The Cell Membrane And Cell Wall
A cell is surrounded by a cell membrane or plasma membrane. The cell membrane has fine pores through which it allows selective substances to pass through.The cell wall is found in plant cells and surrounds the cell membrane. It is made up of cellulose. This cell wall gives shape and makes it rigid, it also allows the free flow of substances.
Cell Structure And Function
Research in cell structure and function seeks to determine mechanisms by which parts of cells undergo change and interact with one another in carrying out basic cellular functions. The field encompasses cell morphology, physiology, biochemistry, and molecular biology. The goals are to understand the organization and activities of cells at all levels,from the behavior of entire cells and cell organelles to relationships between their component molecules. A wide range of approaches is employed, including light and electron microscopy, electrophysiology, molecular genetics, and biochemical analysis. A number of rapidly developing areas are under investigation by members of the Cell and Molecular Biology group.
Mechanisms of cell motility, including movement of whole cells and of their parts, constitute an active area of investigation in cell biology. In recent years, there has been considerable progress in the structure and chemistry of microtubules, microfilaments, and membrane proteins. Research in these areas at the University of Virginia includes studies on the mechanism of chromosome movement during mitosis, of organelle tranport along microtubules and actin filaments, and on the behavior of flagella during cell motility.
There Are Two Main Types Of Cells: Prokaryotic Cells And Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotesorganisms composed of a prokaryotic cellare always single-celled . Prokaryotic cells dont contain a nucleus. Instead, their DNA can be found in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid or in circular chromosomes called plasmids.
