Why Does Limiting A Population Space Decreases The Carrying Capacity
The less space there was, the fewer amounts of individualssupported in the environment. Infer: Why do you think limiting a populations space decreases the carrying capacity? There is less space, food, and prey, so obviously the population decreases because therearent enough resources to support a larger amount.
Stage : Delayed Degenerative Diseases
Though degenerative diseases still exist for countries in this stage, medical advances and technology prolong the life expectancy further than countries in the third stage. Delayed degenerative diseases are reduced further as society makes lifestyle changes in health regarding diet, tobacco and alcohol consumption, and exercise.
Resources For Teaching Students About Doubling Time
Recommended Reading: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Chapter 7 Population And Migration
R. Adam Dastrup
Understanding how the human population is organized geographically helps us make sense of cultural patterns, the political organization of space, food production issues, economic development concerns, natural resource use and decisions, and urban systems. Additionally, themes of location, space, place, the scale of analysis, and pattern can be emphasized when studying fundamental population issues such as crude birth rates, crude death rates, total fertility rate, infant mortality rates, doubling time, and natural increase.
Explanations of why the population is growing or declining in some places are based on patterns and trends in fertility, demographic mortality, and migration. Analyses of refugee flows, immigration, and internal migration help us understand the connections between population phenomena. For example, environmental degradation and natural hazards may prompt population redistribution at various scales, which in turn creates new pressures on the environment, culture, and political institutions.
This chapter will analyze population trends across space and time as ways to consider models of population growth and decline, including Malthusian demographic transition, and the epidemiological transition model.
Free Ap Human Geography Flashcards About Ap Human Geo #
Ap human geography unit 2 study guide answer key but define terms in context and use examples when Friday, 9/25 Objective: Read, define, and calculate doubling time, natural growth rate, and overall growth rate. Analyze data and determine possible population problems Activities. Note: The following concepts transcend all units in AP Human Geography they are central to all geographic thinking and analysis and could even be considered central to any definition of geography. Give a definition, any other information you might need to help you remember, and an example/illustration if it fits AP Human Geography Tuesday, October 5, 2010. Key Issue #4. Doubling time is the number of years needed to double a population. The current doubling time is about 50 years. This is low compared to in the 1960’s when the doubling time was about 35 years. A ecumene is the portion of Earth’s surface occupied by permanent human settlements. Example Items. World Geography Pre-AP . World Geography Pre-AP Example Items are a representative setof items for the ACP. Teachers may use this set of items along with the test blueprint as guides to prepare students for the ACP. On the last page, the correct answer, content SE and SE justification are listed for each item
You May Like: Scientific Definition Of Abiotic
Gender Age And Education
Ravenstein theorized that males were more likely to migrate than females, the longer the distance to relocate. The idea is that men are more likely to find employment than women. For much of human history, this was actually the case. But in the 1990s, gender patterns regarding migration began to change. Now, more women migrate to the United States than males.
Ravenstein also believed that long-distance migration occurred more with young adults, rather than children and elderly. In the United States, over 40 percent of immigrants are young adults. Children make up roughly 16 percent, and elderly make up less than 5 percent of immigration into the United States.
There is a growing concern of unaccompanied minors, between 12 to 17 years old in age, migrating to the United States. The majority of them are males, coming from Honduras and El Salvador because of gang violence.
How Do You Find The Carrying Capacity Of A Population
Carrying capacity is most often presented in ecology textbooks as the constant K in the logistic population growth equation, derived and named by Pierre Verhulst in 1838, and rediscovered and published independently by Raymond Pearl and Lowell Reed in 1920:Nt=K1+eartintegral formdNdt=rNKNKdifferential formwhere N is
Recommended Reading: Abiotic Definition And Examples
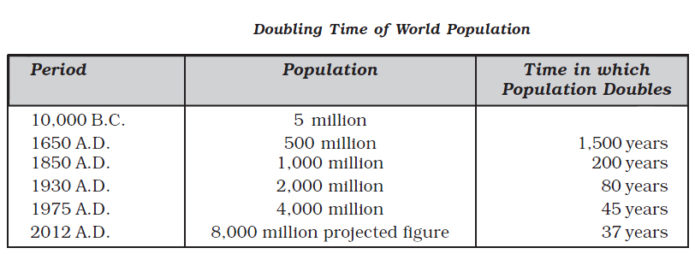
Doubling Time: Definition & Calculation
AP Human Geography Models & Theories Zelinsky was student of Carl Sauer a cultural geographer who, for six decades, has been an original and authentic voice i Study Flashcards On AP Human Geo Chapter 2 Test at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want 7. Define doubling time: 8. In what world regions is most growth occurring? AP Human Geography Chapter 2: Population Example Countries Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 No Country in AP Human Geography Chapter 2: Population 16. Complete the following statement: The first break came to Africa, Asia and Lati The AP Human Geography course is equivalent to an introductory college-level course in human geography. The course introduces students to the systematic study of patterns and processes that have shaped human understanding, use, and alteration of Earth’s surface. Students employ spatial concepts and landscape analysis to examine socioeconomi
What Is Exponential Growth
March 19, 2015
This is the first post in a three-part series on exponential growth and doubling time concepts that are important in not only mathematics courses, but life science and AP Environmental Science courses. The series will explore these concepts, describe the calculations involved, and provide educators with resources for teaching students about these important topics.
You May Like: Lesson 4.5 Practice B Geometry Answers
Where Is It Useful
A constant relative growth rate means simply that the increase per unit time is proportional to the current quantity, i.e. the addition rate per unit amount is constant. It naturally occurs when the existing material generates or is the main determinant of new material. For example, population growth in virgin territory, or fractional-reserve banking creating inflation. With unvarying growth the doubling calculation may be applied for many doubling periods or generations.
In practice eventually other constraints become important, exponential growth stops and the doubling time changes or becomes inapplicable. Limited food supply or other resources at high population densities will reduce growth, or needing a wheel-barrow full of notes to buy a loaf of bread will reduce the acceptance of paper money. While using doubling times is convenient and simple, we should not apply the idea without considering factors which may affect future growth. In the 1950s Canada’s population growth rate was over 3% per year, so extrapolating the current growth rate of 0.9% for many decades is unjustified unless we have examined the underlying causes of the growth and determined they will not be changing significantly over that period.
Structural Changes Of Populations
Before we look at the model used to analyze how populations change, it is essential to look at key factors that influence the structure of a population. A regions population will grow as long as their crude birth rates are greater than their crude death rates. A crude birth rate is the total number of live births for every 1,000 people in a given year. So a crude birth rate of 10 would mean ten babies are born every year for every 1,000 people in that region. Crude death rates are the total number of deaths per 1,000 people in a given year.
The total fertility rate is the average number of children a woman would be expected to have during the childbearing years . The global average for TFRs is about 2.5, but in developing countries, it is as high as 5.0 or higher, and in more developed countries it is as low as 2.0 or less. The total fertility rate is a direct expression of a nations health care system because it reflects a populations access to doctors, nurses, hospitals, and medicine.
The next important term to understand is the infant mortality rate . The IMR is determined by calculating how many children die before the age of 1 per 1,000 live births annually. The highest IMRs are in developing countries where rates can be as high as 80 or more. Conversely, in regions like Europe, it is as low as 5 per 1,000 live births annually.
Don’t Miss: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
What Is The Population Doubling Time For A Constant Growth Rate Of 3% Per Annum
Arithmetic density.
Step-by-step explanation:
The correct answer is arithmetic density. This is because for a country, it is also known as real density and it’s defined as the number of people per unit area of total land in that country.
Thus, the population of a country divided by its area determines its arithmetic density
See attachment for program source file
Explanation:
The source code in the question is not incorrect just that, it was poorly formatted.
So, what I did it that:
See attachment for the modified program source file
Stage : High Growth Rate
Around the mid-1700s, global populations began to grow ten times faster than in the past because of the Industrial Revolution. The Industrial Revolution brought with it a variety of technological improvements in agricultural production and food supply. Increased wealth in Europe, and later North America, because the Industrial Revolution meant that more money and resources could be devoted to medicine, medical technology, water sanitation, and personal hygiene. Sewer systems were installed in cities thus public health improved. All of this dramatically caused CDRs to drop around the world. At first, CBRs stayed high as CDRs dropped, this caused populations to increase in Europe and North America. Over time, this would change.
Africa, Asia, and Latin America moved into Stage 2 of the demographic transition model 200 years later for different reasons than their European and North American counterparts. The medicine created in Europe and North America was brought into these developing nations creating what is now called the medical revolution. This revolution or diffusion of medicine to this region caused death rates to drop quickly. While the medical revolution reduced death rates, it did not bring with it the wealth and improved living conditions, and development that the Industrial Revolution created. Global population growth is most significant in the regions that are still in Stage 2.
You May Like: Eoc Fsa Practice Test Algebra 2 No Calculator Portion Answers
Write Short Note On Doubling Time
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers
NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes, Videos
- 1 answers
Meghna Thapar 10 months, 2 weeks ago
Doubling time is the amount of time it takes for a given quantity to double in size or value at a constant growth rate. We can find the doubling time for a population undergoing exponential growth by using the Rule of 70. To do this, we divide 70 by the growth rate .
The doubling time is time it takes for a population to double in size/value. It is applied to population growth, inflation, resource extraction, consumption of goods, compound interest, the volume of malignant tumours, and many other things that tend to grow over time. When the relative growth rate is constant, the quantity undergoes exponential growth and has a constant doubling time or period, which can be calculated directly from the growth rate.
