Seniority Of Parent Compounds
The systematic name is based on the name of the senior parent compound, which is chosen by applying the following criteria in the order described below and shown in Fig. 1, until a decision is reached. For a complete set of criteria see Ref. . In the examples below, the senior parent compound is shown in blue, and a key reason is given alongside.
Characteristic Groups Suffixes And Prefixes
The presence of a characteristic group is denoted by a prefix or suffix attached to the parent name. The names of common characteristic groups are given in Table 3, in order of decreasing seniority. The most senior one, the principal characteristic group, is cited as the suffix, while all other groups are cited as prefixes. Note that, for nomenclature purposes, CC multiple bonds are not considered to be characteristic groups .
* Here indicates that the carbon atom is implied by the parent name.
** Here means that the group R is expressed as a separate prefixed word.
*** Note: mercapto is no longer acceptable .
Depending on the number and arrangement of carbon-containing suffix groups, the carbon atom can be a part of the parent compound OOH, oic acid) or may be treated as an attachment to a parent compound .
Other characteristic groups on a parent compound are represented by appropriate prefixes cited in alphabetical order , including also ethers , oxy; sulfides , sulfanyl; Br, bromo; Cl, chloro; F, fluoro; I, iodo; and NO2, nitro.
Components Of Systematic Substitutive Names
The most common components of a substitutive chemical name are illustrated with reference to the chemical structure shown in Table 1, along with its systematic name and the components of the name.
Components of the substitutive name
| suffix for principal characteristic group |
| en |
| enclosing marks |
Locants indicate the position of substituents or other structural features. They are generally placed before the part of the name that indicates the corresponding structural feature. Three kinds of enclosing mark are used, in the nesting order , when it is necessary to indicate which parts of a name belong together.
Multiplicative prefixes are used when more than one fragment of a particular kind is present in a structure. Which kind of multiplicative prefix is used depends on the complexity of the corresponding fragment e.g. trichloro, but tris.
Multiplicative prefixes for simple and complicated entities.
| No. |
|---|
| icosakis |
Read Also: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
How Do You Identify Organic Compounds
Organic compound, one of a large class of chemical compounds in which one or more carbon atoms are covalently associated with other elementsâ atoms, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. The few compounds that contain carbon that are not classified as organic include carbides, carbonates, and cyanides.
Known Problems And Limitations
The lack of coverage and limitations for many areas of chemical structures has been noted above. While many of the primary limitations are now being addressed by the various IUPAC Division VIII working groups, some of the most often cited comments are as follows:
-
Standard InChI only distinguishes some types of stereo chemistry .
-
InChI currently does not handle mixtures well .
-
InChI is not a file format .
-
InChIKey, the hashed InChI, is limited, in very few cases to date, in terms of variations it can support .
-
InChI does not yet work for large drug molecules .
-
InChI does not handle all tautomers well in standard InChI, which is now being addressed by a new working group.
-
Standard InChI does not honor bonds to metals.
-
InChI is difficult to read for humans.
Read Also: How Do You Find Displacement In Physics
Number The Carbons In The Carbon Chain
There are two hydroxyl groups attached to the main chain. If we number as shown in red they are attached to the first and second carbon atoms. If we number as shown in blue they are attached to the third and fourth carbon atoms.
The functional groups should have the lowest numbers possible. Therefore the red numbering is correct. The hydroxyl groups are attached to the first and second carbon atoms .
Iupac Nomenclature Of Organic Chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry . It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry . Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
To avoid long and tedious names in normal communication, the official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice, except when it is necessary to give an unambiguous and absolute definition to a compound. IUPAC names can sometimes be simpler than older names, as with ethanol, instead of ethyl alcohol. For relatively simple molecules they can be more easily understood than non-systematic names, which must be learnt or looked over. However, the common or trivial name is often substantially shorter and clearer, and so preferred. These non-systematic names are often derived from an original source of the compound. Also, very long names may be less clear than structural formulas.
Also Check: What Is An Ion In Chemistry
The Selection Of Parent Chain:
The first step in naming an organic compound is to select the parent chain and give the root word based on the number of carbon atoms in it.
The parent chain in an organic molecule is the longest continuous carbon chain containing as many functional groups, double bonds, triple bonds, side chains and substituents as possible.
Examples:
i);In the following molecule, the longest chain has 6 carbons. Hence the word root is “hex-“. Note that the parent chain may not be straight.
ii);The root word for the following molecule is “hept-” since the longest chain contains 7 carbons.;
Do not come under the impression that the ethyl groups are side chains and the longest chain contains 5 carbons.;
The shaded part shows the longest chain that contains 7 carbons. Also look at the alternate way of writing this molecule in which the ethyl groups are expanded to -CH2CH3.
iii) In the following molecule, there are three chains of equal length .
