Basic And Complex Emotions
In emotional psychology, emotions are split into two groups: basic and complex.
Basic emotions are associated with recognizable facial expressions and tend to happen automatically. Charles Darwin was the first to suggest that emotion-induced facial expressions are universal. This suggestion was a centerpiece idea to his theory of evolution, implying that emotions and their expressions were biological and adaptive. In fact, emotions have been observed in animals by researchers for several years, suggesting that theyre pivotal to survival in other species as well. Basic emotions are likely to have played a role in our survival throughout human evolution, signaling to those around us to react accordingly.
Emotional psychologist Paul Ekman identified six basic emotions that could be interpreted through facial expressions. They included happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust. He expanded the list in 1999 to also include embarrassment, excitement, contempt, shame, pride, satisfaction and amusement, though those additions have not been widely adapted.
Data Cleaning And Processing
Before running the focal analyses, experimental data often need to be cleaned and prepared for analysis. Data cleaning involves many choices related to missingness, outliers, or violations of the distributional assumptions. Because of potential drop-out, data collection problems, or a lack of full responses for other reasons , some data might be missing entirely for participants or for some or many of the variables of interest. Missing data can be dealt with by listwise deletion, pairwise deletion, multiple imputation, full information methods, and other methods . This choice creates a researcher DF, namely A1: Choosing between different options of dealing with incomplete or missing data on ad hoc grounds.
Neuroimaging techniques and other data-intense measurement procedures require extensive pre-processing steps that entail considerable maneuverability in the analysis of the data . For instance, with neuroimaging data, decisions related to regions of interest, dealing with head motions, corrections for slice timing, spatial smoothing, and spatial normalization can create a large number of different ways to analyze the data . The processing of such data can be done based on whether they provide preferred results, which offers A2: Specifying pre-processing of data in an ad hoc manner.
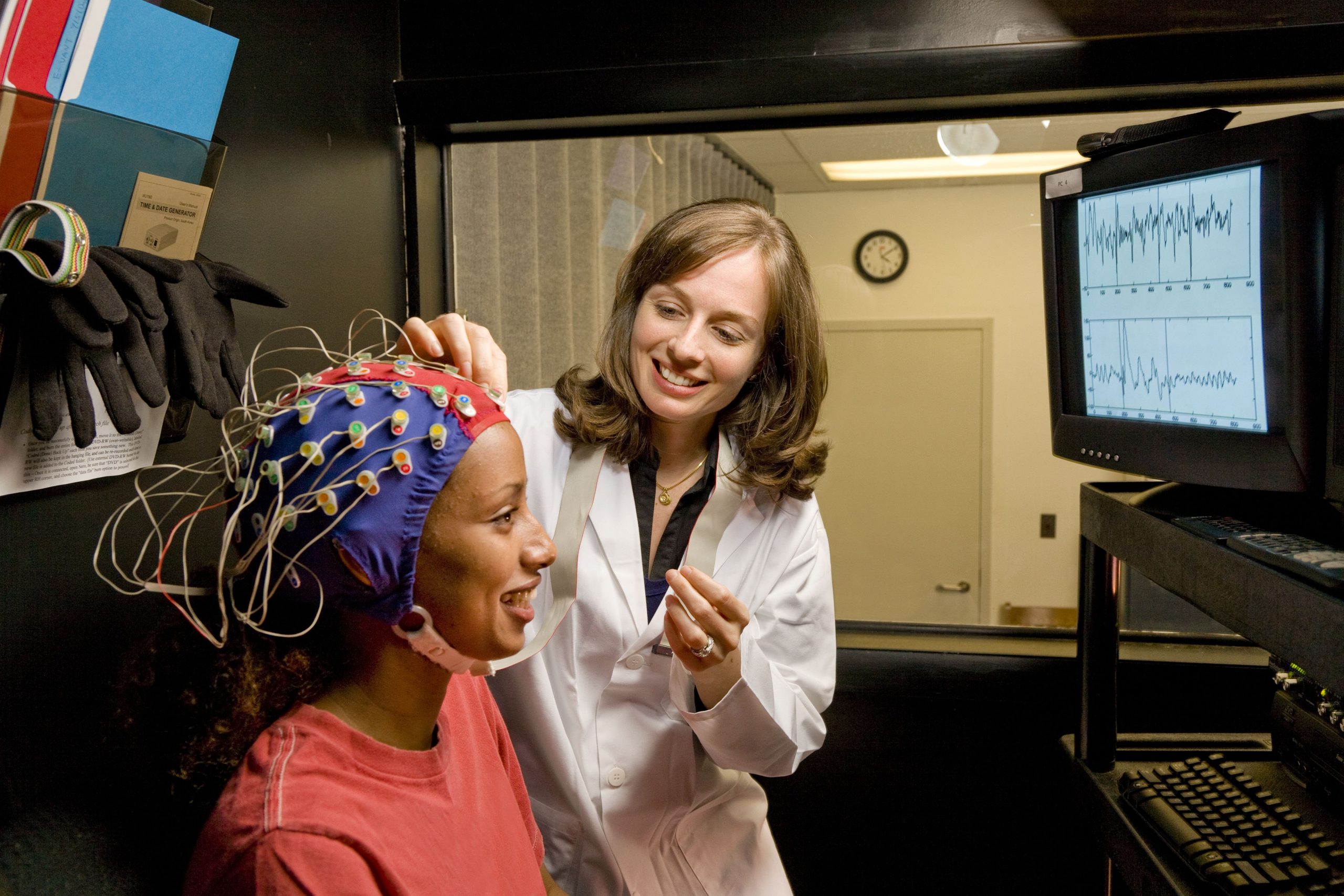
The Science Of Emotion: Exploring The Basics Of Emotional Psychology
Posted June 27, 2019 by UWA | Psychology and Counseling News
Important Dates
How we interpret and respond to the world around us makes up who we are and contributes to our quality of life. The study of emotional psychology allows researchers to dive into what makes humans react as they do to certain stimuli and how those reactions affect us both physically and mentally. While the study of emotional psychology is vast and complex, researchers have discovered quite a bit about what constitutes our emotions and our behavioral and physical reactions to them.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Strengths Of Case Studies
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants with the aim of âaveragingâ.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research which only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension to experience which is so important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas . They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is therefore important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view .