This time can be calculated by dividing the natural logarithm of 2 by the exponent of growth, or approximated by dividing 70 by the percentage growth rate .
The doubling time is a characteristic unit for the exponential growth equation, and its converse for exponential decay is the half-life.
Concepts Of Human Geography Explained
The numbers tell us with a great deal of accuracy where we are now, and how we got here. And they tell us with pretty fair confidence where we’ll be in the near future, because all of the next generations parents have already been born. But the numbers cant tell us for certain where well end up in the long run, because the current trajectories may not remain constant .
Demography:
| Census: Census an enumeration of people, houses, firms, or other important items in a country or region at a particular time . The census is conducted by the United States Census Bureau and is the main source of our demographic data. Other organizations that collect great data are the Pew Research Center and the World Bank. |
Population Explosion:Malthusianism, Neo-Malthusianism and the Irish Potato FamineEssay on the Principles of PopulationBirth Rate, Death Rate, Natural Increase and Fertility Rates:Demographic Transition Model and Population Pyramids:
| The Demographic Transition Model |
Population Bulge, Aging Population and the Baby Boom:Dependency Ratios:
| Youth Dependency in 1985 |
Don’t Miss: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
Ap Human Geography Exam
- AP Human Geography Chapter 2 Study Guide Terms: population density – a measurement of the number of people per given unit of land ·arithmetic population density – the population of a country or region expressed as an average per unit area ·physiologic population density – the number of people per unit area of arable land ·population distribution – description of locations on the Earth’s.
- istered between 2001 and 2019 with sample responses and scoring guidelines
- disciplinary term that we use in AP Human Geography. To use this effectively, identify the key terms and concepts that you learned this year and focus on those. Many of these terms should be words you know/ remember from this year and won’t need to be studied intensely. !! General Geography! geography ! Greek inuence on geography
- geography. The study of the earth and its features and of the distribution of life on the earth, including human life. human geography. The study of where and why human activities are located where they are. physical geography. The study where and why natural forces occur as they do. map. A two-dimension or flat scale model of something. plac
- utes
- Unit I Topics. Topic 1.1 Introduction to Maps A. Geographers use maps and data to depict relationships of time, space, and scale. 1. Identify types of maps. The types of information presented in maps and different kinds of spatial patterns and relationships portrayed in maps
- g method or another. AP Human Geography POPULATION.
Population In South Asia
South Asia has three of the ten most populous countries in the world. India is the second largest in the world, and Pakistan and Bangladesh are numbers five and six, respectively. Large populations are a product of large family sizes and a high fertility rate. The rural population of South Asia has traditionally had large families. Religious traditions do not necessarily support anything other than a high fertility rate. On the other hand, the least densely populated country in South Asia is the Kingdom of Bhutan. Bhutan has a population density of only fifty people per square mile. Bhutan is mountainous with little arable land. More than a third of the people in Bhutan live in an urban setting. Population overgrowth for the realm is a serious concern. An increase in population requires additional natural resources, energy, and food production, all of which are in short supply in many areas.
Table 9.1 Demographics of South Asia and the Worlds Most Populous Countries
| Rank |
|---|
| * Countries noted with an asterisk are part of South Asia |
| Empty cell indicates a negative population doubling time. |
Source: CIA World Factbook, June 2011, accessed September 13, 2011, .
Figure 9.5 Crowded Street in New Delhi, India
Urban areas of South Asia are expanding rapidly.
John Halsam IMG_3555 CC BY 2.0.
Figure 9.6 Population Growth in India
CIA World Factbook public domain.
Read Also: Algebra Age Word Problem
What Are The Positives And Negatives Of The One Child Policy
The policy has been beneficial in terms of curbing population growth, aiding economic growth, and improving the health and welfare of women and children. On the negative side there are concerns about demographic and sex imbalance and the psychological effects for a generation of only children in the cities.
Future Of Population Growth
As noted earlier, the United States Census Bureau estimates that the world population is roughly 7.57 billion people. Governments and other entities can dramatically influence population change as a way to increase or decrease population growth in a particular country. For example, some countries take dramatic steps to reduce their population. Chinas One-Child Policy dictated that each family could legally have only one child. Families that followed this policy were often given more money by the government or better housing. If a family illegally had another child, the family would be fined heavily. Children born illegally cannot attend school and have a difficult time finding jobs, getting government licenses, or even getting married. Some have reported that the government would force abortions on families with more than one child. One of the significant consequences of this policy was a dramatic increase in abortions and infanticides, especially of females. Female infanticide is linked directly to a global cultural trend that privileges males over femalesbaby boys are desired, especially if the family is only allowed, one child. This specific focus on eliminating women is called gendercide. Half the Sky, written by Nicholas Kristof and Sheryl WuDunn, documents global gendercide and what is being done to combat this problem.
Also Check: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet