The Broad Reach Of Suburban Poverty
A key feature of the growth of suburban poverty in the 2000s is that it was not isolated to particular regions or parts of the country. Almost every major metro area experienced a significant increase in the suburban poor population between 2000 and 2015, and two-thirds of those regions now find the majority of the poor population in the suburbs. Some of the steepest upticks occurred in fast-growing metro areas in the Sun Belt and Intermountain West, like the Cape Coral , Austin , Atlanta , and Las Vegas metro areas, each of which saw its suburban poor population more than double.
What Is The Buenos Aires Suburbs
The Buenos Aires suburbs is a strip of territory that surrounds the Federal Capital of Argentina. This has been the case since 1994 thanks to a constitutional reform that determined that the capital became a politically autonomous city.
From that year on, a geographical separation between the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires and the conglomerate that surrounds it, that is, the Buenos Aires suburbs, also called Greater Buenos Aires, begins to be made.
Although the terms “Buenos Aires suburbs” and “Greater Buenos Aires” are often used interchangeably, in reality the latter also includes the Federal Capital.
Another term used to name the suburbs is the Metropolitan Area of Buenos Aires and others are now more obsolete as the Metropolitan Area of Buenos Aires or the Metropolitan Region of Buenos Aires .
In any case, they refer to the same area that begins at the limit point of the Federal Capital, very well identified by Avenida General Paz -which surrounds the city to the north and west- and by the Riachuelo in the south.
The east of the Capital has the natural limit of the Río de la Plata.
Case Study Of Urban Sprawl And The Brownfield Versus Greenfield Debate Newcastle Great Park And Scotswood
Newcastle Great Park is controversial housing and high-tech industrial scheme developed at the Northern edge of the city within the greenbelt. Building of the suburb started in 2001. It is located in the north of Newcastle next to Gosforth and the government gave special permission for this development to go ahead.
There are many different interest groups who think the development should go ahead including the developers , the government and the council and some homeowners. Conservationists and environmentalists, some homeowners and some urban planners think the scheme is a bad idea. Newcastle Great Park is also close to the A1 road.
It is a major development with land allocated for:
- A Business Park
- Play Areas and Outdoor Sport
The scheme is being delivered by the Great Park Consortium, which includes the house builders Persimmon Homes, and Taylor Wimpey. Parts of the development have also been built by Barratt.
Read Also: Is Paris Jackson Michael’s Biological Child
Suburbs: The Geography That Won’t Die
For a half century, suburbs have been blamed for just about everything — from racial division to obesity and even global warming. Yet desperate as life in the burbs is said to be, the majority of Americans — and roughly 85% of those in metropolitan areas — still live in the classic, tree-lined, single-family house and auto-dominated communities that, whether in core city boundaries or not, are essentially suburban communities.
Increasingly, new urbanists, many greens and developers believe that the suburbs peaked, and face an irrepressible decline as the masses swarm into the inner cities. “We’ve reached the limits of suburban development: People are beginning to vote with their feet and come back to the central cities,” said HUD Secretary Shaun Donovanin 2010.
Too bad Mr. Secretary didnt talk to the people over at the Department of Commerce who run the Census. In fact, Americas population growth in the 2010 decennial Census was more suburban than in the previous decade. In the 2000s roughly 90% of metropolitan growth was in the suburbs, somewhat higher than in the previous decade. Overall, notes demographer Wendell Cox, since 1990 the countrys metropolitan regions have gone from 82 to 86% suburban.
