The Basics Of Behaviorism
Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s, largely in response to other popular schools of thought at the timeincluding Freudian psychology, which emphasized the importance of unconscious thoughts and urges. Early behaviorists aimed to transform psychology into a more objective scientific discipline that, like biology or chemistry, focused on measurable, observable phenomenon, rather than the unobservable internal phenomena that Freud and his contemporaries prioritized. Classical behaviorists did not deny that humans have thoughts and emotions rather, they argued that because such internal cognitions could not be measured or documented, they were not relevant for the study of human behavior. Though such theories have been largely discounted, some elements of behaviorismparticularly those related to radical behaviorism, a theory promoted by noted psychologist B.F. Skinnerremain in use today
Factors That Impact Conditioning
During the first part of the classical conditioning process, known as acquisition, a response is established and strengthened. Factors such as the prominence of the stimuli and the timing of the presentation can play an important role in how quickly an association is formed.
When an association disappears, this is known as extinction. It causes the behavior to weaken gradually or vanish. Factors such as the strength of the original response can play a role in how quickly extinction occurs. The longer a response has been conditioned, for example, the longer it may take for it to become extinct.
What Is Behaviorism With An Example
An example of behaviorism is using systematic desensitisation in the treatment of phobias. The individual with the phobia is taught relaxation techniques and then makes a hierarchy of fear from the least frightening to the most frightening features of the phobic object.
He then is presented with the stimuli in that order and learns to associate the stimuli with a relaxation response. This is counter conditioning.
Also Check: What Happened To Cool Math Games
What Does All Of This Mean
If you are attempting to understand what all of this means for you, then you needn’t be too concerned with it. These are all theories, after all. Some of them may seem to have more credibility than others because of scientific data to back up the ideas that are being put forth. However, it would be wrong to say that any of the concepts that we mentioned are the end-all, be-all when it comes to explaining human behavior. In all probability, a part of human behavior can be explained by each of the theories, and they are all worthy of merit or at least consideration.
When it comes to how you conduct yourself, you are the one who gets the final say in what you do. There might be cultural impulses at play that you have learned, biological ones, and others as well. The older you get and the more experienced you become, though, the better control you will presumably have over your actions. This affords you a great degree of freedom as well as personal responsibility because you don’t ever have to say that you acted a certain way based on how you were raised or anything else. Instead, you can govern your actions as you think best whatever it is that is happening around you at any given time.
How Behavioral Techniques Are Used In A Treatment Setting
The ideas supported by behaviorism may also be applied in a treatment setting for therapeutic and behavioral modification purposes.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a great example of applying these concepts as a form of treatment. CBT focuses on the cognitive factors and thoughts behind certain behaviors and helps a person to become aware of those and their effects in an attempt to modify one’s thought processes in reaction to certain stimuli and situations, therefore allowing them to make changes to their behaviors in the process.
Applied behavior analysis uses behavioral techniques by using positive reinforcement to encourage replacing behaviors in an individual with more desired ones. It focuses strictly on the aspect of behavior modification rather than involving any sort of talk therapy like CBT to under the how’s and why’s associated with a person’s behavior.
Social learning theory is a concept displayed in cases such as the Bobo doll experiment: that many behaviors are learned by observation in social situations and then imitated. In a treatment setting, this is often applied to those struggling with addiction and in social work situations. It often involves surrounding those with stimuli and observable negative factors in their lives with positive role models and support systems to encourage more desirable behavior and habits and reduce the likelihood of the actions and reactions one wants to be rid of.
Recommended Reading: How Does Geography Affect Culture
Strengths And Weakness Of Behavioral Psychology
- Behavioral psychology has some strengths. Behaviorism is based on observable behaviors, so it is sometimes easier to quantify and collect data when conducting research. Effective therapeutic techniques such as intensive behavioral intervention, behavior analysis, token economies, and discrete trial training are all rooted in behaviorism. These approaches are often very useful in changing maladaptive or harmful behaviors in both children and adults.
- It also has some weaknesses. Many critics argue that behaviorism is a one-dimensional approach to understanding human behavior. They suggest that behavioral theories do not account for free will and internal influences such as moods, thoughts, and feelings. Also, it does not account for other types of learning that occurs without the use of reinforcement and punishments. Moreover, people and animals can adapt their behavior when new information is introduced even if that behavior was established through reinforcement.
