Examples Of Geographic In A Sentence
geographic Forbesgeographic USA TODAYgeographic orlandosentinel.comgeographic ABC Newsgeographic Scientific Americangeographic Los Angeles Timesgeographic sun-sentinel.comgeographic NBC News
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘geographic.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
What Is Economic Landscape In Geography
The term economic landscape helps to define the complex relationship between the economic activities of human society and their natural environment. Natural resources, environmental conditions and the trans/supra-regional geographical setting provide the basis for the economic development of a region.
Christaller Theory Of Central Places
Central place theory is probably one of the best-known theory on urban settlements in geography and related field. Paradoxically, neither in geography as a discipline nor in his professional life, Walter Christaller became a recognised person for this theory. First, according to Leyshon et al. , Christallers work was never truly appreciated among German geographers, that time very much concerned with idiographic and chronological analysis. Second, while Christallers theory of central places was popular amongst American geographer , in his home country he was reintroduced during 1960s and 1970s through English-speaking textbooks, Christaller was never appreciated in geography during his own time . It might also be caused by his controversial political engagement during Nazi era, he joined the National Socialist Party , after the war he joined communist party ending in social democratic party in 1959 . Nevertheless, this has nothing to do with his theoretical contribution to geography and economy.
Christallers central place theory.
transport principle minimises the length of roads joining adjacent places. Each settlement is located centrally on the boundary line between the hexagons of two places in the next hierarchical level ,
administrative principle every single lower-level settlement and its hinterland is nested within the higher-level hinterland .
You May Like: My.hrw Algebra 1
Relevance And Practical Application
Knowledge from the study of economic geography enables one examine their production in relation to their environment whereas it could bring about disparity from different regions. The disparity is majorly eliminated by mobilization of resources and a clear understanding of the inter-relationship between man and environment.Economic geography is a broad discipline and an essential element to both geographers as well as economists. Different researchers use different methods in its study like the neoclassical theorists who focus on quantitative methods while the Marxist political theory and the new economic geography takes into account all aspects to do with social, cultural, and institutional factors. Therefore it is an important factor when understood and properly used, it is very beneficial for productivity.
What Is Economic Geography

Economic geography is a discipline that studies the location, distribution, and spatial organization of economic activities across the world. Over the years, economic geography has taken various approaches to different subject matters such as the location of industries, the benefits firms obtain by locating near each other , transportation geography which studies the connection and movement between people and goods. Other subject matters include the relationship between the environment and economy, international trade, urban areas economics, real estate, and development, as well as gentrification which is the revival and development of urban neighborhoods which are in bad condition.
Also Check: Segment Addition Postulate Color By Number Worksheet Answer Key
Definitions Of Economics Geography:
Different geographers have forwarded the definition of Economics geography in a different way. However, all the definitions seem to converge at a point. Therefore, it may be summaries as the study of mans economic activities with relation to his environment, physical and culture. However, it would be interesting to have a brief review of how individual authorities deal with this matter.
According to Dudley Stamp, Economic Geography involves consideration of the geographical and other factors which influence mans productivity, but only in limited depths, so far as they are connected with production and trade.
Professor E. W. Zimmermann pointed out that, Economic Geography deals with the economic life of the man with relation to the environment.
S. Thoman in his book The Geography of Economic Activity has remarked, Economic Geography may be defined as an inquiry into the production, exchange, and consumption of goods by people in different areas of the world. Particular emphasis is placed on the location of economic activity upon asking just why economic functions are situated where they are in this world.
MacFarlane describes, Economic Geography as the study of influence exerted on the economic activity of man by his physical environment, and more specifically by the form and structure of the surface of the land, the climatic conditions which prevail upon it and the spatial relations in which its different regions stand to one another.
Definition Of Economic Geography:
Economic Geography is the study of man and his economic activities under varying sets of conditions. Geographers are of different opinions as regarding the definition of the subject.
In fact, different authorities have defined Economic Geography in a variety of ways but their opinions converge at a common point of accord, where it means the study of the spatial distribution of mans economic activities in relation to its environment, be it physical or non-physical.
According to Dudley Stamp, Economic Geography involves consideration of the geographical and other factors which influence mans productivity, but only in limited depths, so far as they are connected with production and trade.
Professor E. W. Zimmermann pointed out that, Economic Geography deals with the economic life of man with relation to environment.
R. S. Thoman in his book The Geography of Economic Activity has remarked, Economic Geography may be defined as an enquiry into the production, exchange and consumption of goods by people in different areas of the world. Particular emphasis is placed on the location of economic activity upon asking just why economic functions are situated where they are in this world.
Surpassing all, Chisholmes says that Economic Geography is presumed to form some reasonable estimate of the future course of commercial development, as determined by geographical factors.
Read Also: How To Figure Out Displacement In Physics
What Are Different Environmental Factors Affecting Human Health
The 8 Environmental Factors That Can Impact Your Health A number of specific environmental issues can impede human health and wellness. These issues include chemical pollution, air pollution, climate change, disease-causing microbes, lack of access to health care, poor infrastructure, and poor water quality.
Definitions And History In Brief
In this subchapter, we will provide a reader with the most used and common definitions of economic geography by various scholars, experts and also scientific-popular sources. We then attempt to summarise the key points from these definitions, helping the reader to understand the main subject of economic geography. We also guide the reader through the history of economic geography to imagine all the consequences leading to the contemporary state-of-the-art in this field.
Don’t Miss: Jonathan Tennant Beth Thomas
Theoretical Background And Influences
There are varied methodological approaches. Neoclassical location theorists, following in the tradition of Alfred Weber, tend to focus on industrial location and use quantitative methods. Since the 1970s, two broad reactions against neoclassical approaches have significantly changed the discipline: Marxist political economy, growing out of the work of David Harvey and the new economic geography which takes into account social, cultural, and institutional factors in the spatial economy.
Economists such as Paul Krugman and Jeffrey Sachs have also analyzed many traits related to economic geography. Krugman called his application of spatial thinking to international trade theory the “new economic geography”, which directly competes with an approach within the discipline of geography that is also called “new economic geography”. The name geographical economics has been suggested as an alternative.
What Does Economic Geography Deal With
4/5Economic GeographyEconomic geographygeographydealseconomic
Then, what do economic geographers do?
Contemporary economic geographers tend to specialize in areas such as location theory and spatial analysis , market research, geography of transportation, real estate price evaluation, regional and global development, planning, Internet geography, innovation, social
Similarly, why is economic geography important? Economic geography is important in developed nations such as the United States because it allows researchers to understand the structure of the area’s economy and its economic relationship with other areas around the world. Because economics is such a large topic of study so too is economic geography.
Beside this, how is economics related to geography?
The geography of a place determines the economy of it. For example , the plain areas have flourishing agriculture because of fertile soil. You have a separate branch of geography – Economic geography , which is concerned with studying the economies, people’s activities in relation to the area.
What is subject matter in economic geography?
Economic geography is that aspect of the subject which deals with the influence of the environment inorganic and organic on the activities of man.Economic geography is concerned with problem of making a living, with world industries, with basic resources and industrial commodities.
Recommended Reading: Beth Thomas Interview
Economy And Regional Development: A Scandinavian School
While the new Nordic economic geography has been extraordinarily engaged in open discussions with international partners and with other economic disciplines, it as a subdiscipline has isolated itself more from the rest of human geography. The consequence is that the emphasis on noneconomic factors of regional development has missed the opportunity of mutual exchange with social and cultural parts of the discipline and that economic geography has lost some of the social engagement characterizing its roots in the critical geography of the 1970s.
