Some Key Migrations Affecting The Geography Of Contemporary Regions:
- Rural-Urban migration in developing economies resulting in rapid urbanisation.
- Suburbanisation and Counter-urbanisation from the cities of mature economies leading to urban sprawl or diffusion of urban characteristics into the rural-urban fringe.
- Refugee migrations from areas of conflict in the Middle East
- Economic migrations between areas of highly contrasting economic situations
- Tourism migrations as more people have disposable income to spend on travel and leisure.
What The Research Says
Researchespecially that performed by the Pew Hispanic Centerrefutes these claims. In fact, studies have shown that family-based immigration has encouraged stability. It has promoted playing by the rules and financial independence. The government caps the number of family members who can immigrate each year, keeping the levels of immigration in check.
Immigrants with strong family ties and stable homes do better in their adopted countries and they’re generally a better bet to become successful Americans than immigrants who are on their own.
What Are 5 Push And Pull Factors
Push and pull factors
- Economic migration to find work or follow a particular career path.
- Social migration for a better quality of life or to be closer to family or friends.
- Political migration to escape political persecution or war.
- Environmental to escape natural disasters such as flooding.
You May Like: The Segment Addition Postulate Answer Key
Keeping Up With The Journal Literature
Want an easy way to keep up with the journal literature for all facets of Geography? And you use a mobile device? You can install the BrowZine app and create a custom Bookshelf of your favorite journal titles. Then you will get the Table of Contents of your favorite journals automatically delivered to you when they become available. Once you have the ToC’s you can download and read the articles you want.
You can get the app from the App Store or Google Play.
Don’t own or use a mobile device? You can still use BrowZine! It’s now available in a web version. You can get to it here. The web version works the same way as the app version. Find the journals you like, create a custom Bookshelf, get ToCs and read the articles you want.
International Migration Measures And Trends
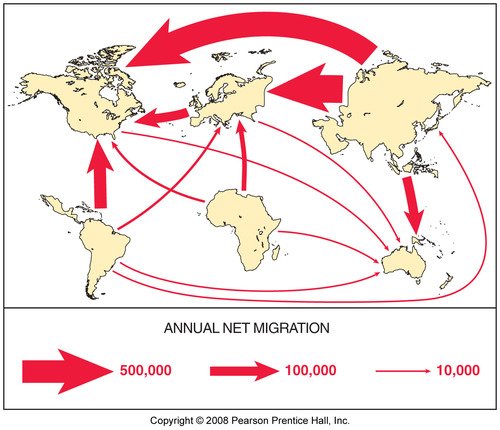
International migration is the movement of people across international borders for the purpose of settlement. International migrants change their usual place of residence from one country to another. The United Nations suggests that the degree of permanence of the migration should be measured over a 12-month period, so that shorter stays in another country are not classified as permanent international migration. When passengers arrive in a country, they are asked whether they intend to stay for less than 3 months, classifying them as visitors for between 3 months and 12 months, classifying them as short-term migrants or for 12 months or more, classifying them as long-term migrants. This is a prospective measurement of migration. Alternatively, people can be surveyed at their current place of residence and asked where they were living 12 months ago. If the answer is another country, then they are classified as international migrants. This is a retrospective measurement of migration. It is also possible to measure international migration by asking migrants leaving a country to register their departure and to ask a question about migration of those new registering in countries which maintain a comprehensive population register.
P. Boyle, in, 2009
I.H. Burnley, in, 2009
B. Lalljee, … Awnindra K. Singh, in, 2018
Read Also: How Do You Find Acceleration In Physics
What Is Step Migration In Human Geography
Step migrationmigrationmigration
. Thereof, what is step migration example?
step migration. Migration that follows a path of a series of stages or steps towards a final destination. For example, someone trying to get to North Korea from America would first have to fly to China, then swim or take a boat to North Korea.
One may also ask, what are the 4 types of migration? There are different types of migration such as counter-urbanization, emigration, immigration, internal migration, international migration and rural-urban migration.
what is migration in human geography?
A short definition for Migration Studies. The movement of groups and individuals from one place to another, involving a change of usual residence. Migration is usually distinguished from mobility in general by conventions of spatial and temporal scale.
What are the three types of movement in AP Human Geography?
Commuting, seasonal movement, and nomadism is what type of movement?
