Start With Active Listening
Slowing down and actively listening are essential to ward off emotional reactivity. When we listen actively, we are attempting to take in what the other is saying at face value. The goal is understand the message without letting our own biases, thoughts and emotions get in the way.
Active listening does not mean shutting down your feelings though. If you feel some emotions while your loved one is speaking, make a mental note of them but dont let them explode.
After actively listening, ask some questions to understand your partners position fully. Once you have a solid grasp of your loved ones position, check in with yourself and explore your feelings and thoughts. After that, its your turn to speak. Share your thoughts and emotions as matter-of-factly and calmly as possible.
Sometimes our emotions are very intense, yet we cant seem to make sense of them or properly articulate them. If thats the case, go back to them on your own or with a therapist and explore further. Theres something there.
With active listening, we can get to the underlying issues with much less conflict.
Psychological Response To A Laboratory Stressor
Three measures of psychological state were administered throughout the laboratory stress reactivity session: the Stress Reactivity Questionnaire , which measures state affect the Emotional Response to Stress Questionnaire , which assesses the amount of effort participants put into completing the tasks and the Rumination Measure , which assesses the extent to which participants were preoccupied by the tasks after having completed them. Additional detail on each of these measures is provided below.
What Is Selection Effect In Psychology
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby ensuring that the sample obtained is not representative of the population intended to be analyzed. It is sometimes referred to as the selection effect.
Don’t Miss: Physics Is The Most Basic Science Because
Is Malignant Reactivity Lethal To Causal Inference Placebo Effects Versus Reactivity
The previous section ends on a somber note regarding the damage that malignant reactivity can do to experimental exercises aimed at inferring the causal impact of a given variable through controlled interventions. Yet, the reader may immediately consider the parallels between malignant forms of reactivity and what routinely occurs in Randomized Controlled Trials when placebo effects are present . After all, the interventions that normally take place in RCTs often include, via placebo effects, a violation of condition IN-iii: the placebo effect created by exposure to any treatment can improve our mood or expectations in ways that in turn impact our health. Yet, as we know, the introduction of control groups routinely solves whatever problems this may create for causal inferential purposes.
In Fig. 5 we can see how the structure of the problem is formally similar in both the DG in the presence of reactivity and in an RCT with placebo effects. In both cases we see how malignant reactivity is present. However, there is a crucial difference between both situations: whereas in the case of RCTs the assumption of placebo effects that are equivalent across treatments seems generally valid , it seems much harder to satisfy in the case of treatments involving some form of mental causation.Footnote 8
Fig. 5
There is no reactivity involved either in the standard DG or on its modified version.
Different Effects Of Reactivity Psychology

Have you ever noticed that peoples behaviour changes when in the presence of different people? This is extremely common in a multitude of different situations and is known as reactivity.
Reactivity psychology is the study of the psychological phenomenon where people change their behaviour both positively and negatively depending upon the situation and the people involved.
It is a particularly interesting phenomenon and it also has a great impact in many situations. All scientists, teachers, and leaders should be aware that reactivity in their industry can happen and take the necessary steps to overcome it.
At the same time, law enforcement departments and others can make use of the psychology behind this to create positive results.
Related Read
Don’t Miss: Abiotic Definition And Examples
Emotional Reactivity Points To Remember
Agility Balance And Reaction Time
For activities requiring agility, balance, and good reaction time, the physical fitness profile should include these items. Balance testing is especially important in the elderly population.155 OBrien155 advocated the Sharpened Romberg test, functional reach test, timed get-up-and-go test , and Tinetti assessment tool for balance and gait. The functional reach test involves the patient reaching forward as far as possible without falling forward or taking a step while the examiner measures for distance horizontally. The Tinetti assessment tool has two parts. The first part measures static and dynamic sitting and standing balance and the second part assesses gait .175 Ideally, testing should be related to the specific activity.Agility is defined as the ability to change directions rapidly when one is moving ata high rate of speed.3 Agility and balance tests are often measured by time or accuracy .3,176
Recommended Reading: Molecular Geometry Report Sheet Answer Key
History Of Reaction Formation
The concept of defense mechanisms was initially proposed in the late 1800s by Sigmund Freud as part of his psychoanalytic theory. While Freud started the discussion on defense mechanisms, his daughter Anna Freud advanced the idea further by proposing 10 important defense mechanisms in her seminal book, The Ego and the Mechanisms of Defense, published in 1936. One of those 10 defense mechanisms was reaction formation.