William Carpenters Mental Physiology
Carpenter, an English physician, had authored a popular text on human physiology with a final chapter outlining psychology. Due to popular acclaim, that chapter was expanded to a 737-page book, Principles of Mental Physiology, first published in 1874. William James frequently cited Carpenter, for instance, in his classic, Principles of Psychology, particularly in Chapter IV, where James included very long excerpts. Here is a sample of what Carpenter taught, with my italicized comments enclosed within brackets. Each of these points was elaborated and illustrated at great length, so the following is not just a recounting of isolated aphorisms :
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Behavior Informatics And Behavior Computing
With the fast growth of big behavioral data and applications, behavior analysis is ubiquitous. Understanding behavior from the informatics and computing perspective becomes increasingly critical for in-depth understanding of what, why and how behaviors are formed, interact, evolve, change and affect business and decision. Behavior informatics and behavior computing deeply explore behavior intelligence and behavior insights from the informatics and computing perspectives.
Behavioral Perspective: Ap Psychology Crash Course
- The Albert Team
The behavioral perspective is all about acting throughout life as a result of some form of motivation or incentive. It relates to the reasons that an individual will participate in any given act rather than the way that they react. This perspective seeks to better explain the physiological needs of any living organism, as well as the way motivation can impact behavior. It considers different types of motivation and how different levels of motivation can impact the amount or type of work or effort that an individual will be willing to put forth.
This AP® Psychology crash course will prep you for the free response questions that you will see on your AP® Psychology exam. It will look at why someone will work harder for a better outcome. Though it hasnt been on the AP® Psychology exams free response section for some time, there have been questions on the differences between the behavioral perspective and other psychological perspectives.
Also Check: Who Was The First Psychologist To Use Psychology In Advertising
What Is Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology is the study of changing human behaviors through analysis and therapy. The theory behind behavior psychology is the environment shapes human behaviors, so therapists can help people change their behaviors by modifying how they react to their environment.
Related:22 Different Types of Psychology
Three Types Of Behaviorism
Methodological behaviorism is a normative theory about the scientificconduct of psychology. It claims that psychology should concern itselfwith the behavior of organisms . Psychology should not concern itself with mental states orevents or with constructing internal information processing accountsof behavior. According to methodological behaviorism, reference tomental states, such as an animals beliefs or desires, adds nothing towhat psychology can and should understand about the sources ofbehavior. Mental states are private entities which, given thenecessary publicity of science, do not form proper objects ofempirical study. Methodological behaviorism is a dominant theme inthe writings of John Watson .
Psychological behaviorism is a research program within psychology. Itpurports to explain human and animal behavior in terms of externalphysical stimuli, responses, learning histories, and reinforcements. Psychological behaviorism ispresent in the work of Ivan Pavlov , Edward Thorndike, as well as Watson. Its fullest and most influentialexpression is B. F. Skinners work on schedules ofreinforcement.
Don’t Miss: What Is Li In Chemistry
Thorndikes Emphasis On Heredity And Eugenics
Skinners appreciation of the importance of heredity is clear in his claim that there are three important names in the history of the study of behavior: Darwin, Lloyd-Morgan, and Watson. For Watson and for Skinner, evolution provides the shaping of innate behaviors .11 But neither promoted eugenics or argued for the inheritance of traits such as intelligence, morality, or artistic ability, as Thorndike did.
I need not present a long argument attesting to Thorndikes well-known and extreme hereditarian bias, I just point out that his first book, The Human Nature Club , was dedicated to the ultimate hereditarian and coiner of the word eugenics, Sir Francis Galton . A few quotations from Thorndikes writings, both early and late in his career, suffice to make the rest of the case:
Grammar school, high school, and college all eliminate certain sorts of minds, and we may be sure beforehand that what the average college students are, that the average of high school students never become that what the average of high school students are, never represents the future of the average of grammar school boys and girls.
As Watsons last year at Johns Hopkins loomed, Thorndike was expressing opinions on nature, nurture, and society. For instance, democracy is good since it allows opportunity for the more able, kind, and intelligent to govern:
Examples Of Behavioral Perspective In Television And Real Life

Its not uncommon to see examples of classical and operant conditioning on TV, but it doesnt always show the larger implications of how that conditioning changes a persons personality. Take The Office. Everyone has seen the scene where Jim trains Dwight to reach out his hand for a mint when Jim reboots his computer. This is a classic example of classic conditioning. Does it show changes to Dwights personality? Not really the scene is just meant to churn up laughs.
Another scene from The Big Bang Theory shows Sheldon training Penny through operant conditioning. Any time that Penny does something considerate for Sheldon, she receives chocolate. One could argue that Pennys experiences could shape her personality. If she recognizes the rewards she receives from being considerate, she may be considerate outside of the apartment where shes receiving chocolate from Sheldon. Does she? Again, this is not part of her story. The scene is mainly for laughs.
How does behaviorism explain habits like addiction? This Reddit post from r/psychology offers an analysis using the Queens Gambit as an example.
Also Check: What Kind Of Jobs Can You Get With Psychology Degree
An Introduction To Behavioral Psychology
Behavioral psychology, or behaviorism, is a theory suggesting that environment shapes human behavior. In a most basic sense, behavioral psychology is the study and analysis of observable behavior.
This field of psychology influenced thought heavily throughout the middle of the 20th century. It is still used by mental health professionals today, as its concepts and theories remain relevant in fields like psychotherapy and education.
Operant Conditioning: Skinner Boxes
Psychologist B.F. Skinner placed a hungry rat in a box containing a lever. As the rat moved around the box, it would occasionally press the lever, consequently discovering that food would drop when the lever was pressed. After some time, the rat began running straight toward the lever when it was placed inside the box, suggesting that the rat had figured out that the lever meant it would get food.
In a similar experiment, a rat was placed inside a Skinner box with an electrified floor, causing the rat discomfort. The rat found out that pressing the lever stopped the electric current. After some time, the rat figured out that the lever would mean that it would no longer be subject to an electric current, and the rat began running straight toward the lever when it was placed inside the box.
The Skinner box experiment demonstrates operant conditioning, in which an animal or human learns a behavior by associating it with consequences The three types of reinforcement are as follows:
- Positive reinforcement: When something good is added to teach a new behavior.
- Negative reinforcement: When something bad is removed to teach a new behavior.
- Punishment: When something bad is added to teach the subject to stop a behavior.
Recommended Reading: What Are Stressors In Psychology
Would Watsons Absence Have Made A Real Difference
If he had gone to medical school and followed a path not directly relevant to psychology, there would have been no 1913 behavioral manifesto. Would it follow that there would then be no Bertrand Russells report on Watsons behaviorism for Skinner to read3 and thus The Behavior of Organisms might never have been written? Perhaps applied behavior analysis would not exist and therapy would be wholly based on Positive Psychology or Self-Actualization. Worse, could the advertising industry possibly have shriveled to the point that we are merely informed of the virtues of products, rather than persuaded that we want them?4 If this scenario seems plausible to us, then we do believe that Watson did possess the superman-ic power that Joseph Jastrow accused him of thinking that he had. But it is almost certain that such a scenario would not have occurred and that behaviorism would have emerged pretty much as it did. That is because Watson probably did not really alter history very much. He did what he wrote a nervous system does: It just speeds up the message, but the message still gets through without it .
Behavioral Approach To Psychology Main Ideas
Within the behavioral approach, psychology is analyzed and studied through the use of solely objective and scientific methods of observing and evaluating the human mind. Whereas some approaches to psychology include taking into account a person’s own subjective and unique views on their mind, their feelings and emotions, and their experiences, behaviorism disregards this data and strictly focuses on data obtained through “careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior,” with its primary goals being control and prediction of behaviors.
Behaviorism rejects internal concepts such as one’s thoughts and emotions and, as the name implies, focuses strictly on observable behaviors. Those who support this approach do not deny the existence of a person using their mind and feeling or processing the stimuli around them, but it is seen as irrelevant to their primary concerns in studying psychology since these internal factors cannot be outwardly observed aside from relying on a person’s interpretations and expressions of these factors. When trying to keep their field as objective and scientific as possible, this does not allow for the admission of data that may be skewed by a person’s opinions or unique perspectives regarding what they may be feeling or doing and why. This approach strongly supports the ideas of reductionism and a nomothetic approach to psychology as well.
