Variety Value And Normativity
Biodiversity as variety provides option/investment and insurancebenefits to humanity, but this leaves open the question as to thenature of the value of such benefits. Haskins had called foran Ethic of Biotic Diversity, in which varietysbenefit has ethical import because we care about the well-being offuture generations. Similarly, when IUCN reviewedthe arguments for the conservation of biotic diversity, they linkedthis to moral principles:
The issue of moral principle relates particularly to speciesextinction, and may be stated as follows. Human beings have become amajor evolutionary force. While lacking the knowledge to control thebiosphere, we have the power to change it radically. We are morallyobliged-to our descendants and to other creatures-to actprudently We cannot predict what species may become useful tous. Indeed we may learn that many species that seem dispensable arecapable of providing important products, such as pharmaceuticals, orare vital parts of life-support systems on which we depend. Forreasons of ethics and self-interest, therefore, we should notknowingly cause the extinction of a species.
The first CBD objective, the conservation of biodiversity, is anurgent act of attaining intergenerational justice an act thatrequires sustained, engaged international collaboration. To depletethe planet of essential resources and leave to future generations aworld which severely limits their options, is unjust.
Eser et al. conclude
Introduced And Invasive Species
Introduced speciesInvasive speciesLophura nycthemeraEast AsiaEurope
Barriers such as large rivers, seas, oceans, mountains and deserts encourage diversity by enabling independent evolution on either side of the barrier, via the process of allopatric speciation. The term invasive species is applied to species that breach the natural barriers that would normally keep them constrained. Without barriers, such species occupy new territory, often supplanting native species by occupying their niches, or by using resources that would normally sustain native species.
Not all introduced species are invasive, nor all invasive species deliberately introduced. In cases such as the zebra mussel, invasion of US waterways was unintentional. In other cases, such as mongooses in Hawaii, the introduction is deliberate but ineffective . In other cases, such as oil palms in Indonesia and Malaysia, the introduction produces substantial economic benefits, but the benefits are accompanied by costly unintended consequences.
At present, several countries have already imported so many exotic species, particularly agricultural and ornamental plants, that their indigenous fauna/flora may be outnumbered. For example, the introduction of kudzu from Southeast Asia to Canada and the United States has threatened biodiversity in certain areas. Nature offers effective ways to help mitigate climate change.
Multiple Benefits Of Biotic Diversity: Insurance And Investment
Those bits of pre-history clearly articulate the idea that varietyitself is important because it maintains future options for humanity.However, this early work did not establish any consistent terminologyto describe this. Later work uses terms like biodiversityoption value and maintenance of options .
Back in 1980, the IUCN reflected on this earlier work, and offered some distinctionsthat are still useful in philosophical discussions about biodiversitydefinitions and values. IUCNs arguments forthe conservation of diversity echoedearlier statements about variety and future options:
we may learn that many species that seem dispensable are capable ofproviding important products, such as pharmaceuticals.
Importantly, IUCN also echoed other early work, in adding a criticalsecond part to that sentence: or are vital parts oflife-support systems on which we depend .IUCN provided terms for these two ways in which variety itselfbenefits humanity:
preservation of genetic diversity is both a matter ofinsurance and investment to keep open future options.
It is informative to trace this insurance and investment duality inthe pre-history of biodiversity. Roush listedfour reasons for preserving natural diversity. Inaddition to the relational values concerning humandelight and ethics, his reasons included not only the idea thatdiversity increases the possibility of future benefitsbut also that diversity supports stability of the life supportsystem.
You May Like: What Does Structure And Function Mean In Biology
Peace Justice And Strong Institutions
We cannot hope for sustainable development without peace, stability, human rights and effective governance, based on the rule of law. Yet our world is increasingly divided. Some regions enjoy peace, security and prosperity, while others fall into seemingly endless cycles of conflict and violence. This is not inevitable and must be addressed.
Armed violence and insecurity have a destructive impact on a countrys development, affecting economic growth, and often resulting in grievances that last for generations. Sexual violence, crime, exploitation and torture are also prevalent where there is conflict, or no rule of law, and countries must take measures to protect those who are most at risk
The SDGs aim to significantly reduce all forms of violence, and work with governments and communities to end conflict and insecurity. Promoting the rule of law and human rights are key to this process, as is reducing the flow of illicit arms and strengthening the participation of developing countries in the institutions of global governance.
Biodiversity And Tropical Rainforests

Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, in all its forms and all its interactions. We do not know how many species of plants and animals live in the rainforest, however, we do know it is the most biodiverse ecosystem in the world. For example, rainforests contain 170,000 of the worlds 250,000 known plant species. In the Indonesian rainforest, there are over 30,000 species of plants and 1,600 species of birds.
Recommended Reading: What Is Self Confidence In Psychology
Csr: Biodiversity Protection And Certification
Protecting biodiversity is also fundamental for businesses. In fact, the protection of biodiversity is part of the specifications and guidelines for sustainable agriculture, particularly in organic farming. It is as well present as an element of the sustainable development strategy of the ISO 26000 standards. These standards work as guidance and proof of companies wanting to have socially responsible behaviors.
For the wider professional world, however, the measures to be developed for biodiversity are often more abstract and less easy to identify than, for example, actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
These difficulties are somewhat mitigated by the initiative of the international organization ECOCERT. Because of it, theres a Biodiversity Commitment certification that not only guides companies on how to have policies that are more biodiversity-friendly. It also officially recognizes these companies efforts by certification this specific component of their corporate social responsibility strategies.
- Related content:
Why Is Biodiversity So High In The Tropical Rainforest
There are a number of reasons for biodiversity in the tropical rainforest including:
- the hot and wet climate provides ideal conditions for many species of plants and animals to thrive.
- nutrients are rapidly recycled speeding up plant growth, providing producers with food, which in turn are consumed by primary consumers.
- large areas of rainforest are untouched by humans, allowing nature to thrive.
Don’t Miss: What Does Convenience Mean In Math
What Are Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity Hotspots are biogeographic regions that have the richest and the most threatened reservoirs of plant and animal life on earth. These regions have been identified as some of the worlds most important ecosystems that are home to a high number of endemic species that also provide crucial ecosystem services for the benefit of humans.
The total combined area of the worlds 36 hotspots once occupied over 15.7% i.e., about 23.7 million sq. km of the earths land area. However, due to the extreme habitat loss in these regions as a result of the anthropogenic activities, the combined area of all the global hotspots currently covers only 2.4% of the earths land area and accounts for about 35% of the worlds ecosystem services.
These regions support more than 152,000 of the global vascular plant species and 42% of all vertebrate species as endemics. It has been estimated that about 3608 amphibians, 3723 reptiles, 3551 birds, and 1845 mammals are found as endemicsin these hotspot regions. As per the Red List of Threatened Species that have been prepared by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources , more than 79% of the threatened amphibians, 63% of the threatened birds, and 60% of the threatened mammals can be found exclusively within these hotspots. The current population data also shows that about 2.08 billion people reside in the hotspot regions and are dependent on these forest areas for their survival.
Taxonomic And Size Relationships
Less than 1% of all species that have been described have been studied beyond simply noting their existence. The vast majority of Earth’s species are microbial. Contemporary biodiversity physics is “firmly fixated on the visible world”. For example, microbial life is metabolically and environmentally more diverse than multicellular life . “On the tree of life, based on analyses of small-subunit ribosomal RNA, visible life consists of barely noticeable twigs. The inverse relationship of size and population recurs higher on the evolutionary ladderâto a first approximation, all multicellular species on Earth are insects”.Insect extinction rates are highâsupporting the Holocene extinction hypothesis.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Growth And Development In Biology
What Is A Biodiversity Hotspot
Our Earth is a treasure house of exceptional biological wealth whose distribution ranges from the high mountain peaks to the deepest ocean depths as well as from the tropical regions to the polar areas. It has been estimated that about 8.7 million species currently exist on Earth, of which only 1.2 million species have been discovered by scientists so far. The distribution of species is, however, not even around the world. Some regions possess a high concentration of endemic species that are not found anywhere else on the planet. Moreover, the earths biodiversity is facing severe threats from various anthropogenic activities. This unequal species distribution together with the concern about the high biodiversity loss has led to the identification of specific areas where high levels of both biodiversity and threats to the same exist simultaneously. The exploration and assessment of the biodiversity of such areas are, hence, very much essential for the formulation of new strategies that are required for the conservation and management of the species. The following article discusses these areas called biodiversity hotspots and the importance of conserving such places for securing our global biodiversity.
Take A Closer Look At Borneo’s Biodiversity
-
Borneo is one of just two places orangutans call home. They spend nearly their entire lives in treesswinging in tree tops and building nests for sleep.
-
This pineapple flower is one of at least 15,000 plant species on the island of Borneo.
-
The Mulu flying frog has been found in the heart of Borneo. It has bright green skin at night, but changes color during the day to a brown hue.
-
This vegetation, which is mostly a peat swamp forest, is rich with biodiversity.
-
Insects play an important role in biodiversity, too. They help keep the balance of the ecosystem.
Recommended Reading: Common Core Algebra 1 Unit 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key
Coral Joins Maui Nui Makai Network
The Coral Reef Alliance is honored to join the Maui Nui Makai Networka network of community groups from across Maui Nui that protect and care for marine and coastal ecosystems. The network was established in 2013 when community organizations decided they would be stronger working together than separately. Network members meet regularly to learnContinue Reading
Later Work On Variety Its Value And The Question Of Normativity
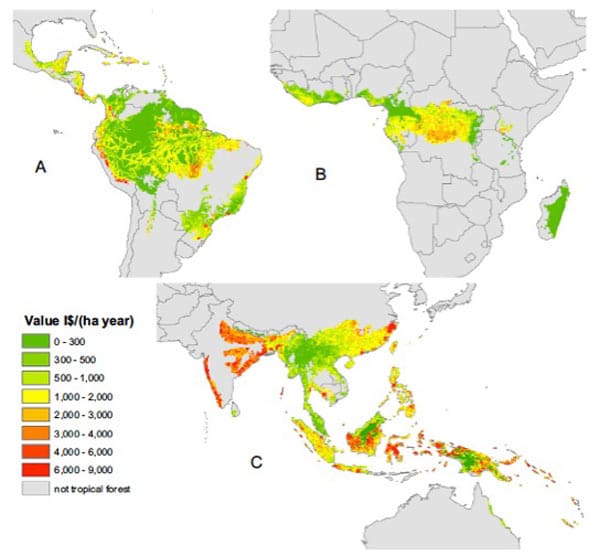
The new term biodiversity, post-1985, marked freshperspectives about what variety or diversity might mean,and what the benefits and values of biodiversity might be. There alsowas a continuation and further development of the core perspectives onvalue established during the pre-history. Wilson made the casefor a biological diversity crisis by arguing that thismeans the loss of potential uses, yet to be discovered. Wilson alsoechoed Myers and Ayensu and others arguing for the importanceof systematics and the need for discovery of species to addressknowledge gaps. Later, Wilson brought these arguments together,arguing that the new term biodiversity reflects our lackof knowledge about the components of lifes variation and theirimportance to humankind.
The pre-history perspectives, in the writings of Myers and others,influenced the Brundtland Report, a landmark United Nations report onsustainable development . This report contains themuch-quoted definition:
Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of thepresent without compromising the ability of future generations to meettheir own needs.
This is followed by a key requirement:
The loss of plant and animal species can greatly limit the options offuture generations so sustainable development requires theconservation of plant and animal species.
The reports call for governments to form a speciesconvention helped catalyse the creation of the Convention onBiological Diversity .
You May Like: How To Do Substitution In Algebra
What Is A Destination Management Organization And How Can A Dmo Protect Coral Reefs In Cozumel
Sandy white beaches, turquoise waters, and vibrant coral reefsits the type of travel destination that many of us dream of. Vacation season is quickly approaching and soon, millions of eager tourists will pack their bags and flock to some of the worlds most beautiful, sought-after destinations. But increased popularity means many of the natural resourcesContinue Reading
Biodiversity : Cooling The Climate By Mastering The Carbon Cycle
12 weekly classes with our staff scientist, Jim Laurie. He will hold two sessions every Wednesday, from 12 2 pm ET and 7 9 pm ET to accommodate students different schedules.
The Excitement and Inspiration of Science for the Curious to the Serious and everyone in-between. A fully interactive online adventure with discussions, experiments and explorations for independent thinkers of any age, suitable for high school and college students, as well as inquiring minds of all levels, from beginner to PhD!