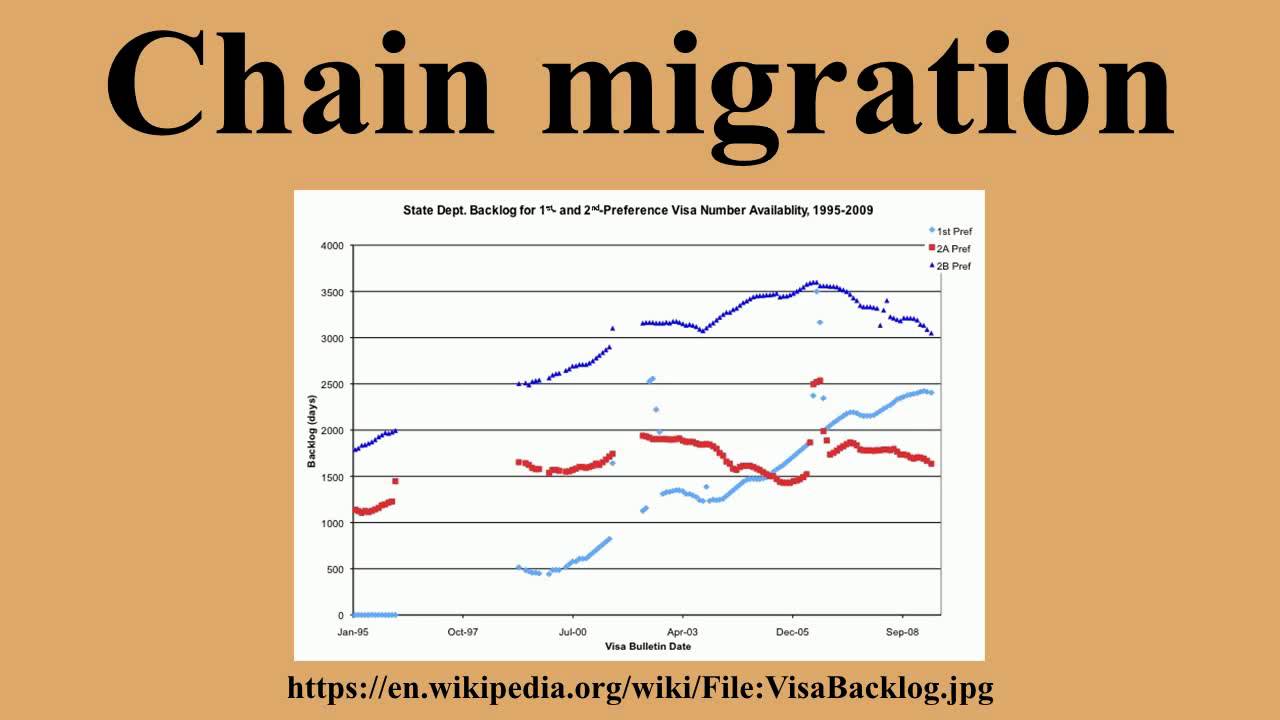
So Is It Chain Migration Or Family Reunification
While “chain migration” and “family reunification” refer to the same process, both have partisan implications. When chain migration first started appearing in academic texts in the 1960s, it was not a pejorative term. Roughly ten years later, the term family reunification entered the immigration lexicon.
Democrats and progressives says that “chain migration” has become a loaded term and have thus adopted the term family reunification, while their Republican counterparts typically stick with chain migration. The Trump administration has favored chain migration over family reunification. In fact, a Google Trends search yields a large uptick in the popularity of chain migration vs. family reunification during the first year of the Trump presidency.
Also Check: Geometry Dash Demon Key Hack
United States After 1965
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. |
In the United States, the term ‘chain migration’ is used by advocates of limiting immigration, to partially explain the volume and national origins of legal immigration since 1965. U.S. citizens and Lawful Permanent Residents ” rel=”nofollow”> Green card” holders) may petition for visas for their immediate relatives including their children, spouses, parents, or siblings. Advocates of immigration restriction believe the family reunification policy is too permissive, leads to higher than expected levels of immigration, and what they consider the wrong type of immigrants. In its place, they favor increasing the number of immigrants with particular job skills. In practice, however, the wait times from when a family reunification petition is filed until the adult relative is able to enter the U.S. can be as long as 1520 years . This is a result of backlogs in obtaining a visa number and visa number quotas that only allow 226,000 family-based visas to be issued annually.
There are four family-based preference levels, data valid as of June 2009:
In The Library’s Collection
To find books about Human Migration, use the subject heading human beings migration. For Involuntary migration use forced migration in the online catalog. For International Migration, use the subject heading emigration and immigration. Many books about Human Migration are shelved in the call number range JV 6001 through JV 9480 located on the 4th floor of Berry Library. However, many others are scattered throughout the collections. Check the online catalog for specific subtopics.
- Used instead of “international migration.”