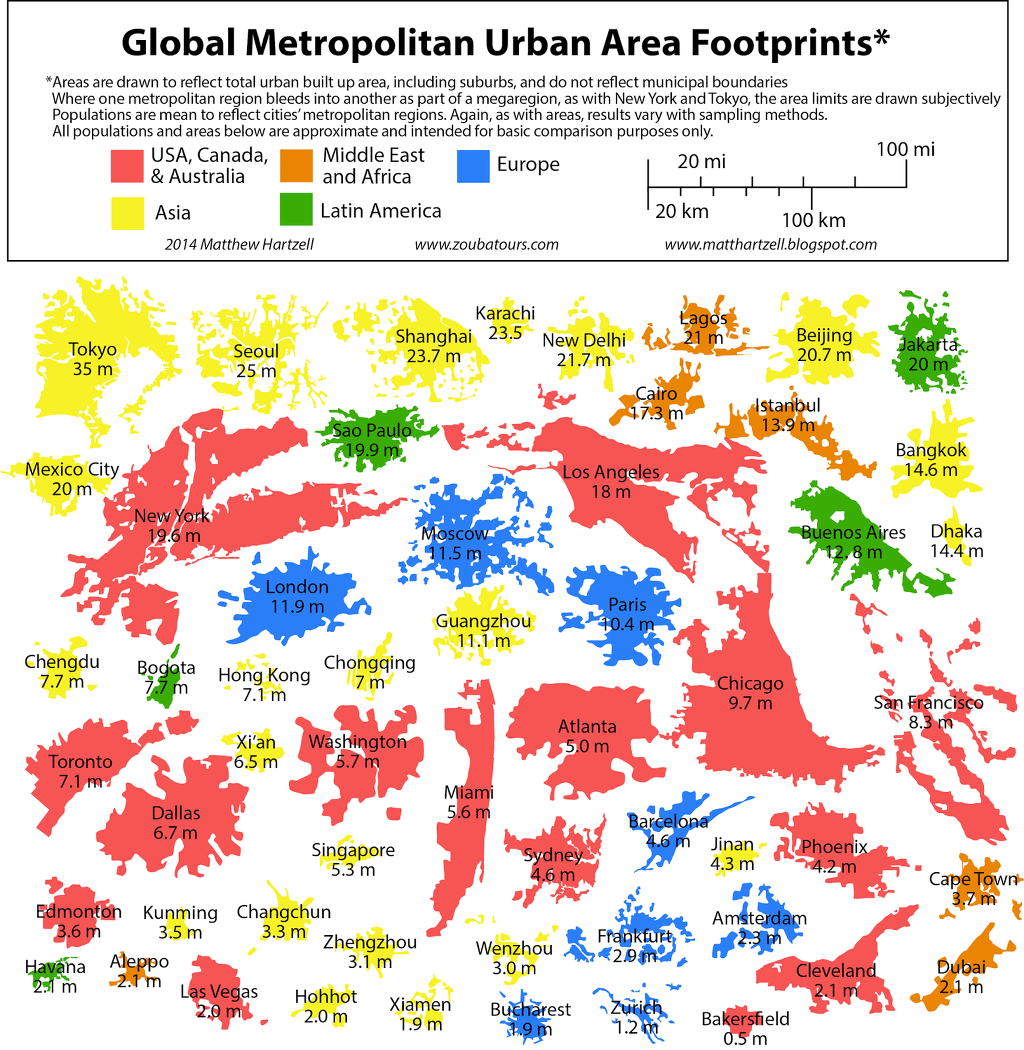
The Changing Geography Of Us Poverty
Editor’s Note:
Testimony before the House Ways and Means Committee, Subcommittee on Human Resources, February 15, 2017
Chairman Smith, Ranking Member Davis, and members of the Subcommittee, thank you for the invitation to appear before you today. In my testimony, I will provide information on the changing geography of poverty in the United States , key factors that have driven these shifts as well as challenges raised by them, and implications for efforts to effectively address poverty and promote opportunity across different kinds of communities.
While these issues have been the subject of my research at the Brookings Institutions Metropolitan Policy Program, the views expressed in this testimony are my own. The Brookings Institution does not take institutional positions on policy issues.
Also Check: How To Find Hybridization Chemistry
Why Is Land Cheaper In The Suburbs
The suburbs Typically, they are detached or semi-detached and the roads around them are arranged in cul-de-sacs and wide avenues. Land prices are generally cheaper than in the CBD and inner city, although the desirability of housing can make some areas expensive.
Does inner city mean poor?
Inner city is a uniquely American term. In its common usage, it signifies poor, black, urban neighborhoods. The term somehow applies regardless of whether such neighborhoods are downtown or central to the city grid. The Bronx is an outer borough of New York City.
The History And Evolution Of Suburbs
Suburbs are generally spread out over greater distances than other types of living environments. For instance, people may live in the suburb in order to avoid the density and untidiness of the city. Since people have to get around these vast stretches of land automobiles are common sights in suburbs. Transportation plays an important role in the life of a suburban resident who generally commutes to work.
People also like to decide for themselves how to live and what rules to live by. Suburbs offer them this independence. Local governance is common here in the form of community councils, forums, and elected officials. A good example of this is a Home Owners Association, a group common to many suburban neighborhoods that determines specific rules for the type, appearance, and size of homes in a community.
People living in the same suburb usually share similar backgrounds with regard to race, socioeconomic status, and age. Often, the houses that make up the area are similar in appearance, size, and blueprint, a layout design referred to as tract housing, or cookie-cutter housing.
Also Check: How Did Life Begin Biology
What Is The Inner City Made Up Of
Location of the inner city In older cities, the inner city area is near the centre and surrounding the CBD. Inner city areas are identified not only by their physical features but often by negative socio-economic features , eg derelict buildings , waste ground and run-down housing.