D. Bell, in, 2009
Approaches To Studying The Economic Geography:
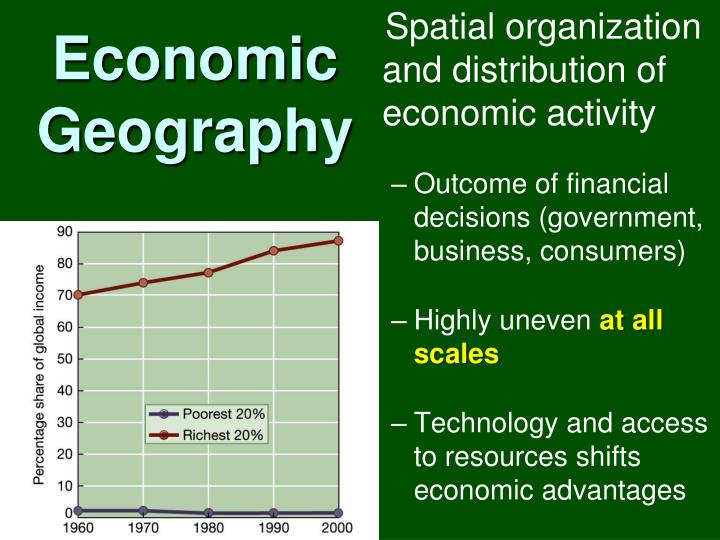
As economic geography is a very wide discipline. In the study of the economic phenomenon using different methodologies, some distinct approaches to study have evolved.
Theoretical economic geography focuses on building theories about spatial arrangement and distribution of economic actions.
Regional economic geography examines the economic conditions of particular regions or countries of the world. It deals with economic rationalization as well as local economic development.
Historical economic geography examines the history and development of the spatial economic structure. Using historical data, it examines how centers of population and economic activity shift, what patterns of regional specialization and localization evolve over time, and what factors explain these changes.
Critically economic geography is one of the most important approaches. This approach is taken from the point of view of contemporary critical geography and its philosophy.
Behavioral economic geography examines the cognitive processes underlying spatial reasoning, place decision making, and behavior of firms and individuals.
Alternatively, the study may focus on the production, exchange, distribution, and consumption of items of economic activity. Allowing parameters of space-time and item to vary, a geographer may also examine material flow, commodity flow, population flow, and information flow from different parts of the economic activity system.
Also Check: Cpm Algebra 2 Chapter 1 Answers
What Is An Economy
An economy is the large set of inter-related production, consumption, and exchange activities that aid in determining how scarce resources are allocated. The production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services are used to fulfill the needs of those living and operating within the economy, which is also referred to as an economic system.
A Short Definition For Economic Geography
However, from the early 1970s a new generation of economic geographers began to question quantitative economic geography. As part of the radical geography movement inspired by the worldwide political protests of 1968, these geographers offered four criticisms of the research pursued by an older generation. First, it was accused of a naive objectivism, or belief that the facts could provide a value-free, unbiased test of a theory. Second, it was criticized for its theoretical assumptions, notably the assumption that economic actors are governed by a universal form of reason . Third, it was accused of focusing on phenomenal forms not underlying economic processes. Fourth, it was criticized for treating the worlds economic geography as if it should display a spatial order, such that place and regional differences were mere noise to be filtered out in the search for general patterns.
Castree, N., Kitchin, R., & Rogers, A. . “Economic geography.” In A Dictionary of Human Geography. : Oxford University Press. Retrieved 14 Mar. 2017
Read Also: Who Is Paris Jackson Father
History Of Economic Geography
The comprehensive knowledge of geography was enhanced several years back due to the development of maps and travel journals which had various descriptions of the native people, climate, landscape, and the productivity levels of various locations, classified as a science of cartography. Due to the vast knowledge provided by these journals, transcontinental trade patterns were established which led to the development of the economic theory and practice from the 16th century. The further popularization of geographical knowledge was contributed to during the Second World War while the growth of economic geography as a discipline was seen after the war during the recovery and development of the economy. Various theories like the climatic determinism by Ellsworth Huntington and the Central place theory of core and periphery by Walter Christaller also played a major role.
Economic Geography Covers A Vast Area
Economic geographers investigate and try to explain the major factors that have driven Chinas spectacular GDP growth over the past two decades, and the European Unions relative decline.
They look at why there is persistent poverty in pockets of global cities such as New York, Tokyo and London, and what triggered the emergence of massive urban slum areas in Calcutta.