Psychology As A Science
Many psychology undergraduate programs are shaped by the goals laid out in the American Psychology Associations “Guidelines for the Undergraduate Psychology Major”, said Dr. Michelle Hill, senior associate dean of psychology programs at Southern New Hampshire University . Goal two of the American Psychology Association guidelines version 2.0 is Scientific Inquiry and Critical Thinking, which includes the following subgoals: Use scientific reasoning to interpret psychological phenomena, demonstrate psychology information literacy, and interpret, design, and conduct basic psychological research.
More widespread recognition of psychology as a science is one of the points of emphasis in the APA guidelines, Hill said.
Read Also: Hawkes Learning Review
Statistical Model Estimation And Inference
Finally, without a specific and precise registration, a researcher can choose inference criteria in different ways, and on the basis of analytic outcomes. Thus A15: Choosing inference criteria is another researcher DF. For instance, a researcher can choose to use a one-sided test if this is the only way to obtain significance, or employ more lenient corrections for multiple testing if the need arises. Preregistrations should explicate these criteria.
The Beginnings Of Psychology As A Discipline
In the early days of psychology there were two dominant theoretical perspectives regarding how the brain worked, structuralism and functionalism.
Structuralism was the name given to the approach pioneered by Wilhelm Wundt , which focused on breaking down mental processes intro the most basic components.
The term originated from Edward Titchener, an American psychologist who had been trained by Wundt. Wundt was important because he separated psychology from philosophy by analyzing the workings of the mind in a more structured way, with the emphasis being on objective measurement and control.
Structuralism relied on trained introspection, a research method whereby subjects related what was going on in their minds while performing a certain task.
However, introspection proved to be an unreliable method because there was too much individual variation in the experiences and reports of research subjects.
Despite the failure of introspection Wundt is an important figure in the history of psychology as he opened the first laboratory dedicated to psychology in 1879, and its opening is usually thought of as the beginning of modern experimental psychology.
An American psychologist named William James developed an approach which came to be known as functionalism, that disagreed with the focus of Structuralism.
Also Check: Ccl4 Lone Pairs
Measuring Affect Behavior And Cognition
One important aspect of using an empirical approach to understand social behavior is that the concepts of interest must be measured . If we are interested in learning how much Sarah likes Robert, then we need to have a measure of her liking for him. But how, exactly, should we measure the broad idea of liking? In scientific terms, the characteristics that we are trying to measure are known as conceptual variables, and the particular method that we use to measure a variableof interest is called an operational definition.
For anything that we might wish to measure, there are many different operational definitions, and which one we use depends on the goal of the research and the type of situation we are studying. To better understand this, lets look at an example of how we might operationally define Sarah likes Robert.
One approach to measurement involves directly asking people about their perceptions using self-report measures. Self-report measures are measures in which individuals are asked to respond to questions posed by an interviewer or on a questionnaire. Generally, because any one question might be misunderstood or answered incorrectly, in order to provide a better measure, more than one question is asked and the responses to the questions are averaged together. For example, an operational definition of Sarahs liking for Robert might involve asking her to complete the following measure:
Who Conducts Scientific Research In Psychology
Scientific research in psychology is generally conducted by people with doctoral degrees and masters degrees in psychology and related fields, often supported by research assistants with bachelors degrees or other relevant training. Some of them work for government agencies , for nonprofit organizations , or in the private sector . However, the majority of them are college and university faculty, who often collaborate with their graduate and undergraduate students. Although some researchers are trained and licensed as cliniciansespecially those who conduct research in clinical psychologythe majority are not. Instead, they have expertise in one or more of the many other subfields of psychology: behavioral neuroscience, cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, personality psychology, social psychology, and so on. Doctoral-level researchers might be employed to conduct research full-time or, like many college and university faculty members, to conduct research in addition to teaching classes and serving their institution and community in other ways.
Recommended Reading: Algebra Nation Section 7: Exponential Functions Answers
Chapter 1 The Science Of Psychology
Many people believe that women tend to talk more than menwith some even suggesting that this difference has a biological basis. One widely cited estimate is that women speak 20,000 words per day on average and men speak only 7,000. This claim seems plausible, but is it true? A group of psychologists led by Matias Mehl decided to find out. They checked to see if anyone had actually tried to count the daily number of words spoken by women and men. No one had. So these researchers conducted a study in which female and male college students wore audio recorders while they went about their lives. The result? The women spoke an average of 16,215 words per day and the men spoke an average of 15,669an extremely small difference that could easily be explained by chance. In an article in the journal Science, these researchers summed up their findings as follows: We therefore conclude, on the basis of available empirical evidence, that the widespread and highly publicized stereotype about female talkativeness is unfounded .Mehl, M. R., Vazire, S., Ramirez-Esparza, N., Slatcher, R. B., & Pennebaker, J. W. . Are women really more talkative than men? Science, 317, 82.
Psychology Classes Can Be Tough
Many students may realize this as they struggle through their general psychology courses. Why do some people mistakenly believe that psychology is simple and easy? One reason might be because many tend to assume that since they have so much personal experience with human behavior, they will naturally be experts on the subject.
Obviously, no one would suggest that an English class should be an easy A simply because you speak English. Just like English can be a challenging subject for any native speaker, psychology classes can be equally tough, particularly for students who have little experience with the subject or who have a limited background in subjects such as science and math.
Fortunately, just because psychology is challenging doesn’t mean that it isn’t accessible to anyone who might take an interest in it. While there might be a learning curve, you can definitely succeed in your psychology classes with effort and determination.
Read Also: Kendall Hunt Geometry Answer Key
Final Thoughts On Psychology Research Methods
The above methods provide a cursory overview of five main psychology research methods. While they are really much more detailed in size and scope, this overview highlights the malleable nature of psychological research and the rigor involved in social science research. There are several other methods derivative of the five methods above, and there are other methodologies that are not listed here.
This type of research occurs at all levels of academia and other settings, as masters and Ph.D. students are learning to become adept researchers while preparing for careers as academics, researchers, and the like.
As with all research, these methodologies have their strengths and weaknesses. However, they have proven rigorous and robust over time and have produced substantive findings in the field of psychology. Despite their differences, strengths, and weaknesses, all of these methods are designed to move forward the discipline of psychology in an attempt to understand the functions of the human mind and how they impact human behaviors in specific contexts and circumstances.
Related:
Marriage And Family Psychology

focus their work on the emotions, thoughts and behaviors of individuals, couples and familiesboth in relation to one another and their broader environments. As such, specialized knowledge in systemic relational systems is required in this role.
Its typical for these types of psychologists to address a wide range of clinical problems. These can include alcohol and drug abuse, youth problem behavior, depression, parent-child conflicts, developmental disorders, sexual or physical abuse, medical issues and more.
Some marriage and family psychologist positions prefer candidates who have a Ph.D. in psychology or a Doctor of Psychology degree. Programs like a Master of Arts in Psychology with a Marriage and Family Therapy concentration, however, can help hopefuls meet licensure requirements in 39 states.