How To Recognize Reaction Formation
Reaction formation is a way for the ego to defend itself against any thoughts or feelings that an individual finds unacceptable due to personal, familial, community, or societal standards. While this may protect the individual’s self-esteem at the moment, this can become problematic over time. It suppresses one’s authentic self, which harms one’s well-being.
Unfortunately, reaction formation can be especially challenging to recognize in everyday life. Someone defending their ego this way can be extremely passionate about the beliefs and preferences they outwardly express while their true beliefs stay buried in the subconscious.
Learning about defense mechanisms and examining your behavior can help you determine whether you may be using reaction formation to shield yourself from unwanted thoughts or feelings. A mental health professional can best guide you through this process, given they can explore your behavior with you and provide a more objective perspective.
Read Also: Glencoe Geometry Concepts And Applications Practice Workbook Answers
When Youre Proactive You Can Choose What To Focus On
When youre reactive, your feelings depend on external events outside your influence or control. Whether you have a good or bad day depends entirely on what happens to you and around you. The weather, what your boss says about your presentation, what mood your partner is in when you get home, how your favorite team played: All these outside things control your emotions you dont. And when your actions are based on your feelings which they usually are youre in dangerous reactive behavior territory. Everything you do is someone elses fault. Youre not in control of your life.
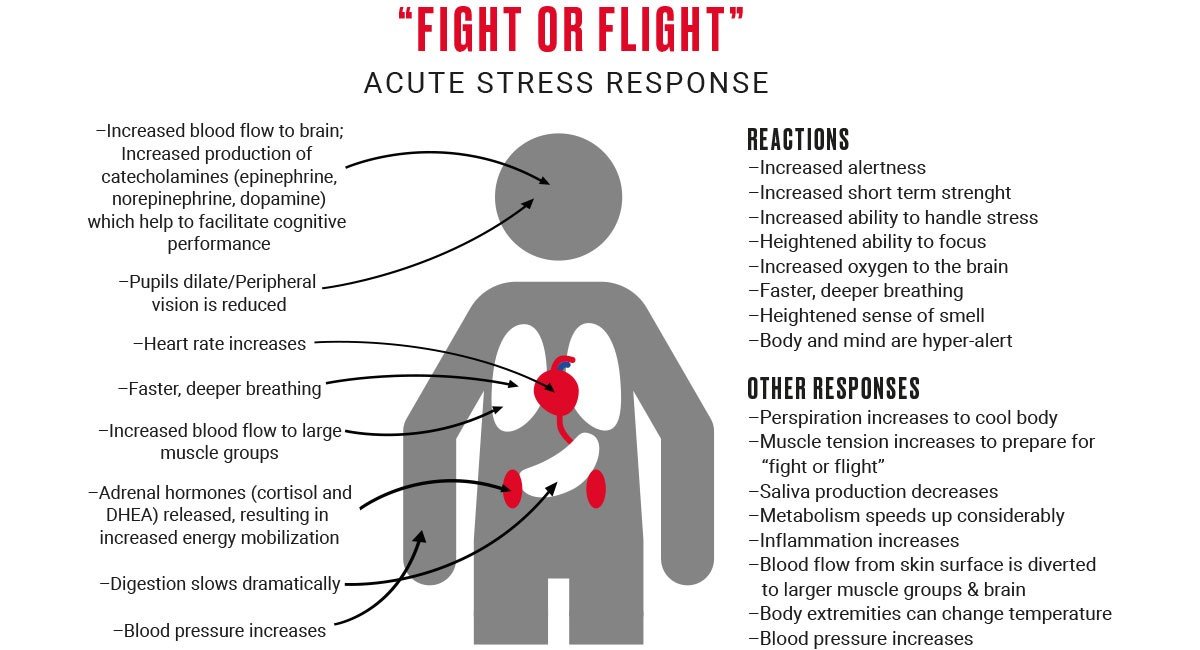
A good friend says something hurtful a romantic partner is in a lousy mood your child refuses to eat what you cooked for dinner your boss asks you to have work done by Monday, and its Friday afternoon. Your reaction comes straight from human evolution: Stresshormones flood your body, shutting down the rational part of your brain, and you enter reactive fight-flight-or-freeze mode. Instead of seeing whether the insult was intended, you respond with an insult of your own instead of inquiring about why your partner is in a bad mood, you give them the cold-shoulder in retaliation you punish your child rather than find a solution and you resentfully accept the work rather than ask for an extension. Your reactive behavior then makes the situation worse. When in reactive mode, you can turn trivial things into full-blown crises.
