Bio Chap 2 Test Flashcards
Start studying Bio Chap. 2 Test. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Upgrade to remove adsOnly RUB 2,325/yearSTUDYFlashcardsLearnWriteSpellTestPLAYMatchGravityTerms in this set Explain how AIDS can be understood at the cellular and molecular levels. Cellular- Patients with AIDS have their helper T cells wiped out, which are very important to the human bodys immune system. Molecular- HIV kills helper T cells by binding to molecules on the outside of helper T cells. Distinguish between matter, chemical elements, and compounds. Give examples. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Found in three states Ex. computer, dog, halloween candy. Chemical elements are substances that cannot be broken down and are found on the periodic table. Ex. nitrogen, radon, potassium. Compounds contain two or more different elements and are much more common than elements. Ex. water, table salt. Explain the significance of trace elements to human health. Trace elements are required in minute quantities, but are essential for human health. There are 14 trace elements that make up less than 0.
Charge To The Committee
This document is the report of the committee formed to examine these matters and to provide recommendations for action to DOE. The committee was asked:
-
To assess current methods and systems for producing and distributing isotopically enriched material and to consider possible alternatives for ensuring adequate supplies of isotopes for a broad range of clinical and biomedical research applications.
-
To examine the relative merits of current and developing technologies for isotope production and the need for new technologies over the long term.
-
To assess the relative needs for involvement of the Department of Energy and private sector in isotope production and distribution. As part of this assessment, the committee was also asked to conduct an in-depth review of national needs for the high-energy accelerator-produced radionuclides to be produced at an NBTF in relation to other requirements in the nuclear medicine and biomedical isotope sectors.
-
To evaluate the comprehensive research and educational components that have been proposed for NBTF in relation in total personnel needs in the these areas.
In its deliberations, the committee was asked to address the following specific questions: What are the current needs for both radioactive and enriched stable isotopes in the United States? What needs can be anticipated for the future on the basis of recent and expected technological improvements? What is the
Suggested Citation:Isotopes for Medicine and the Life Sciences
Radioisotopes Used In Diagnostic Imaging
Radioisotopes can be used as tracers within a living organism to trace what is going on inside the organism at an atomic level that is, radioisotopes can be injected or ingested by the organism, and researchers can trace the internal activities using the radioactivity. Medical specialists can use radioisotopes to see internal processes and conditions inside the human body. Gallium-67, for instance, can be ingested by patients. When the patient undergoes an MRI or PET scan, doctors can trace the substance inside the body and see whats going on without invasive surgery. Other radioisotopes, such as Iodine-123 and Iodine-125, help doctors diagnose thyroid disorders and metabolic disorders in a similar way.
Recommended Reading: Bernard Kolman Elementary Linear Algebra With Applications
Why Is An Isotope Useful
Radioactive isotopes differ in the stability of their nuclei. Measuring the speed of decay allows scientists to date archaeological finds, and even the universe itself. Stable isotopes can be used to give a record of climate change. Isotopes are also commonly used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
What Is A Radioactive Isotope In Biology
A radioactive isotope, also known as a radioisotope, radionuclide, or radioactive nuclide, is any of several species of the same chemical element with different masses whose nuclei are unstable and dissipate excess energy by spontaneously emitting radiation in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma rays.
Why are radioisotopes used in anatomy and physiology?
Radioisotopes in medicine. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radiation to provide information about a persons body and the functioning of specific organs, ongoing biological processes, or the disease state of a specific illness. In most cases the information is used by physicians to make an accurate diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Which Of The Following Best Represents Psychology’s Basic Goals
Question: How Are Radioactive Isotopes Used In Biology
Radioisotopes can be used as tracers within a living organism to trace what is going on inside the organism at an atomic level that is, radioisotopes can be injected or ingested by the organism, and researchers can trace the internal activities using the radioactivity.
How Are Isotopes Used In Biochemistry
One of the most important applications of radioisotopes in biochemistry is their use in determining metabolic pathways and for measuring the flow of metabolites through pathways. Radioisotopic methods have been developed to trace and assay enzymic reactions. … Radioisotopes are also used for tracing metabolic pathways.