Eukaryotic cells can be found in animals, plants, protists, and fungi. Eukaryotesorganisms composed of eukaryotic cellsare multicellular or complex unicellular organisms. Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus where their DNA is stored.
Read Also: Kuta Software Infinite Pre Algebra Proportion Word Problems
Cell Cycle Checkpoints And Dna Damage Repair System
The cell cycle is composed of a number of well-ordered, consecutive stages that result in cellular division. The fact that cells do not begin the next stage until the last one is finished, is a significant element of cell cycle regulation. Cell cycle checkpoints are characteristics that constitute an excellent monitoring strategy for accurate cell cycle and divisions. Cdks, associated cyclin counterparts, protein kinases, and phosphatases regulate cell growth and division from one stage to another. The cell cycle is controlled by the temporal activation of Cdks, which is governed by cyclin partner interaction, phosphorylation by particular protein kinases, and de-phosphorylation by Cdc25 family phosphatases. In response to DNA damage, a cell’s DNA repair reaction is a cascade of signaling pathways that leads to checkpoint engagement, regulates, the repairing mechanism in DNA, cell cycle alterations, and apoptosis. Numerous biochemical structures, as well as processes that detect damage in DNA, are ATM and ATR, which induce the DNA repair checkpoints
Description Of Cell Structure And Function
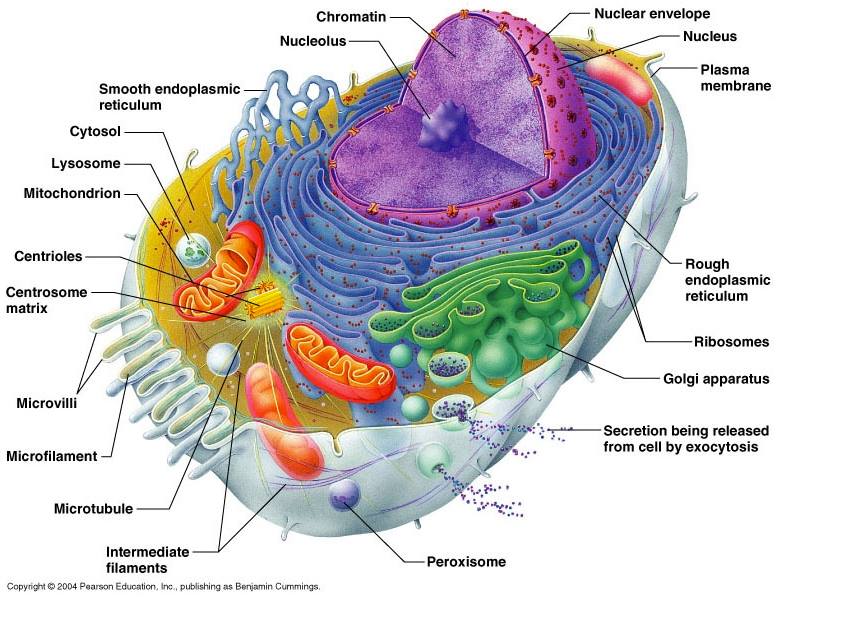
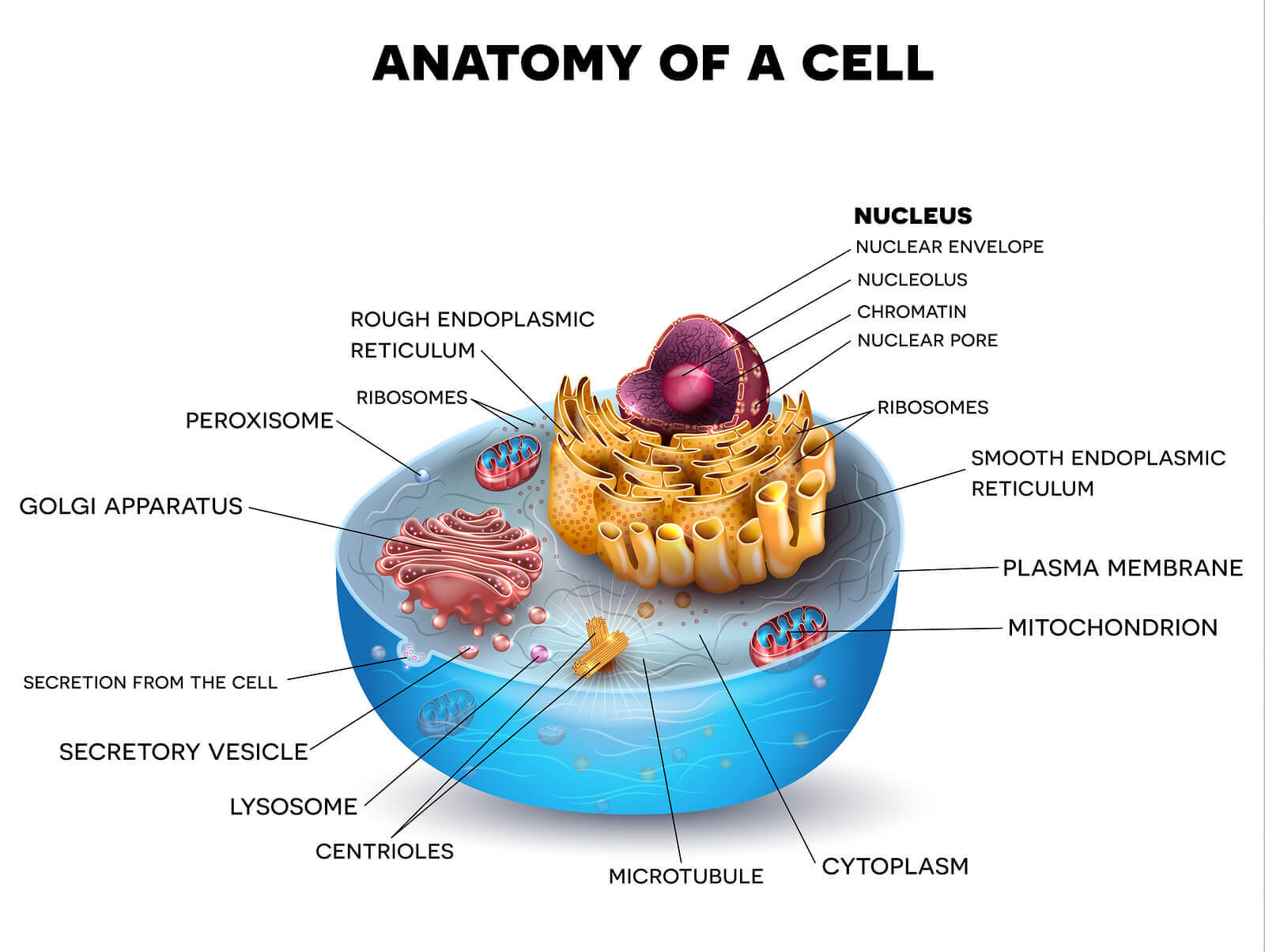
Cells are fundamental to the study of biology. Every living thing is composed of cells, they are the building blocks of life. All cells share similar characteristics and can be defined by the cell theory.