Analysis Of Group Differences
Missing dates for blockage or CAUTI occurrence was an indication that the calendar was not used in these instances, despite the participants’ report of the occurrence and frequency of these catheter-related problems. Details on blockage, including dates of the events, were asked only on the first four blockages per participant , and a few individuals had blockage as often as 20 times in 2 months. Recorded dates were missing for 1.8% of the reports of the first four blockages in nine individuals, six in the experimental group and three in the control group. These included 19 blockage events recorded as âdon’t knowâ and 5 events recorded as ârefused to answerâ . Only three dates for CAUTI were missing as âdon’t knowâ in three individuals, one in the experimental group and two in the control group. Therefore, we believe that the groups were similar in their use of their calendars for reporting blockage and CAUTI events.
Recommended Reading: Example Of Elastic Force
What Is Psychological Reactivity
In psychology, reactivity is a concept that serves to designate the tendency that individuals have to modify their behavior when they feel like someone is watching them. The presence or absence of psychological reactivity causes us to behave in one way or another, whether we are alone or accompanied. In fact, reactivity may not exist in contexts in which we are surrounded by many people, precisely because the fact of being in a very crowded place can make us think that no one is going to notice us. What matters is the fact of being aware that someone is watching us, not so much our physical proximity to other people who might see us.
So that, psychological reactivity may appear at times when we are alone, if we come to believe that there are incorporeal entities looking at us, something typical of magical thinking. But neither does this belief need to be very firm The simple fact of evoking a person we want to make a good impression on can cause us, without realizing it, to behave in a way more similar to how we would if that someone were really observing us.
It is this phenomenon that makes, for example, Social Psychology not only study the influence that others have on the person, but also the influence they have on these imaginary entities that are perceived as real or partially real in the here and now .
Being Aware Of Yourself

Another aspect of learning about reactivity is learning to be aware of ones actions.
We tend to live our lives on autopilot, not looking critically at everything life throws at us. Because of this, many of us may avoid being aware of how we change depending on the person.
Practicing mindfulness, or the full awareness of the present, is one technique you can try whenever you want to improve your mental health.
Also Check: Beth Child Of Rage Where Is She Now
What Is A Reactive Personality
Now that weve explained the two aspects of reactivity, it should be easier to recognize a reactive personality.
Its someone who allows their current situation to dictate their thoughts and actions.
From an outside perspective, it might seem like these reactive individuals are simply being spontaneous, but reactivity can go too far in both directions both positive and negative.
So, what is the antidote to a reactive personality? Being more proactive.
How To Manage Reactivity
Reactivity psychology is a really interesting topic to explore, however, if youre experiencing reactivity first hand it can be quite a negative experience. It is always a good idea to understand what is actually happening in these situations so that you are able to deal with the situation appropriately and effectively.
If you feel that you cannot manage reactivity on your own it might be worth speaking to a counsellor to help you overcome the situation.
Have you experienced reactivity psychology before? We would love to hear your experiences in the comments section below. As always, if you have found this article of any value we would love for you to and share with your friends and family across social media and beyond!
Also Check: Half Life Calculation Formula
What Is The Name For The Problem That People Might Change Their Behavior When They Know They’re Being Studied
The Hawthorne Effect is when subjects of an experimental study attempt to change or improve their behavior simply because it is being evaluated or studied. The term was coined during experiments that took place at Western Electric’s factory in the Hawthorne suburb of Chicago in the late 1920s and early 1930s.