However, the chain with more number of;substituents is to be taken as the parent chain. Thus “hept” appears as word root in the IUPAC name of this compound.
iv) The double bonds and triple bonds have more priority than the alkyl side chains and some other substituents like halo, nitro, alkoxy etc. Hence, whenever there are two or more chains with equal number of carbons, the chain that contains double or triple bond is to be selected as the parent chain irrespective of other chain containing more number of substituents.;
Iupac Nomenclature For Organic Compounds
When it comes to the naming of organic compounds using IUPAC standards, the naming has three fundamental parts. These include the substituents, mainly the atoms or group of atoms that have replaced one or more hydrogen atoms on the hydrocarbon chain, then the carbon chain length, and the third is the chemical end.;
The substituents are any of the functional groups that have been linked with the main carbon chain. The main carbon chain is also the longest unbroken chain that is possible. As for the chemical end, it signifies the precise kind of molecule that is present. To illustrate, if it ends in ane, it refers to a carbon chain with a single bond, like hexane or propane.;
Another instance of the IUPAC naming system for organic compounds will be with a compound called cyclohexanol. The name sounds simple enough, but it packs a lot of meanings. For example, the substituent name here cyclo stands for a ring compound, and it denotes a set of atoms in the compound arranged in the shape of a ring.;
Then there is an indication of the substituent name, which points to a six-carbon chain, explaining the hex. The ol is the chemical ending denoting alcohol, while the ane is a chemical ending that shows for a single-bonded carbon chain. Then, of course, the anol indicates a pair of chemical ends that have been combined these refer to a carbon chain with a single bond but with alcohol that has been linked to it.;
Read Also: What Does Algebra 2 Look Like
Roman Lusitania And Gallaecia
Romans first invaded the Iberian Peninsula in 219 BC. The Carthaginians, Rome’s adversary in the , were expelled from their coastal colonies. During the last days of , almost the entire peninsula was annexed to the .
The Roman conquest of what is now part of Portugal took almost two hundred years and took many lives of young soldiers andthe lives of those who were sentenced to a certain death in the slave mines when not sold as slaves to other parts of the empire. It suffered a severe setback in 155 BC, when a began in the north. The and other native tribes, under the leadership of , wrested control of all of western Iberia.
Rome sent numerous legions and its best generals to Lusitania to quell the rebellion, but to no avail the Lusitanians kept conquering territory. The Roman leaders decided to change their strategy. They bribed Viriathus’s allies to kill him. In 139 BC, Viriathus was assassinated and became leader of the Lusitanians.
Rome installed a colonial regime. The complete Romanization of Lusitania only took place in the era.
Several works of engineering, such as baths, temples, bridges, roads, circuses, theatres and laymen’s homes are preserved throughout the country. Coins, some coined in Lusitanian land, as well as numerous pieces of ceramics, were also found. Contemporary historians include and , bishop of , who reported on the final years of the Roman rule and arrival of the .
What Is The Iupac And What Does It Do
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
The IUPAC is the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. It is an international scientific organization, not affiliated with any government. The IUPAC strives to advance chemistry, in part by setting global standards for names, symbols, and units. Nearly 1200 chemists are involved in IUPAC projects. Eight standing committees oversee the Union’s work in chemistry.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Like Biology
Overview Of The Iupac Naming Strategy
No headers
learning objectives
- name alkanes, cycloalkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alkyl halides, ethers, alcohols, amines, benzene and its derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives using IUPAC and selected common name nomenclature
- draw the structure of alkanes, cycloalkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alkyl halides, ethers, alcohols, amines, benzene and its derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives from the IUPAC and selected common names
Overview of the IUPAC System for Naming Organic Compounds
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry has established the rules of nomenclature of all chemical compounds. IUPAC nomenclature can also be called “systematic” nomenclature because there is an overall system and structure to the names. This section provides an overview of the general naming strategy and structure for organic compounds.
Naming organic compounds according to the IU{AC system requires up to four pieces of information
1. recognize & prioritize the functional group present
2. identify & number the longest continuous carbon chain to give the highest ranking group the lowest possible number
3. cite the substituents alphabetically using the numbering determined above
4. recognize & classify any stereochemistry
With these four pieces of information, the IUPAC name is written using the format below. This same format applies to ALL the organic compounds.