Recommended Reading: What Is Compressibility In Chemistry Class 9
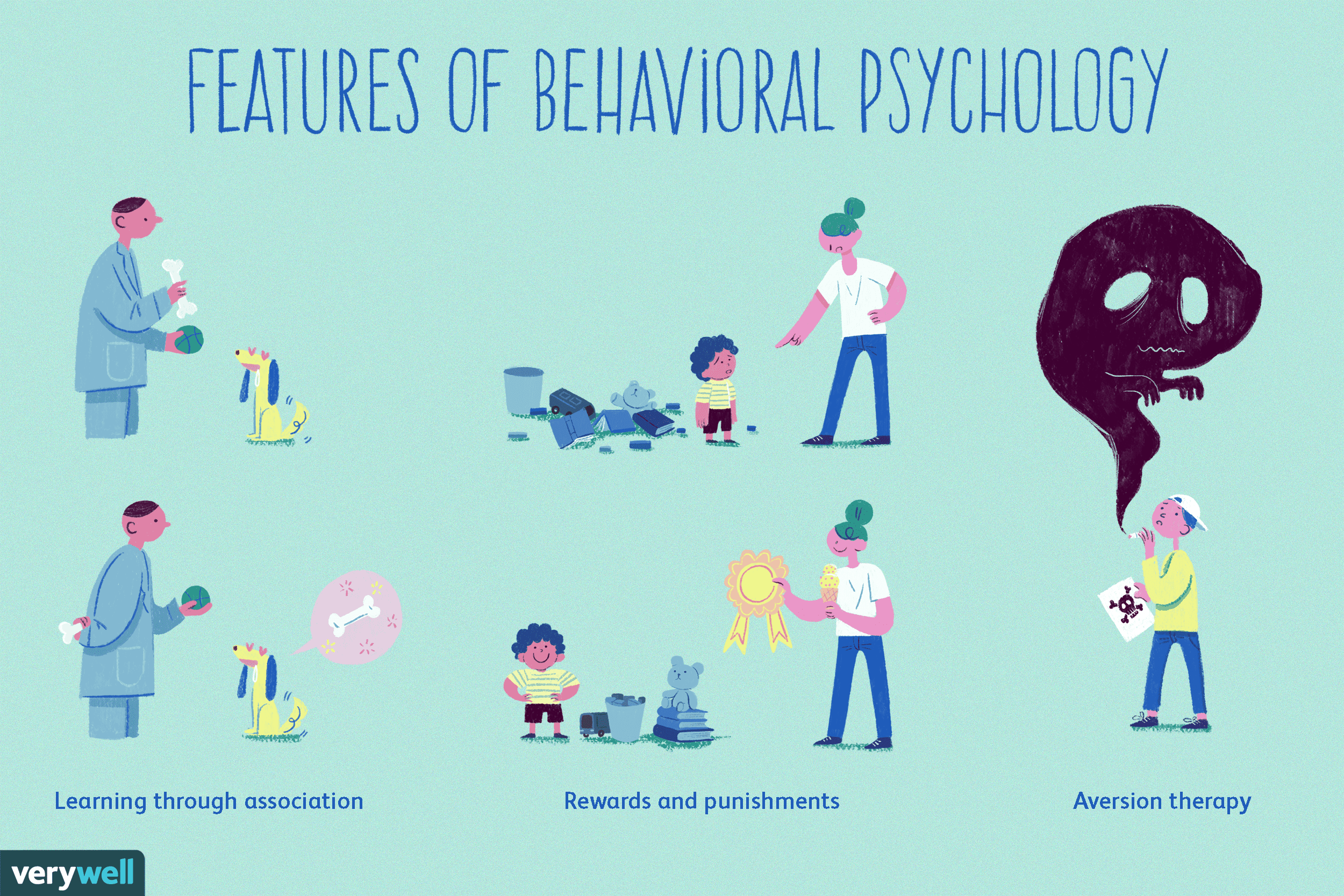
Classical Conditioning Vs Operant Conditioning
Behaviorists believe humans learn behaviors through conditioning, which associates a stimulus in the environment, such as a sound, to a response, such as what a human does when they hear that sound. Key studies in behaviorism demonstrate the difference between two types of conditioning: classical conditioning, which is associated with psychologists like Ivan Pavlov and John B. Watson, and operant conditioning, associated with B.F. Skinner.
All Behavior Is Learned From The Environment
Behaviorists believe that environmental factors have a strong impact on our learning. We adopt new behaviors through conditioning.
Conditioning is the process of accustoming someone to act in a certain way under specific circumstances.
The two main types of conditions are classical, and operant conditioning collectively referred to as learning theory.
Classical Conditioning
Discovered by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov, classical conditioning is a type of unconscious learning that emerges as a conditioned response to a specific stimulus. Continuous influence to such stimulus fosters the formation of a specific behavior.
Pavlov famously did his experiments on dogs. But John B. Watson also tested classical conditioning responses among humans. In the experiment with Little Albert, he found that the child developed a fear of rats after repeatedly showing a lab rat alongside loud, scary sounds. Alberts fear also generalized to other white fuzzy objects resembling a rat.
Among adults, classical conditioning often happens too. For example, at your previous job, everyone went to lunch at noon. Now, you always feel hungry around that time. Or you were always criticized by your former boss for your PowerPoint presentations. Now you hate doing business presentations for an audience.
In essence, a positive or negative conditioning stimulus fosters the development of an unconditional response to a certain stimulus.
How You Can Apply Classical Conditioning Principles
Also Check: How Much Is Math Tutoring Per Hour
What Does Behavioral Psychology Focus On
Behavioral psychology focuses on human behaviors rather than thought processes, emotions or motivations. This involves measuring external behaviors, analyzing how they correspond to environmental stimuli, and then using conditioning to shape or reshape those reactions. Behavioral psychology can be a useful approach for psychological research because researchers can apply conditioning and measure the changes in external behavior more easily than they can measure internal states. Behavioral psychologists work with two types of conditioning, classical and operant conditioning. Here is what each involves: