The Stages Of Childhood Development Physical Cognitive
motor responses,â . Research in biology and human development shows that infants are developing their sensorimotor skills by engaging with objects, particularly by reaching and grabbing . Also evident at the sensorimotor stage is the infantâs ability to learn via both classical and operant conditioning, such as with the introduction of stimuli to induce specific behavioral responses . Infants demonstrate the ability to form social attachments and exhibit individualized emotional responses, too, with differences depending on environmental factors like parental behavior and culture (Lightfoot, Cole & Cole, 2009. While their ability toâ¦Continue Reading…
What Are The Eight Stages Of Human Development
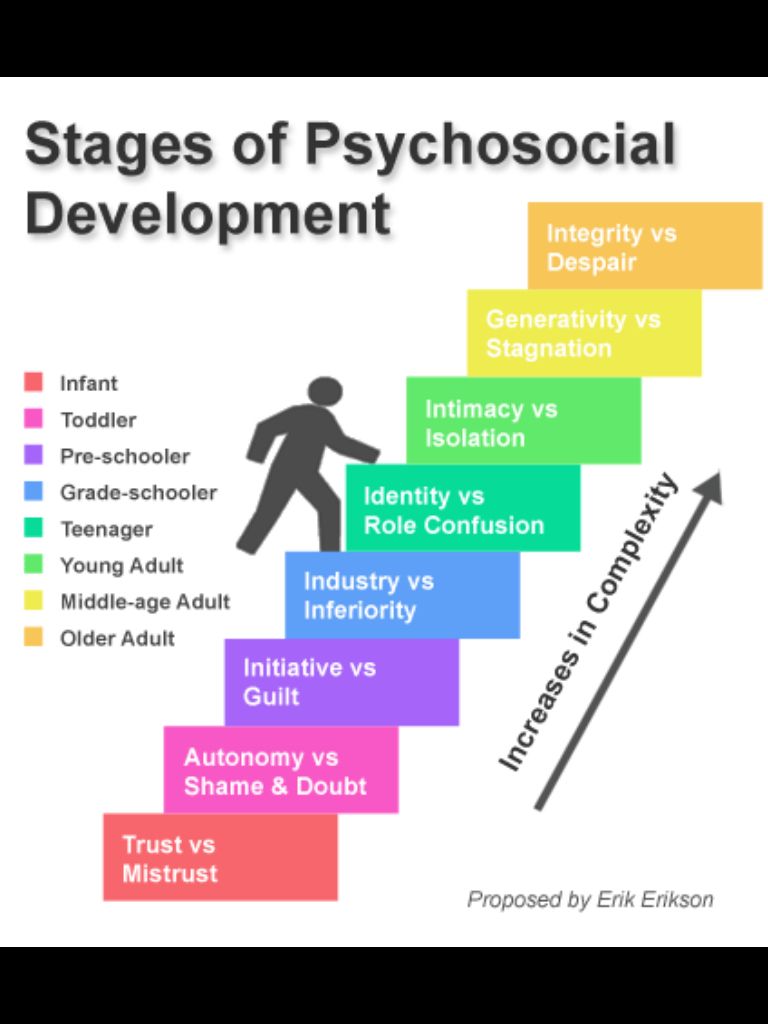
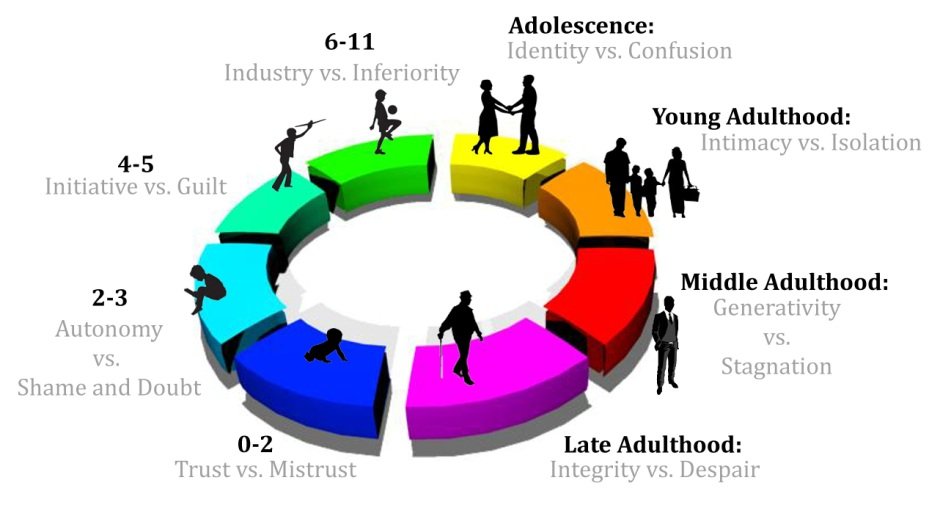
If human development is the study of how people change throughout their lives, how and when does this development happen? Many scientists and psychologists have studied various aspects of human development, including ego psychologist Erik Erikson. He examined the impact of social experiences throughout an individuals life and theorized that psychosocial development happens in eight sequential parts. What are the eight stages of human development?
Piagets Developmental Psychology Theory
Piagets theory of cognitive development suggested that there were fundamental differences in how children think versus how adults think. Piaget broke down this development into four distinct stages that typically occur at different stages of development.
The earliest stage is centered on gaining awareness of the self and the world, while later stages build on this knowledge as kids gain an increasingly sophisticated understanding of themselves, others, and the world around them.
Don’t Miss: Does Mj Have Any Biological Kids
What Is Human Development
2015 marks 25 years since the first Human Development Report introduced a new approach for advancing human flourishing. And while the expression human development is widely used, it is understood in different ways around the world. So on the occasion of the 25th anniversary year of human development reporting, wed like to highlight how the Human Development Report Office presents human development.
Human development grew out of global discussions on the links between economic growth and development during the second half of the 20th Century. By the early 1960s there were increasingly loud calls to dethrone GDP: economic growth had emerged as both a leading objective, and indicator, of national progress in many countries i, even though GDP was never intended to be used as a measure of wellbeing ii. In the 1970s and 80s development debate considered using alternative focuses to go beyond GDP, including putting greater emphasis on employment, followed by redistribution with growth, and then whether people had their basic needs met.
These ideas helped pave the way for the human development approach, which is about expanding the richness of human life, rather than simply the richness of the economy in which human beings live. It is an approach that is focused on creating fair opportunities and choices for all people. So how do these ideas come together in the human development approach?
Beings: well fed, sheltered, healthy
Notes:
Freuds Developmental Psychology Theory

Freuds theory of psychosexual development was an early theory that focused on how personality develops during early childhood. Sigmund Freud believed that psychosexual energy became focused on various erogenous zones at different points of development. He also suggested that failing successfully to address the primary crisis of each stage could lead to a psychological fixation at that point of development.
Don’t Miss: Draw The Lewis Structure For Ccl4.
Stages Of Moral Development
Piaget claimed that logic and morality develop through constructive stages. Expanding on Piaget’s work, Lawrence Kohlberg determined that the process of moral development was principally concerned with justice, and that it continued throughout the individual’s lifetime.
He suggested three levels of moral reasoning pre-conventional moral reasoning, conventional moral reasoning, and post-conventional moral reasoning. The pre-conventional moral reasoning is typical of children and is characterized by reasoning that is based on rewards and punishments associated with different courses of action. Conventional moral reason occurs during late childhood and early adolescence and is characterized by reasoning based on rules and conventions of society. Lastly, post-conventional moral reasoning is a stage during which the individual sees society’s rules and conventions as relative and subjective, rather than as authoritative.
Kohlberg used the Heinz Dilemma to apply to his stages of moral development. The Heinz Dilemma involves Heinz’s wife dying from cancer and Heinz having the dilemma to save his wife by stealing a drug. Preconventional morality, conventional morality, and post-conventional morality applies to Heinz’s situation.
Stage 7 Middle Adulthood: Generativity Vs Stagnation
In middle adulthood, people tend to struggle with their contributions to society. They may be busy raising children or pursuing careers. Those who feel that theyre contributing experience generativity, which is the sense of leaving a legacy. On the other hand, those who dont feel that their work or lives matter may experience feelings of stagnation. For example, a middle-aged adult whos raising a family and working in a career that presumably helps people may feel more fulfilled than an adult whos working at a day job that feels meaningless.
Read Also: Algebra 1 Eoc Fsa Practice Test Calculator Portion
What Is Human Growth And Development Psychology
Developmental psychologypsychologydevelopment
Thus, growth refers to an increase in physical size of whole or any of its part and can be measured. 1.3.2. DEVELOPMENT: CONCEPT AND DEFINITION. Development refers to the qualitative changes in the organism as whole. Development is a continuous process through which physical, emotional and intellectual changes occur.
Secondly, what is psychological growth? Psychological growth means different things to different people. For some people it means greater freedom to do what they want, live as they want and pursue their interests. Others seek to understand themselves better, develop their personal capacities, experience new things.
In this regard, what is human growth and development?
Growth and Development. Human development is a lifelong process of physical, behavioral, cognitive, and emotional growth and change. In the early stages of lifefrom babyhood to childhood, childhood to adolescence, and adolescence to adulthoodenormous changes take place.
What are the theories of human growth and development?
Psychoanalytic theory Learning theory Cognitive development theory Systems theory
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The health care team should understand the developmental stages that their patients go through during early childhood. We should increase the awareness of health care professionals about the importance of standardized growth monitoring and the appropriate use of growth charts. Also, they need adequate training for using standard developmental screening tools.
Every clinician and nurse managing pediatric patients should have appropriate awareness of referral service to early intervention for eligible patients. Interprofessional collaboration between clinicians, mid-level practitioners, and nurses can improve patient outcomes as developmental delays require prompt intervention when caught, and earlier is always better. Children up to three years with developmental delay are referred to early intervention programs, and children above three years of age are referred to special education services.
Don’t Miss: Reasoning Minds Math Login
Appreciate Development Through Life
When we think of human development, it’s easy to think of it as a process that is largely complete once we hit early adulthood. It is important to realize, however, that development is an ongoing process that continues all throughout life.
As you enter adulthood, navigate middle age, and face the onset of old age, having a greater understanding of how people continue to grow and change as they get older can help you appreciate and manage all the stages of your life.
Psychology As A Science
What is Developmental Psychology?
Why is it Important to Study Developmental Psychology?
Theoretical study:
Empirical study:
For psychologists:
For educators:
For parents:
For the community:
For individuals:
Current Trends in Developmental Psychology
Descriptiveor normative trend: Behavioralor environmental trend:Emergingfield service trend: Analyticalor psychological trend:
Characteristics of Human Growth
Growthis a differentiated process:Growth is a regular process:Growth is a holistic process:Growth is a continuous process:Growth is a changing process:
Goals and Objectives of DevelopmentalPsychology
Principles of Developmental Psychology
Continuation and Sequence: Integration:Differentiation rate of growth: Growth trend:The longitudinal direction of growth:The horizontal direction of growth:Individual Differences: The transition from the public to private :
Don’t Miss: Algebra Age Problems
What Is Human Development According To Psychology
4.2/5infancythis is here
The four stages of Piaget’s theory of cognitive development correspond with the age of the child they include the sensorimotor , preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational stages.
One may also ask, what is Erikson’s theory of human development? Erik Erikson’s theory of the stages of human development.The theory describes eight stages through which a healthily developing human should pass from infancy to late adulthood. In each stage the person confronts, and hopefully masters, new challenges. Each stage builds on the successful completion of earlier stages.
Also, what is the difference between human development and psychology?
A degree in psychology can lead to a fulfilling career that makes a difference in people’s lives. Developmental psychologists study changes in human development across the lifespan, including physical, cognitive, social, intellectual, perceptual, personality and emotional growth.
What is human growth and development in psychology?
Human Growth and Development. The study of developmental psychology is essential to understanding how human beings learn mature and adapt through the various stages in life. The guiding theories and research into the physical, cognitive and social developments from infancy to aging is covered.
The eight stages of development are:
Zone Of Proximal Development
Lev Vygotsky was a Russian theorist from the Soviet era, who posited that children learn through hands-on experience and social interactions with members of their culture. Unlike Piaget, he claimed that timely and sensitive intervention by adults when a child is on the edge of learning a new task could help children learn new tasks. This adult role is often referred to as the skilled “master,” whereas the child is considered the learning apprentice through an educational process often termed “cognitive apprenticeship” Martin Hill stated that “The world of reality does not apply to the mind of a child.” This technique is called “scaffolding,” because it builds upon knowledge children already have with new knowledge that adults can help the child learn. Vygotsky was strongly focused on the role of culture in determining the child’s pattern of development, arguing that development moves from the social level to the individual level. In other words, Vygotsky claimed that psychology should focus on the progress of human consciousness through the relationship of an individual and their environment. He felt that if scholars continued to disregard this connection, then this disregard would inhibit the full comprehension of the human consciousness.
Also Check: Eoc Fsa Practice Test Algebra 1 Calculator Portion
Human Development In Context
The Human Development in Context program, formerly called Human Development and Psychological Services, examines how people throughout the lifespan develop in, are influenced by, and shape the social settings they encounter . HDC courses focus on theories of individual and family development the local and global dynamics of learning and cognition, social relations, and policy. This interdisciplinary program draws from current and actionable theory, research, and practice from areas as diverse as psychology, sociology, intercultural studies, gender studies, economics, and policy science.
Debates Within Developmental Psychology
There have been a number of important debates and issues throughout the history of developmental psychology.
Some of the major questions posed by psychologists and researchers are centered on:
- The relative contributions of genetics versus environment
- The processes through which development occurs
- The overall importance of early experiences versus that of later events
As mentioned earlier, the classic issue in child development research is the nature vs. nurture debate. Sometimes referred to as the nativism versus empiricism debate, it centers on the question of whether genetic inheritance plays a larger role in influencing development and behavior or whether the environment has a stronger effect?
Today, most psychologists recognize that both elements play an essential role, but the debate continues over many developmental questions about topics ranging from academic aptitude to sexual orientation.
Read Also: Fsa Algebra 1 Eoc Practice Test Answers
Human Development Degree Programs
Human Development is a psychology subspecialty that focuses on the development of children into becoming biologically and psychologically mature adults. It addresses changes in cognitive, motivational, psychophysiological and social functioning that occur over time.
How a child develops will go a long way in determining the course of his life. A number of external forces can influence the development of any child. These forces include whether he is raised in a happy and healthy environment if he is the victim of abuse or neglect and if he comes from a single parent household, to name a few.
Theories Of Developmental Psychology
Developmental psychologists still study the ways in which children develop, and how their development affects them later in life. Extensive research in the area of child development has birthed a number of theories that provide insight into what factors affect a childs development and the actions that maximize a childs development while minimizing potential developmental setbacks.
The following are some of the most widely-recognized theories in this field.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
What Is Lifespan Development
| Staff Writers
Are you ready to find your fit?
Find the information you need to find, get into, pay for, and thrive in the best college for you.
Lifespan Development refers to the full process of human development from conception to death. It is a holistic approach to understanding all of the physiological, cognitive, emotional, and social changes that people go through. Since humans live according to the customs and values of a wide range of cultures, this is a rich and diverse area of study. This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the four facets of lifespan development and how they interconnect to shape the human existence.
Is Development Continuous Or Discontinuous
Continuous development views development as a cumulative process, gradually improving on existing skills . With this type of development, there is a gradual change. Consider, for example, a childs physical growth: adding inches to their height year by year. In contrast, theorists who view development as discontinuous believe that development takes place in unique stages and that it occurs at specific times or ages. With this type of development, the change is more sudden, such as an infants ability to demonstrate awareness of object permanence .
Figure 2. The concept of continuous development can be visualized as a smooth slope of progression, whereas discontinuous development sees growth in more discrete stages.
Don’t Miss: Eoc Fsa Practice Test Algebra 1 No Calculator Portion
Dreams The Unconscious Mind And Defense Mechanisms
Psychodynamic and Psychoanalytic theory suggest that early stages of human development have a significant impact on our relationships and our ego throughout the life span. According to Freudian theories, manifested behavior is based on latent problems of the past. The therapeutic process of psychoanalysis is designed to help the client become aware of past problems or latent desires that have been suppressed during the process of psychological development. Key themes that emerge in the literature on psychoanalytic theory include the role of the unconscious mind in shaping self-concept and behavior, dreams as the language of the unconscious mind, andâ¦Continue Reading…
Stage 8 Late Adulthood: Integrity Vs Despair
As adults reach the end of life, they look back on their lives and reflect. Adults who feel fulfilled by their lives, either through a successful family or a meaningful career, reach ego integrity, in which they can face aging and dying with peace. If older adults dont feel that theyve lived a good life, they risk falling into despair.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Math Is On The Ged
Stage 4 Early School Years: Industry Vs Inferiority
When children begin school, they start to compare themselves with peers. If children feel theyre accomplished in relation to peers, they develop strong self-esteem. If, however, they notice that other children have met milestones that they havent, they may struggle with self-esteem. For example, a first grader may notice a consistently worse performance on spelling tests when compared with peers. If this becomes a pattern, it can lead to feelings of inferiority.
The key components of Eriksons model of human development include stage one, infancy, trust versus mistrust stage two, toddlerhood, autonomy versus shame and doubt stage three, preschool years, initiative versus guilt stage four, early school years, industry versus inferiority stage five, adolescence, identity versus role confusion stage six, young adulthood, intimacy versus isolation stage seven, middle adulthood, generativity versus stagnation and stage eight, late adulthood, integrity versus despair.
Harry Harlow And The Rhesus Monkeys
In order to demonstrate the importance of social and emotional development in people, Harry Harlow studied the attachment patterns of Rhesus monkeys. This was based on the belief of John Bowlby that maternal attachment is a necessity for proper emotional and social development. Harlow raised baby Rhesus monkeys in a nursery-type setting away from their mothers he gave them surrogate mothers made out of wire and wood, to which the babies developed attachment bonds. His alternative rearing technique, also called maternal deprivation, is considered highly controversial today.
Harlow next chose to investigate if the baby monkeys had a preference for bare wire mothers or cloth-covered mothers. For this experiment, he presented the infants with a cloth mother or a wire mother under two conditions. In one situation, the wire mother held a bottle with food and the cloth mother held no food in the other, the cloth mother held the bottle and the wire mother had nothing. In the end, even in the situations in which the wire mother had food and the cloth mother had none, the baby monkeys preferred to cling to the cloth mother for comfort. Harlow concluded that there was much more to the mother/infant relationship than milk, and that this contact comfort was essential to the psychological development and health of infants.
Read Also: Ccl4 Angle
The History Of Developmental Psychology
Although scholars have contemplated the nature of human existence for thousands of years, the field of developmental psychology was formalized in the past 150 years. Scientists in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including biologist Charles Darwin, primarily focused their studies on childhood development. An important early text was German physiologist Wilhelm Preyers 1882 The Mind of the Child, in which he described the development of his own daughter from birth through childhood.
It wasnt until the mid-20th century that the focus of developmental psychology moved beyond just children and adolescents. Researchers realized development continues throughout life and started studying adults and the elderly. During this period, many of developmental psychologys most influential scientists published their theories, including Jean Piaget , Erik Erikson , and John Bowlby . Their research and ideas continue to influence modern professionals in the field and their views of human development in psychology.