Read Also: Valence Electrons In Ccl4
Organization Of This Volume
We begin this volume with a section on broad psychological theories. This section includes basic psychological theories that concern personality, early childhood and adult development, rational choice, decision-making, the study of emotion, evolutionary psychology, genetics, and political rhetoric. Then we move to the substantive focus of different areas of political psychological research, which tend to cut across theoretical approaches. We start with elite behavior, first in the area of international relations and then in the area of domestic politics. The next section focuses on mass political behavior, including an analysis of political reasoning, political ideology, social justice, social influence, political communications, and political deliberation. The final section considers collective behavior, including identities, social movements, racial prejudice, migration and multiculturalism, discrimination, and intractable conflict.
The current Handbook is a companion to these volumes in political psychology and political behavior that has a somewhat different purpose. This Handbook is the place to go to find out what is currently known about the many different fields in the umbrella topic of political psychology and learn more about psychology, political science, and their vibrant intersection.
The Goals Of Psychology
The four main goals of psychology are to describe, explain, predict and change the behavior and mental processes of others
Describing a behavior or cognition is the first goal of psychology. This can enable researchers to develop general laws of human behavior.
For example, through describing the response of dogs to various stimuli, Ivan Pavlov helped develop laws of learning known as classical conditioning theory.
Once researchers have described general laws behavior, the next step is to explain how or why this trend occurs. Psychologists will propose theories which can explain a behavior.
For example, classical conditioning predicts that if a person associates a negative outcome with a stimuli they may develop a phobia or aversion of the stimuli.
Once psychology has described, explained and made predictions about behavior, changing or controlling a behavior can be attempted.
For example, interventions based on classical conditioning, such as systematic desensitization, have been used to treat people with anxiety disorders including phobias.
You May Like: What Is Abiotic In Biology
Psychology Is A Real Science
Some may think that psychology is not a real science. First, let’s examine exactly what science is and is not.
Some key characteristics of a science:
- Allows for hypothesis testing
- Findings allow researchers to predict future occurrences
- Objective
- Researchers control and manipulate variables
- Results can be replicated
- Uses empirical methods
Psychology relies on all of these methods in order to investigate human and animal behavior. Researchers utilize the scientific method to conduct research, which means that variables are controlled and operationally defined.
Experimenters are able to test different hypotheses and use statistical analysis to determine the likelihood that such results are due merely to chance. Psychologists also present their findings in a way that makes it possible for other researchers to replicate their experiments and methods in the future.
Psychology might be a relatively young science in the grand scheme of sciences, but it is indeed a real science. However, it’s important to note that scientific psychology does have some limitations. Human behavior can vary and change over time, so what is true in one particular time and place might not necessarily apply in different situations, settings, cultures, or societies.
The Perspectives Of Psychology
Structuralism and functionalism have since been replaced by several dominant and influential approaches to psychology, each one underpinned by a shared set of assumptions of what people are like, what is important to study and how to study it.
Psychoanalysis, founded by Sigmund Freud was the dominant paradigm in psychology during the early twentieth century.Freud believed that people could be cured by making conscious their unconscious thoughts and motivations, thus gaining insight.
Freudâs psychoanalysis was the original psychodynamic theory, but the psychodynamic approach as a whole includes all theories that were based on his ideas, e.g., , Adler and Erikson .
The classic contemporary perspectives in psychology to adopt scientific strategies were the behaviorists, who were renowned for their reliance on controlled laboratory experiments and rejection of any unseen or unconscious forces as causes of behavior.
Later, the humanistic approach became the ‘third force’ in psychology and proposed the importance of subjective experience and personal growth.
During the 1960s and 1970s, psychology began a cognitive revolution, adopting a rigorous, scientific, lab-based scientific approach with application to memory, perception, cognitive development, mental illness, and much more.
Read Also: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
The Most Effective Learning Techniques
If you have only limited time to read this page, at least check out the following two points. Forfurther details, click on the links to learn more.
Based on decades of learning science research, the two most effective methods known to date are:
- Spaced practice / distributed practice learning that occurs over multiple sessions at different points in time . This technique refers to when you should be preparing for course exams .
Further information: Spaced Practice
- Retrieval practice / practice testing instead of simply restudying information, attempting to recall that information from memory . This technique refers to what you should be doing to prepare for course exams .
Further information: Retrieval Practice
Spaced practice involves when you should study and retrieval practice involves how you should study. When you use both , they make a powerful combination.
Additionally, if you perform retrieval practice across multiple days and, each time, practice recalling information until you attain 100% accuracy then recent research shows that your ability to retain that information over long periods of time is maximized.6
Finally, besides spaced and retrieval practice, there are some additional learning techniques that you may wish to try. These included interleaved practice, self-explanation, and others.