Also Check: How To Teach Geography To Preschoolers
Food Preservation And Sterilization
As per WHO reports, about 2535% of world food production is susceptible to the attack by pests, insects, bacteria, and fungi causing a great loss of the economy of the country. Food irradiation has more advantages than conventional methods. All types of radiations are not recommended for food irradiation only three types of radiation are recommended by CODEX general standard for food irradiation which are 60Co or 137Cs, X-rays, or electron beams from particle accelerators . The food products are exposed to -radiations from the intense controlled sources to kills pests, bacteria, insects, and parasites and extends shelf-life but also reduces the foods nutritional value somewhat by destroying vitamins A, B1 , C, and E. No radiation remains in the food after treatment.
Depending on the radiation dose and its application, radiations are classified into three categories: they are low dose , medium dose , and high dose .
4.4.1. Low-dose applications
4.4.1.1. Sprout inhibition in bulbs and tubers
Irradiated potato can be stored at higher temperature of around 15°C. This not only conserves energy but also prevents sweetening of potato, commonly occurring at low temperatures. It gives advantage to the manufacturers of chips as low-sugar potato gives desired lighter color to fries and chips.
4.4.1.2. Delayed ripening of fruits
4.4.2. Medium-dose applications
4.4.3. High-dose applications
Why Are Radioactive Isotopes Harmful To Human Life
Radioactive materials are hazardous. Nuclear radiation can ionise chemicals within a body, which changes the way the cells behave. It can also deposit large amounts of energy into the body, which can damage or destroy cells completely. Radioactive isotopes can sit in the stomach and irradiate for a long time.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Physics And Engineering
How Are Isotopes Useful In Biology
- Uses of Radioisotopes
Radioactive isotopes are widely used as tracers or labels for substances separated by TLC for following the causes of chemical and biochemical reactions, determining the distribution of substances in a reaction mixture, elucidating metabolic pathways of drugs, pesticides, pollutants, and natural substances in human, animal and plant tissues, and assessing the purity of isotopes. From: Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology , 2003Marine LifeW. A. Montevecchi, in Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences , 2019RadionuclidesRadionuclides are released from weapon testing and use and from industrial accidents, such as those associated with power-generating facilities. As is the case with many other pollutants, specific radionuclides are taken up in specific tissues. These chemicals are monitored in shellfish with concerns for human consumption. Hence, shellfish predators including shorebirds, gulls, and sea ducks are likely the best avian species to assay with reference to this source of pollution.
Video advice: Isotopes and Half-Life: What are medical Isotopes?
UPDATE: I have fixed the mass number location on the isotopic notation!
Evolution In Action: Carbon Dating
Carbon-14 is a naturally occurring radioisotope that is created in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. This is a continuous process, so more 14C is always being created. As a living organism develops, the relative level of 14C in its body is equal to the concentration of 14C in the atmosphere. When an organism dies, it is no longer ingesting 14C, so the ratio will decline. 14C decays to 14N by a process called beta decay it gives off energy in this slow process ). After approximately 5,730 years, only one-half of the starting concentration of 14C will have been converted to 14N. The time it takes for half of the original concentration of an isotope to decay to its more stable form is called its half-life.
Because the half-life of 14C is long, it is used to age formerly living objects, such as fossils. Using the ratio of the 14C concentration found in an object to the amount of 14C detected in the atmosphere, the amount of the isotope that has not yet decayed can be determined. Based on this amount, the age of the fossil can be calculated to about 50,000 years below). Isotopes with longer half-lives, such as potassium-40, are used to calculate the ages of older fossils. Through the use of carbon dating, scientists can reconstruct the ecology and biogeography of organisms living within the past 50,000 years.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Powers Of I In Math
Phosphorus Uptake By Plants
Plants take up phosphorus-containing compounds from the soil through their roots. By adding a small amount of radioactive phosphorus-32 to fertiliser and then measuring the rate at which radioactivity appears in the leaves, it is possible to calculate the rate of uptake of phosphorus from the soil. The information gathered could help plant biologists to identify plant types that can absorb phosphorus quickly. These plants may give better yields resulting in more food or fibre at less expense.
What Are The Three Biological Uses Of Isotopes
Radioactive isotopes find uses in agriculture, food industry, pest control, archeology and medicine. Radiocarbon dating, which measures the age of carbon-bearing items, uses a radioactive isotope known as carbon-14. In medicine, gamma rays emitted by radioactive elements are used to detect tumors inside the human body.