Stereochemistry
What Is Iupac Name
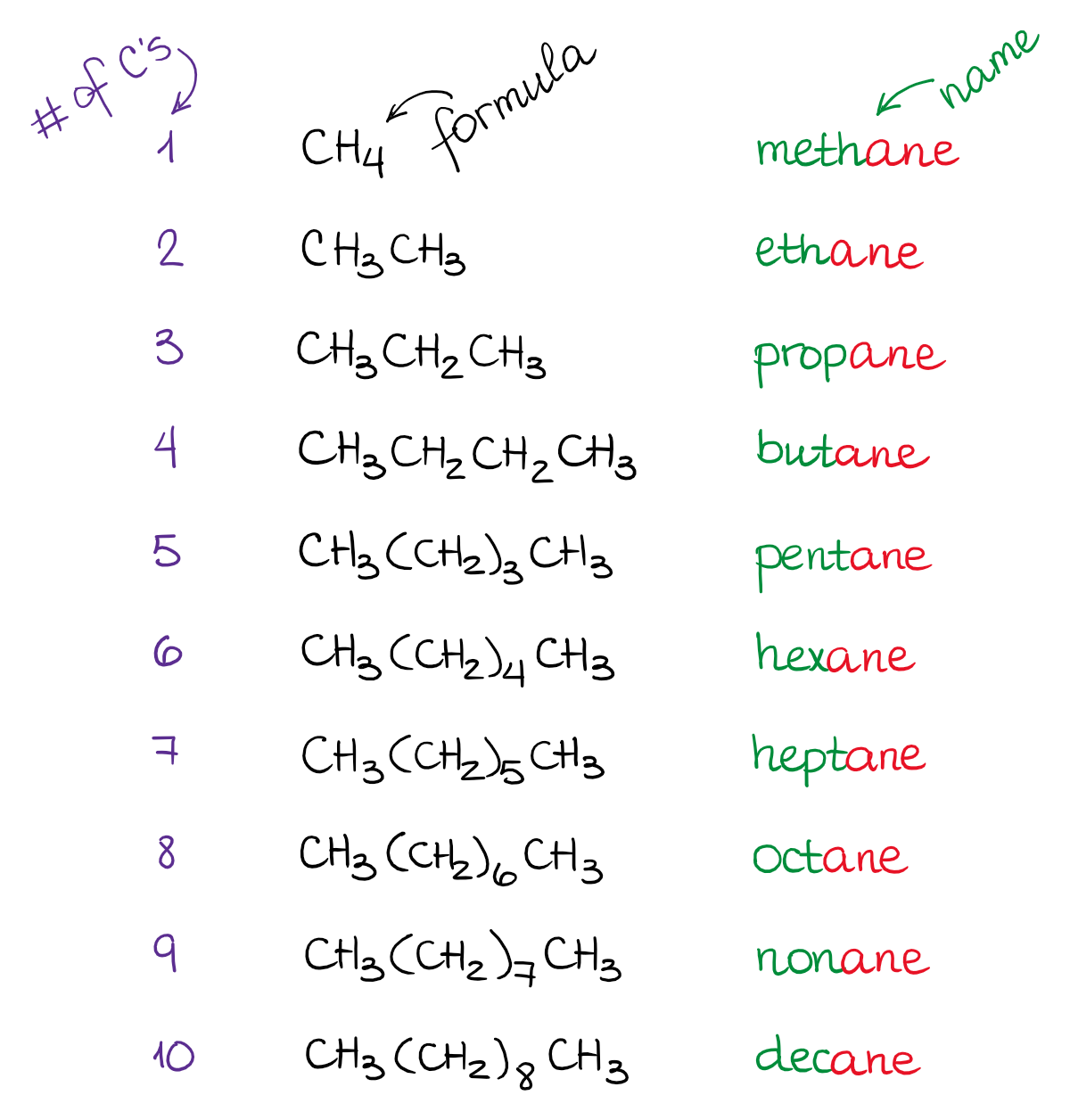
The IUPAC names are the internationally accepted method of naming chemical compounds. In general, it can be further divided into two main categories; inorganic compounds and organic compounds. No matter how many branches and how long the molecular structure is; IUPAC names can be used to name any range of molecules. But, it is really difficult to name chemical compounds accurately, without having the proper knowledge about these rules.
CaCO3 Calcium Carbonate
You May Like: What Does Competition Mean In Biology
Reconstruction Era Through Late 19th Century
Following the collapse of the Confederacy in 1865, North Carolina, along with the rest of the former Confederate States, was put under direct control by the and was relieved of its and representation within the in what is now referred to as the . In order to earn back its rights, the state had to make concessions to Washington, one of which was ratifying the . Congressional Republicans during Reconstruction, commonly referred to as “”, constantly pushed for new constitutions for each of the Southern states that emphasized on equal rights for African-Americans. In 1868, a constitutional convention restored the state government of North Carolina. Though the was also adopted that same year, it remained ineffective for almost a century, not to mention paramilitary groups and their with impunity.