What is outer suburbs in geography?
Outer Suburbs residential area towards the edge of a city, characterised by larger often detached houses and modern housing estates. Urban Sprawl the uncontrolled growth of an urban area into the surrounding countryside.
Suburban Sprawl: History In The Us
Suburban sprawl began in the early 1800s as larger estate developments outside of cities by wealthy individuals in both the US and UK. Although unattainable for middle-class workers, much of this changed after World War II. As war veterans flew back to the US and needed to integrate as civilians again, the US federal government took proactive measures to help them through a series of legislation and programsnotably through the creation of the GI Bill in 1944 and through President Truman’s Fair Deal legislation from 1945 to 1953.
The creation of the GI Bill in 1944 provided veterans with a series of benefits from employment, free tuition, loans for homes, businesses, farms, and universal healthcare. Later, the Housing Act of 1949, part of the Fair Deal, created housing developments outside of cities for very cheap, in the form of what we would now call suburban sprawl. The combination of the GI Bill and the Housing Act began to fuel initial suburban sprawl development in the US.
Fig. 3 – Levittown, Pennsylvania one of the earliest suburban developments made possible with the Fair Deal and GI Bill
Aside from cheaper land costs, major waves of migration to the suburbs also occurred due to racism. Rising stigmas not only against minority groups, but the social and economic mixing seen in cities drove white, more affluent people out of cities . Racial segregation, along with practices such as redlining and blockbusting were supported at financial and institutional levels.
Recommended Reading: What Does Relationship Mean In Math Terms
Interwar Suburban Expansion In England
Suburbanisation in the interwar period was heavily influenced by the garden city movement of Ebenezer Howard and the creation of the first garden suburbs at the turn of the 20th century. The first garden suburb was developed through the efforts of social reformerHenrietta Barnett and her husband inspired by Ebenezer Howard and the model housing development movement , as well as the desire to protect part of Hampstead Heath from development, they established trusts in 1904 which bought 243 acres of land along the newly opened Northern line extension to Golders Green and created the Hampstead Garden Suburb. The suburb attracted the talents of architects including Raymond Unwin and Sir Edwin Lutyens, and it ultimately grew to encompass over 800 acres.
During the First World War the Tudor Walters Committee was commissioned to make recommendations for the post war reconstruction and housebuilding. In part, this was a response to the shocking lack of fitness amongst many recruits during World War One, attributed to poor living conditions a belief summed up in a housing poster of the period “you cannot expect to get an A1 population out of C3 homes” referring to military fitness classifications of the period.
Post-war suburban expansion
Causes Of Suburban Sprawl
There are several questions people must ask themselves: Where will they live? Where will they work, go to school, start a business, or retire? How will they transport themselves? What can they afford?
Suburban sprawl is primarily caused by increasing housing costs, population growth, lack of urban planning, and changes in consumer preferences. Among these issues, there’s also the matter of the history of suburban sprawl, especially in the US.
Although there are other causes of suburban sprawl, these are the main contributors!
Housing demands and costs have steadily increased in the US over the last few decades.2 This is due to the high demand for homes and lower home construction. As a result, house prices within cities are high, while prices in more sprawled areas outside of urban cores are significantly lower. Population growth contributes to this, as more people move into cities and compete for housing.
A lack of strong urban planning both within cities and regionally, where most of the sprawl occurs, is also an important factor. The US federal government has few strong laws on urbanizing states, regions, and cities often have their own different laws. With a lack of centralized planning, sprawl appears as an easier and cheaper remedy.
Read Also: Predict The Geometry And Polarity Of The Cs2 Molecule
Growing Concentrations Of Poverty
Differences are less striking across the urban and suburban poor populations as a whole than they are across neighborhoods at different levels of poverty, regardless of where they are located. Poor neighborhoods tend to cluster disadvantages that create a drag on upward mobility and the long-term prospects of residents getting out of poverty over time.5
That is especially concerning because, after making gains in the 1990s toward de-concentrating poverty , the 2000s marked a rapid re-emergence of concentrated disadvantage, particularly in the post-recession period, that essentially erased earlier progress.6
The number of extremely poor neighborhoods in the United States more than doubled between 2000 and 2010-14, as did the share of poor residents living in them. While concentrated poverty historically has been a largely urban challenge, the fastest growing concentrations of poverty in the 2000s emerged beyond the urban core. Suburbs saw the number of poor residents living in distressed neighborhoods grow by 188 percent, ahead of small metro areas , rural communities , and cities .
