What Does Pepsin Do
Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme released by chief cells, which are specialized in the stomach. It is a component of gastric juice that aids in food digestion. Pepsin is a digestive enzyme that breaks down large polypeptides into smaller peptide fragments in the stomach’s acidic environment .
Pepsin preferentially hydrolyzes peptide bonds containing the aromatic amino acids’ amine group . Pepsin is a stomach enzyme that aids in the digestion of proteins in food. Pepsin is secreted by gastric chief cells as pepsinogen, an inactive zymogen. Hydrochloric acid is secreted by parietal cells in the stomach lining, which lowers the pH of the stomach.
The function of pepsin in the stomach is to break down proteins in foods like meat and eggs into smaller pieces . It just breaks down proteins at specific stages, so the protein isn’t fully digested to the amino acid level.
Defining The Structure Of Dna
DNA-PKcs was isolated from HeLa cells using a modification of the purification protocol of Gell and Jackson as described in Sibanda et al. . DNA-PKcs was purified in the presence of 0.55 mM EDTA to prevent autophosphorylation. Heavy metal ion solutions, the best of which was involved the dodeca–bromo-hexatantalum cation as a bromide salt, were used to form crystals for isomorphous replacement but the resulting crystals were less well ordered. However, the use of multiple-wavelength anomalous dispersion allowed determination of the molecular structure of DNA-PKcs:Ku80ct194 complex at ~ 6.6 Å resolution . This has subsequently been improved using multicrystal anomalous diffraction analysis for low-resolution macromolecular phasing in a method pioneered by Hendrickson et al. . However, the presence of large variations in cell parameters, due to soaking of Ta6Br122 +, significantly reduced the number of datasets that could be used.
Anna Villa, … Fabio Candotti, in, 2014
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
You May Like: How To Pass Ap Human Geography
Approximation Of The Reactant
During enzyme catalytic reaction, the substrate and active site are brought together in a close proximity. This approach has various purposes. Firstly, when substrates bind within the active site the effective concentration of it significantly increases than in solution. This means the number of substrate molecules involved in the reaction is also increased. This process also reduces the desolvation energy required for the reaction to occur. In solution substrate molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules and energy is required for enzyme molecules to replace them and contact with the substrate. Since bulk molecules can be excluded from the active site this energy output can be minimised. Next, the active site is designed to reorient the substrate to reduce the activation energy for the reaction to occur. The alignment of the substrate, after binding, is locked in a high energy state and can proceed to the next step. In addition, this binding is favoured by entropy as the energy cost associated with solution reaction is largely eliminated since solvent cannot enter active site. In the end, the active site may manipulate the Molecular orbital of the substrate into a suitable orientation to reduce activation energy.:1558
What Do Enzymes Do
The digestive system enzymes help the body break down larger complex molecules into smaller molecules, such as glucose, so that the body can use them as fuel.
