William Dement: The Father Of Sleep
How do we know anything about sleep if we are, well, asleep? We canât administer a questionnaire mid nap or have people have a conversation while unconscious. Fortunately, we have a man named Dr. William Dement to thank for most of what we know about sleep.
Dr. Dement, known as the âFather of Sleep Medicine,â is a Washington state-native who had dreams of becoming a journalist. Unfortunately, all of the journalism classes at the University of Washington were full, so Dement opted to enroll in an introduction to psychology course instead.
He found this class to be so interesting that he scrapped his plans of becoming a journalist and decided he wanted to become a psychoanalyst .
After attending the University of Washington, Dement went on to the University of Chicago School of Medicine where the only person studying sleep was faculty member Nathaniel Kleitman . The two began to work together in the 1950s, making some of the greatest sleep discoveries in the field. Their first discovery, in 1953, was that of rapid eye movement sleep .
About the Author
Charlotte Ruhl is a member of the Class of 2022 at Harvard University. She studies Psychology with a minor in African American Studies. On campus, Charlotte works at an implicit social cognition research lab, is an editor for the undergraduate law review, and plays softball.
Fact Checking
How to reference this article:
How to reference this article:
APA Style References
Stage 2 Sleep Is Characterized By The Appearance Of Both Sleep Spindles And K
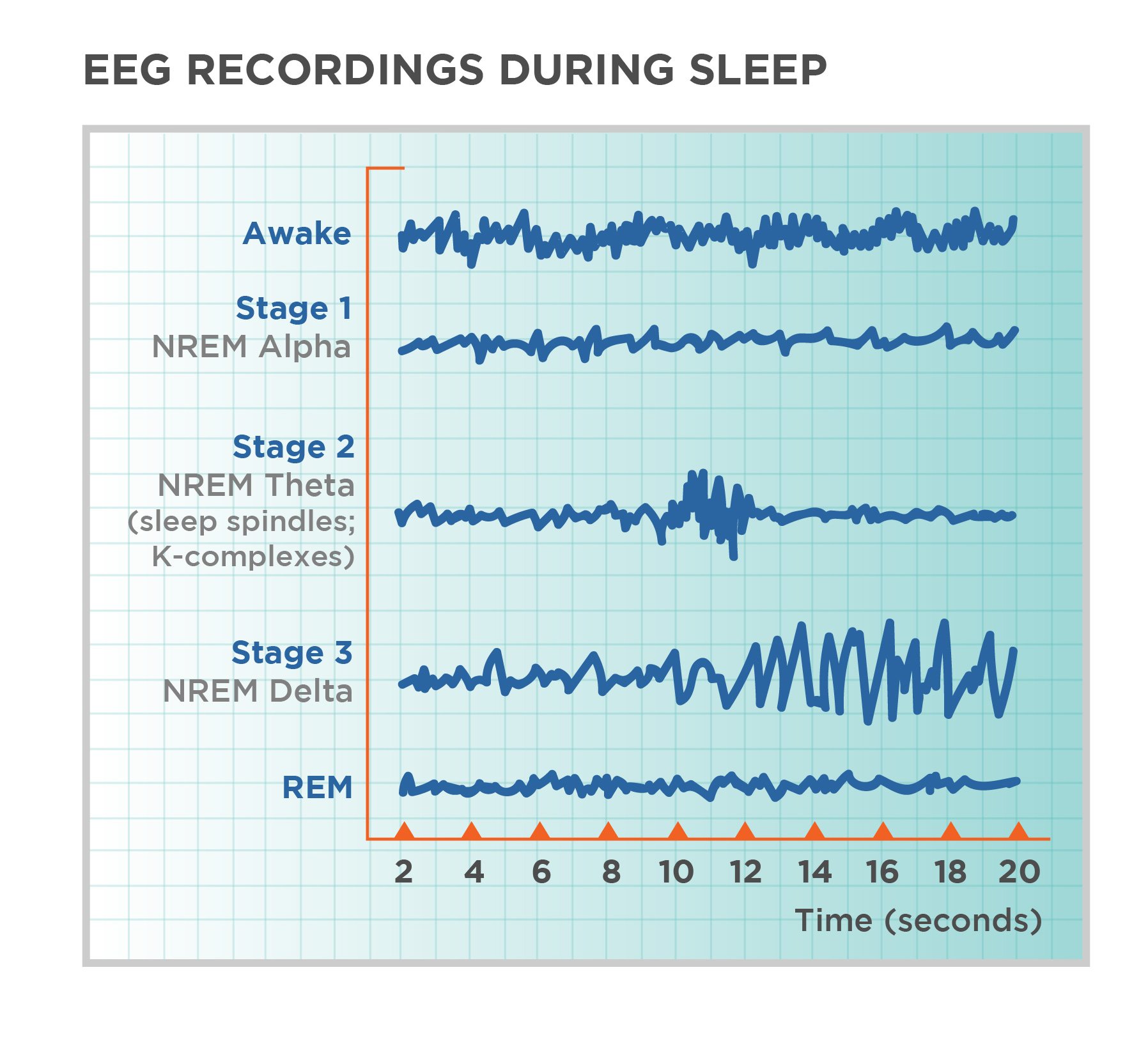
Stage 3 and stage 4 of sleep are often referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep because these stages are characterized by low frequency , high amplitude delta waves . During this time, an individuals heart rate and respiration slow dramatically. It is much more difficult to awaken someone from sleep during stage 3 and stage 4 than during earlier stages. Interestingly, individuals who have increased levels of alpha brain wave activity during stage 3 and stage 4 often report that they do not feel refreshed upon waking, regardless of how long they slept .
