Verification Of Intrinsic Safety According To Ptb
The method to calculate interconnections according to EN 60079-14 or IEC 60079-14 shows certain drawbacks:
-
the reference curves for inductive circuits are applicable for voltages not higher than 24 V only
-
the reference curves are applicable for pure ohmic, capacitive or inductive circuits only. Mixed circuits with combined capacitances C and inductances L are not in the scope
-
the reference curves are not applicable to non-linear sources.
To prove intrinsic safety with more complex interconnections by way of calculation, it is recommended to follow PTB-Report ThEx-10* in this matter.
The core of this procedure is a graphic summation of the output characteristics of all sources involved. The summation characteristic is to be plotted in a suitable diagram which indicates the compliance of the circuit with intrinsic safety even in the case of a simultaneous inductive and capacitive wiring.
Figure 6.226. Example of a limiting characteristic diagram according to PTB-Report PTB-ThEx-10. The output current/voltage diagram is indicated .
As an essential advantage of this method, all safety-related information and boundary conditions can be deduced from one diagram. The safety factor 1.5 has been incorporated into the diagram already.
Fredric Beck, Eric Martinot, in, 2004
What Is Interconnection And Why Is It Important
You’re in the section: Frequently Asked Questions -> Telecommunication Regulation Interconnection -> What is interconnection and why is it important?
According to ITU surveys, interconnection-related issues are ranked by many countries as the single most important problem in the development of a competitive marketplace for telecommunications services
This statement exemplifies the importance of the role that telecommunications regulators have on interconnection. Interconnection, which is the linking of telecommunications networks so that of one can communicate with of another , is important for several reasons, including:
For example in some countries, mobile carriers sometimes become ensnarled in interconnection disputes and delink their . Many in these countries find it necessary to have a SIM card for each mobile to ensure that they can reach on all during the times of these interconnection disputes. This raises for and decreases the rate of call completion, which time.
A general overview of interconnection issues can be found in Module 2 of the ICT Regulation Toolkit , a new Internet-based resource available at: http://www.ictregulationtoolkit.org/en/index.html
Gain to incumbents:
Impacts Of Global Connectivity On People And Places
Positive:
Negative:
|
- Social – There are countries that cannot keep pace with others and will fall further behind the leading nations. There is also the issue of ‘westernisation’ and the loss of cultural identity.
- Environment – More resources and infrastructure takes a toll on the environment . Also, the disposal of these products is becoming a global concern.
You May Like: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Resource : The Story Of Solutions
| Part of the story of stuff project. The Story of Solutions explores how we can move our economy in a more sustainable and just direction, starting with orienting ourselves toward a new goal. That is moving away from simply trying to acquire more stuff to aiming for something better. The video runs for 9 minutes and was published in October 2013. You can watch the video at: |
What Is An Example Of Interconnectedness

4.4/5Examples of interconnectednessinterconnectednessinterconnectedness
Also asked, what does interconnectedness mean in social studies?
Interconnectedness. Interconnectedness provides a framework for students to explore the ways in which people, nature, and objects interact with one another to form a complex whole that operates as a system. It focuses on the properties of social-ecological systems, which are interwoven systems of humans and nature.
Additionally, what is interconnectedness in geography? Terms in this set Interconnections. a key concept in geography: the relationship between all things, both animate and inanimate, and all processes, both natural and human. e.g. relationship between child and parents. Space. a key concept in geography: the way things are arranged on the Earth’s surface.
Also to know is, what does interconnectivity mean?
interconnectivity. Noun. The state or quality of being interconnected. This network has great interconnectivity.
What is another word for interconnectedness?
interrelation, correlation, connection, communion, association, analogy, correspondence, mutuality, reciprocity, interdependence, togetherness.
You May Like: Sample Space Definition Math
How Does Geography Influence Religion
It is a common knowledge that civilizations ordinarily develop in and around river systems where there are easy access to water, food sources, and irrigation systems. This geographical state permits people to grow crops and thus shift from the hunter gatherer lifestyle to becoming agriculturistfarming and domesticating livestock.