What Is Emotional Reactivity
When we feel stressed, angry, or hurt, we tend to react impulsively. We are in a state of fight-or-flight and tend to react emotionally, that is, to overreact. That overreaction is emotional reactivity. In that moment, our perceptions of the situation are altered. The emotional charge prevents us from seeing the situation for what it is. Instead, we react. At this point, there is no listening going on anymore. Our emotions and defenses are driving our behaviors.
Recommended Reading: Kendall Hunt Algebra 1
Examples Of Reaction Formation
While reaction formation may seem counterintuitive, there are many scenarios in which an individual may outwardly support one view while unconsciously feeling its exact opposite.
Here are some additional examples of reaction formation:
- During adolescence, when people want to psychologically separate from their parents, a teenager expresses contempt for their parents to avoid acknowledging any feelings of love or affection toward them.
- A man’s self-esteem is threatened by the possibility that he is not masculine enough, so he overcompensates by acting aggressive and macho.
- A drug addict loudly preaches against substance abuse and for abstinence from them.
- Individuals who cannot consciously accept their anger and aggressive desires act in a calm, passive manner.
- A young man who craves romance but can’t seem to find a woman who will return his affection protects his ego by expressing sexist and misogynistic beliefs.
- A woman proclaims she and her mother have the perfect relationship when, in fact, the pair have a history of strife and conflict.
Pygmalion Effect And Golem Effect
Reactivity psychology is very common in a school setting. The Pygmalion Effect is where students change their behaviour based on what they feel the teachers expect from them. If the performance expectations are high, students will perform well where as if there are no expectations, performance may be lower.
The Golem Effect is similar however this is the effect when teachers have lower expectations of their students. When this happens students tend to show worse performance and slack off in lessons. This can also be applied to teachers too. When students are more attentive, teachers grade them higher even if their work is a substandard effort to those who didnt pay attention.
These two effects can also be applied in industrial settings too.
Recommended Reading: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Worksheet Answer Key
Keeping Your Life Going
We change how we behave if our manager or boss is watching us because we do not want to lose our jobs. If you dont keep productivity going, then you may end up being fired.
The same applies to school. You may want to make sure you are listening to your teacher so you can get ahead in class. If you arent, then you end up failing.
However, when youre not being supervised, you may relax more. You may pay less attention as a result.
As we said, most of this is common sense. We all have to change how we present ourselves according to our occupation. With reactivity psychology, however, you may start to realize just how much you change because of your behaviors.
What Is Maturation Effect
The maturation effect is any biological or psychological process within an individual that systematically varies with the passage of time, independent of specific external events. Examples of the maturation effect include growing older, stronger, wiser, and more experienced. These examples involve longlasting changes.
Recommended Reading: Math Nation Independent Practice Answers
What Does It Mean For Me
Reactivity in psychology can tell us a lot about human nature.
Of course, the main takeaway from it is that our behaviors change depending on the person observing us. Meanwhile, if we are alone, or believe we are alone, we will behave differently altogether.
There are different motivations for wanting to change your behavior, and these include:
How Can You Identify Reaction Formation
As with many things that have to do with the mind, reaction formation can be difficult to identify. Its wrapped up in questions of motivation, desire, and intent, all of which require self-awareness and honesty on the part of the acting individual to assess properly. If someone angrily rails against something, its not necessarily because they secretly want that thing, and they may never admit it even if they do.
This is also why a reaction formation is more likely when the desire is partly or wholly subconscious. Dealing with embarrassing emotions is hard enough, but it becomes harder to do it with others when you dont know how to describe them yourself. Also, if someone acts like they hate something, were more likely to assume they hate it than assume deep down they love it.
All of this is even further complicated because reaction formation is a response to thoughts we feel negative about. Fear, shame, and confusion are some of the primary motivators for reaction formation. Because we all experience those feelings for different reasons, its hard to know for sure whats going on.
The good news is that noticing reaction formation is the first step to breaking it. Deep down, you might be aware that youre saying or doing something you dont believe in. Though it can take time and bravery to acknowledge this, thats the first step for many people.
You May Like: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Worksheet Answers