Richard Hartshorne , a prominent American geographer who specialized in economic and political geography, once said: The border position of geography between the natural and the social sciences is fairly generally recognized. Concerned primarily with differences in the different areas of the world, geography studies both natural and cultural features. In some universities, it is included among the natural sciences, in other among the social scientists. In England and America, geographers have particularly cultivated that portion of their field which leads naturally into economics, i.e. economic geography.
Economic geography examines the impacts of globalization on peoples livelihoods and jobs across the globe, and tries to explain the causes and consequences of uneven development between and within different regions.
Professor Yoko Aoyama, who works at the Graduate School of Geography at Clark University, Worcester, Massachusetts, wrote the following about economic geography:
Also Check: What Influence Did Geography Have On The Development Of Greek Society
What Does Tertiary Industry Mean In Geography
4.8/5tertiary industry isistertiary sectorindustrysector
Keeping this in view, what does industry mean in geography?
Definition of industrial geography. : a branch of geography that deals with the location of industries, the geographic factors that influence their location and development, the raw materials used in them, and the distribution of their finished products.
Similarly, what are examples of a tertiary industry? Examples of tertiary industries may include:
- Telecommunication.
Critical Resource Geography: An Economic Geography Research Agenda
Anglophone economic geography has addressed a wide range of concerns in the post-war period but has avoided a sustained engagement with natural resource questions. An earlier period of geographical inquiry had no such aversion: it inventoried, cataloged, and speculated about resources with an unswerving instrumentalism. The paradoxical legacies of this earlier period are a richly detailed set of resource descriptions, assessments, and maps that can provide a fascinating account of the evolution of a global resource economy and a heterodox tradition of critical inquiry located on the margins of economic geography which considers how resource geographies are structured by economic, political, and social processes and, therefore, owe a debt to more than nature alone. These legacies provide the foundation for a critical resource geography which engages questions of knowledge, scarcity, governance, and sustainability that are at the heart of modern human geography. Critical resource geography accounts for the political, economic, and cultural processes by which particular components of the natural world become produced as resources, and subsequently proliferate through the economy in the form of commodities and examines how the biophysical and material properties of resources influence the social organization of their production.
K. Simonsen, in, 2009
Read Also: How To Calculate Half Life From Rate Constant
Topics Within Economic Geography
Theoretical economic geography is the broadest of the branches and geographers within that subdivision mainly focus on building new theories for how the world’s economy is arranged. Regional economic geography looks at the economies of specific regions around the world. These geographers look at local development as well as the relationships that specific regions have with other areas. Historical economic geographers look at the historical development of an area to understand their economies. Behavioral economic geographers focus on an area’s people and their decisions to study the economy.
Critical economic geography is the final topic of study. It developed out of critical geography and geographers in this field attempt to study economic geography without using the traditional methods listed above. For example, critical economic geographers often look at economic inequalities and the dominance of one region over another and how that dominance impacts the development of economies.
In addition to studying these different topics, economic geographers also often study very specific themes related to the economy. These themes include the geography of agriculture, transportation, natural resources, and trade as well as topics such as business geography.
How Would You Define Economic
Economics is a social science concerned with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics can generally be broken down into macroeconomics, which concentrates on the behavior of the economy as a whole, and microeconomics, which focuses on individual people and businesses.
Recommended Reading: Geometry Dash World Vault
History And Development Of Economic Geography
The field of economic geography continued to grow as European nations later began to explore and colonize different regions around the world. During these times European explorers made maps describing economic resources such as spices, gold, silver and tea that they believed would be found in places like the Americas, Asia and Africa . They based their explorations on these maps and as a result, new economic activity was brought to those regions. In addition to the presence of these resources, explorers also documented the trading systems that the people native to these regions engaged in.
In the mid-1800’s farmer and economist, Johann Heinrich von Thünen developed his model of agricultural land use. This was an early example of modern economic geography because it explained the economic development of cities based on land use. In 1933 geographer Walter Christaller created his Central Place Theory that used economics and geography to explain the distribution, size, and number of cities around the world.