You May Like: Algebra 1 Chapter 4 Practice Workbook Answers
Effects Of Chain Migration
Chain migration leads to family reunification hence social structure is maintained. New settlers may provide cheaper labor or unavailable skills in a certain profession in the country they settle in. More effect is on the economy of the beneficially country or region due to increased manpower. However, the wrong type of immigrants in terms of behavior and skills proficiency may come in. Backlog in issuing of visa due to annual quotas may lead to illegal immigrants who cohabit with relatives as they wait for processing of visa. Immigrants may overwhelm the nation in terms of resources. Other problems such as language barrier, cultural erosion, racial, or ethnic discrimination or fear of job loss by citizens to emigrants may cause tension between immigrants and the locals.
Migration Based On Duration
Daily: Commuting to and from work each day often resulting in rush hours
Seasonal: Winter snow-sport enthusiasts to the Alps Summer sun-seekers to the Mediterranean nomadic herders to fresh grazing pastures.
Medium-term temporary: Working in an overseas TNC branch office for a few years taking up a university course working in a developing city to pay off rural debts.
Permanent: Emigrating to another country with no intention of returning.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Migration Based On Distance
Intra-building: Movement within a building
Inter-building: Pedestrian patterns between a complex of buildings
Local scale: Moving house to another within a town or city
Regional scale: Migrating within a country from one county/state to another
International scale: Migrating from one country to another
Global scale: Migrating between distant continents
Why Does President Trump Want To End Chain Migration
The White House’s most recent immigration proposal aims to limit chain migration to only spouses and minor children while excluding sponsorship of extended family.
Mr. Trump claims that immigrants entering the country through chain migration take jobs away from U.S. citizens and pose a threat to national security. The Trump administration has expressed its goal to move away from chain migration and toward a “merit-based” means of immigration, or a system that prioritizes highly educated, english speaking immigrants.
Mr. Trump announced his administration’s opposition to the system after the New York City terror attack on Halloween that killed 8 people and injured 12 more, although the suspect in that attack entered the country through the diversity visa lottery program, which is separate from chain migration.
The Trump administration re-upped its call to end the chain migration system when suspect Akayed Ullah attempted to bomb the passageway under 42nd Street connecting the subway stations at Times Square and the Port Authority Bus Terminal in December. CBS News confirmed that Ullah entered the country from Bangladesh in February 2011 through chain migration sponsorship, although he became a legal permanent resident of the United States.
The White House’s website provides this infographic on chain migration that does not cite any specific numbers:
It’s time to end Chain Migration:
The White House
You May Like: Reducing In Math
Pull And Push Factors Of Migration
People migrate to other places because of different reasons. Lees laws divide these reasons into two factors: pull factors and push factors.
Pull factors are the factors that would attract or encourage the persons to leave their place of origin. These would include better living conditions, job opportunities, enjoyment, better medical care, feeling of having religious or political freedom, education, attractive climates, and better chances of marrying, among others.
Push factors are the factors that could force the persons to move their place of origin. These would include few or not enough job opportunities, inadequate conditions, famine, political fear, poor medical care, desire for freedom, poor housing, condemned housing, war, death threats, and natural disasters, among others.
A Short Definition For Migration Studies
The movement of groups and individuals from one place to another, involving a change of usual residence. Migration is usually distinguished from mobility in general by conventions of spatial and temporal scale. For example, by convention international migration requires crossing a national boundary for an actual or intended period of at least one year. Residential mobility, by contrast, may consist of a short-distance move between properties in the same city.
Typologies of migration differentiate between internal and international migration, and the two forms are usually studied separately. Looked at historically, however, the movement of people long predates nation-states homo sapiens left Africa some 150,000 years ago. Geographers are interested in inter-regional, rural-urban, and urban-rural movements, especially in societies with low birth and death rates where migration is often the major cause of population change . In 2008, about 3 per cent of Americans moved to another county, for example, and in China, it is estimated that there were 140 million migrants, mostly from rural to urban areas .
Castree, N., Kitchin, R., & Rogers, A. . “Migration.” In A Dictionary of Human Geography. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 27 Oct. 2021
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Ethnic Enclaves And Gender Ratios
Immigrants from specific ethnic groups settled in America and continued inviting more members thereby forming ethnic homogenous territories. Ethnic enclaves were built in regions with names such as Little Italy and Chinatown. The enclave led to some towns in the US and Brazil having settlers who spoke the only German language. Young, energetic and single men were the first to migrate to America and other places. Latter some invited their spouses. This led to more men than women in the new countries. Italian and Chinese men initially migrated to America in search of work but once they had money and met the legal requirements, they invited their families. There is an imbalanced sex ratio in most of the chain migration instances.
What Is Periodic Movement In Human Geography
movementperiodic movementsmovementperiodic movement
. Similarly, you may ask, what is cyclic movement in human geography?
Cyclic Movement. movement that has a closed route repeated annually or seasonally. Distance Decay. the various degenerative effects of distance on human spatial structures and interactions.
One may also ask, what is an example of cyclic movement? Cyclic movement. Or circulation – for example, nomadic migration – that has closed route and is repeated annually or seasonally e.g., activity space – space within which daily activity occurs commuting, seasonal, nomadism.
In this regard, what are the three types of movement in AP Human Geography?
Commuting, seasonal movement, and nomadism is what type of movement? International migration and internal migration is what type of movement?
What is transhumance in human geography?
transhumance. A pattern of regular seasonal movement by human groups. It can be seen as a form of pastoralism or nomadism.livestock is moved seasonally between one area of pasture and another. international refugee. fleeing from one country to another.
Read Also: My Hrw Com Algebra 1
What Are Different Types Of Migration
Migration could come in different forms depending on the nature and the reason of the movement.
The first and the most common classification of migration refer to the nature of movement. This would include immigration and emigration. Immigration refers to the movement of persons or population to another country. Emigration, on the other hand, refers t o the movement of persons or populations from one country. For example, immigration of Filipinos to the United States and emigration of Indians from India.
The second classification of migration refers to permanence. Under permanence, we have permanent, temporary, voluntary, and forced. Permanent migration refers to the movement from one area to another without plans of returning to the place of origin. Temporary migration refers to the migration done on a limited time. Forced migration involves migrants leaving without any choice. Voluntary migration is the opposite of forced.
The third classification of migration refers to the nature of location. Under such classification, we have internal and international. Internal migration refers to a chance of residence within the country. It is also known as internal migration. International migration, on the other hand, refers to the change of residence to different nations or countries. It is also known as external migration.
There are other types of migration. Here are as follows.
Debate On Chain Migration In The Us
After President Donald Trump took over, there was a raging debate on chain migration. Trump said he will work towards ending extensive chain migration by ensuring that only the immediate family members are considered for issuance of visa. During Trumps maiden State of the Nation address, he called for merit-based immigration rules that would bring in only essential high skilled professionals. In this era of terrorism, it is only prudent to be vigilant. Stopping chain migration was one of the four pillars of the Trump administration.
Those arguing against the Trump view state that some immigrants have assisted build the economy. Others have nowhere else to call home. Though there are concerns that there are far too many people entering the US, the size and economy is large enough to accommodate them. Of the 34 million legal immigrants in America, two-thirds arrived through chain migration and have shown high levels of social integration into the American system.
Recommended Reading: The Segment Addition Postulate Answer Key With Work
What Is Chain Migration
“Chain migration” — officially known as “family reunification” under federal law — is the process by which green card holders or legal U.S. residents may sponsor a family member for immigration to the United States.
It is the most common legal form of immigration to the United States. According to the Department of Homeland Security, 238,087 immigrants were categorized as a “family-sponsored preference” in 2016, and 566,706 came as “immediate relatives of U.S. citizens” .
Between 60 and 70 percent of all lawful permanent immigration to the United States in the past decade has family-based roots.
The application process for the permanent residency of certain family members varies depending on the petitioners’ status of green card holder vs. citizen.
Citizenship is not automatically granted to those who are sponsored by their family members in the United States, and the waiting period with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services can last anywhere from a few months to decades.
Settlement And Economic History
The various population movements of the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries have made Mauritius a unique blend of different races, cultures and religions. People of European, African, Indian and Chinese origins have created a multiracial society, in which the various cultures and traditions flourish in peace and harmony. The population started to grow under the French rule in the 18th century. Later in 1735, the population had grown to almost 1000 and reached nearly 20,000 in 1767. When the British abolished slavery in 1835, the population stood at 100,000. It increased rapidly with the coming of Indian labourers. Between 1835 and 1865, some 200,000 labourers were brought in. By the turn of the century, the population grew to 371,000, and in 1944 it stood at 419,000. After the Second World War, the increase was more rapid, particularly because of a baby boom and a drop in the infantile mortality rate. The rate of natural increase, which was about 3% in the 60s, has considerably dropped with family planning campaigns and greater awareness due to better education. The population of the Republic of Mauritius was estimated at 1,291,456 as at July 2012, growing at a rate of 0.4% since the end of 2010.
J. Crush, C. Hughes, in, 2009
Recommended Reading: Ksp Chemistry