The Ganges, Indus Valley, the Nile, and Amazon River are geographical regions where various kinds of people have developed over time. Dissimilarities in culture result in diverse religious inclinations which incorporate their environments into their rituals, mythologies, and iconography. This partially explains the rise of various religions in these places.
The origin of some features within a religion can also be explained by geography. For instance, shrines in Shintoism have been built for reasons that include geography . Every shrine typically has a kami , which may be a natural or topographical feature. The kami is said to normally reside in an object, such as a stone.
Many examples also prove that the physical environment of a place or geography elucidates many aspects of the religions in it:
Olympus was the home of the ancient Greek pantheon and Mt. Fuji was the dwelling place of gods in Japan. Man even built artificial mountains in an attempt to reach the divine in the form of pyramids, ziggarats, and mounds.
Mapping The Clothing Industry
| Below is a website with a Prezi that maps the global process of creating your average t-shirt. As we go through this as a class, you are to note down each place that is mentioned and the process of creation that is mentioned there. There is too much information for you to copy down so practice your summarising skills! | Where Does Your T-Shirt Come From? |
| Once we have gone through the entire Prezi, you are going to map this process on the A3 maps provided. For each place, make sure you write down what is happening and what stage of the creation process it is. These will be displayed on the walls so keep them neat and informative. |
You May Like: Algebra 1 Eoc 2015
Geographical Inquiry And Skills Strand
Geographical inquiry is a process by which students learn about and deepen their holistic understanding of their world. It involves individual or group investigations that start with geographical questions and proceed through the collection, evaluation, analysis and interpretation of information to the development of conclusions and proposals for actions. Inquiries may vary in scale and geographical context.
Geographical skills are the techniques that geographers use in their investigations, both in fieldwork and in the classroom. Students learn to think critically about the methods used to obtain, represent, analyse and interpret information and communicate findings. Key skills developed through Geography in the Australian Curriculum include formulating a question and research plan, recording and data representation skills, using a variety of spatial technologies and communicating using appropriate geographical vocabulary and texts.
The stages of an investigation are:
Observing, questioning and planning: Identifying an issue or problem and developing geographical questions to investigate the issue or find an answer to the problem.
Collecting, recording, evaluating and representing: Collecting information from primary and/or secondary sources, recording the information, evaluating it for reliability and bias, and representing it in a variety of forms.
Concepts For Developing Geographical Understanding
The Australian Curriculum: Geography identifies the concepts of place, space, environment, interconnection, sustainability, scale and change, as integral to the development of geographical understanding. These are high-level ideas or ways of thinking that can be applied across the subject to identify a question, guide an investigation, organise information, suggest an explanation or assist decision-making.
In Years 710, students build on their understanding of place, space, environment, interconnection, sustainability and change and apply this understanding to a wide range of places and environments at the full range of scales, from local to global, and in a range of locations. These concepts are the key ideas involved in teaching students to think geographically in the Australian Curriculum: Geography and are developed in the following ways:
Place
The concept of place is about the significance of places and what they are like:
Space
The concept of space is about the significance of location and spatial distribution, and ways people organise and manage the spaces that we live in:
Environment
The concept of environment is about the significance of the environment in human life, and the important interrelationships between humans and the environment:
Interconnection
The concept of interconnection emphasises that no object of geographical study can be viewed in isolation:
Sustainability
Scale
Change
Don’t Miss: How To Study For Ap Human Geography
What Is Interconnection In Geography
4.7/5interconnections
Beside this, what is the definition of interconnection in geography?
Interconnection The relationship between all things, both animate and inanimate, and all processes, both natural and human. The concept of INTERCONNECTION emphasises that no object of geographical study can be viewed in I S O L A T I O N.
Subsequently, question is, what is an example of interconnection? Examples of interconnect in a SentenceThe systems are interconnected with a series of wires. The lessons are designed to show students how the two subjects interconnect. a series of interconnecting stories.
Beside this, why is interconnection important in geography?