Cell Theory
1. All living things are composed of cells.2. All cells arise from preexisting cells through cell division.3. Cells contain hereditary material, which they pass to daughter cells during cell division.4. The chemical composition of all cells is quite similar.5. The metabolic processes associated with life occur within cells.
All cells have a few basic features in common:
1. Plasma membrane: a selective barrier which encloses a cell .
2. Cytosol: located inside the plasma membrane, this is a jelly-like fluid that supports organelles and other cellular components.
3. Cytoplasm: the cytosol and all the organelles other than the nucleus.
4. Ribosomes: the organelles on which protein synthesis takes place.
5. DNA: the genetic material which is contained in one or more chromosomes.
Despite the fact that all cells share the above characteristics, they can be remarkably different in size, shape and function.
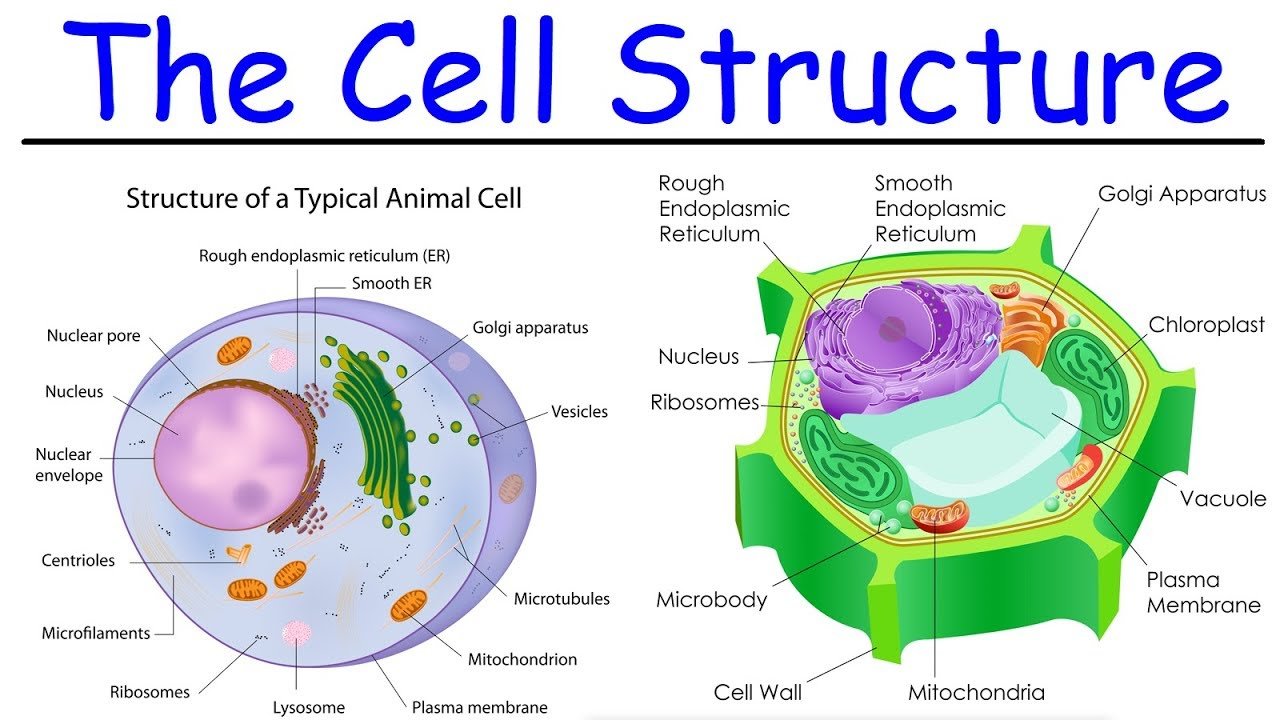
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
There are two major categories or types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Figure \. prokaryotic cell
Figure \. animal cell
Figure \.
Figure \. plant cell
Cell Structure and Function Tutorial by Dr. Katherine Harris is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Recommended Reading: Klohe Kardashians Real Father
What Do Cell Membranes Do
The cell membrane surrounds every living cell and delimits the cell from the surrounding environment. It serves as a barrier to keep the contents of the cell in and unwanted substances out. It also functions as a gate to both actively and passively move essential nutrients into the cell and waste products out of it. Certain proteins in the cell membrane are involved with cell-to-cell communication and help the cell to respond to changes in its environment.
Special emphasis is given in this article to animal cells, with some discussion of the energy-synthesizing processes and extracellular components peculiar to plants.
Structures Outside The Cell Membrane
Many cells also have structures which exist wholly or partially outside the cell membrane. These structures are notable because they are not protected from the external environment by the semipermeable cell membrane. In order to assemble these structures, their components must be carried across the cell membrane by export processes.
You May Like: Exponential Modeling With Percent Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 2 Homework
Cell Structure Crossword Puzzle Answer Key Biology
Cell Structure Crossword Puzzle Answer Key Biology. Ad bring learning to life with thousands of worksheets, games, and more from education.com. We found 1 answers for this crossword clue.
In fact, there are so many free crossword puzzles that they can make your head spin. Cell biology answers for a cell structure and function crossword puzzle? Vacuole, cilia, hooke, smoother, 8.
Source: studylib.net
We found 1 answers for this crossword clue. View all science crosswords to see puzzles.
Source: www.biologycorner.com
There are hundreds of free puzzle websites on the internet. You can even make your very own crossword.
Source: microspedia.blogspot.com
This product includes the cell structure and function crossword puzzle and the answer key. This product includes the cell structure and function crossword puzzle and the answer key.
Source: www.slideshare.net
This product includes the cell structure and function crossword puzzle and the answer key. You can find cell structure crossword puzzle answer key over the internet by typing the keyword into search engines.
Source: www.worksheeto.com
This crossword puzzle is great for vocabulary building and can be used during a cell unit as a post test activity, homework assignment, etc. Cell parts crossword puzzle answers.
Source: www.worksheeto.comSource: biologycorner.comSource: studylib.net
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Biology crossword puzzles with answers.
What Other Components Do Cells Have
As previously mentioned, a cell’s cytoplasm is home to numerous functional and structural elements. These elements exist in the form of molecules and organelles picture them as the tools, appliances, and inner rooms of the cell. Major classes of intracellular organic molecules include nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, all of which are essential to the cell’s functions.
Nucleic acids are the molecules that contain and help express a cell’s genetic code. There are two major classes of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid . DNA is the molecule that contains all of the information required to build and maintain the cell RNA has several roles associated with expression of the information stored in DNA. Of course, nucleic acids alone aren’t responsible for the preservation and expression of genetic material: Cells also use proteins to help replicate the genome and accomplish the profound structural changes that underlie cell division.
Proteins are a second type of intracellular organic molecule. These substances are made from chains of smaller molecules called amino acids, and they serve a variety of functions in the cell, both catalytic and structural. For example, proteins called enzymes convert cellular molecules into other forms that might help a cell meet its energy needs, build support structures, or pump out wastes.
Recommended Reading: Sacred Geometry Moon Phases Tattoo Spine
Allows Transport Of Substances
Various nutrients are imported by the cells to carry out various chemical processes going on inside the cells. The waste produced by the chemical processes is eliminated from the cells by active and passive transport. Small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and ethanol diffuse across the cell membrane along the concentration gradient. This is known as passive transport. The larger molecules diffuse across the cell membrane through active transport where the cells require a lot of energy to transport the substances.