Don’t Miss: What Is Human Development In Psychology
What Are Isotopes And Its Uses
Radioactive isotopes find uses in agriculture, food industry, pest control, archeology and medicine. Radiocarbon dating, which measures the age of carbon-bearing items, uses a radioactive isotope known as carbon-14. In medicine, gamma rays emitted by radioactive elements are used to detect tumors inside the human body.
What Is An Isotopic Signature
An isotopic signature is the set of ratios between the amount of the various isotopes of an element in a sample.
Isotopic signatures are commonly known as fingerprints, because they are similar to human fingerprints and are used to track and trace. They are found in water, land, plants and animals. By tracing these fingerprints, scientists can evaluate:
- the migration of species on land and in water
- the age and quality of water bodies including groundwater aquifers
- origins of water and atmosphere pollution
For example, the naturally occurring isotope carbon-14 present in water is used to understand the age of water and other organic materials.
Read the IAEA Bulletins to learn more about the importance and uses of isotopes and their signatures.
Also Check: Is The Geometry Eoc Hard
How Do Radioisotopes Occur
The unstable nucleus of a radioisotope can occur naturally, or as a result of artificially altering the atom. In some cases a nuclear reactor is used to produce radioisotopes, in others, a cyclotron. Nuclear reactors are best-suited to producing neutron-rich radioisotopes, such as molybdenum-99, while cyclotrons are best-suited to producing proton-rich radioisotopes, such as fluorine-18.
The best known example of a naturally-occurring radioisotope is uranium. All but 0.7 per cent of naturally-occurring uranium is uranium-238 the rest is the less stable, or more radioactive, uranium-235, which has three fewer neutrons in its nucleus.
Radioactive decay
Atoms with an unstable nucleus regain stability by shedding excess particles and energy in the form of radiation. The process of shedding the radiation is called radioactive decay. The radioactive decay process for each radioisotope is unique and is measured with a time period called a half-life. One half-life is the time it takes for half of the unstable atoms to undergo radioactive decay.
Radioactivity In The Life Sciences
This article is about radioactivity as a tool in life science. For the effect of radiation on living organisms, see Radiation poisoning. For organisms which harness radiation, see Radiotrophic fungus. For the bacterium highly resistant to radiation, see Deinococcus radiodurans.
Breeman, W.A. P. De Blois, E. Sze Chan, H. Konijnenberg, M. Kwekkeboom, D.J. Krenning, E.P. . 68Ga-labeled DOTA-Peptides and 68Ga-labeled Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography: Current Status of Research, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives. Workshops in Nuclear Medicine. 41 : 314321. doi:10. 1053/j. semnuclmed. 2011. 02. 001. PMID 21624565.
All atoms exist as stable or unstable isotopes and the latter decay at a given half-life ranging from attoseconds to billions of years radioisotopes useful to biological and experimental systems have half-lives ranging from minutes to months. In the case of the hydrogen isotope tritium and carbon-14 , these isotopes derive their importance from all organic life containing hydrogen and carbon and therefore can be used to study countless living processes, reactions, and phenomena. Most short lived isotopes are produced in cyclotrons, linear particle accelerators, or nuclear reactors and their relatively short half-lives give them high maximum theoretical specific activities which is useful for detection in biological systems.
Video advice: A List of Some Uses of Radioactive Isotopes in Biology & Medicine : Chemistry Help
Read Also: What Does And Mean In Math
Which Isotope Is Commonly Used In Biology
Some elements, such as carbon, potassium, and uranium, have naturally occurring isotopes. Carbon-12, the most common isotope of carbon, contains six protons and six neutrons.
How are radioactive isotopes used to diagnose medical conditions?
Radioisotopes are widely used to diagnose disease and as effective treatment tools. For diagnosis, the isotope is administered and then located in the body using a scanner of some sort. The decay product can be located and the intensity measured.
Isotopes Used In Biology
Application: Food Safety Isotopes are variations of chemical elements containing different numbers of neutrons. Because isotopes are recognizable, they provide an efficient way to track biological processes during experimentation. There are many potential uses for isotopes in experimentation, but several applications are more prevalent. Isotopes Differentiated Each chemical element has a unique number of protons, a fact that gave rise to the periodic table. Similarly, an isotope of any given element has its own unique number of neutrons the designation of an isotope is determined by the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus . An element can have any number of isotopes. For instance, carbon-12 and carbon-13 both have six protons, but the latter contains one additional neutron. Because the number of neutrons in an atoms nucleus has a negligible effect on chemical properties, isotopes provide an efficient means of studying various biological processes without significantly affecting their natural course.