The elections in April 1868 following the constitutional convention led to a narrow victory for a Republican-dominated government, with 19 African-Americans holding positions in the . In attempt to put the reforms into effect, the new Republican Governor declared martial law on any county allegedly not complying with law and order using the passage of the .
What Is Iupac Nomenclature
| A column about the Principles of Chemical NomenclatureA Guide to IUPAC Recommendations, 2011 Edition |
What is IUPAC Nomenclature?
This series, written by Jeffery Leigh, will provide short notes and briefs about Principles of Chemical Nomenclature. Each column will address a specific topic such as systematic nomenclature, the constructing of names, or the use of abbreviations. Questions, suggestions, and reactions are welcome: .
Nobody, except a few pedants, enjoys working on chemical nomenclature. However, accurate and widely accepted nomenclature is a vital need for communication amongst more than academic chemists. For example, politicians writing treaties and customs officers inspecting trade goods need to know exactly what materials they are dealing with. It is now generally accepted that IUPAC should be responsible for providing this kind of nomenclature for the world to use. IUPAC chemical nomenclature is widely regarded as the world standard. When a nomenclature question arises, the first reaction is often: what is the name that IUPAC gives? Principles of Chemical Nomenclature is an attempt to show people how to find the name they require, but it also explains the misunderstandings that may arise before such a process is complete.
Next in this series will be a review of the contents of Principles.
Recommended Reading: What Is Psychometrics In Psychology
Largest Combined Statistical Areas
North Carolina has three major with populations of more than 1.6;million :
- : CharlotteConcordGastonia, North CarolinaSouth Carolina population 2,728,933
- : RaleighDurhamChapel Hill, North Carolina population 2,238,315
- : GreensboroWinston-SalemHigh Point, North Carolina population 1,677,551
| 1.3% | 2.3% |
At the 2010 U.S. census, the racial composition of North Carolina was: : 68.5% , or : 21.5%, and of any race: 8.4%, : 4.3%, : 2.2%, : 2.2%, and and : 1%. At the 2019 , the racial and ethnic makeup of North Carolina was 62.6% non-Hispanic white, 22.2% Black and African American, 1.6% American Indian or Alaska Native, 3.2% Asian, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 2.3% two or more races, and 9.8% Hispanic or Latin American of any race.
| 0.01% |
North Carolina is home to a spectrum of different dialects of and .
In 2010, 89.66% of North Carolina residents age five and older spoke English at home as a , while 6.93% spoke Spanish, 0.32% French, 0.27% German, and Chinese was spoken as a by 0.27% of the population five and older. In total, 10.34% of North Carolina’s population age five and older spoke a other than English. In 2019, 87.7% of the population aged 5 and older spoke English and 12.3% spoke another language. The most common non-English language was Spanish at the 2019 .
| Other faith | 1% |
Independence And Afonsine Era
On 24 June 1128, the occurred near . , Count of Portugal, defeated his mother and her lover , thereby establishing himself as sole leader. Afonso then turned his arms against the Moors in the south.
Afonso’s campaigns were successful and, on 25 July 1139, he obtained an overwhelming victory in the , and straight after was unanimously proclaimed by his soldiers. This is traditionally taken as the occasion when the County of Portugal, as a fief of the Kingdom of León, was transformed into the independent .
Afonso then established the first of the at , where he was crowned by the Archbishop of Braga, though the validity of the Cortes of Lamego has been disputed and called a myth created during the . Afonso was recognized in 1143 by King , and in 1179 by .
During the period, Christians reconquered the Iberian Peninsula from domination. Afonso Henriques and his successors, aided by military , pushed southward to drive out the Moors. At this time, Portugal covered about half of its present area. In 1249, the Reconquista ended with the capture of the and complete expulsion of the last Moorish settlements on the southern coast, giving Portugal its present-day borders, with minor exceptions.
The reigns of , , and for the most part saw peace with the Christian kingdoms of Iberia.
Recommended Reading: Is Ap Physics C Hard
Scope Of Nomenclature For Organic Compounds
For nomenclature purposes all compounds containing carbon as the principal element to be organic compounds are qualified. Oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen are the three elements usually associated with carbon to form the system of functional or characteristics groups. Other elements, among them the halogens and sulfur complete the basic core of elements found in organic compounds. Substitutive nomenclature was first applied to compounds containing this set of atoms. The success of this type of nomenclature was such that it was extended to all elements of Groups 14, 15, 16, 17 and in Group 13 to boron; it could be extended to all elements of Group 13.