DNA replication each cell in your body contains DNA. Each time a cell divides, that DNA needs to be copied. Enzymes help in this process by unwinding the DNA coils and copying the information.
Liver enzymes the liver breaks down toxins in the body. To do this, it uses a range of enzymes.
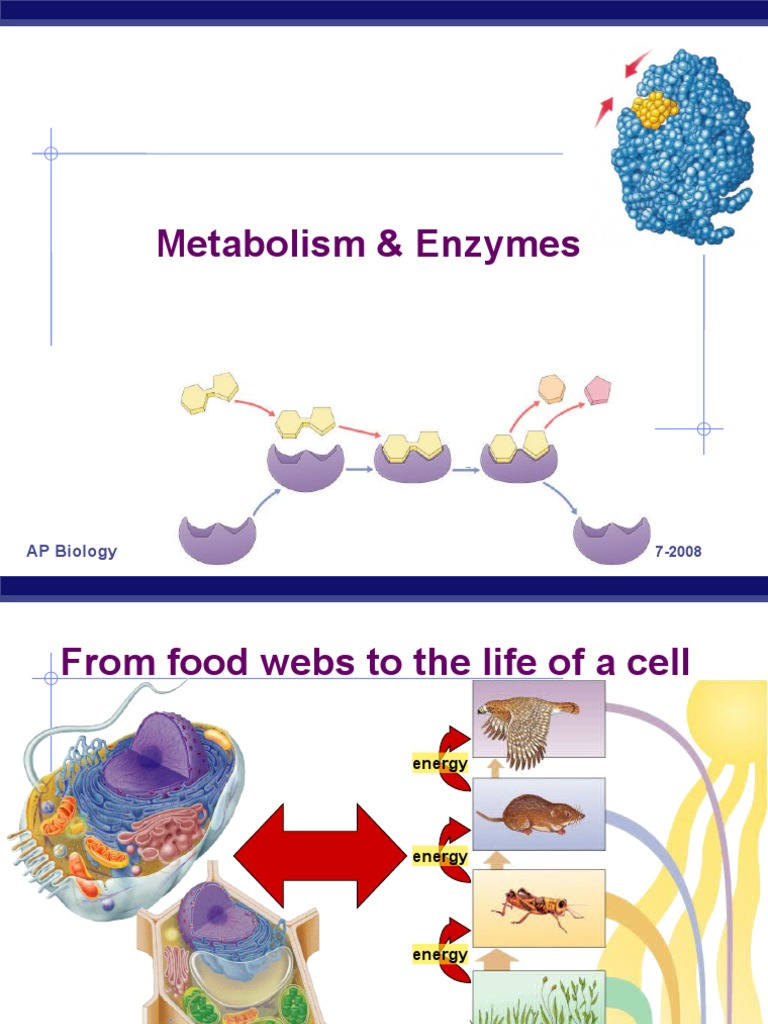
The lock and key model was first proposed in 1894. In this model, an enzymes active site is a specific shape, and only the substrate will fit into it, like a lock and key.
This model has now been updated and is called the induced-fit model.
In this model, the active site changes shape as it interacts with the substrate. Once the substrate is fully locked in and in the exact position, the catalysis can begin.
Read Also: Lesson 4.5 Practice B
Substrate Definition In Biology
Substrate Biology: An enzyme is a molecule which works as a biological catalyst which speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. In living organisms, enzymes act on many substances. Substrates are a substance or surface which is acted by an enzyme. Substrates are transmitted into the active site of the enzyme. When enzyme substrates are formed, for its reaction enzymes exert force on the substrates, and in the result, the product does the reaction.
The substrates and enzyme form a bond, which is cause to change conformation and shape in enzymes. In the result, the shape is formed that how much pressure on substrates applied by enzymes, either force applied on molecules together or taking it apart. In our body, almost all molecule work as a substrate for different functions. Because for perform different functions or done works, our body requires a large amount of energy and time, and reactions take a specific enzyme to works along. Once a reaction acts, the substrates become different chemically and called a Product.
Substrate Synonyms:
Some possible synonyms are given below:
- Substratum
- Sublayer
Substrate Biochemistry:
Control Of Metabolism Through Enzyme Regulation
Cellular needs and conditions vary from cell to cell and change within individual cells over time. For example, a stomach cell requires a different amount of energy than a skin cell, fat storage cell, blood cell, or nerve cell. The same stomach cell may also need more energy immediately after a meal and less energy between meals.
A cells function is encapsulated by the chemical reactions it can carry out. Enzymes lower the activation energies of chemical reactions in cells, they promote those reactions that are specific to the cells function. Because enzymes ultimately determine which chemical reactions a cell can carry out and the rate at which they can proceed, they are key to cell functionality.
Recommended Reading: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
Atp And Muscle Contraction
Examples Of Active Site In A Sentence
active site The Conversationactive sitechicagotribune.comactive siteForbesactive site Forbesactive site Ars Technicaactive sites alactive site San Diego Union-Tribuneactive site latimes.com
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘active site.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Recommended Reading: How Do Noise Canceling Headphones Work Physics
Enzyme Active Site And Substrate Specificity
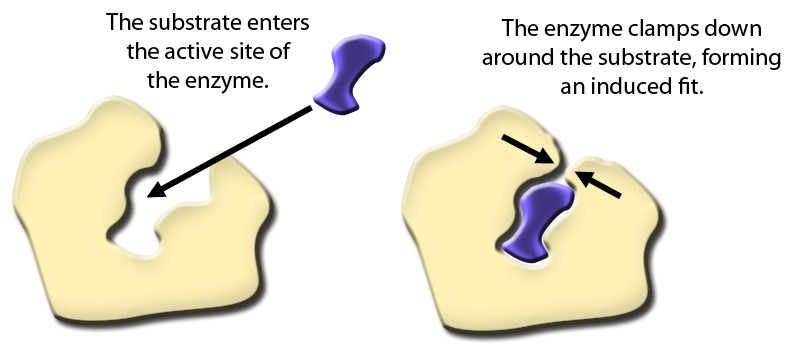
Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme, depending on the particular chemical reaction. In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. Two reactants might also enter a reaction, both become modified, and leave the reaction as two products.
