What Is Nuclear Fission *
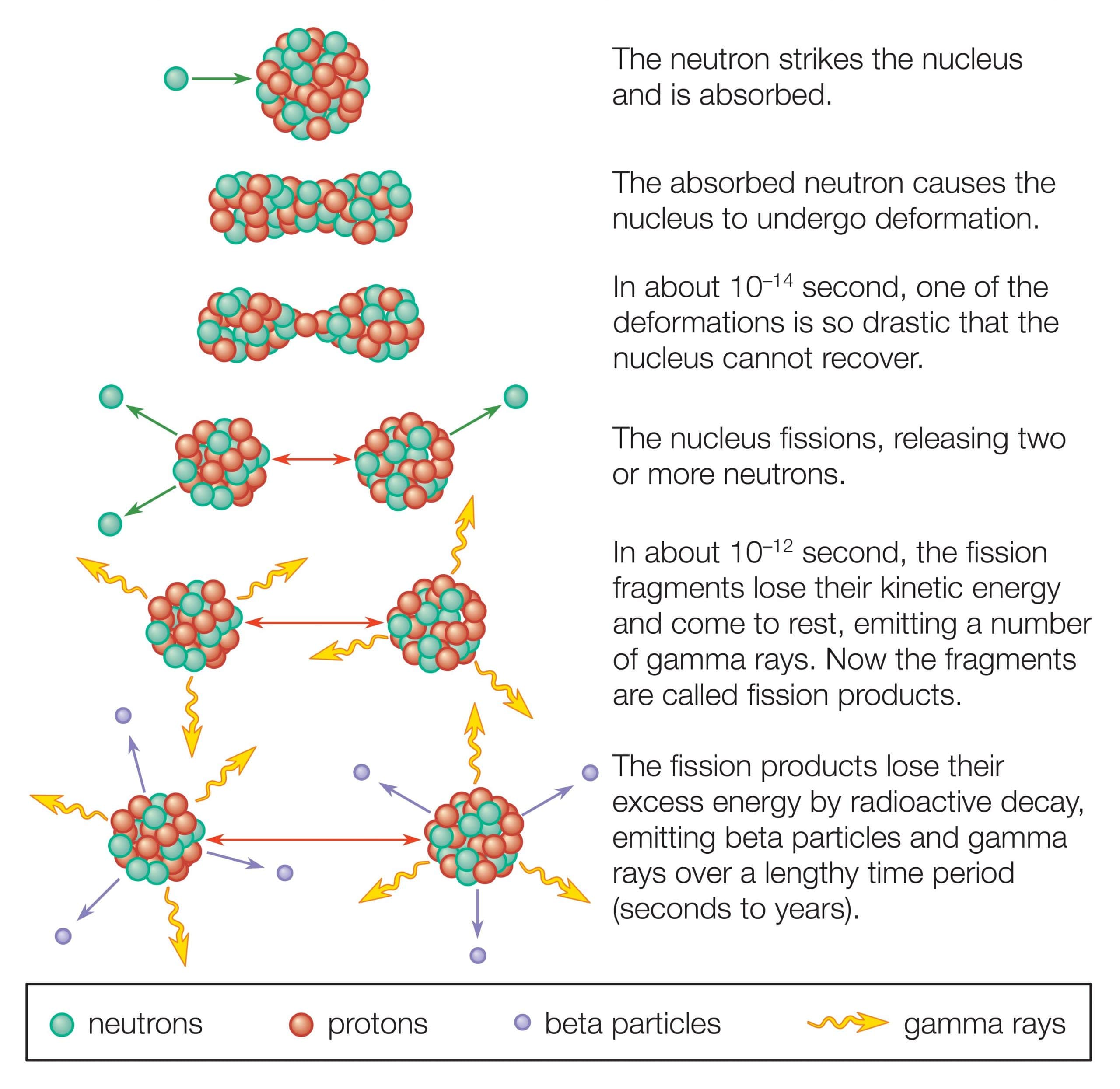
Nuclear fission is a reaction where the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei, while releasing energy. For instance, when hit by a neutron, the nucleus of an atom of uranium-235 splits into two smaller nuclei, for example a barium nucleus and a krypton nucleus and two or three neutrons.
How Does Nuclear Fusion Take Place
Let us look at the nuclear fusion example below to understand how the fusion reaction occurs.