Significant Events In Cell Biology
- B.A., Biology, Emory University
- A.S., Nursing, Chattahoochee Technical College
Cell biology is the subdiscipline of biology that studies the basic unit of life, the cell. It deals with all aspects of the cell including cell anatomy, cell division , and cell processes including cell respiration, and cell death. Cell biology does not stand alone as a discipline but is closely related to other areas of biology such as genetics, molecular biology, and biochemistry.
Read Also: Physics Vs Chemistry Which Is Harder
What Is The Relationship Between Structure And Function Of The Cell Membrane
Structure of Plasma Membranes
The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Who Discovered Cells
Robert Hooke discovered the cell in 1665. Robert Hooke observed a piece of bottle cork under a compound microscope and noticed minuscule structures that reminded him of small rooms. Consequently, he named these rooms as cells. However, his compound microscope had limited magnification, and hence, he could not see any details in the structure. Owing to this limitation, Hooke concluded that these were non-living entities.
Later Anton Van Leeuwenhoek observed cells under another compound microscope with higher magnification. This time, he had noted that the cells exhibited some form of movement . As a result, Leeuwenhoek concluded that these microscopic entities were alive. Eventually, after a host of other observations, these entities were named as animalcules.
In 1883, Robert Brown, a Scottish botanist, provided the very first insights into the cell structure. He was able to describe the nucleus present in the cells of orchids.
You May Like: Algebra 2 Radical Worksheet
Why Do Cells Move
Cell movement is necessary for a number of cell functions to occur. Some of these functions include cell division, cell shape determination, fighting off infectious agents and tissue repair. Internal cell movement is needed to transport substances into and out of a cell, as well as to move organelles during cell division.
Segmentation Of Spatial Regions With Distinct Biological Functions
While clustering cells into groups with similar expression is a common task in scRNA-seq analysis, spatial data allows for the much more powerful segmentation of data into distinct spatial regions. Cells contribute to various biological functions when cooperating with other nearby cells, and using spatial transcriptomics data, we can identify these spatially associated groups to understand how different cells work together to perform complex functions. This leads to the task of dissecting the tissue into spatial domains. Depending on the type and resolution of data, the spatial locations that are being segmented into regions may be, for example, individual cells or spots in a spatial barcoding array, but below we will refer to any such single location in a spatial transcriptomics dataset as a spot for brevity.
Fig. 2: Illustration of different traits that can separate spatial regions.
Also Check: Climate Of The New England Colonies
Why Is It Important To Understand The Relationship Between Structure And Function
Function and structure are related, because of a certain structure a living thing make contain makes the object function the way it does. The relationship of a structure and function is the structuring levels from molecules to organism ensure successful functioning in all living organism and living system.
Cell Structure And Tissues
The understanding of cell structure and function, the cell theory, is a unifying concept in biology. All living organisms have similarities as well as differences in relation to cell structure, cell biochemistry and cell function. At level 3/KS5, students need to extend their knowledge and understanding of cell structure and function from previous studies and be able to apply this understanding to a range of biological processes. The similarities and differences in the structure and ultra structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells being key to developing understanding of a range of biological functions.
Students should be provided with a variety of practical opportunities to develop microscopy skills to support their understanding of cell structure. For this reason, the resources that are listed below should also be viewed alongside those listed under the categories of classifying and observing microorganisms and exchange and transport.
Quality AssuredCategory:SciencePublisher:Wellcome Trust
This resource includes videos, activities, articles and a poster covering aspects of cell biology for post-16 students. The aspects of cell biology covered include: cell structure, cell signalling, cell division, apoptosis lysosomes and stem cell research
Quality AssuredCategory:SciencePublisher:Wellcome Trust
Note: The videos are no longer available.
Quality AssuredCategory:SciencePublisher:Catalyst
Quality AssuredCategory:SciencePublisher:Gatsby Science Enhancement Programme
You May Like: How To Calculate Half Life Of A Reaction
Teach Biology Essentials With Crosswords About Molecular Biology
Cell structure crossword puzzle answer key science stuff cell structure and function crossword puzzle answer key cell structure crossword puzzle answer key vanessa jason biology roots chapter 3 cell structure crossword puzzle answer key cell structure and processes crossword puzzle answer key cell structure crossword puzzle answer key pdf cell structure crossword. You can find cell structure crossword puzzle answer key over the internet by typing the keyword into search engines. There are hundreds of free puzzle websites on the internet.