Places, environments and systems may also be linked by cause-and-effect relationships between them. Interconnections are important in understanding why things are changing or need to be changed in different places or environments.
What are the 7 concepts of geography?
The seven geographical concepts of place, space, environment, interconnection, sustainability, scale and change are the key to understanding the places that make up our world. These are different from the content-based concepts such as weather, climate, mega cities and landscapes.
- Place
- Density, Dispersion, Pattern.
What Can I Do To Prevent This In The Future
If you are on a personal connection, like at home, you can run an anti-virus scan on your device to make sure it is not infected with malware.
If you are at an office or shared network, you can ask the network administrator to run a scan across the network looking for misconfigured or infected devices.
Another way to prevent getting this page in the future is to use Privacy Pass. You may need to download version 2.0 now from the Chrome Web Store.
Cloudflare Ray ID: 6a5d1ce0ba6b5986Your IP: 3.80.182.10Performance & security byCloudflare
You May Like: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
The Concept Of Interconnectionin Geography Emphasises That No Object Of Geographical Study Can Be Viewed Inisolation It Is About The Ways That Geographical Phenomena Are Connected Toeach Other Through Environmental Processes The Movement Of People Flows Oftrade And Investment The Purchase Of Goods And Services Cultural Influencesthe Exchange Of Ideas And Information Political Power Internationalagreements And Other Types Of Interaction Across Space
exploringthe networks that channel the interconnections between places, and which canadvantage some places and disadvantage others learningto see their own locality in a wider national and global context, and gainingan understanding of the external factors that influence the localitys presentand future
The conceptof interconnection is particular alive and well in the following units of thedraft curriculum
The Year 9 unit calledNavigating global connections
Year 10 unit called Global well-being Content descriptions from unit
- There aresignificant spatial variations in human well-being within nations, at bothregional and local scales
- A non-government program which attempts to improve human well-being in anothercountry, and why such programs may be spatially targeted at specificregions within the country
- People areconnected to places across the world through their cultural interests andactivities
There aremany other places across the draft curriculumDoes this notsound like geography with its spatial and interconnection conceptualisation asdiscussed in the draft curriculum document?
As a footnote to this reference to Kony2012it is worth examining the controversy
The Age of Interconnection: The Anthropocene
the Anthropocene is the mostrecent period of the Quaternary, succeding to the Holocene.
What Is The Definition Of Interconnection In Geography
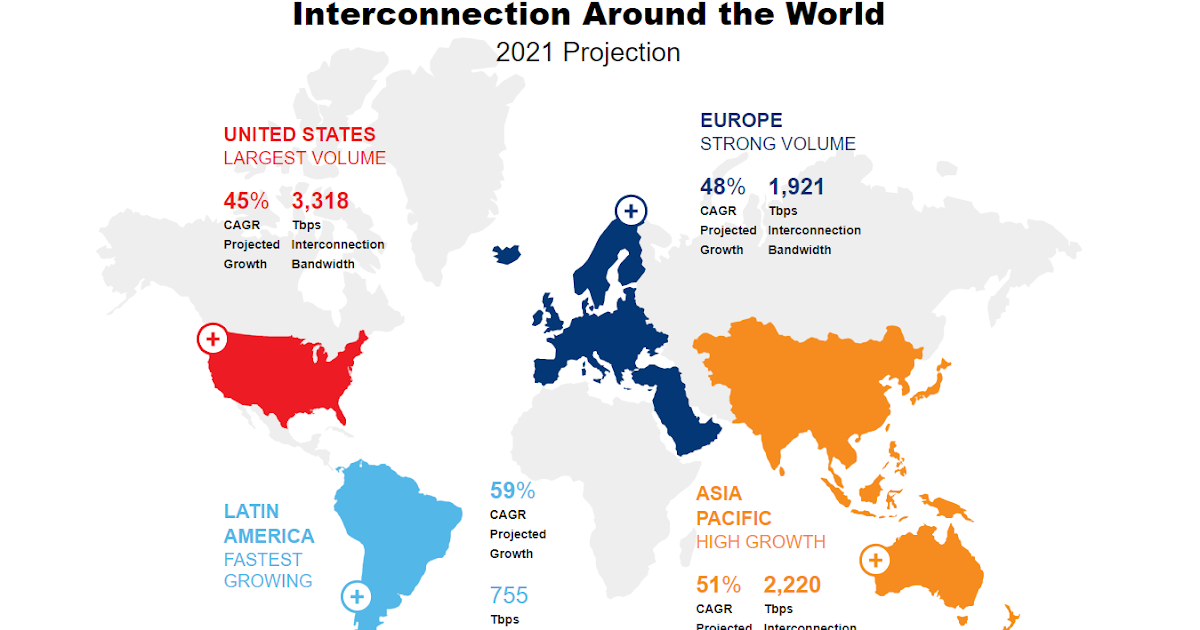
InterconnectionINTERCONNECTIONgeographical
. Similarly, it is asked, what does Interconnection mean in geography?
Geographies of interconnections focuses on investigating how people, through their choices and actions, are connected to places throughout the world in a wide variety of ways, and how these connections help to make and change places and their environments.
Furthermore, what is an example of interconnection? Examples of interconnect in a SentenceThe systems are interconnected with a series of wires. The lessons are designed to show students how the two subjects interconnect. a series of interconnecting stories.
Also to know is, why is interconnection important in geography?
Places, environments and systems may also be linked by cause-and-effect relationships between them. Interconnections are important in understanding why things are changing or need to be changed in different places or environments.
What is the definition of change in geography?
The concept of change is about explaining geographical phenomena by investigating how they have develop over time. The concepts of interconnection emphasises that no object of geographical study can be viewed in isolation. An understanding of the current processes of change can be used to predict change in the future.
Don’t Miss: Countdown To The Algebra 1 Eoc Answers
Resource : Biofuel And Globalisation
Biofuels have been touted by many to be the solution to emissions. But in this globalised world who bears the cost of the production of biofuels. Find the video here: Biofuel and globalisationLinks to the curriculum:
|
Online Activity : Where Does My Stuff Come From
Using the National Geographic global closet calculator. Students produce a map of their interdependencies based on the clothes in their closets. This activity is limited by the fact that it requires students to be at home. However it can be used as a great extension activity, and results can be brought back into the classroom. Links to the curriculum:
|
Recommended Reading: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
What Is Spicess Used For In Geography
4.1/5S.P.I.C.E.S.Sgeographicalin-depth answer
SPICESS – Geographic concepts. DESCRIPTION. A helpful acronym to remember the 7 aspects of geography
Also, what are the key concepts of geography? Basic geographic concepts are:
- Location.
- Place
- Density, Dispersion, Pattern.
- Size and Scale.
In this manner, what are the 7 concepts of geography?
The seven geographical concepts of place, space, environment, interconnection, sustainability, scale and change are the key to understanding the places that make up our world. These are different from the content-based concepts such as weather, climate, mega cities and landscapes.
What is interconnection in Spicess?
Interconnection The relationship between all things, both animate and inanimate, and all processes, both natural and human. The concept of INTERCONNECTION emphasises that no object of geographical study can be viewed in I S O L A T I O N.
An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie
This site uses cookies to improve performance. If your browser does not accept cookies, you cannot view this site.
Setting Your Browser to Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Why Does this Site Require Cookies?
This site uses cookies to improve performance by remembering that you are logged in when you go from page to page. To provide access without cookies would require the site to create a new session for every page you visit, which slows the system down to an unacceptable level.
What Gets Stored in a Cookie?
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
You May Like: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Resource : Sweat Shops
This resource is an article from the Daily Mail looking at a Chinese ‘sweatshop’ factory where workers are paid just £1.12 per hour to produce iPhones and iPads. Conditions are so poor that the factories covered in suicide nets to stop workers leaping to their deaths and 18 people have killed themselves at the facility to date. The article is from January 2013.Read more here: Links to the curriculum:
|