Why We Have Nightmares
Nightmares can create feelings of terror, anxiety, or despair, and lead to psychological distress or sleep problems like insomnia. Research has identified a range of causes for nightmares, including post-traumaticstress, anxietyespecially the presence of generalized anxiety disorder, dissociation, and physiological changes.
Don’t Miss: What Is Elastic Force
How To Know If You Experience Rem Rebound
Though vivid dreams or nightmares might be a clue, the most accurate way to determine if you are experiencing REM rebound sleep is by having an electroencephalogram measure your brain waves as you sleep. EEG measurements are one element of a sleep study, also called polysomnography. However, for most people who undergo a sleep study, information about REM rebound activity will not be included in the results.
Usually, professionals only identify REM rebound in research study participants, not clinical patients. Although REM rebound might occur in conjunction with sleep disorders, REM rebound itself is not a diagnosis or a diagnostic criterion. As a result, doctors in a clinical setting do not have a need to identify REM rebound incidences in the people they treat.
What Are The 5 Stages Of Sleep In Psychology
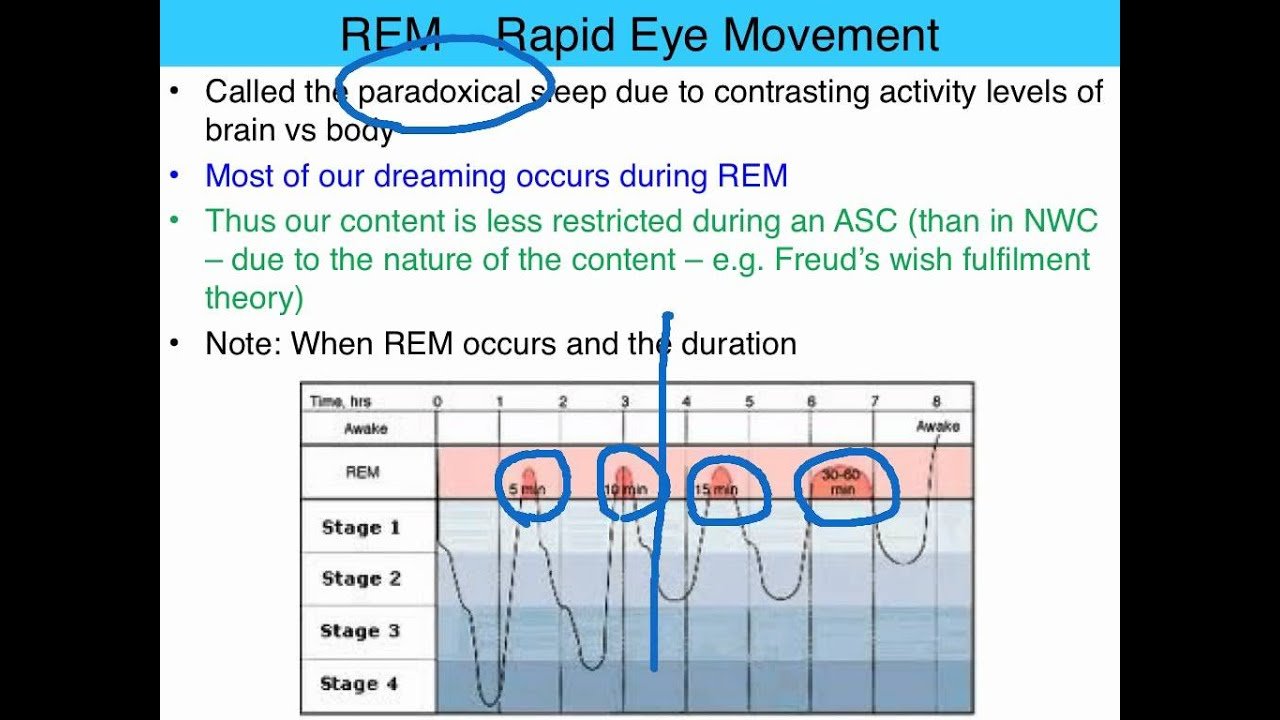
In general, each cycle moves sequentially through each stage of sleep: wake, light sleep, deep sleep, REM, and repeat. Cycles earlier in the night tend to have more deep sleep while later cycles have a higher proportion of REM. By the final cycle, your body may even choose to skip deep sleep altogether.
Recommended Reading: What Does Nc Stand For In Physics
Neural Control Of Rem Sleep
Research over the past decades has identified, with increasing precision, key areas and neural populations involved in the control of REM sleep . The core circuitry generating REM sleep is localized in the brainstem, but populations of neurons powerfully regulating REM sleep by either promoting or suppressing its occurrence have been found throughout the medulla, pons, midbrain, and hypothalamus.
Rem As Part Of Your Sleep Cycle
All of the sleep stages are important to maintaining a healthy sleep lifestyle. The other stages before REM are known as Non-REM sleep, and account for about 75 percent of your sleeping time, with the remaining 25 percent spent in REM sleep. Youll likely go through this entire cycle four times each night, needing about 90 to 110 minutes to complete the process each time.
Learning about all the stages of sleep is critical to taking sleep health into your own hands. Learn more about all the sleep stages and how to get more deep sleep in our blog.
Get The App
Recommended Reading: Math Nation Independent Practice Answers
Oxygen Supply To Cornea
Dr. David M. Maurice, an eye specialist and former adjunct professor at Columbia University, proposed that REM sleep was associated with oxygen supply to the cornea, and that aqueous humor, the liquid between cornea and iris, was stagnant if not stirred. Among the supportive evidence, he calculated that if aqueous humor was stagnant, oxygen from the iris had to reach the cornea by diffusion through aqueous humor, which was not sufficient. According to the theory, when the organism is awake, eye movement enables the aqueous humor to circulate. When the organism is sleeping, REM provides the much needed stir to aqueous humor. This theory is consistent with the observation that fetuses, as well as eye-sealed newborn animals, spend much time in REM sleep, and that during a normal sleep, a person’s REM sleep episodes become progressively longer deeper into the night. However, owls experience REM sleep, but do not move their head more than in non-REM sleep and is well known that owls’ eyes are nearly immobile.
Benefits Of Lucid Dreaming
Lucid dreaming appeals to people who desire to explore their inner dream world with more awareness since it is such a vivid experience. People are fascinated by the notion of lucid dreaming because, according to some academics, it is the ultimate type of immersive experience.
Because lucid dreaming enables the dreamer to develop or construct anything inside the dream, it might be a fun method to experiment with creativity while remaining safe.
Because the dreamer has some influence over the people, setting, and events of the dream, it may be a chance for the dreamer to experience and explore things that they would not be able to accomplish in real life.
If you want to achieve lucid dreaming, start using a dream journal such as the Dreambook App. With the Dreambook App, you can have a journal in your pocket and take it wherever you go! As you start journaling, you will realize how fast you are getting the control of your dreams.
You May Like: My.hrw Algebra 1
What Is Rem Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep is one of the four stages that the brain goes through during the sleep cycle. This period of the sleep cycle usually takes place about 90 minutes after a person first falls asleep. It is marked by a number of physiological changes that include muscle relaxation, eye movement, faster respiration, and increased brain activity.
You May Have Heard The Term But Do You Know What It Means Understanding The Importance Of Rem Helps Explain Why A Solid Nights Sleep Is So Important
Most people climb into bed at night without ever thinking about the different stages of sleep that their brain and body cycle through or how these stages can affect their health. But understanding the role of REM sleep is important. This particular stage of sleep has a major impact on your memory, mental focus, and mood.