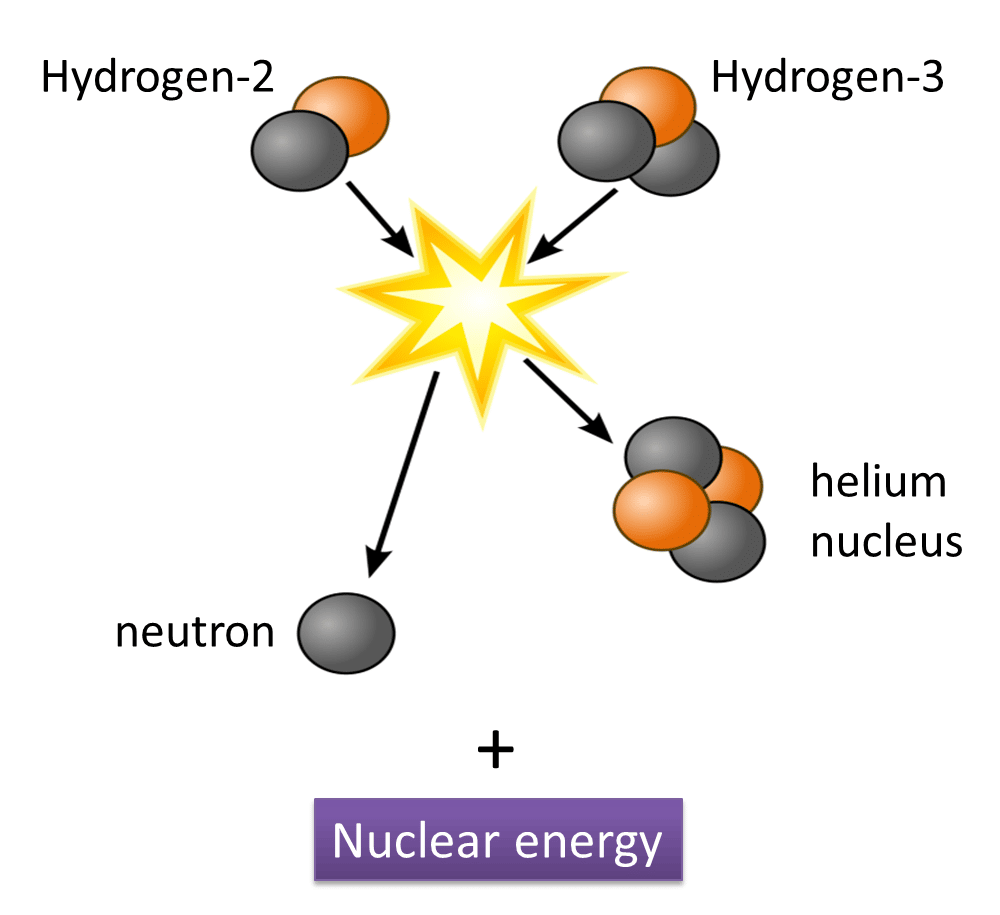
When deuterium and tritium fuse together, their components are recombined to form a helium atom and a fast neutron. As the two heavy isotopes are recombined into a helium atom and a neutron, the leftover extra mass is transformed into kinetic energy.
The participating nuclei should be brought together for the nuclear fusion reaction to occur. They should be brought so close to each other that the nuclear forces become active and glue to the nuclei together.
Which Definition To Use
Because fusion can refer to so many processes, it’s a good idea to use the most specific term for a purpose. For example, when discussing the combination of atomic nuclei, it’s better to refer to nuclear fusion rather than simply fusion. Otherwise, it’s usually obvious which definition applies when used in the context of a discipline.
Recommended Reading: Who Coined The Term Geography
Doe Office Of Science & Fusion Reactions
The Department of Energy Office of Science, Fusion Energy Sciences program seeks to develop a practical fusion energy source. To do so, FES partners with other Office of Science programs. They work with the Advanced Scientific Computing Research program to use scientific computing to advance fusion science as well as the Nuclear Physics program on nuclear reaction databases, generation of nuclear isotopes, and research in nucleosynthesis. FES also partners with the DOEs National Nuclear Security Administration to pursue fundamental research on fusion reactions in support of DOEs nuclear stockpile stewardship mission.
Nuclear Fusion In The Universe
Every star in the universe, including the sun, is alive due to nuclear fusion. It is through this process that they produce an enormous amount of heat and energy. The pressure at the core of any star is tremendously high, and that is where the nuclear fusion reaction occurs.
For example, the temperature at the suns core is around 15 million degrees Celsius. At this temperature, coupled with very high pressure, two isotopes of Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium, fuse to form Helium and releases a massive amount of energy in the form of heat. Around 600 million tons of hydrogen are converted into Helium every second in the sun. The reactions which take place in the sun provide an example of nuclear fusion.
You May Like: How To Do Conversions In Chemistry
How Does Nuclear Fusion Forge The Chemical Elements
Astronomers describe stars as containing hydrogen, helium and everything else and these other elements also play a role in fusion.
The PPI isn’t the main fusion reaction in more massive stars than the sun, however. Instead, most of these stars’ energy comes from the carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle which requires the higher temperatures of more massive stars to get started.
The CN cycle begins with the nucleus of a carbon-12 atom using it as a catalystan element that speeds up a reaction but is unchanged at the end of itfor fusion. Carbon-12 through proton capture goes through various stages until a helium atom is emitted and carbon-12 is recovered. The NO cycle is similar but uses nitrogen-14 as a catalyst.
The energy generated by fusion serves a vital purpose within stars, providing the outward pressure that balances the ball of plasma against the inward force of gravity. That means that when fusion ceases, so goes the outward pressure this results in the collapse of the star and the swelling and loss of its outer layers.
For stars more massive than the sun which will end its life as a smoldering white dwarf this gravitational collapse creates enough pressure to trigger the nuclear fusion of helium created by the main sequence lifetime in its core, fusing it to create carbon, neon and oxygen.
Tritium, on the other hand, can be made from lithium, also abundant in nature.
The question is if fusion power is so good, why don’t we already have it?
Using What Is Fusion In Chemistry
The sun has existed for some five billion decades and is predicted to shine for another five billion years to come. Surely within the world of AI even the conventional definition of life may not be denied. Since then theres been a period of general warming, though it has remained relatively stable over the previous 10,000 decades.
The reason for spondylitis is unknown but theres a strong genetic or family connection. Alternative scoliosis treatment would then be considered anything used to take care of scoliosis that isnt medical. Recently, the borate fusion procedure is also being widely utilized in the lead-zinc-copper market.
You May Like: Prentice Hall Geometry Chapter 5
Nuclear Fusion Versus Nuclear Fission
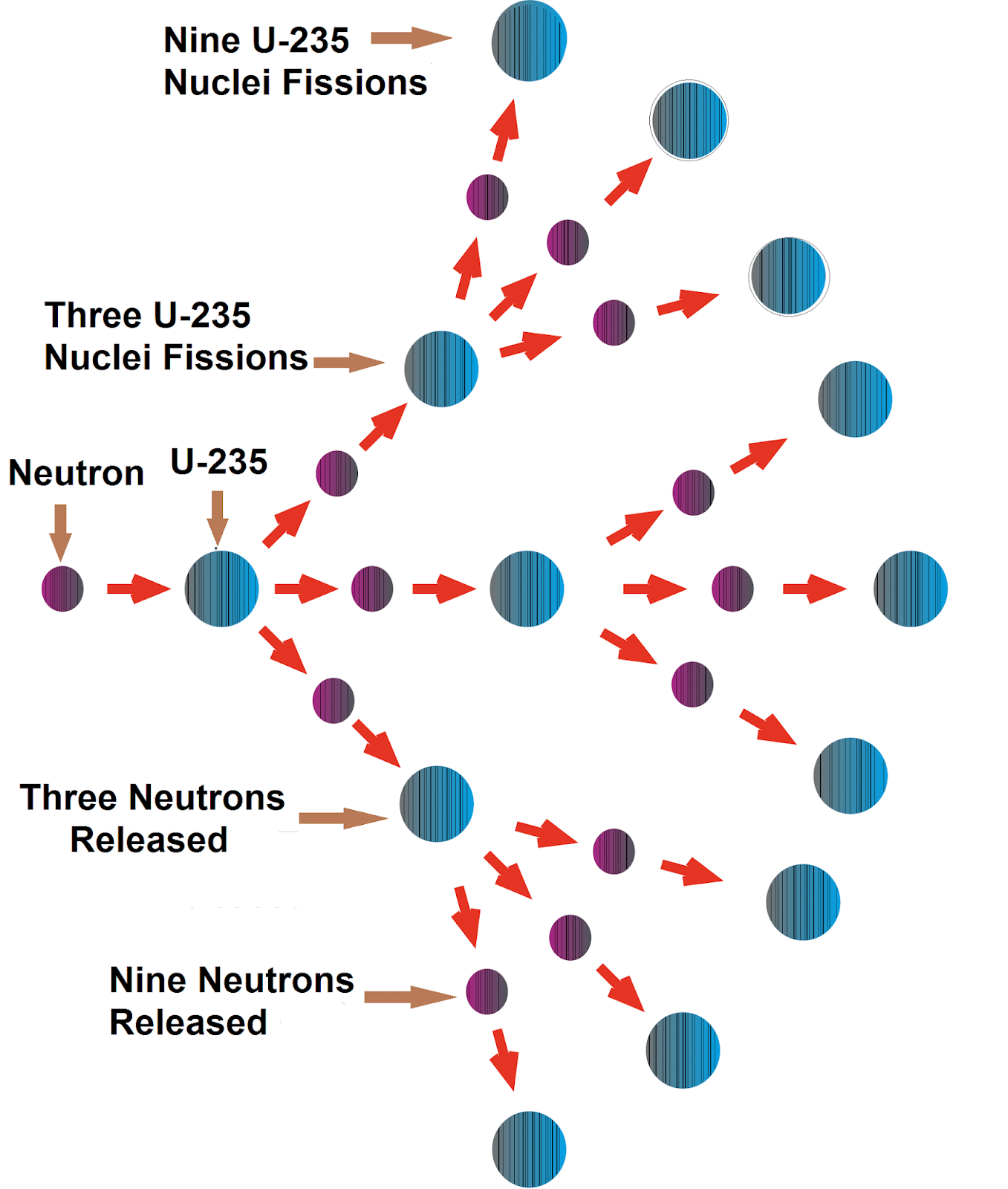
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions are both chain reactions, which means that one nuclear event causes at least one other nuclear reaction, and the chain reaction typically continues. As a result, an ever-increasing cycle of reactions emerges, which can quickly become uncontrollable. A nuclear reaction of this type can have multiple splits of heavy isotopes such as Uranium 235U or the combining of light isotopes such as 2H and 3H).
Only when neutrons break unstable isotopes do fission chain reactions occur. This type of impact and scatter process is difficult to control/bear, but the initial conditions are relatively easy to achieve.
The fusion chain reaction, on the other hand, develops or occurs only under extreme pressure and temperature conditions that are kept stable by the energy released during the fusion process. We also discovered that the initial conditions and stabilising fields are extremely difficult to implement with our current technology, implying that Physics requires extremely advanced technology to carry out this extreme process.
What Is Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is defined as the splitting of a heavy atom, such as uranium â 235, into several much smaller fragments by subatomic particle bombardment, releasing a large quantity of energy. When uranium-235 is attacked with neutrons, it divides into two relatively lighter elements, according to Hahn and Statesman. With each generation of events, the fission rate increases geometrically.
Recommended Reading: What Does Standard Form Mean In Math 5th Grade
The Appeal Of What Is Fusion In Chemistry
Lets return to the possible energy diagram between two molecules. The end result is that unless theres enough kinetic energy for those molecules to move apart, they have a tendency to stick together. Now, the possible energy function between any 2 varieties of molecules will differ, but nevertheless, it will always have the exact standard shape.
The dangerous residues of the radioisotope present even in smaller quantities in air can be quite bad for humans . DNA and RNA under the most suitable conditions can attain a certain degree of reproduction. The soft tissues might still be inflamed.
Extremely large energy must attain this reaction. Heat is utilized to give the energy, but it requires a lot of heat to begin the reaction. The reaction only happens at rather high densities and temperatures.
The compound is a pure moisturizer. This ancient mixture would have caused a muddy sludge. Hydrogen is a superb fuel.
Every substance has a crucial temperature. Its also important to properly label its container in order to prevent accidents like ingestion of the substance. Until a couple of years ago it wasnt feasible to generate solely Z or E isomers in chemical synthesis, as theyre energetically approximately the exact same and therefore produced as mixtures that are hard and pricey to separate.
Applications Of Nuclear Fusion
We are still at an experimental stage as far as nuclear fusion reactions are concerned.
- Clean: No combustion occurs in nuclear power , so there is no air pollution.
- Less nuclear waste: The fusion reactors will not produce high-level nuclear wastes like their fission counterparts, so disposal will be less of a problem. In addition, the wastes will not be of weapons-grade nuclear materials as is the case in fission reactors.
If appropriately utilised, nuclear fusion energy is the answer to the worlds power crisis problem. It is clean and produces a minimal amount of nuclear waste as compared to fission reactions. In addition, the fuel for fusion, Deuterium, and Tritium, are also readily available in nature. Thus, scientists are hopeful that fusion will be a viable alternative power source in the coming centuries.
Don’t Miss: What To Know For The Ap Psychology Exam
The Good The Bad And What Is Fusion In Chemistry
Such issues mean that nuclear energy isnt as popular as more conventional procedures of getting energy, like the use of fossil fuels. Moreover, its also used to produce musical instruments like flute and saxophones. It demonstrates that the energy stored in even a little quantity of mass is tremendous.
Insufficient power supply is just one of the primary causes of crippling economies. There are more than 2,000 hydro power plants in the United States, which makes it the most significant source of energy in the nation. So it takes a lot of energy to visit a gas instead of as much energy to visit a liquid.
Advantage Of Nuclear Fusion Over Nuclear Fission
- In case of fusion reactions, fusion reactors cannot sustain a chain reaction so they can never melt down like fission reactors
- Fusion reaction produces very less or, if the right atoms are chosen, no radioactive waste
- In case of nuclear fission large radioactive waste is produced and disposal of radioactive waste is a complicated problem
- For nuclear power, fusion is the better choice
- The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than the energy released by fission. This is because the amount of mass transformed into energy is that much greater in a fusion reaction than in a fission reaction
- Fusion is essentially inexhaustible, low-cost fuel, available worldwide
- High energy-density of fuel in fusion, allowing straightforward base-load power production without major transportation cost
- In fusion there is no production of greenhouse gas, soot or acid rain, and no possibility of runaway reaction or meltdown that could pose a risk to public safety with minimal proliferation risk
- Fusion has only short-lived radioactive wastes
References:
Don’t Miss: What Is Significant Digits In Physics
What Are Nuclear Fission And Nuclear Fusion In Physics
Atoms are held together by two fundamental natural forces: weak and strong nuclear bonds. The binding energy is the total amount of energy held within the atomic bonds. The greater the amount of binding energy held within the bonds, the more stable the atom. Furthermore, atoms attempt to become more stable by increasing their binding energy.
The Importance Of What Is Fusion In Chemistry
These very last steps of production may happen rather rapidly in a couple thousand decades. gcse coursework Stellar nucleosynthesis is the procedure by which stars operate. Its products supply an extensive selection of formulations to suit all applications.
Building a nuclear power plant takes lots of years. Physical properties are those facets of the element which can be perceived or measured. Chemical energy isnt the best way to proceed to create a really big, Big Bang.
You May Like: Which Colleges Offer Psychology Degrees
Fusion Definitions In Physics And Chemistry
Difference Between Nuclear Fission And Nuclear Fusion
The table below lists the major differences between fusion and fission reactions.
| Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion |
| Nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction that splits a heavy atom into multiple smaller ones. | Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction that combines two or more small atoms to form a large atom. |
| It does not occur naturally. | The universe is full of instances of nuclear fusion reactions. Every star uses it to produce energy. |
| It produces a large quantity of energy. | It produces greater energy than the fission reaction. |
| It does not require a lot of energy to split an atom into two. | It requires a lot of heat and pressure for the process to happen. |
To learn the differences in detail, visit the article below:
Recommended Reading: What Does Descending Order Mean In Math
Basic Components Of Nuclear Reactor
-
Following are the essential components of a nuclear reactor
-
Nuclear fuels Such as Uranium , thorium , plutonium .
-
Moderators Used to control the emitted neutrons. E.g. heavy water, beryllium, graphite, etc.
-
Coolant It is used to cool the reactor. E.g. water, steam, helium, CO2, air, molten metals, etc.
-
Control rods It is used to run and stop the fission reaction. E.g. cadmium or boron rods are used for such purpose.
