A Biological Understanding Of Human Nature
The main question is: “Why are empirical questions about how the mind works so weighted down with political and moral and emotional baggage? Why do people believe that there are dangerous implications to the idea that the mind is a product of the brain, that the brain is organized in part by the genome, and that the genome was shaped by natural selection?” This idea has been met with demonstrations, denunciations, picketings, and comparisons to Nazism, both from the right and from the left. And these reactions affect both the day-to-day conduct of science and the public appreciation of the science. By exploring the political and moral colorings of discoveries about what makes us tick, we can have a more honest science and a less fearful intellectual milieu.
Introduction
Every few years a book is published that commands our attention and causes us to consider questions that challenge our basic assumptions about ourselves. This month marks the publication of such a book, The Blank Slate: The Modern Denial of Human Nature by MIT research psychologist Steven Pinker.
His book The Language Instinct discussed all aspects of language in a unified, Darwinian framework, and in How the Mind Works he did the same for the rest of the mind, explaining “what the mind is, how it evolved, and how it allows us to see, think, feel, laugh, interact, enjoy the arts, and ponder the mysteries of life.”
A BIOLOGICAL UNDERSTANDING OF HUMAN NATURE
EDGE: Why?
Ii The Phases Of The Evolution Of Human Beings
Even though evolution, as an event, is supported by many elements, a completely satisfactory explanation of the causes and mechanisms underlying it has not been found yet. Darwinism is often mistaken for a synonym of evolution or theory of evolution. Even the modern version of Darwinism, holding that random and thus fortuitous genetic mutations and natural selection are the mechanisms ensuring evolution, is only one of the possible explanations for given moments in the evolutionary process. Although it may sound well-based from a microevolutionary point of view, nonetheless it appears to be unsatisfactory as far as evolution as a whole is concerned, with particular reference to the privileged directions it took, for which further mechanisms are being searched.
Along with the presence of , also territorial organization has been found: researchers identified areas corresponding to huts built and used by men for different reasons: dwelling, flintstone carving or food distribution. Of considerable interest is also the level of development achieved in the regions of brain associated with articulated language . It is the endocranial cast, where the first brainprints were taken, which gave these results. In many authors’ opinions, these elements show that the species was undoubtedly human.
Social And Biological Factors
To understand the problem of the relationship of biological and social need to learn more about the underlying factors on both sides of the person. In this case we are talking about factors of anthropogenesis. Relative to the biological entity, in particular, stands out for the development of hands and brain, bipedalism and speech ability. Among the key social factors allocate work, communication, ethics and teamwork.
The example of the abovementioned factors it can be concluded that the unity of biological and social in man is not just permissible but organically there. Another thing is that this does not negate the contradictions, which have to cope on different levels of life.
It is Important to note the value of labor, which was one of the key factors in the process of formation of modern man. This example clearly expresses the relationship of two seemingly opposite entities. On the one hand, bipedalism freed the hand and did effective work, and on the other collective efforts have helped to expand the possibilities of the accumulation of knowledge and experience.
In the future, the social and the biological in man have evolved in close conjunction, which, of course, did not rule out contradictions. For a clearer understanding of conflicts of this kind is more familiar with the two concepts in the understanding of human nature.
Recommended Reading: What Does W Stand For In Physics
Reason As The Unique Structural Property
MacIntyre, Hursthouse and Nussbaum all aim tolocate the human capacity for reasoning within a framework thatencompasses other animals. Each argues that, although the capacitiesto recognise reasons as reasons and for deliberation on their basistransform the needs and abilities humans share with other animals, thereasons in question remain in some way dependent on humansembodied and social form of life. This emphasis is intended todistinguish an Aristotelian approach from other approaches for whichthe capacity to evaluate reasons for action as reasons and to distanceoneself from ones desires is also the central differencebetween humans and other animals . According to Korsgaards Kantianinterpretation of Aristotles ergon argument, humanscannot act without taking a normative stand on whether their desiresprovide them with reasons to act. This she takes to be the keystructural feature of their life, which brings with it a wholenew way of functioning well or badly . In such an account, human nature ismonistically understood as this one structural feature which is sotransformative that the concept of life applicable to organisms thatinstantiate it is no longer that applicable to organisms thatdont. Only humanslive their lives,because only they possess the type of intentional control over theirbodily movements that grounds in evaluation of their actions andself-evaluation as agents .
Biological Theories Of Gender
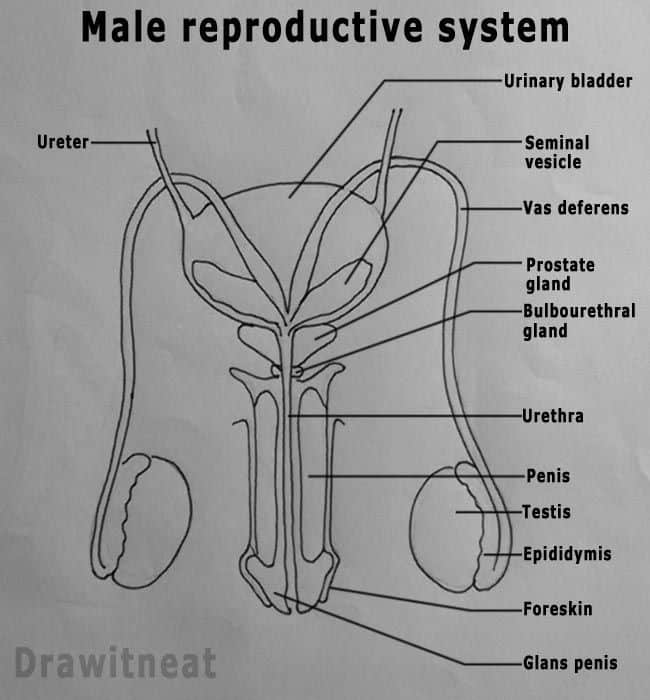
By Dr. Saul McLeod, published 2014
People often get confused between the terms sex and gender. Sex refers to biological differences between males and females. For example, chromosomes , reproductive organs , hormones .
Gender refers to the cultural differences expected of men and women according to their sex. A personâs sex does not change from birth, but their gender can.
In the past people tend to have very clear ideas about what was appropriate to each sex and anyone behaving differently was regarded as deviant.
Today we accept a lot more diversity and see gender as a continuum rather than two categories. So men are free to show their âfeminine sideâ and women are free to show their âmasculine traitsâ.
The biological approach suggests there is no distinction between sex & gender, thusbiological sex creates gendered behavior. Gender is determined by two biological factors: hormones and chromosomes.
You May Like: Determine The Molecular Geometry Of Each Of The Following Molecules
Assumption 2 Of The Biological Approach: Brain Functions Are Localised
Biopsychology assumes that different parts of the brain have different functions, rather than the whole brain working at all times. There are many methods for studying brain anatomy, including brain imaging like fMRI, PETscans, post mortems, or studying the behaviour of people who have pre-existing brain damage. Research has revealed that different areas of the brain correlate with specific functions.
One of the ways that brain localisation can be proved, is through transcranial magnetic stimulation , which temporarily blocks the electrical activity of specific parts of the brain. Depending on which specific brain areas are targeted, people lose speech or control of their hands for a minute or two . This demonstrates that specific regions in the brain control the normal use of the brain.
Biological Diversity Is Inherent In Humanity
The Human Genome and the Human Genome Project
Humans have about 75,000 different genes. They are made of a chemical known as DNA. Each gene is composed of a string of thousands of modular chemical building molecules, called nucleotides, of which there are four different types. Genes, in turn, are connected by the thousands in bead-like fashion into 23 larger molecular structures known as chromosomes. The set of chromosomes together is known as the “genome.” In all, it consists of about 3 billion nucleotides, and every person carries two complete sets – one set received from each parent.
Genes are a type of molecular “code,” each specifying a particular biological function. From a chemical point of view, the four different types of nucleotides can occur in any order or number. The way the coding system takes advantage of this is that the particular “sequence” of nucleotides of which a gene is composed determines that gene’s function. This sequence is related to the active biological molecules, called proteins, which are specified by that code. If the DNA coding sequence of a gene is altered, it may lead the coded protein to work differently, which can lead to a variety of possible outcomes, including disease.
Read Also: How To Find Density In Chemistry
Genetic Expression Is Influenced By Experience
The science of «epigenetics», which is mentioned with increasing frequency in medicine , is concerned with the way experiences enable contextual «programming» of genetic material. Genes are regarded less and less as determinative templates. Instead they are looked upon as dynamic agents in an organisms life, capable of responding to both external and internal stimuli. Accordingly, which part of the DNA becomes expressed and under which conditions will depend on experienced and interpreted impressions . It is therefore more appropriate to speak of genetic predisposition than genetic predestination .
Some scientists claim that epigenetic mapping is likely to provide answers to more questions relating to health and disease than genome mapping has done. In January 2010, the International Human Epigenome Consortium was launched for the purpose of mapping epigenetic marks in the genome. The journal Nature followed up with an expert commentary which stressed that the human genome is «singular and finite», while the epigenome is almost infinite, as it «changes in different states and different tissues» .
On The Status Of The Traditional Slogan
The traditional package specifies a set of conditions some or all ofwhich substantial claims about human nature are supposedto meet. Before we turn to the systematic arguments central tocontemporary debates on whether such conditions can be met, it will behelpful to spend a moment considering one highly influentialsubstantial claim. Aristotles writings prominently contain twosuch claims that have been handed down in slogan form. The first isthat the human being is an animalthat is in some important sense social . According to the second,he is a rational animal .
Aristotle makes both claims in very different theoretical contexts, onthe one hand, in his zoological writings and, on the other, in hisethical and political works. This fact, together with the fact thatAristotles philosophy of nature and his practical philosophyare united by a teleological metaphysics, may make it appear obviousthat the slogans are biological claims that provide a foundation fornormative claims in ethics and politics. The slogans do indeedfunction as foundations in the Politics and theNicomachean Ethics respectively . It is, however, unclear whether they are to beunderstood as biological claims. Let us focus on the slogan that hastraditionally dominated discussions of human nature in Westernphilosophy, that humans are rational animals.
Read Also: What Is On The Sat Subject Test Math Level 2
The Concept Of A Holistic Social Nature
That’s one idea, which leaves equal space for consideration of both entity and person. It is usually seen as an integral concept of the social nature in which it is possible an organic combination of biological and social in man and in society. Proponents of this theory considers the human being as a social being, and which retains all the characteristics with the natural laws of the sphere. This means that biological and social identity of the person do not contradict each other, and contribute to its harmonious development. Experts do not deny the influence of any of the factors in the development and aim them correctly to fit into the overall picture of the formation of the person.
The Role Of The Biological Perspective In Psychology
There are many different ways of thinking about topics in psychology. The biological perspective is a way of looking at psychological issues by studying the physical basis for animal and human behavior. It is one of the major perspectives in psychology and involves such things as studying the brain, immune system, nervous system, and genetics.
One of the major debates in psychology has long centered over the relative contributions of nature versus nurture. Those who take up the nurture side of the debate suggest that it is the environment that plays the greatest role in shaping behavior. The biological perspective tends to stress the importance of nature.
Read Also: What Is Co2 In Chemistry
Allostatic Overload May Be Quantified By Measurement Of Autonomous Hormonal Immunological And Genetic Variables:
-
Cardiovascular readings
-
Lung function tests
-
Inflammation markers
-
Glucose metabolism
-
Lipid metabolism
-
Obesity measures
-
Chromosome-related variables: telomere length and telomerase level
Biological parameters that form part of an evaluation of allostatic load in the scientific models and studies that have been discussed . Abbreviations: PEF peak expiratory flow DHEA-S dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate A adrenaline NA noradrenaline CRP C-reactive protein IL-6 interleukin 6 TNF tumour necrosis factor HbA1c glycosylated haemoglobin TG triglycerides HDL high density lipoprotein LDL low density lipoprotein WHR waist-hip ratio BMI body mass index
Recent trauma research provides insight into how detrimental childhood experiences may lead to toxic stress which is reflected in disturbed maturation of brain structure in the developing individual. Neuroimaging studies have linked such structural changes to experiences of verbal abuse, harsh corporal punishment and sexual abuse . The plasticity and vulnerability of the brain appear to vary with the individuals age the detrimental potential of adverse experiences will depend on when they occur and how long they last .
What Are The Weaknesses Of The Biological Approach
Although there are many advantages to the biological approach, itâs not perfect. Letâs take a look at some of the weaknesses of this approach:
Oversimplification
Bodies are so complex itâs too simple to claim that a lack or excess of one neurotransmitter is the only factor responsible for the behaviour of the entire organism. Also, the many influences in our environment impact behaviour, so reducing the cause of an illness to a molecule might mean not taking other factors into account.
We know that major depression is linked to a deficit of serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitters.
The biological model would treat major depression by administering a drug to correct the imbalance. However, it does not consider the emotions and environmental stressors that can play a part in the development and continuation of the illness. Recently, health psychology has started applying an updated version of the biological approach to illnesses, called the biopsychosocial model, which tries to address all the different social, psychological and biological factors.
Determinism
Individual differences ignored
Lateralisationrefers to the side that something is located or something happens in the brain. We know that the area responsible for speech and language called Wernickeâs area is located on different sides of the brain, depending on whether the person is right-handed or left-handed.
Correlation is not causation
You May Like: Is Physics Required To Graduate High School
Responding To The Evolutionary Verdict On Classificatory Essences
The lack of a human essence in the sense of intrinsicnecessary and sufficient conditions for belonging to the species taxon, has led a number of philosophers to deny thatthere is any such thing as human nature . As this negative claim concerns propertiesintrinsic both to relevant organisms and to the taxon, it is equallydirected at the nature of the organisms as speciesspecimens and at that of the species taxon itself. An alternativeconsists in retracting the condition that a classificatory essencemust be intrinsic, a move which allows talk of a historical orrelational essence and a corresponding relational conception oftaxonomic human nature .
Which of these ways of responding to the challenge from evolutionarytheory appears best is likely to depend on how one takes it that theclassificatory issues relate to the other matters at stake in theoriginal human nature package. These concern the explanatory andnormative questions raised by TP1TP4. We turn to these in thefollowing three sections of this article.
Learning And Teachers Attitudes
The biological conception of man may also influence the way teachers think about human beings and learning, and this can affect the way they approach their students. As was explained above, biological determinism explains the distinction between human beings on basis of brain size, genetic makeup and other biological characteristics . Consequently, people are different because they have diverse biological features. The theory implies that people have unique characteristics that require selective teaching and learning, as proposed by proponents of educational genomics.
If a teacher has a biological conception of man, they will believe that the students skills and abilities are pre-determined, inherited, and that they will not be able to break the bounds of the limits set by their biological makeup. It may thus be believed that the students parents are a good indication of what their child may become. If the parents are menial workers, it is a sign that their genetic inheritance has led them to such professions and thus their offspring will share similar tendencies. A teacher with such beliefs may decide to focus on specific students with superior biological characteristics that predispose them to learn while ignoring the needs of other students. These ideas of human beings may also include polygenist attitudes that are generally deemed racist in todays world: some human races are seen as more capable in some areas rather than others.
You May Like: How To Find Distance In Physics
Secondary Altriciality As A Game
Explanatory accounts that emphasise developmental plasticity in theproducts of human DNA, in the neural architecture of the brain and inthe human mind tend to reject the assumption that explanations of whathumans are like should focus on intrinsic features. It should,however, be noted that such accounts can be interpreted as assigningthe feature of heightened plasticity the key role in such explanations. Accounts that make plasticity causally centralalso raise the question as to whether there are not biologicalfeatures that in turn explain it and should therefore be assigned amore central status in a theory of explanatory human nature.
Of course, these features are themselves contingent products ofevolution that could be outlived by the species. Gould sees them ascomponents of a general retardation of development that hascharacterised human evolution , wherehuman should be seen as referring to the cladeallthe descendants of a common ancestorrather than to the species.Anthropologists estimate that secondary altriciality characterised thelineage as from 1.5 million years ago . We are, then, dealing with a set of deeplyentrenched features, features that were in place long beforebehavioural modernity.