Provides Support And Structure
All the organisms are made up of cells. They form the structural basis of all the organisms. The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide support and structure to the organism. For eg., the skin is made up of a large number of cells. Xylem present in the vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural support to the plants.
Read Also: Math Nation Section 2 Test Yourself Answers
Determining Spatial Distribution Of Cell Types In Multi
Widely used ST techniques such as the Visium technology collect data at a spatial resolution that often corresponds to 28 cells. In order to understand spatial tissue structure in terms of single cells, the ST data can be augmented with cell type information either from a provided atlas or in an unsupervised manner from scRNA-seq data through standard clustering analysis such as with the Louvain algorithm.
One way to quantify the presence of cell types at each spot is to compute enrichment scores, which represent the relative expression level of some set of genes. By identifying a set of marker genes for a particular cell type, the enrichment score of that gene set at some spot is informative of the presence of that cell type at that spot . The Seurat package allows for computation of enrichment scores through the AddModuleScore function. The Giotto package computes enrichment scores in three ways: using the PAGE algorithm in which a normal-distribution based statistical test is used to assess significance an algorithm that uses gene expression rankings to avoid the need to compute explicit sets of marker genes, and a hypergeometric test on an expression contingency table. Multimodal Intersection Analysis computes an enrichment score for cell types over spatial regions by identifying marker genes for each cell type and each spatial region, and measuring the extent of overlap between corresponding sets of marker genes.
Defining And Identifying Spatially Variable Genes
A key step in scRNA-seq pipelines is the identification of highly-variable genes , for which expression exhibits significant differences between cells. However, a gene may exhibit variation from cell-to-cell but not in a way that produces a clear spatial pattern when viewed using ST data. As such, in order to understand spatial cellular variation, analysis of ST data requires the identification of spatially variable genes . These spatial variations in gene expression can reflect cell type compositions that perform specific spatial functions or spatial patterns in cell-cell interactions. Spatial expression of SVGs may exhibit patterns such as clustering and periodicity, depending on the tissue structure and function. Methods for detecting spatially-variable genes can be mathematically understood as expressing the cell-to-cell variation exhibited in gene expression as a combination of spatial variation, which occurs on a coherent pattern in space, and non-spatial variation, including intrinsic variation between cells and possibly other terms, such as variation due to cell-cell interaction . When the variation of a particular gene is primarily due to spatial variation, that gene can be said to be spatially variable.
You May Like: Which Of The Following Perspectives Dominated American Psychology For Decades
Origin Of Eukaryotic Cells
The eukaryotic cell seems to have evolved from a symbiotic community of prokaryotic cells. DNA-bearing organelles like the mitochondria and the chloroplasts are descended from ancient symbiotic oxygen-breathing proteobacteria and cyanobacteria, respectively, which were endosymbiosed by an ancestral archaean prokaryote.
There is still considerable debate about whether organelles like the hydrogenosome predated the origin of mitochondria, or vice versa: see the hydrogen hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotic cells.
What Is A Cell In Biology
A cell is the basic unit of life or a cell is the structural and functional unit of life is determined by Robert Hooke. The body of all livings things is made of cells. Cells were first discovered by Robert Hooke with the help of a microscope in 1665. The number of cells varies in different organisms. Some cells are unicellular , whereas others are multi-cellular.
In single-celled organisms like paramecium, Amoeba, all the functions have to be performed by a single cell.
The single-celled organism may be Prokaryotes or Eukaryotes. Multi-cellular organisms develop from a single cell and may have trillions of cells when they grow up.
| Study of Cell | |
| The cell of the Liver is called | Hepatic Cell |
| The cell of the Lungs is called | Alveoli |
| The cell of the Brain is called | Neuron |
| The cell of Kidney is called | Nephron |
Shapes of cells also vary from being irregular to round, polygonal, cylindrical, etc. The size of cells also varies from 0.1 micrometers to 170 mm x 130 mm.
Read Also: Unit Test Edgenuity Algebra 2