Geography As A Career
Geography is a fairly small profession and a large percentage of peoplewho identify themselves professionally as geographers work inuniversities as professors/researchers, or as teachers in secondary education.
However, there are quite a number of other career opportunities for geographersin the public and private sector, usually working in some way with GeographicInformation Systems :
- Geographic information systems and services providers
- Surveyers for contracting and engineering firms
- Energy and natural resource management companies
- State departments of transportation and health
- Urban and regional planning departments
The Association of American Geographersis the primary professional organization for geographers in the United States and theirwebsite provides more information on geography careers.
Dont Miss: Pre Algebra Road Trip Project
The Branches Of Geography
Geography can be regarded as an interdisciplinary science. The subject encompasses an interdisciplinary perspective that allows the observation and analysis of anything distributed in Earth space and the development of solutions to problems based on such analysis. The discipline of geography can be divided into several branches of study. The primary classification of geography divides the approach to the subject into the two broad categories of physical geography and human geography.
Receiver In Continuous Operation
The description above is representative of a receiver start-up situation. Most receivers have a track algorithm, sometimes called a tracker, that combines sets of satellite measurements collected at different timesin effect, taking advantage of the fact that successive receiver positions are usually close to each other. After a set of measurements are processed, the tracker predicts the receiver location corresponding to the next set of satellite measurements. When the new measurements are collected, the receiver uses a weighting scheme to combine the new measurements with the tracker prediction. In general, a tracker can improve receiver position and time accuracy, reject bad measurements, and estimate receiver speed and direction.
The disadvantage of a tracker is that changes in speed or direction can be computed only with a delay, and that derived direction becomes inaccurate when the distance traveled between two position measurements drops below or near the random error of position measurement. GPS units can use measurements of the Doppler shift of the signals received to compute velocity accurately. More advanced navigation systems use additional sensors like a compass or an inertial navigation system to complement GPS.
Read Also: Figure And Ground Psychology Definition
Gps Accuracy: Hdop Pdop Gdop Multipath & The Atmosphere
Have you ever wondered about your GPS accuracy?
A well-designed GPS receiver can achieve a horizontal accuracy of 3 meters or better.
For vertical accuracy, it can achieve an accuracy of 5 meters or better 95% of the time. Augmented GPS systems can provide sub-meter accuracy.
But its still not perfect. What are the sources of GPS errors that can leave you meters off your mark?
Human Physical And Gis
Whileactivities that can be considered geography are performedin a variety of different professions, many people that call themselves geographers work in theacademy . Within universitygeography departments there are three broad areas of study:
Dont Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Recommended Reading: Three Types Of Expansion Diffusion
Who Has Heard Of Gps
GPS Stands for Global Positioning Systems and they are now used throughout the world. A GPS unit is actually a receiver that collects signals from satellites.
Global Positioning System satellites transmit signals to GPS receivers on the ground. Receivers require a clear view of the sky, so they are only used outdoors and do not perform well in forests or near tall buildings.
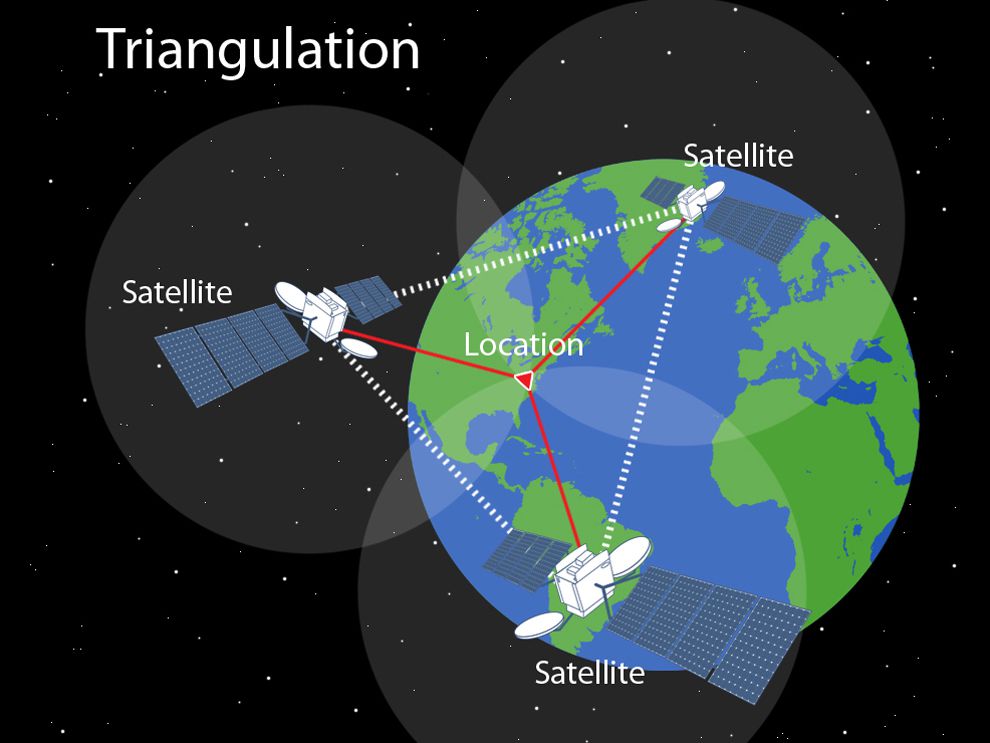
Each GPS satellite has an atomic clock and sends a signal stating its location and the exact time. All GPS satellites transmit at the same instant. The signals move at the speed of light and arrive at a GPS receiver at slightly different times because some satellites are further away than others. The distance to the GPS satellites can be calculated by estimating the amount of time it takes for their signals to reach the receiver. When the receiver estimates the distance to at least four GPS satellites, it can calculate its position in latitude, longitude and height.