Course Description
In this fifth course in the Biodiversity series, we will take on the challenge of maximizing photosynthesis in forests, grasslands, and oceans.
We begin the course by exploring how a healthy forest works. The class will read Finding the Mother Tree by Suzanne Simard. In this autobiography, published a few months ago, Simard describes her curiosity and love for the forests of British Columbia where she grew up. Her discoveries show a very complex symbiosis and nutrient trading system between the forest tree and the mycorrhizal fungi below the surface a wood wide web. In our previous course, Biodiversity #4, we learned how intelligent processes in the fungi networks make forests possible. Simards book shows how this was figured out from the forest perspective.
Also Check: What Does The Word Physics Mean
We Work At Multiple Scales From Local To Global To Ensure That Coral Reefs Thrive For Generations To Come
When we reduce local-level threats to reefssuch as pollution, sedimentation, overfishing, or unsustainable tourismreefs are healthier and more capable of withstanding the effects of climate change. We work in partnership with local communities, nonprofit organizations, scientists, corporations, governments, and funders to build effective and sustainable management systems that ensure reefs thrive.
We work to save coral reefs in two critically important reef regions:
Ego Vs Eco: How Human Animal And Planet Health Interconnect With Tania Roa
Beginning Wednesday, March 2, 2022, the course meets for an hour and a half each week for 8 weeks .
Tania Roa, MSc in Animals and Public Policy and advocate for wildlife and intersectional environmentalism, will lead students on an exploration of the connections between human, animal, and planet health.
You May Like: How To Calculate Ap Biology Score
Bees: Crucial Agricultural Workers
CNN , One third of all our foodfruits and vegetableswould not exist without pollinators visiting flowers. But honeybees, the primary species that fertilizes food-producing plants, have suffered dramatic declines in recent years, mostly from afflictions introduced by humans.
As German bee expert Professor Joergen Tautz from Wurzburg University adds:
Bees are vital to bio diversity. There are 130,000 plants for example for which bees are essential to pollination, from melons to pumpkins, raspberries and all kind of fruit trees as well as animal fodder like clover.
Bees are more important than poultry in terms of human nutrition.
What Factors Influence Biodiversity
Biodiversity is heavily influenced by both human and non-human factors. Throughout the module, we will spend a significant amount of time studying the negative impacts of humans on biodiversity. However, its important to remember that humans have a very complicated relationship with biodiversity. In some cases, human activities enhance biodiversity through habitat modification or periodic disturbance. In others, certain types of biodiversity are favored over others because of human influences. For these and other reasons, it is helpful to always think of biodiversity as part of a human-environment coupled system.
Biodiversity varies significantly among different regions. Polar icecaps and tropical deserts are almost devoid of life, while tropical rainforests and coral reefs are extremely biodiverse. A forest in the mid-latitudes, in places like Pennsylvania, might have 30-40 tree species per square kilometer, whereas a square kilometer of tropical rainforest in Borneo or Ecuador might have 300-400 species.
On a smaller scale, other factors have a significant influence as well. Factors that seem to foster an increase in biodiversity include:
Physically diverse habitats. If a region has a variety of different microclimates caused by variability in topography, water availability, and sunlight, its likely to have more biodiversity than a more uniform landscape.
Don’t Miss: What Is Positive Thinking In Psychology
Why Biodiversity Matters
Humans have many reasons to value biodiversity, including anthropocentric reasons and ecocentric reasons.
Anthropocentric reasons to value biodiversity include the many potentials for different lifeforms to provide scientific information, recreational benefits, medicine, food, or other materials that are useful to us. Even if we dont know what exactly some species or ecological community might be useful for, we may choose to protect it, just in case it turns out to be useful.
Ecosystem services are the services that ecosystems perform for humanity. They are a popular way of characterizing the variety of anthropocentric values surrounding parts of nature, including biodiversity. Animals, plants, and other components of every ecosystem do many things for humans such as purifying water and air, pollinating crops, maintaining a proper heat balance in the atmosphere, and cycling critical nutrients.
Ecocentric reasons to value biodiversity are based on the idea of biodiversity having intrinsic value irrespective of any potential human uses . An ecocentric perspective on valuing biodiversity would include conserving coral reefs or redwood forests on the basis that these ecosystems have a right to exist, irrespective of how, if at all, they might benefit human society.