Difference Between Urban And Suburban
Categorized under Geography,Miscellaneous | Difference Between Urban and Suburban
Urban vs. Suburban
What are urban and suburban areas? The cause of confusion lies in the definition attached to each term. Nevertheless, it is important to know that the meaning of an urbanized or suburban territory may be differently perceived among the various countries.
Generally, suburban areas , pertain to residential districts. A suburb can also mean the surrounding residential areas of a bigger city, and a group of these can collectively be regarded as the suburbs. They can actually form a part of a really big city, or they can be several aggregates of distant residential areas. Quite often, it is seen that suburbs have a lower population density when compared to urban territories.
As mentioned, suburban areas are defined differently in some countries. Take Canada and America for example these countries both define suburban as a different municipality from the major city. In the Australian region, suburban can also refer to a residential area, which is more or less a subdivision of the city. This scheme is devised for better postal servicing. Lastly, other population and statistics experts commonly agree that suburban areas are places outside the inner, or main, city. The only mistake is these places are sometimes considered as urban areas, which adds even more confusion.
1. Urban areas have a bigger population density compared to suburban areas
Read Also: What Is The Physical Geography Of Africa
In Australia New Zealand And South Africa
In Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, suburban areas have become formalised as geographic subdivisions of a city and are used by postal services in addressing. In rural areas in both countries, their equivalents are called localities ” rel=”nofollow”> suburbs and localities). The terms inner suburb and outer suburb are used to differentiate between the higher-density areas in proximity to the city centre , and the lower-density suburbs on the outskirts of the urban area. The term ‘middle suburbs’ is also used. Inner suburbs, such as Te Aro in Wellington, Eden Terrace in Auckland, Prahran in Melbourne and Ultimo in Sydney, are usually characterised by higher density apartment housing and greater integration between commercial and residential areas.
In New Zealand, most suburbs are not legally defined, which can lead to confusion as to where they may begin and end. A geospatial dataset defining suburbs for use by emergency services is developed and maintained by Fire and Emergency New Zealand and is published under an open license.
Characteristics Of The Buenos Aires Suburbs
This area bordering the Argentine capital sits on a plateau with depressions through which rivers and streams run, and has a large river front over the delta of the Paraná River and the Río de la Plata.
It has a benign climate whose temperatures are usually between 2 and 3 degrees below the temperature of the capital. Together with the capital, it produces more than half of the country’s Gross Domestic Product , thanks to a booming industry.
You May Like: How To Study For Chemistry In College
Brief History Of Gated Communities Developments
Since the nineteenth century, suburbs of the Western world increasingly became the preferred location of urban visions that sought to make up for the perceived shortcomings of urban centres. Garden cities, planned suburban developments, and gated communities are all different models of urbanisation associated with this tradition. Yet, while their urban forms are similar, their aims and historical contexts differ. The British planned suburb that gives rise to the Garden City movement of the nineteenth century is not the inspiration for the gated communities of the global South. While these suburban developments were conceived to be self-sufficient, providing places for living and working, and including residential and industrial land uses , gated communities of today are dormitory communities.
Tanveer Islam, Jeffrey Ryan, in, 2016
Effects Of Suburban Sprawl
Aside from car dependency, there are also numerous environmental effects of suburban sprawl. The discussion of the negative effects of suburban sprawl has taken a long time not only to witness but to calculate. This is primarily because institutions have promoted suburban sprawl for a long time, believing it was a healthier and more environmentally sustainable form of development. However, suburban sprawl is linked with land loss, higher vehicle travel, resource use, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Read Also: Intermediate Algebra Custom New York City College Of Technology Custom
Suburbanisation: Characteristics Causes And Effects
Suburbanisation can be defined as the outward growth of urban development which may engulf surrounding villages and towns into a larger urban agglomeration. Indeed, the suburbs are the outlying areas of a city which are close enough to the city centre to be accessible by commuters.
Both people and businesses can be involved in this suburbanisation process.
Essentially it is a part of urbanisation, in that it increases the proportion of people that live in towns and cities in comparison to those in rural areas. As suburbs grow they attract both people from rural areas AND from inner city and CBD areas, who are attracted by the greater amount of space within the suburb. Suburbanisation results in the physical spreading of a city into surrounding countryside areas, known as URBAN SPRAWL, and this puts pressure on greenfield sites and on nature. In Britain the suburbs are predominantly residential in nature and have often rural characteristics such as larger gardens and to tree-lined avenues.
Types of suburbs
Not all suburbs are the same, and there are several distinguishable types. Although many suburbs are populated by the urban middle class, they are not uniform in many respects. In the UK, the TIME when they were built, the planners that were involved and the physical surroundings of the environment can all influence the characteristics and layout of a suburb.
4. Councils also built social housing estates at the edge of cities, such as Kenton in Newcastle.