Also Check: What Is Fixation In Psychology
Doe Office Of Science & Isotopes
Isotopes are needed for research, commerce, medical diagnostics and treatment, and national security. However, isotopes are not always available in sufficient quantities or at reasonable prices. The DOE Isotope Program addresses this need. The program produces and distributes radioactive and stable isotopes that are in short supply, including byproducts, surplus materials, and related isotope services. The program also maintains the infrastructure required to produce and supply priority isotope products and related services. Finally, it conducts research and development on new and improved isotope production and processing techniques.
The Type Of Emission Of Ionizing Radiations
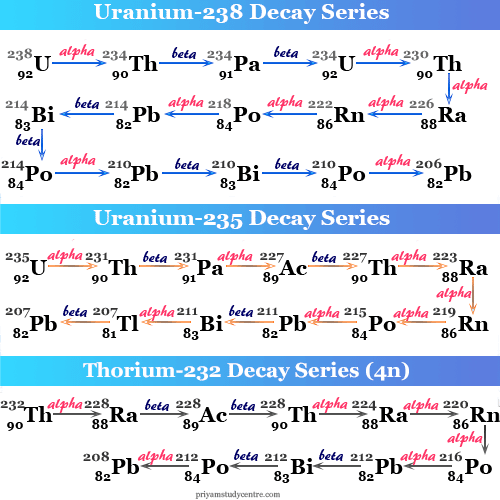
The ionizing radiations such as , , and except neutron are originated from unstable nuclei of an atom in an element undergoing radioactive decay.
2.1.1. Alpha radiation
Some naturally occurring heavy nuclei with atomic number 82 < Z < 92 and artificially produced transuranic element Z > 92 decay by alpha emission, in which the parent nucleus loses both mass and charge. The alpha particle is emitted in preference to other light particles such as deuteron , tritium , and helium . Because energy must be released in order for decay to take place at all. The alpha particle has very stable and high binding energy, has tightly bound structure, and can be emitted spontaneously with positive energy in alpha decay, whereas 2H, 3H, and 3He decay would require an input energy. The parent nucleus is transformed via
It has less penetrating and high ionizing power.
2.1.2. Beta radiation
Beta particles are fast electron or positron these are originated from weak interaction decay of a neutron or proton in nuclei, which contains an excess of the respective nucleon. In a neutron-rich nucleus, neutron can transform itself in to a proton by emission of beta particles and antineutrino. Similarly, in the nuclei with rich proton, it transforms into neutron by emission of neutrino and positron. These radiations are high penetrating and less ionizing power:
Similarly in the nuclei with rich proton, the decay is
2.1.3. Gamma radiation
2.1.4. X-ray radiation
2.1.5. Neutron radiation
You May Like: What Does The Word Biology Mean
How Are Radioisotopes Used
Radioisotopes are an essential part of radiopharmaceuticals. In fact, they have been used routinely in medicine for more than 30 years. Every Australian is likely to benefit from nuclear medicine and, on average, will have at least two nuclear medicine procedures in their lifetime.
Some radioisotopes used in nuclear medicine have short half-lives, which means they decay quickly and are suitable for diagnostic purposes others with longer half-lives take more time to decay, which makes them suitable for therapeutic purposes.
Industry uses radioisotopes in a variety of ways to improve productivity and gain information that cannot be obtained in any other way.
Radioisotopes are commonly used in industrial radiography, which uses a gamma source to conduct stress testing or check the integrity of welds. A common example is to test aeroplane jet engine turbines for structural integrity.
Radioisotopes are also used by industry for gauging or to measure the thickness of materials.
Radioisotopes are also widely used in scientific research and are employed in a range of applications, from tracing the flow of contaminants in biological systems to determining metabolic processes in small Australian animals.
They are also used on behalf of international nuclear safeguards agencies to detect clandestine nuclear activities from the distinctive radioisotopes produced by weapons programs.
What is a radioactive source?
What are some commonly-used radioisotopes?
| Radioisotope |
|---|