Watch this Youtube video to find out more about how GPS works.
The Relationship Of Physical Geography To Human Geography
In an Introduction to Geography classes a fellow instructor likes to stress the point that physical and human geography are completely separate disciplines and that there can be NO mixing between the two. In fact, he makes a big deal that they must write this down and put stars by it in their notes as this important point will most certainly be on the test. He then stops and lets them think about this statement as they dutifully write it down.
Now you might be thinking that this contention that physical and human geography are completely separate and can never be mixed seems nonsensicaland you would be correct. Eventually, a few of the students start to grin and perhaps a bold one might challenge the instructor .
The instructor then gets to point out to the students the fallacy of such a contention and makes the point that physical and human geography, like the sides of a coin, are absolutely inseparable. We know that physical systems can have enormous impacts on human systems . We also know that human impacts on the environment have been great, as humans have always modified the surface of the planet to scratch out a living or to build great civilizations .
Here is the fundamental contention that justifies this whole course:
Required Reading
Don’t Miss: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
What Is The Definition Of Place In Geography
5/5PlacePlacegeographyplace
These physical and human characteristics can include landforms, waterways, people, climate, languages, communication, and transportation. For example, a well-known place is Antarctica and the South Pole.
Secondly, why is place important in geography? An understanding of place is fundamental to the concept of livability, including transportation-related aspects of livability. People live in places, move within and between places, and depend on the movement of goods to and from places. The individual characteristics of places are vital in determining quality of life.
Similarly, you may ask, how do you define a place?
Definition of place
What is a place in human geography?
One of the oldest tenants of geography is the concept of place. Location is the position of a particular point on the surface of the Earth. Locale is the physical setting for relationships between people, such as the South of France or the Smoky Mountains.
Types of location and places
- Locality.
Introduction To Global Positioning System:
The Global Positioning System is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth. Global Positioning Systems usually refer to the GPS receiver. It was developed by the U.S. military and after a while, the U.S. government opened it up for the public.
The GPS receiver receives signals coming from 27 satellites orbiting the Earth and from those signals the GPS receiver can calculate its absolute position of Earth. These satellites circle the Earth, making two complete rotations everyday. Their orbits are planned in such a way that at any time and anywhere on Earth, there are at least four satellites visible in the sky.
Don’t Miss: Paris Jackson’s Biological Father
Facts About Gps Satellites
The GPS Satellite system is made up of 31 satellites that constantly orbit the earth at an altitude of 20,194 km. Each satellite completes two revolutions around the earth in one day, following a precise orbit. The earth completes one spin in that duration, so in effect, each satellites completes one sweep of the earth in one day.
Although the GPS system requires precise time reference, leap seconds and other time anomalies cause a lag of up to 14 seconds. GPS satellites last for 10 years, after which they are replaced by a new one. The defunct satellites are then sent into graveyard orbit.
GPS is sure is amazing isnt it?
For more information Weather Satellites visit :
Why Would A Geographer Use A Gps
Geographers use GPS for a variety of activities, including monitoring changes in the environment, collecting more accurate field data when surveying or mapping, and making decisions about how to best prevent or address natural disasters. A handheld GPS device is a navigation tool for finding a location.
Also Check: What Is Figure Ground Perception Psychology
Chapter : Introduction To The World
Dont Miss: Math Caching Algebra 1 Answers
Reading Coordinates On Google Maps
Most GPS devices provide coordinates in the Degrees, Minutes and Seconds format, or most commonly the Decimal Degrees format. The popular Google Maps provides their coordinates in both DMS and DD formats.
The image above shows the location of the Statue of Liberty on Google Maps. The coordinates given for its location are:
40° 41 21.4 N 74° 02 40.2 W
This is read as: 40 degrees, 41 minutes, 21.4 seconds north and 74 degrees, 2 minutes, 40.2 seconds west
40.689263 -74.044505
Just to recap, the Decimal Degree coordinates does not have the letters N or S to signify whether the latitude coordinate is above or below the Equator. Neither does it have the letters W nor E to signify whether the longitude coordinate is to the west or east of the Prime Meridian.
This is done through the use of positive and negative numbers. Since the latitude coordinate is positive, the coordinate is above the Equator. Since the longitude coordinate is negative, the coordinate is west of the Prime Meridian.
Recommended Reading: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
Geography As A Three Key Issues
Rubenstein defines geography as addressing three key issues:
| How do geographers address where things are? | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The Necessity For Geographic Literacy
The world is getting smaller, more crowded, and more integrated as the population expands, resources diminish, and globalization brings us all closer together. The US is a hyper-power with unprecedented influence around the globe. For the citizens of such a country that is also a democracy comes a duty to be geographically literateto understand how this planet works in terms of its physical and human geographies. Geographically illiterate citizens will at best be ignorant of what their government is doing globally, and at worst support their government in making bad decisions that are detrimental to national, regional, and global stability and well being.
Globalization means that America will interact with its global neighbors through combinations of cooperation, competition, and occasional conflicts. Thus it is essential that American citizens be geographically literate so that they may hopefully cooperate most of the time, compete some of the time, and occasionally engage in conflict. Viewed this way, geographic illiteracy might be seen as a threat to national security. Of course this is true for citizens of other nations as well, however national rankings of geography literacy show that our neighbors abroad understand the importance of geographic knowledge and do not suffer our illiteracy.
Required Reading
Why Geography MattersMore than Ever
Registered students can access a PDF of the reading in Lesson 01 in Canvas.
Recommended Reading: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
What Is Geography And Examples
The definition of geography is the study of the Earth. An example of geography is the study of where the states are located. An example of geography is the climate and natural resources of the land. The scientific study of the Earths surface and its various climates, countries, peoples, and natural resources.
Dont Miss: How Many Questions Can You Miss On The Ged Math Test To Pass
What Is Where Why Is It There And Why Do We Care
In 2002, geographerCharles Gritzner asserted that geography seeks to answer three types of questions:
Also Check: Which Founding Contributors To Psychology Helped Develop Behaviorism
Restrictions On Civilian Gps Devices :
While there are many benefits from using a GPS device, the U.S. Government controls the export of some civilian receivers. All GPS receivers capable of functioning above 18 kilometers altitude and 515 meters per second are classified as weapons for which export licenses are required. These limits attempt to prevent the use of a receiver in a ballistic missile and other weaponry.
Geography Is What Geographers Do
Everything that is happens in a space and time. Therefore, everything has ahistory and everything has a geography. There is no Pope in geography that sayswhat can and cannot be studied in geography, and since few people know what contemporary academic geography is, academic geographers are oftenfree to be interdisciplinary and study what they want. Thereforealmost anything can be and is studied within geography. If you visit theannual meetingof the Association of American Geographers, you cansee presentations on a very wide variety of topicsby a very heterogeneous collection of researchers.
Recommended Reading: Algebra Age Word Problems
A Brief History Of Geography As A Field Of Study
The Greeks are the first known culture to actively explore geography as a science and philosophy, with major contributors including Thales of Miletus, Herodotus, Eratosthenes, Hipparchus, Aristotle, Dicaearchus of Messana, Strabo, and Ptolemy. Mapping by the Romans as they explored new lands added new techniques.
During the Middle Ages, Arabs such as Idrisi, Ibn Battuta, and Ibn Khaldun built on and maintained the Greek and Roman learnings. Following the journeys of Marco Polo, interest in geography spread throughout Europe.
During the Renaissance and into the 16th and 17th centuries the great voyages of exploration revived a desire for solid theoretical foundations and accurate detail. The Geographia Generalis by Bernhardus Varenius and Gerardus Mercators world map are prime examples.
Glossary Of Geography Terms And Definitions
Incomprehensible terms in geography make reading and understanding really boring. This ScienceStruck article lists the comprehensive compilation of geography definitions, geographical terms, and terminology.
Like it? Share it!
Incomprehensible terms in geography make reading and understanding really boring. This ScienceStruck article lists the comprehensive compilation of geography definitions, geographical terms, and terminology.
All of us, at some point of time, have studied geography. But remembering all the geography terms is next to impossible. Geographical terms such as acid rain, barometer, atmosphere, climate, and weather are used in our day-to-day lives for purposes such as academic projects or making travel plans. Many a time, these geography terms are misunderstood. For example, weather is misused for climate and atmosphere is mistakenly used for environment.
Also Check: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Read Also: Ccl4 Geometric Shape
How Does Global Positioning System Work
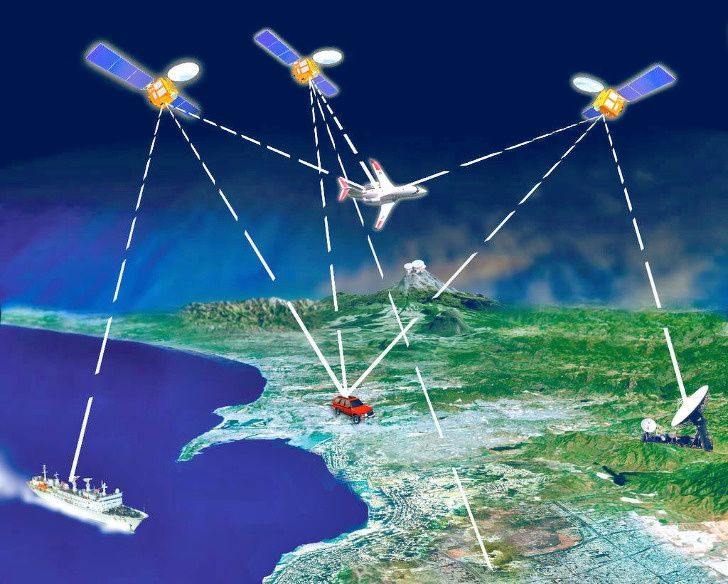
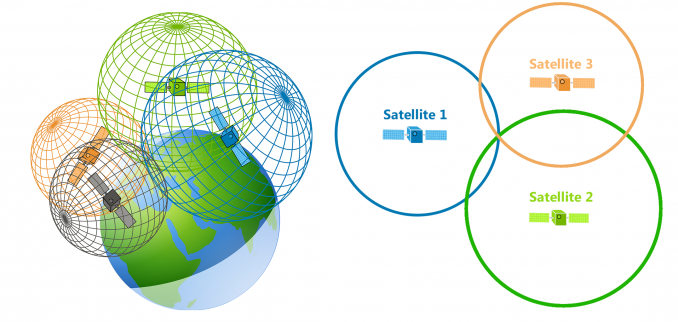
How GPS works. GPS satellites circle the Earth twice a day in a precise orbit. Each satellite transmits a unique signal and orbital parameters that allow GPS devices to decode and compute the precise location of the satellite. GPS receivers use this information and trilateration to calculate a users exact location.
What Is Gps And How Does It Work
The Global Positioning System is a navigation system using satellites, a receiver and algorithms to synchronize location, velocity and time data for air, sea and land travel.
The satellite system consists of a constellation of 24 satellites in six Earth-centered orbital planes, each with four satellites, orbiting at 13,000 miles above Earth and traveling at a speed of 8,700 mph .
While we only need three satellites to produce a location on earths surface, a fourth satellite is often used to validate the information from the other three. The fourth satellite also moves us into the third-dimension and allows us to calculate the altitude of a device.
Recommended Reading: Geometry Angle Addition Worksheet Answers
Factors To Use When Choosing A Gps Unit
Waypoints: How many waypoints can the unit store? How does the number of waypoints stored relate to your recreational and fieldwork needs?
Electronic Compass: Reminder the GPS receiver does not determine the direction or location of a user is headed, if the user is not moving. Electronic compass aid in the real-time navigation by letting the user know cardinal directions .
Display: Are you seeking specific display features, such as widescreen or touch screen, and/or other viewing characteristics?
Memory: Will you be loading additional content, basemaps, or auxiliary data to your GPS? Some GPS Units have the ability to add additional memory through an SD card.
Receiver Characteristics: How well does the receiver receive satellite signals? Does the receiver support WAAS capability?
Accessories: Are additional accessories available to improve accuracy, such as an antenna? Is additional battery power available for the unit? Are the required cables available for transfer of GPS data from the unit to computer and/or other devices? Is there a carrying case available for the unit?
Price: How much are you looking spend on a GPS unit? Are there tradeoffs if going with a more/less expensive model?
- What you need to know when purchasing a GPS for field work. Fromm Geospatial Innovation Facility, UC Berkeley