In this article youll learn about what REM is, why the REM portion of your sleep is so important, and how to make sure youre achieving the right amount every night.
Don’t Miss: Does Michael Jackson Have Any Biological Kids
Tips To Get Quality Sleep
Practicing good sleep hygiene is the best way to get quality sleep at night. Here are some ways you can improve your sleep hygiene:
- Spend time outside in the sun during the day. Exposing your body to natural light during the day can help maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
- Exercise or move your body throughout the day. Getting in at least one exercise or movement session each day is a great way to improve your sleep quality.
- Limit your nap time to no more than 20-30 minutes. There are benefits to napping. But if you nap for longer than 30 minutes, it can leave you wide awake when its finally time for bed.
- Avoid stimulants and certain foods before bed. Caffeine, nicotine, or alcohol before bed can interrupt your sleep, as can foods that cause indigestion or stomach upset.
- Limit your screen time an hour before sleeping. TVs, phones, and other electronic devices emit blue light, which can interrupt the hormones that help you fall asleep.
- Create a comfortable bedroom environment. Investing in a high-quality mattress, pillow, blanket, and other relaxing bedroom items, can help you sleep better.
Incorporating these tips slowly over time can greatly improve your sleep quality. But if youre still having trouble falling or staying asleep, it may be time to visit a doctor to discuss more options.
Circadian Modulation Of Rem Sleep
Besides homeostatic mechanisms, the daily expression of REM sleep is also modulated by circadian influences. REM sleep propensity is largest toward the end of the rest phase, when sleep tendency is highest and coincides with the rising slope of the body temperature rhythm, which is also under circadian control . REM sleep deprivation experiments in rats with SCN lesions suggest that the circadian clock facilitates REM sleep during the rest, but not the activity phase, as quantified by the number of attempts to enter REM sleep during deprivation . Lesioning orexin/hypocretin neurons led to an increase of REM sleep only during the dark period, suggesting that these neurons suppress REM sleep during the active phase . Hence, the daily expression of REM sleep may depend on both facilitatory and suppressive mechanisms, respectively mediated by the SCN and orexin/hypocretin neurons.
You May Like: Beth Child Of Rage Now
What Going Into Rem Rebound Means
Going into REM rebound is the human bodyâs natural and normal response to sleep deprivation, stressors, and suppression of REM sleep. Despite the similarities in name, REM rebound is not necessarily related to REM sleep behavior disorder, a disorder in which sleepers act out their dreams.
Generally, experiencing REM rebound does not indicate that a person has an underlying sleep disorder. That said, REM rebound episodes are often triggered by sleep deprivation. Since many people with sleep disorders experience sleep deprivation, REM rebound tends to occur in people with parasomnias, narcolepsy, and obstructive sleep apnea.
What Is Rem Rebound
REM rebound, also called REM rebound sleep or the REM rebound effect, is a phenomenon in which a person temporarily receives more REM sleep than they normally would. During REM rebound, the time spent in REM can increase, along with the frequency and intensity of REM sleep stages.
Most people associate REM sleep with dreams. Although it is not the only sleep stage during which we dream, REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements and brain activity patterns that are very similar to the patterns we experience while we are awake. The majority of REM sleep tends to occur once people have been asleep for a while, meaning it may not occur as often for people with a disrupted sleep schedule.
REM rebound often occurs after stress or sleep deprivation, and it happens in both humans and animals. It is not unique to a single culture and appears to happen to people around the world.
You May Like: Sf5+ Lewis Structure
What Is A Sleep Cycle
As a person sleeps, their body rests but the brain remains active. This allows the brain to perform a number of different functions, including consolidating memory and improving how our neurons communicate with each other. Some researchers say sleep serves as a chance for our brain to remove toxins. This is why sleep is considered as essential as food and water for the human condition.
There are two basic types of sleep in a sleep cycle: Rapid Eye Movement and Non-Rapid Eye Movement . During NREM sleep, there are three separate stages of sleep. The amount of sleep occurring during each of these stages changes throughout a persons life, particularly as a person ages. Each stage, including REM, affects the brain in different ways, and sleep cycles between REM and NREM sleep several times a night depending on how long one sleeps and the quality of that sleep.
Typically, sleep begins with a NREM sleep stage, cycles through the three NREM stages, and is followed by a REM period. Throughout the night, NREM and REM sleep alternate in a cyclical fashion, over approximately 90 minutes with REM sleep periods getting progressively longer. A sleep cycle can average 70 to 120 minutes, with an average of three to four cycles occurring over a night of sleep.
How To Get More Rem Sleep
Overall, whatever you can do to improve your sleep habits and behaviors will also help you get more REM sleep. This begins with simply making an effort to spend more time in bed. Here are 45 tips to help you sleep better.
There are also two other things in particular that stand out with how to increase REM sleep. The first is a concept we refer to as sleep consistencygoing to bed and waking up at the same time each day . Your body functions more efficiently when it is on a regular schedule, and this applies to sleep as well. We ran an analysis of sleep data from 25,000 WHOOP members, and the results showed a significant rise in the nightly amount of REM sleep as the percentage of sleep consistency over a 4-day span increased:
Better sleep consistency allows for more REM sleep.
The second big thing is to stay away from alcohol before bed. When your body is forced to process alcohol during sleep, it has difficulty getting past light sleep and into the deeper stages.
Learn More:Tips to Increase REM Sleep
Recommended Reading: Automatic Processing Examples
Consequences Of A Lack Of Rem Sleep
Some studies link a lack of REM sleep to:
- Reduced coping skills:
further review of historic sleep research found several instances in which the duration and quality of REM sleep were lower following alcohol intoxication.
Alcohol affects sleep in other ways, too. For example, it contributes to sleep apnea and snoring, causes an increase in bathroom visits, and interrupts the bodys circadian rhythm, which is the internal clock that regulates sleep and wake times.
Sleep Strengthens Recent Learning And Negative Memories
In particular, surprise-related information points to how much work we have to do to update our models, beliefs, and expectations. The work involved in belief updating involves the generation of counterfactuals -endless “what if…” scenario spinning and evaluation. Generation of counterfactuals to the information of supreme value occurs as REM dreaming.
The degree of surprise I experience encodes the information on how well my current self is adapted to coming challenges and how much work I will need to do to transform myself to meet those upcoming challenges. Will I need to scrap my priors completely and build a whole new self from scratch? Or will simple editing procedures suffice?
Given that surprise encodes this kind of informationinformation absolutely crucial for the sense of self and model updating, it follows that my sense of self is necessarily anchored in estimations of the surprisingness of the things I encounter in the world. But surprisingness, in turn, may be measured by the ease with which or the number of the counterfactuals triggered by the surprising event.
I conclude that the brain/mind is actively seeking out information that can recruit REM physiology during the day. REM runs the show.
Don’t Miss: Does Elton John Have Children
Why Do I Have Vivid Dreams During Rem Sleep
REM sleep is often associated with very vivid dreams due to the increase in brain activity. Because the muscles are immobilized yet the brain is very active, this stage of sleep is sometimes called paradoxical sleep. Before entering the REM sleep phase, the body goes through each of the stages of non-REM sleep.
Stages Of Sleep: Rem And Non
By Charlotte Ruhl, published July 09, 2020
Fact checkedby Saul Mcleod, PhD
Take-home Messages
- There are five different stages of sleep including both REM and NREM sleep. The five stages make one sleep cycle which usually repeat every 90 to 110 minutes.
- Stage 1 non-REM sleep marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep. This stagetypically lasts less than 10 minutes and is marked by a slowing of your heartbeat, breathing, and eye movements , as well as the relaxation of your muscles.
- Stage 2 non-REM sleep is a period of light sleep before you enter deeper sleep, lasts roughly 20 minutes. Stage two is characterized by further slowing of both the heartbeat and breathing, and the brain begins to produce bursts of rapid, rhythmic brain wave activity known as sleep spindles.
- Formerly known as stages 3 and 4, stage 3 is the final stage of non-REM sleep. This is the deepest period of sleep and lasts 20 to 40 minutes. Your heartbeat and breathing slow to their lowest levels, and your muscles are so relaxed that it may be hard to awaken you.
- REM sleep occurs 90 minutes after sleep onset, and is a much deeper sleep than any of the three stages of non-REM sleep. REM sleep is defined by rapid eye movements and an almost complete paralysis of the body, and a tendency to dream.
Put simply, sleep is a state of perceptual disengagement from and unresponsiveness to the environment, marked by unique physiological and behavioral processes .
Recommended Reading: Molecular Geometry Ccl4