The enzymes active site binds to the substrate. Since enzymes are proteins, this site is composed of a unique combination of amino acid residues . Each amino acid residue can be large or small weakly acidic or basic hydrophilic or hydrophobic and positively-charged, negatively-charged, or neutral. The positions, sequences, structures, and properties of these residues create a very specific chemical environment within the active site. A specific chemical substrate matches this site like a jigsaw puzzle piece and makes the enzyme specific to its substrate.
What Is A Catalytic Domain Of An Enzyme
Is this another name for the active site of an enzyme? What does the structure of the catalytic domain of an enzyme look like?
- 4$\begingroup$Quick answers: yes, and it varies tremendously. Enzymes catalyze a huge variety of reactions, from cutting DNA to adding amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain, to breaking down complex sugars, and many more besides. Catalytic domains vary from enzyme family to family, and even between enzymes in a single family. There really is no generalization you can make about structure or function, as it is so different from one to another.$\endgroup$ MattDMoSep 25 ’14 at 20:36
- $\begingroup$AFAIK MattDMo is correct. The catalytic site is the active site where the reaction takes place that triggers the conformation change. He is also correct about there being nearly infinite potential catalytic site designs.$\endgroup$Sep 25 ’14 at 21:38
- 4$\begingroup$I would say that catalytic domains are a little different from active sites. The active site is the location where the substrates bind and the reaction occurs, the catalytic domain is the portion of the enzyme that contains the active site. Many proteins have multiple domains.$\endgroup$ user137Sep 25 ’14 at 22:13
Don’t Miss: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
Activity And Stability Of Pepsin
In acidic environments with a pH of 1.5 to 2.5, pepsin is most active. Pepsin works best at temperatures between 37 and 42 degrees Celsius. As a result, the stomach is the main site of synthesis and function .
In humans, pepsin concentrations in the stomach range from 0.5 to 1 mg/mL. At pH 6.5 and above, pepsin is inactive, but it is not completely denatured or irreversibly inactivated until pH 8.0. As a result, re-acidification will reactivate pepsin in solutions up to pH 8.0. The safety of pepsin at high pH has important consequences for laryngopharyngeal reflux disease.
Following a gastric reflux case, pepsin persists in the larynx. Pepsin will be inactive at the mean pH of the laryngopharynx , but it may be reactivated during subsequent acid reflux events, causing damage to local tissues. Pepsin has a wide range of cleavage specificity.
Concentration And Type Of Substrate
Enzymes have a saturation point, i.e., once all the enzymes added are occupied by the substrate molecules, its activity will be ceased. When the reaction begins, the velocity of enzyme action keeps on increasing on further addition of substrate. However, at a saturation point where substrate molecules are more in number than the free enzyme, the velocity remains the same.
The type of substrate is another factor that affects the enzyme action. The chemicals that bind to the active site of the enzyme can inhibit the activity of the enzyme and such substrate is called an inhibitor. Competitive inhibitors are chemicals that compete with the specific substrate of the enzyme for the active site. They structurally resemble the specific substrate of the enzyme and bind to the enzyme and inhibit the enzymatic activity. This concept is used for treating bacterial infectious diseases.
Don’t Miss: Algebra 1 Age Word Problems
Difference Between Substrate And Active Site
July 24, 2018 Posted by Madhu
The key difference between substrate and active site is that the substrate is a chemical compound that can undergo a chemical reaction whereas the active site is a specific region on an enzyme.
Enzymes are biological catalysts. These are proteins that can decrease the activation energy of a chemical reaction in order to reduce the energy barrier of that reaction. Hence, it can increase the rate of a reaction. The reactant of the reaction in which enzymes involve is the substrate. This substrate binds with the active site of the enzyme. The reactions take place there. Eventually, it releases the products of the reaction.
Irreversible Inhibitor: Diisopropyl Fluorophosphate
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate is an irreversible inhibitor that blocks the action of serine protease. When it binds to the enzyme a nucleophilic substitution reaction occurs and releases one hydrogen fluoride molecule. The OH group in the active site acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphorus in DIFP and form a tetrahedral intermediate and release a proton. Then the P-F bond is broken, one electron is transferred to the F atom and it leaves the intermediate as F anion. It combines with a proton in solution to form one HF molecule. A covalent bond formed between the active site and DIFP, so the serine side chain is no longer available to the substrate.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Example Of Movement In Geography
Summary Active Site Vs Binding Site
Active sites are regions on enzymes that can increase the reaction rate of a chemical reaction via reducing the activation energy barrier of that reaction. A binding site is any region to which a ligand can bind. Active site also contains a binding site. The difference between active site and binding sites lies upon the existence and functionality. Therefore, the key difference between active site and binding site is that an active site aids the catalysis of a chemical reaction whereas a binding site aids on the binding of a ligand to a large molecule.
Reference:
1. âActive Site.â Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 24 July 2018. Available here 2. âBinding Site.â Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 28 Aug. 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.âEnzyme structureâBy Thomas Shafee â Own work, via Commons Wikimedia
What Is Binding Site
Binding site is a region on a protein, DNA or RNA to which ligands can bind. There, the ligand can form a chemical bond with this site. These regions show specificity a particular ligand will bind to a particular binding site. Therefore, this site is a measure of the types of ligands that can bind with a molecule.
Furthermore, we often use these regions for the functional characterization of biomolecules. For example, we can characterize the functionality of an active site through its binding site. Moreover, in the case of DNA, the specific type of binding site is the transcription factor binding site present on the DNA.
You May Like: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Active Transport In Plants
Like humans and animals, plants also require transport systems which are mainly involved in the transport of materials, such as water, minerals, and necessary nutrients to all parts of the plant for its survival.
Active transport is a mode of transportation in plants, which uses stored energy to move the particles against the concentration gradient. In a plant cell, it takes place in the root cells by absorbing water and minerals. Active transport always leads to accumulation of molecules are ions towards one side of the membrane. This mode of transportation in plants is carried out by membrane proteins and transports the substance from the lower concentration to higher concentration.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Recommended Reading: Holt Geometry Lesson 4.5 Practice B Answers
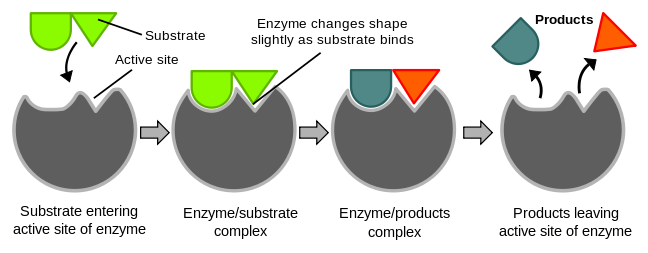
Mechanism Of Enzyme Reaction
Any two molecules have to collide for the reaction to occur along with the right orientation and a sufficient amount of energy. The energy between these molecules needs to overcome the barrier in the reaction. This energy is called activation energy.
Enzymes are said to possess an active site. The active site is a part of the molecule that has a definite shape and the functional group for the binding of reactant molecules. The molecule that binds to the enzyme is referred to as the substrate group. The substrate and the enzyme form an intermediate reaction with low activation energy without any catalysts.
\ + reactant \rightarrow product\\ reactant + enzyme \rightarrow intermediate\\ intermediate + reactant \rightarrow product + enzyme\)
The basic mechanism of enzyme action is to catalyze the chemical reactions, which begins with the binding of the substrate with the active site of the enzyme. This active site is a specific area that combines with the substrate.
Active Site Blocked Factor Ixa
Active site blocked fIXa is a competitive inhibitor of fIXa assembly into the intrinsic Xase activation complex. Animal studies have shown that fIXai blocks intravascular thrombosis without substantially disturbing normal hemostasis.259,268,269 In a human ex vivo blood flow system, fIXai inhibits fibrin deposition.270 It accomplishes long-term patency and decreased aneurysmal dilation in polytetrafluoroethylene vascular repair, while eliminating the intraoperative morbidity of needle-hole bleeding.271 In addition, fIXai appears to be an effective alternative anticoagulant strategy in cardiopulmonary bypass when heparin is contraindicated, affording inhibition of intravascular and extracorporeal circuit thrombosis with enhanced hemostasis in the surgical wound.272 Active site blocked fIXa limited fibrin deposition within the extracorporeal circuit, comparable with the antithrombotic effect seen with heparin. In contrast to heparin, effective antithrombotic doses of fIXai significantly diminished blood loss in the thoracic cavity and in an abdominal incisional bleeding model.273 The efficacy of fIXai in atherothrombosis remains unknown.
A.M. Doweyko, in, 2007
Don’t Miss: Why Are There Different Branches Of Chemistry