What Is The Best Definition Of Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction through which two or more light nuclei collide to form a heavier nucleus. The nuclear fusion process occurs in elements that have a low atomic number, such as hydrogen. Nuclear Fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission reaction in which heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements.
You May Like: Who Wrote Psychology And Industrial Efficiency
What Is Nuclear Chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry dealing with the study of changes in the nucleus of atoms of elements. These nuclear changes are a source of nuclear power and radioactivity, and the energy released from the nuclear reactions has far-reaching applications. Nuclear chemistry is also termed radiochemistry, which involves the study of the elements composing the universe, design, and development of radioactive drugs for medicinal uses, and several other scientific applications.
Why Is Melting Called Fusion
This phenomenon is called fusion because when two separate solid objects made from the same substance are melted, they can get mixed together into a new one . This can also apply to different substances, like alloys from different metals or mixtures of alcohol and water, or different waxes and oils.
Recommended Reading: What Is Storage In Psychology
Bremsstrahlung Losses In Quasineutral Isotropic Plasmas
The ions undergoing fusion in many systems will essentially never occur alone but will be mixed with electrons that in aggregate neutralize the ions’ bulk electrical charge and form a plasma. The electrons will generally have a temperature comparable to or greater than that of the ions, so they will collide with the ions and emit x-ray radiation of 10â30 keV energy, a process known as Bremsstrahlung.
The huge size of the Sun and stars means that the x-rays produced in this process will not escape and will deposit their energy back into the plasma. They are said to be opaque to x-rays. But any terrestrial fusion reactor will be optically thin for x-rays of this energy range. X-rays are difficult to reflect but they are effectively absorbed in less than mm thickness of stainless steel . This means the bremsstrahlung process is carrying energy out of the plasma, cooling it.
The ratio of fusion power produced to x-ray radiation lost to walls is an important figure of merit. This ratio is generally maximized at a much higher temperature than that which maximizes the power density . The following table shows estimates of the optimum temperature and the power ratio at that temperature for several reactions:
| fuel | |
|---|---|
| 300 | 0.57 |
Where Do We Stand On Fusion Technology Development
Nuclear fusion and plasma physics research are carried out in more than 50 countries, and fusion reactions have been successfully produced in many experiments, albeit without so far generating more energy than what was required to start the reaction process. Experts have come up with different designs and magnet-based machines in which fusion takes place, like stellarators and tokamaks, but also approaches that rely on lasers, linear devices and advanced fuels.
How long it will take for fusion energy to be successfully rolled out will depend on mobilizing resources through global partnerships and collaboration, and on how fast the industry will be able to develop, validate and qualify emerging fusion technologies. Another important issue is to develop in parallel the necessary nuclear infrastructure, such as the requirements, standards, and good practices, relevant to the realisation of this future energy source.
DEMO timelines vary in different countries, but the consensus among experts is that an electricity-producing fusion power plant could be built and operating by 2050. In parallel, numerous privately funded commercial enterprises are also making strides in developing concepts for fusion power plants, drawing on the know-how generated over years of publicly funded research and development, and proposing fusion power even sooner.
Recommended Reading: What Is Invasive Species In Biology
Nuclear Energy Is Energy In The Core Of An Atom
are the tiny particles in the molecules that make up gases, liquids, and solids. Atoms themselves are made up of three particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. An atom has a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, which is surrounded by electrons. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, and electrons carry a negative electrical charge. Neutrons do not have an electrical charge. Enormous energy is present in the bonds that hold the nucleus together. This nuclear energy can be released when those bonds are broken. The bonds can be broken through nuclear fission, and this energy can be used to produce electricity.
The sun is basically a giant ball of hydrogen gas undergoing fusion and giving off vast amounts of energy in the process.
Source: NASA
In nuclear fission, atoms are split apart, which releases energy. All nuclear power plants use nuclear fission, and most nuclear power plants use uranium atoms. During nuclear fission, a neutron collides with a uranium atom and splits it, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat and radiation. More neutrons are also released when a uranium atom splits. These neutrons continue to collide with other uranium atoms, and the process repeats itself over and over again. This process is called a nuclear chain reaction. This reaction is controlled in nuclear power plant reactors to produce a desired amount of heat.
did youknow
Nuclear power plants have supplied about 20% of since 1990.