsand actual distances
21 Index-alphabetical list of places shown on a gridded map or set of maps
22 Grid-Set of intersecting lines that determine absolute location
23 Source-used if information not obtained by direct experience or observation
Recommended Reading: Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 2 Arithmetic Series Answers
Elements Of Geography: Containing A Concise And Comprehensive View Of That Useful Science As Divided Into 1 Astronomical
Boston: Thomas and Andrews, 1804. Hardcover. “On a new Plan…Adapted to the capacities of Children and Youth: designed for a Reading and Classical Book in Common Schools and as a useful Winter Evening’s Entertainment for Young People in Private Families Illustrated with a neat Map of the United States, and a beautiful Chart of the whole World. … Fifth Edition — Improved.” J.T. Buckingham, printer. 143, p.: 2 folded leaves of engraved maps 15 cm. Original calf spine and marbled paper over boards. Metal-engraved maps have imprint: Published by Thomas & Andrews Boston 1801. Early American Imprints, Ser. 2 , 6829. In attractive modern box with gilt-tooled title on black calf spine. Former owner’s inscription on front free endpaper: “John Worleys Book York April the 27, 1817.” Book is in Good+ Condition: lacking part of each board and leather at head of spine boards are attached and text block is solid browning along fore-edges of first folded map and title page occasional light foxing clean and tight. Box is in Fine Condition. Good +. Item #003864
Price: $225.00
What Is The Purpose Of Geographers Using The Five Themes Of Geography And The Six Essential Elements
The five themes of geography help us organize our studies of the world. The six essential elements of geography highlight some of the subjects most important ideas. The five themes of geography help us organize our studies of the world. Geographers use themes that can be applied to nearly everything that they study.
Read Also: What Does One Year Of Biology Mean
What Are The Essential Elements Of Geography
Are you familiar with the various terms that constitute the Essentials of Geography program, including what are the primary ingredients of geography? If youre unfamiliar with this curriculum, I suggest you check it out as a primer for those who want to become part of the nations greatest educational institution.
Geography is an important component of education, and it should never be left out. In fact, when it comes to learning about the world around us, many of the most essential concepts are taught in elementary school. This is because we have access to so much information at such a young age, and even if we dont, we should take the time to learn about what is important to the world as a whole.
Some of the basic concepts that are taught in geography include geographical location, landforms, the physical environment, climate, and population. You may be wondering why it is important to teach basic geography in elementary school. Its all about knowing where we live and what the rest of the world is like. By the same token, we can also learn about how much landmass there is on the earth, as well as where the continental shelves are located.
The physical environment, which encompasses both climate and human populations, is also important to teach in elementary schools. This is because it encompasses the effects of the natural environment on humans. This includes how severe weather affects cities and towns alike.
The 6 Elements Of Geography
6 Elements Many geographers use the six essential elements to organize their study. 1. The World in Spatial Terms 2. Places and Regions 3. Physical Systems 4. Human Systems 5. Environment and Society 6. Uses of Geography
The World in Spatial Terms Geography is the study of the special physical and human characteristics of a place or region. An important part of geography is the relationship between humans and their environment. A geographer may study culture .
The World in Spatial Terms Geographers look at where things are on the Earths surface. Changes in settlement patterns over time are also important.
The World in Spatial Terms Geographers use many tools in their studies, including maps, charts, and graphs. They also use field notes, interviews, photographs, reference books, and videos High-tech tools such as satellites provide detailed images of the Earth Computer databases, like Geographic Information Systems, store huge amounts of data. Satellite image of Texas, Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico
Latitude, Longitude, and Location
The World in Spatial Terms It also tells us where this place is in relation to other places? Absolute Location: The exact latitude and longitude or address of a place. Relative Location: The location of a place in relationship to other locations
T.O.D.A.L.S.I.G.S. The acronym TODALSIGSs defines nine essential elements to help map users get the most information from a map.
Recommended Reading: What Is 9th Grade Math
What Do The Six Essential Elements Of Geography Mean
The essential elements are based on the geography standards. Each element is a big idea that links several standards together. The six essential elements are The World in Spatial Terms, Places and Regions, Physical Systems, Human Systems, Environment and Society, and The Uses of Geography.
Contents:
What Elements Do We Use Everyday
The most important elements that we use in everyday life include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, with smaller amounts of things like chlorine, sulfur, calcium, iron, phosphorus,nitrogen, sodium, and potassium. Apart from these, other elements include magnesium, zinc, neon, and helium are also in our daily existence.
Read Also: How To Prepare For Sbac Math
Four Traditions Of Geography
Geography is an extremely broad field. Because of this, many view the various definitions of geography proposed over the decades as inadequate. To address this, William Patterson proposed the concept of the “Four traditions of Geography” in 1964. These traditions are the Spatial or Locational Tradition, the Man-Land or Human-Environment Interaction Tradition, the Area Studies or Regional Tradition, and the Earth Science Tradition. These concepts are broad sets of geography philosophies bound together within the discipline. They are one of many ways geographers organize the major sets of thoughts and philosophies within the discipline.
Spatial or locational tradition
The spatial or locational tradition is concerned with employing quantitative methods to describe the spatial characteristics of a location. The spatial tradition seeks to use the spatial characteristics of a location or phenomena to understand and explain it. The contributors to this tradition were historically cartographers, but it now encompasses what we call technical geography and geographic information science.
Area studies or regional tradition
Human-Environment interaction tradition
Earth science tradition
Essential Element #2 Places & Regions

Standard 4. The physical and human characteristics of places. Standard 5. That people create regions to interpret Earth’s complexity. Standard 6. How culture and experience influence people’s perceptions of places and regions.
Regions
Areas united by specific factors How the earth is divided for study. Geographers choose how they will classify the world based on common characteristics.
Regions Formal region A place with similar attributes that might include physical, government, economic, or cultural characteristics. Example political region such as a city, state or country. People are governed by the same laws and the same government.
FORMAL REGION
Also Check: Hcn Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry